本实验利用Python,搭建了一个用于识别猫的单神经元神经网络,最终实现在测试集上的准确率在70%以上。
实验环境: python中numpy、matplotlib、h5py和skimage库
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 用于画图
import h5py # 用于加载训练数据集
import skimage.transform as tf # 用于缩放图片
训练样本: 209张64*64的带标签图片
测试样本: 50张64*64的带标签图片
关于本实验中所用数据集与完整代码详见:
https://github.com/PPPerry/AI_projects/tree/main/1.cats_identification
构建的神经网络模型如下:
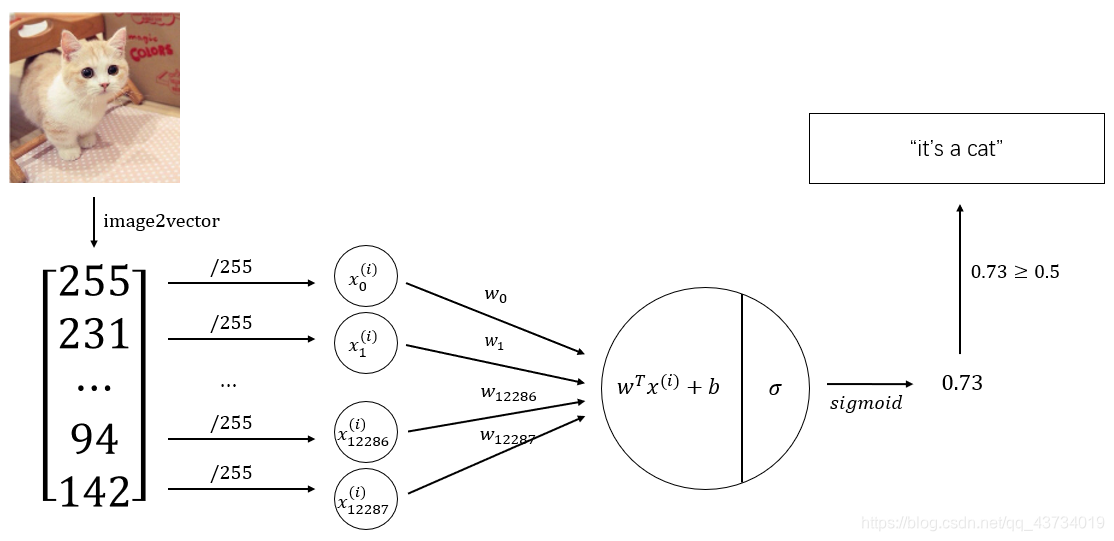
基于该神经网络模型,代码实现如下:
首先,对数据集数据进行预处理。
def load_dataset():
"""
加载数据集数据
:return: 训练数据与测试数据的相关参数
"""
train_dataset = h5py.File("datasets/train_catvnoncat.h5", "r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_x"][:]) # 提取训练数据的特征数据,格式为(样本数, 图片宽, 图片长, 3个RGB通道)
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # 提取训练数据的标签数据,格式为(样本数, )
test_dataset = h5py.File("datasets/test_catvnoncat.h5", "r")
test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) # 提取测试数据的特征数据
test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) # 提取测试数据的标签数据
classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # 提取标签,1代表是猫,0代表不是猫
train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape((1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0])) # 统一类别数组格式为(1, 样本数)
test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes
train_set_x_orig, train_set_y, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y, classes = load_dataset() # 加载数据集数据
m_train = train_set_x_orig.shape[0] # 训练样本数
m_test = test_set_x_orig.shape[0] # 测试样本数
num_px = test_set_x_orig.shape[1] # 正方形图片的长/宽
train_set_x_flatten = train_set_x_orig.reshape(train_set_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T # 将样本数据进行扁平化和转置,格式为(图片数据, 样本数)
test_set_x_flatten = test_set_x_orig.reshape(test_set_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
train_set_x = train_set_x_flatten/255. # 标准化处理,使所有值都在[0, 1]范围内
test_set_x = test_set_x_flatten/255.
