首次适应算法
首次适应算法找到一个可以分配的内存块就进行分配,下一次分配时还是从空闲分区链头开始找,该算法倾向于优先利用内存中低址部分的空闲分区,从而保留了高址部分的大空闲区,这为以后到达的大作业分配大的内存空间创造了条件。
但是低址部分不断被划分,会留下许多难以利用的,很小的空闲分区(碎片)。而每次查找又都是从低址部分开始的,会增加查找可用空闲分区时的开销;
定义内存块,作业,分区链结构体。空闲分区用循环链表串起,正在运行的作业用数组记录,分配失败的作业用另一个数组记录。设置开始分配时起始指针(上一次分配的内存块的后一块),查找时使用的遍历指针,分区起始地址最小的链头指针,一个空闲分区的最小大小。
查找过程如果找到符合的分区,就分配给作业,将作业放入运行中数组;否则放入分配失败数组
回收过程查找运行作业数组,从链头开始对比分区起始地址加上大小后 与作业分配的起始地址的大小;
若小于则往后找分区;
若大于则判断作业起始地址加上分配的大小 与分区起始地址的关系,关系为等于则修改分区内容,否则将分配给作业的内存空间构造新分区插入空闲分区链合适位置;
若等于则判断作业起始地址加上分配的大小 与下一空闲分区起始地址的关系,若相等则修改当前分区并删除下一分区,不等则只修改分区
代码如下
#include<iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
struct block
{
int address; //内存块起始地址
int size; //内存块大小
}BLOCK; //内存块
struct job
{
char id[10]; //作业id
int address; //作业分配的内存起始地址
int size; //作业需要的大小
int alloc_size; //作业分配的大小
}; //作业
struct free_blocks_linklist
{
block free_block; //空闲内存块
free_blocks_linklist* next; //指向下一内存块的指针
}Free_Blocks_linklist; //空闲分区链
job running_job[10]; //运行中的作业数组
int running_job_num = 0;
job waiting_job[10]; //分配失败后等待的作业数组
int waiting_jon_num = 0;
job finish_job[10]; //完成的作业数组
int finish_job_num = 0;
free_blocks_linklist * header = nullptr; //内存分区链头指针
void Init()
{
header = new free_blocks_linklist;
cout << "请输入内存大小(kB) : ";
cin >> header->free_block.size;
cout << "请输入内存起始地址 : ";
cin >> header->free_block.address;
header->next = header;
/*cin >> hex >> a;
cout << a << endl;
cout << hex <<a;*/
}
bool alloc_memory(job &j)
{
free_blocks_linklist* temp = header;
if (temp == nullptr)
{
cout << "\n\n内存不足分配失败" << endl;
return false;
}
while (1)
{
if (temp->free_block.size < j.size && temp->next != header)
temp = temp->next; //分区内存不够且后面还有分区
else if (temp->free_block.size == j.size) //分区内存正好
{
if (temp->next == temp) //只剩一个分区
{
j.address = temp->free_block.address;
j.alloc_size = j.size;
delete temp;
header = nullptr;
cout << "\n\n分配内存成功" << endl;
return true;
}
else //有多个分区
{
j.address = temp->free_block.address;
j.alloc_size = j.size;
temp = temp->next;
delete temp;
cout << "\n\n分配内存成功" << endl;
return true;
}
}
else if (temp->free_block.size > j.size) //内存块分配后还有空间
{
j.address = temp->free_block.address;
j.alloc_size = j.size;
temp->free_block.size -= j.size;
temp->free_block.address += j.size;
cout << "\n\n分配内存成功" << endl;
cout << "\n\n请按任意键继续" << endl;
_getch();
return true;
}
else
{
cout << "\n\n没有合适内存块分配" << endl;
return false;
}
}
}
void run_job(job j)
{
if (true == alloc_memory(j)) //分配成功
running_job[running_job_num++] = j;
else
waiting_job[waiting_jon_num++] = j;
}
void show_message()
{
system("cls");
free_blocks_linklist* temp = header;
int i = 1;
cout << "\n\n当前运行的作业数量为:" << running_job_num <<endl;
cout << "正在等待分配内存的作业数量(分配内存失败)为:" << waiting_jon_num << endl;
cout << "已完成作业数量为: " << finish_job_num << endl;
cout << "\n当前内存空间信息如下 : " << endl;
if (header != nullptr)
{
do
{
cout << "\n内存块" << i << "起始地址为: " << temp->free_block.address << endl;
cout << "内存块" << i << "大小为: " << temp->free_block.size << endl;
temp = temp->next;
i++;
} while (temp != header);
}
else cout << "\n内存空间已经用完" << endl;
cout << "\n\n请按任意键继续" << endl;
_getch();
}
void input_job()
{
job temp;
cout << "请输入作业名: " << endl;
cin >> temp.id;
cout << "请输入作业大小: " << endl;
cin >> temp.size;
run_job(temp);
show_message();
return;
}
void release_memory(int count) //count为要释放作业的序号
{
if (header == nullptr)
{
header = new free_blocks_linklist;
header->free_block.address = running_job[count].address;
header->free_block.size = running_job[count].alloc_size;
