文章目录
ThinkPHP6 模型
- 请确保你已经在数据库配置文件中配置了数据库连接信息
- 模型会自动对应数据表,模型类的命名规则是除去表前缀的数据表名称,采用驼峰法命名,并且首字母大写
- 模型自动对应的数据表名称都是遵循小写+下划线规范,如果你的表名有大写的情况,必须通过设置模型的table属性。
一、创建模型
| 模型名 | 数据库前缀 |
|---|---|
| Cat | cafe_cat |
| Goods | cafe_goods |
| UserOrder | cafe_user_order |
表前缀设置:config/database.php 文件里 prefix
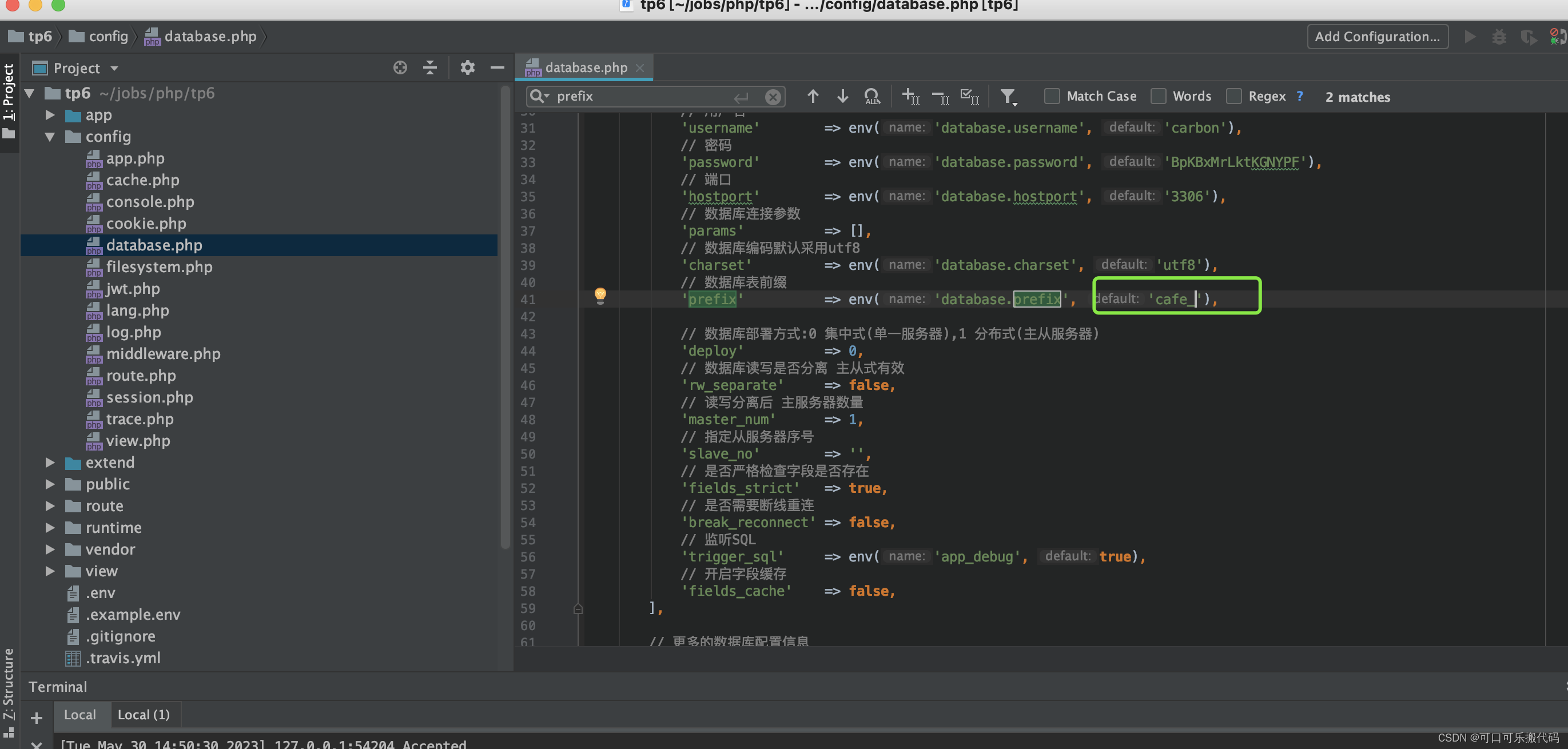
在以上代码中,`cafe_`就是数据库表的前缀,可以根据实际情况进行修改。
- 第一步:创建一个跟控制器平级的目录,目录名:
model - 第二步:在
model创建Goods.php文件
二、模型操作
在模型中除了可以调用数据库类的方法之外(换句话说,数据库的所有查询构造器方法模型中都可以支持),可以定义自己的方法,所以也可以把模型看成是数据库的增强版
- 模型文件里的自定义方法,不要和
thinkphp方法一样名称 - 模型里的
Goods::也可以用static::关键词 - 链式操作,都可以在模型里使用
1、find查询数据
- find 获取单条数据,返回的是当前模型的对象实例
namespace app\model;
use think\Model;
class Goods extends Model{
public function find(){
$find = Goods::find(2);
$find = Goods::where('id',7)->find();
return $find;
}
}
2、controller调用model
namespace app\controller;
use app\model\Goods;
class Index{
public function index(){
$db = new Goods();
$index = $db->find();
print_r($index);
}
}
find(2) 查询失败,是因为数据库主键名称不是 id
3、select查询数据
- select 获取多条数据,返回的是当前模型的对象实例
public function select(){
$select = Goods::select();
$select = Goods::select(6);
$select = Goods::where('id','>',7)->select();
return $select;
}
4、数据转换
- toArray方法将当前的模型实例输出为数组
public function select(){
$select = Goods::select();
$select = Goods::select(2);
$select = Goods::where('id','>',7)->select();
return $select->toArray();
}
5、增加数据
- create 静态方法添加数据,返回的是当前模型的对象实例
public function create(){
$create = Goods::create([
'cat' => 3,
'title' => '新商品',
'price' => '59.99',
'add_time' => time()
]);
echo $create->id; // 可以直接获取自增id
return $create;
}
新增数据的最佳实践原则:使用create方法新增数据,使用saveAll批量新增数据。
6、修改数据
update静态方法修改数据,返回的是当前模型的对象实例save在取出数据后,更改字段更新数据。这种方式是最佳的更新方式
namespace app\model;
use think\Model;
class Goods extends Model{
public function update(){
# 更新方式1
$update = Goods::update(
['price'=>'99.99'],
['id'=>22]
);
return $update;
# 更新方式2
$user = Goods::find(23);
$user->price = '102.99';
$save = $user->save();
return $save;
}
}
7、删除数据
delete静态方法删除数据,返回的是当前模型的对象实例destroy根据主键删除
public function delete(){
# 删除方法1
$delete = Goods::where('id',3)->delete();
# 删除方法2
$delete = User::destroy(4);
return $delete;
}
TP模型如果只能增删查改,不如在 Controller 执行了。TP模型很多特点,下面为大家一一介绍
三、模型设置
- 为了和数据库更好的适配,模型可以提前设置对应的数据库属性,一个文件配置一个数据表
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| name | 模型名(相当于不带数据表前后缀的表名,默认为当前模型类名) |
| table | 数据表名(默认自动获取) |
| pk | 主键名(默认为 id ) |
| schema | 模型对应数据表字段及类型 |
| type | 模型需要自动转换的字段及类型 |
| disuse | 数据表废弃字段(数组) |
1、name和table
- 当你的数据表没有前缀的时候,name和table属性的定义是没有区别的,定义任何一个即可
class Goods extends Model{
protected $name = 'Goods';
protected $table = 'cafe_goods';
public function select(){
$select = Goods::select();
return $select->toArray();
}
}
2、pk 改变主键名称
model默认的主键是id
