case 表达式从SQL-92标准开始引入,因此是不依赖于具体的数据库技术,可提高SQL代码的可移植性。
case表达式注意事项:
1. 统一各个分支返回数据类型,并保证各个when字句的排他性,因为在发现为真的when字句时, case表达式真假值判断会终止,不会执行后边的判断;
2. 不要忘记写END;
3. 养成写ELSE字句的习惯,尽管不写ELSE语法并不会报错,但是如果前面条件不满足会返回NULL,有助于调试查找问题
case表达式常见用例:
1、用CHECK约束定义多个列的条件关系
比如规定公司男员工工资不得高于2000, 就可以写成
constriant check_salary check(case when sex = '2' then case when salary <= 2000 then 1 else 0 end else 1 end =1)
不能写成逻辑与的关系 constraint check_salary check(sex = '2' and salary<= 2000),这样的话女性也不满足这个条件,无法被写入。
2、UPDATE字句进行调节分支
比如有需求将工资小于10000的调薪10%, 大于20000的降薪5%
| name | salary |
|---|---|
| June | 25000 |
| lucy | 9000 |
| sherry | 9800 |
| alina | 15000 |
如果你想用两个update,那就出错了,因为你会把salary给更新掉,一般情况会增加一个字段为调薪后字段,salary字段保持不变,但如果直接更新salary,就可以用case表达式
update Salaries set salary = case when salary <= 10000 then salary *1.1 when salary > 20000 then salary*0.95 else salary end;
注意最后的else字句千万不能丢,否则没有被捕获到的员工的工资会变为NULL
3、表之间数据匹配
有两张表,一张是课程表course,一张为每月开设的课程open_course
| course_id |
course_name |
|---|---|
| 1 | 计算机网络 |
| 2 | 数据结构与算法 |
| 3 | 高性能MySQL |
| 4 | python核心编程 |
| month_tab |
course_id |
|---|---|
| 201806 |
1 |
| 201806 |
3 |
| 201806 |
4 |
| 201807 |
4 |
| 201808 |
2 |
| 201808 | 4 |
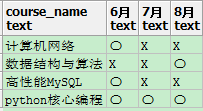
Q3.1:将两张表转为交叉表,便于查看每月开设的课程
SQL1:
select course_name, case when course_id in ( select course_id from sherry.openCourse where month_tab = '201806') then '〇' else 'X' end as "6月", case when course_id in ( select course_id from sherry.openCourse where month_tab = '201807') then '〇' else 'X' end as "7月", case when course_id in ( select course_id from sherry.openCourse where month_tab = '201808') then '〇' else 'X' end as "8月" from sherry.courseMaster
SQL2:
select month_tab, case when max(case when course_id = 1 then 1 else 0 end) = 1 then '〇' else 'X' end as "计算机网络", case when max(case when course_id = 2 then 1 else 0 end) = 1 then '〇' else 'X' end as "数据结构与算法", case when max(case when course_id = 3 then 1 else 0 end) = 1 then '〇' else 'X' end as "高性能MySQL", case when max(case when course_id = 4 then 1 else 0 end) = 1 then '〇' else 'X' end as "python核心编程" from sherry.openCourse group by month_tab order by month_tab

4、将已有编号方式转换为新的方式并统计(聚合函数嵌套进case表达式)
Q4.1:比如查询某个城市男女分别有多少人,源表如下
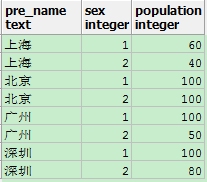
select pre_name, sum(case when sex = 1 then population else 0 end) as "男", sum(case when sex = 2 then population else 0 end) as "女" from sherry.popTbl2 group by pre_name

Q4.2:如果查询结果求每个地区共多少人
select case when pre_name in ('上海') then '华东地区' when pre_name in ('北京') then '华北地区' when pre_name in ('广州','深圳') then '华南地区' end as area, sum(population) from sherry.popTbl2 group by case when pre_name in ('上海') then '华东地区' when pre_name in ('北京') then '华北地区' when pre_name in ('广州','深圳') then '华南地区' end
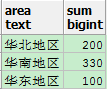
注意group by 也要再写一遍,PostgreSQL可以直接写group by area,好像是因为在进行group by 操作前会先扫描一下select后面的字段。
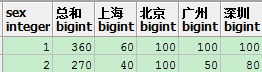
5、聚合函数使用case表达式
仍然是源表sherry.popTbl2,如果把行结构数据转为列结构,即列为全国和各个地区,行为不同性别
select sex,sum(population) as "总和",sum(case when pre_name = '上海' then population else 0 end) as "上海", sum(case when pre_name = '北京' then population else 0 end) as "北京", sum(case when pre_name = '广州' then population else 0 end) as "广州", sum(case when pre_name = '深圳' then population else 0 end) as "深圳" from sherry.popTbl2 group by sex
6、order by字句使用case表达式
比如上述课程表course, 我们使用order by course_id, 则结果是1,2,3,4
Q6.1:但如果我们想结果为3,2,1,4呢,就可以用case表达式实现
select course_id from sherry.courseMaster order by case when course_id = 3 then 1 when course_id = 2 then 2 when course_id = 1 then 3 when course_id = 4 then 4 end
参考:SQL进阶教程