header->next = header;
}
else
{
free_blocks_linklist* temp = header;
while (temp->next != header)
{
temp = temp->next;
} //找到链尾
if (running_job[count].address == temp->free_block.address + temp->free_block.size)
{ //作业分配的内存地址最大且可合并
temp->free_block.size += running_job[count].alloc_size;
}
else if (running_job[count].address > temp->free_block.address + temp->free_block.size)
{ //作业分配的内存地址最大且不可合并
free_blocks_linklist* temp1 = new free_blocks_linklist;
temp1->free_block.address = running_job[count].address;
temp1->free_block.size = running_job[count].alloc_size;
temp1->next = header;
temp->next = temp1;
}
else if (header->free_block.address == running_job[count].address + //作业分配的地址最小且可合并
running_job[count].alloc_size)
{
header->free_block.address = running_job[count].address;
header->free_block.size += running_job[count].alloc_size;
}
else if (header->free_block.address > running_job[count].address + //作业分配的地址最小且不可合并
running_job[count].alloc_size)
{
temp = new free_blocks_linklist;
temp->free_block.address = running_job[count].address;
temp->free_block.size = running_job[count].alloc_size;
temp->next = header;
free_blocks_linklist* temp1 = header;
while (temp1->next != header)
temp1 = temp1->next;
temp1->next = temp;
header = temp;
}
else //作业回收的地址在分区链中间
{
temp = header;
while (temp->next->free_block.address + temp->next->free_block.size < running_job[count].address)
temp = temp->next; //找到要插入的前一分区位置temp
if (temp->free_block.address + temp->free_block.size == running_job[count].address)
{ //前分区可以合并
if (running_job[count].address + running_job[count].alloc_size == temp->next->free_block.address)
{ //回收时可以和前后分区合并
temp->free_block.size += running_job[count].alloc_size + temp->next->free_block.size;
free_blocks_linklist* temp1 = temp->next;
temp->next = temp1->next;
delete temp1;
}
else //只能与前分区合并
{
temp->free_block.size += running_job[count].alloc_size;
}
}
else //前分区不可合并
{
if (temp->next->free_block.address == running_job[count].address + running_job[count].alloc_size)
{//后分区可以合并
temp->next->free_block.address -= running_job[count].alloc_size;
temp->next->free_block.size += running_job[count].alloc_size;
}
else
{//后分区不可以合并
free_blocks_linklist* temp1 = new free_blocks_linklist;
temp1->free_block.address = running_job[count].address;
temp1->free_block.size = running_job[count].alloc_size;
temp1->next = temp->next;
temp->next = temp1;
}
}
}
}
finish_job[finish_job_num++] = running_job[count];
running_job[count] = running_job[--running_job_num];
cout << "释放内存成功" << endl;
cout << "\n\n请按任意键继续" << endl;
_getch();
}
void show_running_job()
{
system("cls");
int i = 0;
cout << "当前正在运行的作业信息如下:\n" << endl;
while (i < running_job_num)
{
cout << "序号: " << i
<< "\t作业名: " << running_job[i].id
<< "\t大小: " << running_job[i].size << endl;
i++;
}
cout << "请输入要释放的作业序号 : ";
cin >> i;
if (i >= running_job_num || i < 0)
{
cout << "\n\n输入序号有误,请按任意键重新输入" << endl;
show_running_job();
}
else
{
release_memory(i);
show_message();
}
}
void release_job()
{
show_running_job();
}
void menu()
{
char choice;
while (1)
{
system("cls");
cout << " 1: 输入作业" << endl;
cout << " 2: 释放作业" << endl;
cout << " 3: 离开" << endl;
cout << "\n\n\n请输入选择: " << endl;
choice = _getch();
if (choice == '1')
input_job();
else if (choice == '2')
release_job();
else if (choice == '3')
exit(0);
else
{
cout << "输入有误,请按任意键继续" << endl;
_getch();
}
}
}
int main()
{
Init();
menu();
return 0;
}输入内存大小640kb,起始地址0