// 可以把主键改为shop_id 试试
ALTER TABLE `ouyangke`.`cafa_goods`
CHANGE COLUMN `id` `cafa_id` int(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT ' 商品ID' FIRST,
DROP PRIMARY KEY,
ADD PRIMARY KEY (`cafa_id`) USING BTREE;
class Goods extends Model{
protected $name = 'Goods';
protected $table = 'shop_goods';
protected $pk = 'shop_id';
public function find($id=1){
$find = Goods::find($id);
return $find->toArray();
}
}
3、schema 设置模型对应数据表字段及类型
- 默认会自动获取(包括字段类型),但自动获取会导致增加一次查询
- schema 属性一旦定义,就必须定义完整的数据表字段类型
- 类型根据php数据类型定义,如果是json类型直接定义为json即可
class Goods extends Model{
protected $name = 'Goods';
protected $table = 'cafa_goods';
protected $pk = 'cafa_id';
protected $schema = [
'cafa_id' => 'int',
'cat' => 'int',
'title' => 'string',
'price' => 'float',
'discount' => 'int',
'stock' => 'int',
'status' => 'int',
'add_time' => 'int'
];
# 对某个字段定义需要自动转换的类型,可以使用type属性
protected $type = [
'cafa_id' => 'int'
];
public function select(){
$select = Goods::select();
return $select->toArray();
}
}
4、disuse 数据表废弃字段(数组)
class Goods extends Model{
protected $name = 'Goods';
protected $table = 'cafa_goods';
protected $pk = 'cafa_id';
protected $disuse = [
'discount',
'stock'
];
public function select(){
$select = Goods::select();
return $select->toArray();
}
}
5、其他属性(不常用)
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| suffix | 数据表后缀(默认为空) |
| connection | 数据库连接(默认读取数据库配置) |
| query | 模型使用的查询类名称 |
| field | 模型允许写入的字段列表(数组) |
| strict | 是否严格区分字段大小写(默认为 true ) |
| readonly | 字段只读 |
| json | 设置字段为JSON数据 |
| jsonType | 设置JSON字段的类型 |
| jsonAssoc | 设置JSON数据返回数组 |
| autoWriteTimestamp | 自动写入创建和更新的时间戳字段(默认关闭) |
| createTime | 创建时间戳字段 |
| updateTime | 更新时间戳字段 |
| deleteTime | 用于定义你的软删除标记字段 |
四、模型 主要功能
1、获取器
- 获取器的作用是对模型实例的(原始)数据做出自动处理
- 命名规则:get + 字段名 + Attr
- 字段名是数据表字段的驼峰转换
class Goods extends Model{
public function index(){
$find = Goods::find(10);
echo $find->status;
return $find->toArray();
}
public function getStatusAttr($v){
$status = [
1=>'开启',
2=>'关闭'
];
return $status[$v];
}
}
2、修改器
- 修改器的主要作用是对模型设置的数据对象值进行处理
- 命名规则:
set+ 字段名 +Attr
class Goods extends Model{
public function index(){
$create = Goods::create([
'cat' => 3.33,
'title' => '新商品',
'price' => '59.99',
'add_time' => time()
]);
return $create;
}
public function setCatAttr($v,$all){
// $all 全部参数
return (int)$v;
}
}
3、搜索器
- 搜索器的作用是用于封装字段(或者搜索标识)的查询条件表达式
- 命名规则:
search+ 字段名 +Attr
class Goods extends Model{
public function index(){
$select = Goods::withSearch(['title'],[
'title' => '新'
])->select();
return $select->toArray();
}
public function searchTitleAttr($query,$v){
$query->where('title','like', $v . '%');
}
}
4、检查数据
- 如果要判断数据集是否为空,不能直接使用
empty判断 - 必须使用数据集对象的
isEmpty方法判断
class Goods extends Model{
public function index(){
