特性:C#特性是指我们可以对类、以及C#程序集中的成员进行进一步的描述,比如我们写一个关于人的类Person,该类可以对人的属性以及某些行为(方法)进行描述。那么如果我们要对人类进行进一步描述呢,比如人这个类是属于动物的灵长类动物。有人会说我们可以为这个Person类去写一个灵长动物类的父类,再用人类去继承这个类去解决。但是我们要求的是仅仅是描述性的,就是对这个人类进行进一步的描述,而在实际操作中不需要去操作。这样的情况我们就可以用特性的概念去解决,特性简而言之就是程序集的特定程序元素所具有的另外的性质。
使用方法: 由方括号,中间包裹着特性名和参数列表(也可以无参)。放置在它所要应用的元素之前(类前,方法前等等)。
特性与注释区别:1.特性会影响编译器,而注释不会
2.特性是一个类,直接或间接的继承自Attribute
特性可以标识的位置
特性可以标识在:类(AttributeTargets.Class)、方法(AttributeTargets.Method)、字段(AttributeTargets.Field)
/// <summary>
/// 代表该类可以标识在类(AttributeTargets.Class)、方法(AttributeTargets.Method)、字段(AttributeTargets.Field)上
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class| AttributeTargets.Method| AttributeTargets.Field)]
public class PersonAttri:Attribute
{
}
[PersonAttri]
public class clas1
{
}
[PersonAttri]
public static void Ff()
{
}
[PersonAttri]
private string S = "FBDB";
Conditional条件特性
public class MyClass
{
//代表只能在DEBUG模式下执行
[Conditional("DEBUG")]
public static void mess(string a)
{
Console.WriteLine(a);
}
}
class Test
{
public static void Function1()
{
MyClass.mess("in Function1 ");
Function2();
}
public static void Function2()
{
MyClass.mess("in Function2 ");
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("=====>Conditional特性测试");
MyClass.mess("In MyClass");
Test.Function1();
}
运行结果展示
debug 模式下:
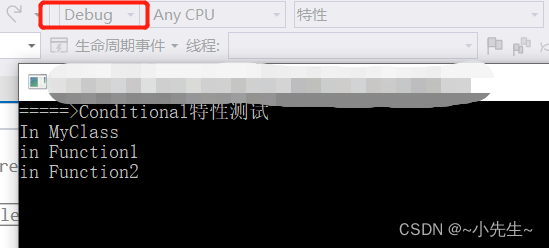
release模式下:

Obsolete 特性
一个程序可能在其生命周期中经历多次发布,而且很可能延续多年。在程序生命周期的后半部分,程序员经常需要编写类似功能的新方法替换老方法。处于多种原因,你可能不再使用哪些调用过时的旧方法的老代码。而只想用新编写的代码调用新方法。旧的方法不能删除,因为有些旧代码也使用的旧方法,那么如何提示程序员使用新代码呢?可以使用Obsolete特性将程序结构标注为过期的,并且在代码编译时,显示有用的警告信息。
[Obsolete("该方法已过时")]
public static void OTest()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是Obsolete特性");
}
/// <summary>
/// 当error为true时,该方法编译不了
/// </summary>
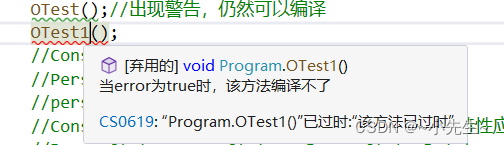
[Obsolete(message: "该方法已过时",error: true)]
public static void OTest1()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是Obsolete特性");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("=====>Obsolete特性测试");
OTest();//出现警告,仍然可以编译
OTest1();//出现错误,无法编译
}

Seriallizeable特性
序列化是将对象状态转换为可保持或传输的格式的过程。与序列化相对的是反序列化,它将流转换为对象。这两个过程结合起来,可以轻松地存储和传输数据。
[Serializable]//代表该类可以被序列化
public class Student
{
public int id {
get; set; }
}
自定义特性
自定义特性类继承自Attribute抽象类
1.AttributeUsage默认可以标注所有(类、方法、字段[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.All)]),也可以进行指定: AttributeTargets.Method| AttributeTargets.Property,多个用|符号进行指定;
2.AllowMultiple =true表示可以在同一类或方法等上面进行多次标识
3.Inherited=true代表被继承的类可以继承该特性类的属性
4.AttributeTargets.ReturnValue| AttributeTargets.Parameter代表特性可以修饰返回值和参数
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method|
AttributeTargets.Property| AttributeTargets.Class| AttributeTargets.ReturnValue| AttributeTargets.Parameter,
AllowMultiple = true, Inherited =true)]
public class CustomAttribute : Attribute
{
public CustomAttribute()
{
}
public CustomAttribute(string a)
{
Console.WriteLine($"这是string参数{
a}");
}
public CustomAttribute(int a)
{
Console.WriteLine($"这是int参数{
a}");
}
}
//[CustomAttribute] 或
[CustomAttribute()]
public class Person
{
[CustomAttribute]
[CustomAttribute(89)]
public int id {
get; set; }
[CustomAttribute("这是name")]
public string name {
get; set; }
//[CustomAttribute("这是方法")]
[return: CustomAttribute]
public static void Test([CustomAttribute]string msg)
{
}
}
特性中Inherited属性详解
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class|AttributeTargets.Method,Inherited =true)]
public class ScopeAttribute : Attribute
{
public ScopeAttribute()
{
}
}
[Scope]
public class StudentInher
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Inherited=true 代表标记类被继承,那么特性也会继承过去
/// </summary>
public class NewStudentInher: StudentInher
{
}
public static void TestInhretied()
{
Type type = typeof(NewStudentInher);
if (type.IsDefined(typeof(ScopeAttribute), true))
{
Console.WriteLine("NewStudentInher上面存在ScopeAttribute特性");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("NewStudentInher上面不存在ScopeAttribute特性");
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("=====>基于特性的Inherited应用测试");
TestInhretied();
Console.ReadKey();
}
特性使用举例
/// <summary>
/// 定义放到字段上面的特性
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Field)]
public class RemarkAttribute : Attribute
{
public int Id {
get; set; }
public string Describe {
get; private set; }
public RemarkAttribute(string des,int id)
{
Describe = des;
Id = id;
}
public RemarkAttribute(string des)
{
Describe = des;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 扩展方法:针对已有类进行方法扩展
/// 步骤:1.必须是静态类
/// 2.定义的方法第一个参数前面是this 扩展类名称 参数名称
/// </summary>
public class AttributeExtend
{
public static string GetDescribeInfor(Enum value)
{
//获取枚举type类型
Type type = value.GetType();
FieldInfo filed = type.GetField(value.ToString());
if (filed.IsDefined(typeof(RemarkAttribute), true))
{
var attribute = (RemarkAttribute)filed.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(RemarkAttribute), true);
return $"id={
attribute.Id},describe={
attribute.Describe}";
}
else
{
return value.ToString();
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 用户枚举
/// </summary>
public enum PersonState
{
[RemarkAttribute("正常状态", 1001)]
Normal,
[RemarkAttribute("冻结状态",1002)]
Frozen,
[RemarkAttribute("删除状态",1003)]
Delete,
}
//测试
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("=====>基于枚举扩展方法与特性应用测试");
PersonState personState = PersonState.Delete;
var result = AttributeExtend.GetDescribeInfor(personState);
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
参考文章1:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38507850/article/details/79181319
参考文章2:https://blog.csdn.net/lym940928/article/details/80550416