其次,构造神经网络中用到的相应函数。
其中,前向传播的公式为
A = σ ( w T X + b ) = ( a ( 1 ) , a ( 2 ) , ⋯ , a ( m − 1 ) , a ( m ) ) J = − 1 m ∑ i = 1 m l o g ( a ( i ) ) + ( 1 − y ( i ) ) l o g ( 1 − a ( i ) ) \begin{array}{c} A=\sigma(w^TX+b)=(a^{(1)},a^{(2)},\cdots,a^{(m-1)},a^{(m)})\\ \\ J = -\frac{1}{m}\sum^m_{i=1}log(a^{(i)})+(1-y^{(i)})log(1-a^{(i)}) \end{array} A=σ(wTX+b)=(a(1),a(2),⋯,a(m−1),a(m))J=−m1∑i=1mlog(a(i))+(1−y(i))log(1−a(i))
反向传播的公式为
∂ J ∂ w = 1 m X ( A − Y ) T ∂ J ∂ b = 1 m ∑ i = 1 m ( a ( i ) − y ( i ) ) \begin{array}{c} \frac{\partial J}{\partial w} = \frac{1}{m}X(A-Y)^T\\ \\ \frac{\partial J}{\partial b} = \frac{1}{m}\sum^m_{i=1}(a^{(i)}-y^{(i)}) \end{array} ∂w∂J=m1X(A−Y)T∂b∂J=m1∑i=1m(a(i)−y(i))
def sigmoid(z):
"""
sigmod函数实现
:param z: 数值或一个numpy数组
:return: [0, 1]范围数值
"""
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
return s
def initialize_with_zeros(dim):
"""
初始化权重数组w和偏置b为0
:param dim: 权重值的数量
:return:
w: 权重数组
b: 偏置bias
"""
w = np.zeros((dim, 1))
b = 0
return w, b
def propagate(w, b, X, Y):
"""
实现正向传播和反向传播,分别计算出成本与梯度
:param w: 权重数组
:param b: 偏置
:param X: 图片的特征数据
:param Y: 图片的标签数据
:return:
cost: 成本
dw: w的梯度
db:b的梯度
"""
m = X.shape[1]
# 前向传播
A = sigmoid(np.dot(w.T, X) + b)
cost = -np.sum(Y * np.log(A) + (1 - Y) * np.log(1 - A)) / m
# 反向传播
dZ = A - Y
dw = np.dot(X, dZ.T) / m
db = np.sum(dZ) / m
# 梯度保存在字典中
grads = {
"dw": dw,
"db": db
}
return grads, cost
def optimize(w, b, X, Y, num_iterations, learning_rate, print_cost=False):
"""
梯度下降算法更新参数
:param w: 权重数组
:param b: 偏置bias
:param X: 图片的特征数据
:param Y: 图片的标签数据
:param num_iterations: 优化迭代次数
:param learning_rate: 学习率
:param print_cost: 为真时,每迭代100次,打印一次成本
:return:
params: 优化后的w和b
costs: 每迭代100次,记录一次成本
"""
costs = []
for i in range(num_iterations):
grads, cost = propagate(w, b, X, Y)
dw = grads["dw"]
db = grads["db"]
# 梯度下降
w = w - learning_rate * dw
b = b - learning_rate * db
# 记录成本变化
if i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
if print_cost:
print("优化%d次后成本是:%f" % (i, cost))
params = {
"w": w,
"b": b
}