$select = Goods::where('title','1')->select();
if(empty($select)){
echo 111;
}
if($select->isEmpty()){
echo 111;
}
}
}
五、右侧列表改为model示例
model代码
namespace app\model;
use think\Model;
use think\facade\Db;
class Goods extends Model{
protected $name = 'Goods';
protected $table = 'shop_goods';
public function get_all($where,$order='add_time DESC',$p=1,$total=10){
$count = Goods::where($where)->count();
$list = Goods::where($where)
->order($order)
->page($p,$total)
->select();
if($list->isEmpty()){
return null;
}
$data = $list->toArray();
foreach($data as &$data_v){
$data_v['cat'] = Db::table('shop_cat')->where('id',$data_v['cat'])->value('name');
}
$arr = [
'count' => ceil($count/$total),
'data' => $data
];
return $arr;
}
public function getStatusAttr($v){
$status = [
1=>'开启',
2=>'关闭'
];
return $status[$v];
}
public function getAddTimeAttr($v){
return date('Y-m-d',$v);
}
}
controller代码
public function index(){
$title = '商城';
$login = '欧阳克';
# 左侧菜单
$menu = Db::table('shop_menu')->where('fid',0)->select();
$left = [];
foreach($menu as $menu_k=>$menu_v){
$left[$menu_k] = $menu_v;
$left[$menu_k]['lists'] = Db::table('shop_menu')->where('fid',$menu_v['id'])->select();
}
# 右侧列表
$param = Request::param();
if(isset($param['status']) && $param['status'] == 1){
$where['status'] = 1;
}else if(isset($param['status']) && $param['status'] == 2){
$where['status'] = 2;
}else{
$where = true;
}
$p = isset($param['p']) ? $param['p'] : 1;
$db = new Goods();
$order = [
'add_time DESC',
'id DESC'
];
$right = $db->get_all($where,$order,$p,5);
View::assign([
'title' => $title,
'login' => $login,
'left' => $left,
'right' => $right['data'],
'count' => $right['count'],
'p' => $p,
'status' => isset($param['status']) ? $param['status'] : 0
]);
return View::fetch();
}
html代码
<td>{
$right_v.status}</td>
<td>{
$right_v.add_time}</td>
六、模型事件
- 模型事件是指在进行模型的查询和写入操作的时候触发的操作行为
- 模型事件只在调用模型的方法生效,使用查询构造器操作是无效的
| 编号 | 事件 | 描述 | 事件方法名 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | after_read | 查询后 | onAfterRead |
| 2 | before_insert | 新增前 | onBeforeInsert |
| 3 | after_insert | 新增后 | onAfterInsert |
| 4 | before_update | 更新前 | onBeforeUpdate |
| 5 | after_update | 更新后 | onAfterUpdate |
| 6 | before_write | 写入前 | onBeforeWrite |
| 7 | after_write | 写入后 | onAfterWrite |
| 8 | before_delete | 删除前 | onBeforeDelete |
| 9 | after_delete | 删除后 | onAfterDelete |
| 10 | before_restore | 恢复前 | onBeforeRestore |
| 11 | after_restore | 恢复后 | onAfterRestore |
namespace app\model;
use think\Model;
class Goods extends Model{
public function one_update(){
$update = Goods::update(
['price'=>'99.99'],
['id'=>22]
);
return $update;
}
# 执行更新操作,就会之下onBeforeUpdate方法
public static function onBeforeUpdate($goods){
print_r($goods->price);
return true;
}
}