作业1申请130KB后

作业2申请60KB后

作业3申请100KB后

作业2释放60KB后

作业4申请200KB后

作业3释放100KB后

作业1释放130KB后

作业5申请140KB后
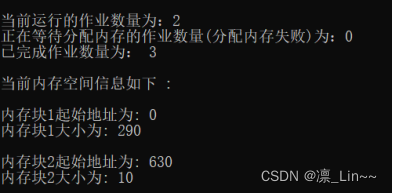
作业6申请60KB后

作业7申请50KB后

作业8申请60KB后

最佳适应算法
最佳适应算法在分区链中寻找可以分配且分配后剩余空间最小的分区,这样可以使分区碎片最小化,留下一些大分区,但是每次都要遍历分区链表,效率较低。(或者事先进行排序,维护空闲分区大小升序,但开销还是会比较大,而且合并时也需要查一次分区链)
最佳适应算法与首次适应算法只在分配时策略不同。最佳适应算法分配时从分区链头开始找,直到有一个分区大小 不小于作业大小。如果找不到说明没有分区块可以分配。如果找到,将这个分区块标记下,然后往后寻找大小满足作业要求,又尽可能小的分区,找到就将标记替换。
得到最佳块后,分情况讨论;
若分区块大小等于作业大小且内存只剩这个块,分配后header置null,分区链内存释放
若分区块大小等于作业大小且内存还有多块,将此分配分区 后一个分区的内容赋值给该分区,修改指针后释放后一分区
若分区块大小大于作业大小,只修改分区信息
代码如下
#include<iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
struct block
{
int address; //内存块起始地址
int size; //内存块大小
}BLOCK; //内存块
struct job
{
char id[10]; //作业id
int address; //作业分配的内存起始地址
int size; //作业需要的大小
int alloc_size; //作业分配的大小
}; //作业
struct free_blocks_linklist
{
block free_block; //空闲内存块
free_blocks_linklist* next; //指向下一内存块的指针
}Free_Blocks_linklist; //空闲分区链
job running_job[10]; //运行中的作业数组
int running_job_num = 0;
job waiting_job[10]; //分配失败后等待的作业数组
int waiting_jon_num = 0;
job finish_job[10]; //完成的作业数组
int finish_job_num = 0;
free_blocks_linklist * header = nullptr; //内存分区链头指针
void Init() //初始化内存
{
header = new free_blocks_linklist;
cout << "请输入内存大小(KB) : ";
cin >> header->free_block.size;
cout << "请输入内存起始地址 : ";
cin >> header->free_block.address;
header->next = header;
/*cin >> hex >> a;
cout << a << endl;
cout << hex <<a;*/
}
bool alloc_memory(job &j) //给作业分配内存
{
free_blocks_linklist* temp = header;
free_blocks_linklist* temp1 = nullptr; //最佳块指针
if (temp == nullptr)
{
cout << "\n\n内存不足分配失败" << endl;
return false;
}
do
{
if (temp->free_block.size >= j.size) //可以分配
{
temp1 = temp;
temp = temp->next;
break;
}
temp = temp->next;
}while (temp != header); //是否有能分配的块
if(temp1 == nullptr)
{
cout << "\n\n没有合适内存块分配" << endl;
return false;
}
do
{
if (temp->free_block.size >= j.size && temp->free_block.size < temp1->free_block.size)
temp1 = temp; //找到更合适的分区
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp!= header);
if (temp1->free_block.size == j.size) //分区内存正好
{
if (temp1->next == temp1) //只剩一个分区
{
j.address = temp1->free_block.address;
j.alloc_size = j.size;
delete temp1;
header = nullptr;
cout << "\n\n分配内存成功" << endl;
return true;
}
else //有多个分区
{
j.address = temp1->free_block.address;
j.alloc_size = j.size;
temp = temp1->next;
temp1->free_block = temp->free_block;
temp1->next = temp->next;
if (temp == header)
header = header->next;
delete temp;
cout << "\n\n分配内存成功" << endl;
return true;
}
}
else if (temp1->free_block.size > j.size) //内存块分配后还有空间
{
j.address = temp1->free_block.address;
j.alloc_size = j.size;
temp1->free_block.size -= j.size;
temp1->free_block.address += j.size;
cout << "\n\n分配内存成功" << endl;
cout << "\n\n请按任意键继续" << endl;
_getch();
return true;
}
}
void run_job(job j) //调度运行作业
{
if (true == alloc_memory(j)) //分配成功
running_job[running_job_num++] = j;
else
waiting_job[waiting_jon_num++] = j;
}
void show_message() //显示系统信息
{
system("cls");
free_blocks_linklist* temp = header;
int i = 1;
cout << "\n\n当前运行的作业数量为:" << running_job_num <<endl;
cout << "正在等待分配内存的作业数量(分配内存失败)为:" << waiting_jon_num << endl;
cout << "已完成作业数量为: " << finish_job_num << endl;
cout << "\n当前内存空间信息如下 : " << endl;
if (header != nullptr)
{
do
{
cout << "\n内存块" << i << "起始地址为: " << temp->free_block.address << endl;
cout << "内存块" << i << "大小为: " << temp->free_block.size << endl;