return params, costs
def predict(w, b, X):
"""
预测函数,判断是否为猫
:param w: 权重数组
:param b: 偏置bias
:param X: 图片的特征数据
:return:
Y_predicition: 预测是否为猫,返回值为0或1
p: 预测为猫的概率
"""
m = X.shape[1]
Y_prediction = np.zeros((1, m))
p = sigmoid(np.dot(w.T, X) + b)
for i in range(p.shape[1]):
if p[0, i] >= 0.5:
Y_prediction[0, i] = 1
return Y_prediction, p
最终,组合以上函数,构建出最终的神经网络模型函数。
def model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, num_iterations=2001, learning_rate=0.5, print_cost=False):
"""
最终的神经网络模型函数
:param X_train: 训练样本的特征数据
:param Y_train: 训练样本的标签数据
:param X_test: 测试样本的特征数据
:param Y_test: 测试样本的标签数据
:param num_iterations: 优化迭代次数
:param learning_rate: 学习率
:param print_cost: 为真时,每迭代100次,打印一次成本
:return:
d: 返回相关信息的字典
"""
w, b = initialize_with_zeros(X_train.shape[0]) # 初始化参数
parameters, costs = optimize(w, b, X_train, Y_train, num_iterations, learning_rate, print_cost) # 训练参数
w = parameters["w"]
b = parameters["b"]
Y_prediction_train, p_train = predict(w, b, X_train)
Y_prediction_test, p_test = predict(w, b, X_test)
print("对训练数据的预测准确率为:{}%".format(100 - np.mean(np.abs(Y_prediction_train - Y_train)) * 100))
print("对测试数据的预测准确率为:{}%".format(100 - np.mean(np.abs(Y_prediction_test - Y_test)) * 100))
d = {
"costs": costs,
"Y_prediction_test": Y_prediction_test,
"Y_prediction_train": Y_prediction_train,
"w": w,
"b": b,
"learning_rate": learning_rate,
"num_iterations": num_iterations,
"p_train": p_train,
"p_test": p_test
}
return d
现在调用上面的模型函数对我们最开始加载的数据进行训练。
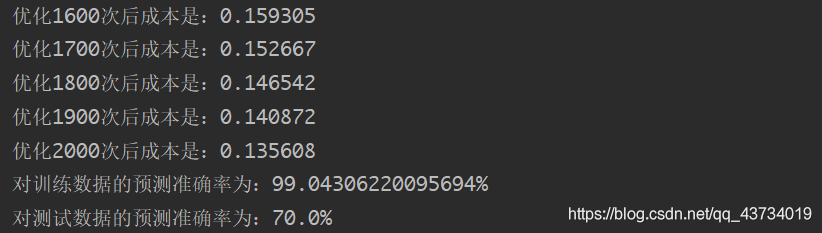
d = model(train_set_x, train_set_y, test_set_x, test_set_y, num_iterations=2001, learning_rate=0.005, print_cost=True)
输出:优化2000次后的成本是0.1356。对训练数据的准确率为99%左右,对测试数据的准确率为70%左右。
试验模型预测功能:
- 查看训练集和测试集中图片及其对应的预测结果
def show_predict(index, prediction=np.hstack((d["Y_prediction_train"], d["Y_prediction_test"])),
data=np.hstack((train_set_x, test_set_x)), origin=np.hstack((train_set_y, test_set_y)),
px=num_px, p=np.hstack((d["p_train"], d["p_test"]))):
if index >= prediction.shape[1]:
