简单A-B
描述
这是一道简单题,给出一串数以及一个数字C,要求计算出所有A - B = C的数对的个数(不同位置的数字一样的数对算不同的数对)。
输入
输入共两行。
第一行,两个整数N, C。1=<N<=2e5 , C>=1
第二行,N个整数,作为要求处理的那串数。
输出
一行,表示该串数中包含的满足A - B =C的数对的个数。
输入样例 1
4 1
1 1 2 3
输出样例 1
3
输入样例 2
6 1
1 1 1 2 2 2
输出样例 2
9
本题值得注意的是,有可能暴int
比如
输入
200000 1
1e5个1,1e5个2
输出
1e10 > int型
(int存最大的数约等于2e9)
二分
简单二分模板题
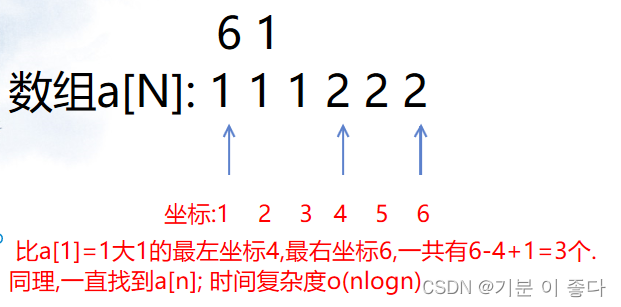
先排序,找出比第i个数大C的最左端点的坐标和最右端点的坐标,(右端点坐标减去左端点坐标加1)就表示有多少个比第i个数大C
例如样例2中
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int const N=2e5+10;
int n,c,a[N];
ll res;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
//节约cin,cout时间;
cin>>n>>c;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>a[i];
sort(a+1,a+1+n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int l=i+1,r=n;
while(l<r) //找最左端点;r=mid;
{
int mid=l+r >>1;
//相当于(l+r)/2,这么写看着厉害一点hh,+优先级大于>>(右移)优先级;
if(a[mid]-a[i]>=c)
r=mid;
else
l=mid+1;
}
int k=l;
l=i+1,r=n;
while(l<r)//找最右端点;l=mid;
{
int mid=l+r+1 >> 1;//改l,要+1,防止死循环
if(a[mid]-a[i]<=c)
l=mid;
else
r=mid-1;
}
int kk=l;
if(a[kk]-a[i]==c&&a[k]-a[i]==c)
res+=kk-k+1;
}
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}
lower_bound()
upper_bound()
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int const N=2e5+10;
int n,c,a[N],b[N];
ll res;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
//节约cin,cout时间;
cin>>n>>c;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
b[i]=a[i]+c;//用b[N]数组存(对应的)的大C的值
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int k=lower_bound(a+1,a+n+1,b[i])-a;//返回第一个大于等于b[i]的a数组的下标
int kk=upper_bound(a+1,a+n+1,b[i])-a;//返回大于
res+=kk-k;//因为upper_bound返回大于的下标,所以无需加1
}
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}
双指针
具体的实现就是,我们维护两个端点kk , k,每次kk右移到a[kk] - a[i] <= c的最后位置的下一位,k右移到满足a[k] - a[l] < c最后一位.
也就是说, 此时如果a[kk] - a[i] == c && a[k] - a[i] == c,中间的那一段一定都是满足条件的,我们让res += kk - k即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int const N=200010;
typedef long long ll;
int a[N],n,c;
ll res;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
//节约cin,cout时间;
cin>>n>>c;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>a[i];
sort(a+1,a+1+n);
int kk=2,k=2;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
while(kk<=n&&a[kk]-a[i]<=c)
kk++; //因为是有序的,下次寻找从kk开始;减少不必要的枚举
while(k<=n&&a[k]-a[i]<c)
k++;
if(a[kk-1]-a[i]==c&&a[k]-a[i]==c)
res+=kk-k;
}
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}
MAP 时间复杂度O(n)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map> //map头文件;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int const N=2e5+10;
int n,c,a[N],b[N];
ll res;
map<int,int> mp;//key-value;建立一个数字到出现次数的映射 map<a[i],times>
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
//节约cin,cout时间;
cin>>n>>c;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
mp[a[i]]++;
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
res+=mp[a[i]+c];
}
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}