print("index超出数据范围")
return
plt.imshow(data[:, index].reshape((px, px, 3)))
plt.show()
print("这张图的标签是" + str(origin[0, index]) + ",预测分类是" + str(int(prediction[0, index])) + ",预测概率是" + str(p[0, index]))
return
以第19张图片为例:
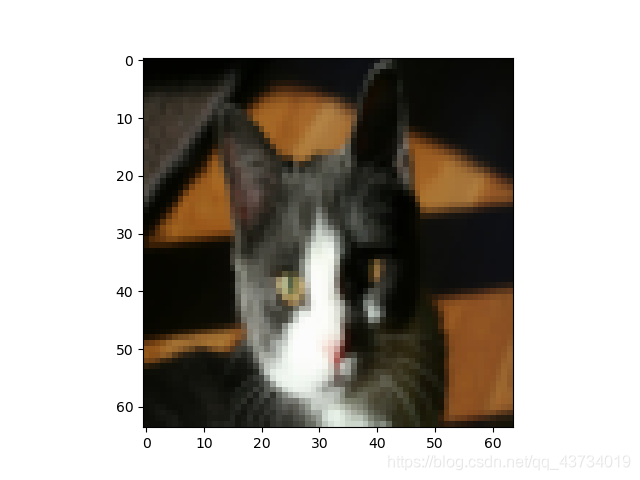
输出:这张图的标签是1,预测分类是1,预测概率是0.93。

- 查看自己输入的图片及其对应的预测结果
# 预测自己的图片
# 在同目录下创建一个文件夹images,把你的任意图片改名成my_image1.jpg后放入文件夹
my_image = "my_image1.jpg"
image = np.array(plt.imread(my_image))
my_image = tf.resize(image, (num_px, num_px), mode='reflect').reshape((1, num_px*num_px*3)).T
my_prediction, my_p = predict(d["w"], d["b"], my_image)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
print("预测分类是" + str(int(my_prediction[0, 0])) + ",预测概率是" + str(my_p[0, 0]))
以下图为例:
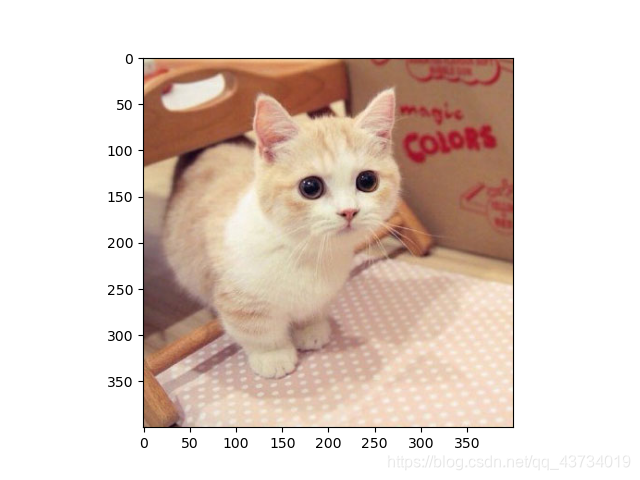

输出:预测分类是1,预测概率是0.89。
进一步实验得到的结论:
- 成本随迭代次数增加时的变化情况
# 绘制成本随迭代次数增加时的变化情况
costs = np.squeeze(d['costs']) # 将表示向量的数组转换为秩为1的数组,便于matplotlib库函数画图
plt.plot(costs)
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per hundreds)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(d["learning_rate"]))
plt.show()

结论:训练次数越多,成本越小,预测结果越精确。
- 不同学习率下成本随迭代次数增加时的变化情况
# 绘制在不同学习率下成本随迭代次数增加时的变化情况
learning_rates = [0.01, 0.001, 0.0001]
models = {
}
for i in learning_rates:
models[str(i)] = model(train_set_x, train_set_y, test_set_x, test_set_y, num_iterations=2001, learning_rate=i,
print_cost=False)
for i in learning_rates:
plt.plot(np.squeeze(models[str(i)]["costs"]), label=str(models[str(i)]["learning_rate"]))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per hundreds)')
legend = plt.legend(loc='upper right', shadow=True)
plt.show()
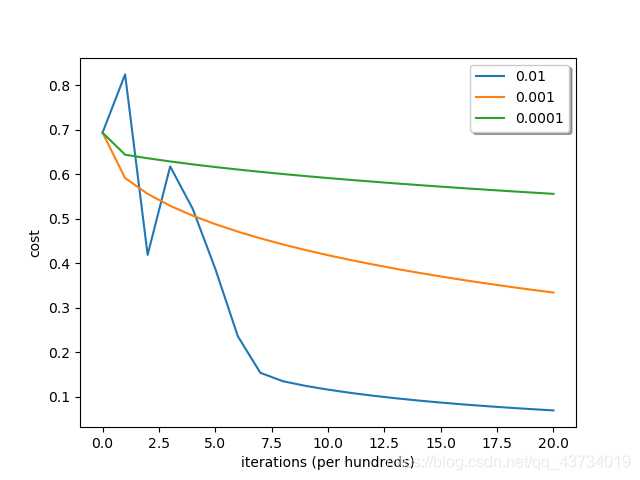
结论:选择一个正确的学习率很重要,不一定越大越好。设置不合理,神经网络有可能永远都不能下降到损失函数的最小值处;相反,设置合理,可以使神经网络的收敛达到很好的效果。
结束语:
- 实验过程中,一定要搞清楚变量的维度,否则做数据处理、写数组操作时会容易出现问题。
- 数据集、图片等需要和代码在同一目录下。
- 本实验几乎基于纯Python的numpy库函数进行神经网络模型的搭建,没有使用任何机器学习框架,重在理解数学原理及意义。在后续的实验中,我会对TensorFlow等经典框架进行学习与运用。
- 相关代码可能会不断更新改进,以github中的代码为准。
- 这是我在系统学习人工智能中实现的第一个人工智能程序,后续还会不断更新系列实验。写博客以督促自己不能总摸鱼233,希望自己能在神经网络这条路上走的尽可能远一些。