temp = temp->next;
i++;
} while (temp != header);
}
else cout << "\n内存空间已经用完" << endl;
cout << "\n\n请按任意键继续" << endl;
_getch();
}
void input_job() //输入作业
{
job temp;
cout << "请输入作业名: " << endl;
cin >> temp.id;
cout << "请输入作业大小: " << endl;
cin >> temp.size;
run_job(temp);
show_message();
return;
}
void release_memory(int count) //释放作业内存, count为要释放作业的序号
{
if (header == nullptr)
{
header = new free_blocks_linklist;
header->free_block.address = running_job[count].address;
header->free_block.size = running_job[count].alloc_size;
header->next = header;
}
else
{
free_blocks_linklist* temp = header;
while (temp->next != header)
{
temp = temp->next;
} //找到链尾
if (running_job[count].address == temp->free_block.address + temp->free_block.size)
{ //作业分配的内存地址最大且可合并
temp->free_block.size += running_job[count].alloc_size;
}
else if (running_job[count].address > temp->free_block.address + temp->free_block.size)
{ //作业分配的内存地址最大且不可合并
free_blocks_linklist* temp1 = new free_blocks_linklist;
temp1->free_block.address = running_job[count].address;
temp1->free_block.size = running_job[count].alloc_size;
temp1->next = header;
temp->next = temp1;
}
else if (header->free_block.address == running_job[count].address + //作业分配的地址最小且可合并
running_job[count].alloc_size)
{
header->free_block.address = running_job[count].address;
header->free_block.size += running_job[count].alloc_size;
}
else if (header->free_block.address > running_job[count].address + //作业分配的地址最小且不可合并
running_job[count].alloc_size)
{
temp = new free_blocks_linklist;
temp->free_block.address = running_job[count].address;
temp->free_block.size = running_job[count].alloc_size;
temp->next = header;
free_blocks_linklist* temp1 = header;
while (temp1->next != header)
temp1 = temp1->next;
temp1->next = temp;
header = temp;
}
else //作业回收的地址在分区链中间
{
temp = header;
while (temp->next->free_block.address + temp->next->free_block.size < running_job[count].address)
temp = temp->next; //找到要插入的前一分区位置temp
if (temp->free_block.address + temp->free_block.size == running_job[count].address)
{ //前分区可以合并
if (running_job[count].address + running_job[count].alloc_size == temp->next->free_block.address)
{ //回收时可以和前后分区合并
temp->free_block.size += running_job[count].alloc_size + temp->next->free_block.size;
free_blocks_linklist* temp1 = temp->next;
temp->next = temp1->next;
delete temp1;
}
else //只能与前分区合并
{
temp->free_block.size += running_job[count].alloc_size;
}
}
else //前分区不可合并
{
if (temp->next->free_block.address == running_job[count].address + running_job[count].alloc_size)
{//后分区可以合并
temp->next->free_block.address -= running_job[count].alloc_size;
temp->next->free_block.size += running_job[count].alloc_size;
}
else
{//后分区不可以合并
free_blocks_linklist* temp1 = new free_blocks_linklist;
temp1->free_block.address = running_job[count].address;
temp1->free_block.size = running_job[count].alloc_size;
temp1->next = temp->next;
temp->next = temp1;
}
}
}
}
finish_job[finish_job_num++] = running_job[count];
running_job[count] = running_job[--running_job_num];
cout << "\n释放内存成功" << endl;
cout << "\n\n请按任意键继续" << endl;
_getch();
}
void show_running_job() //显示正在运行的作业
{
system("cls");
int i = 0;
cout << "当前正在运行的作业信息如下:\n" << endl;
while (i < running_job_num)
{
cout << "序号: " << i
<< "\t作业名: " << running_job[i].id
<< "\t大小: " << running_job[i].size << endl;
i++;
}
cout << "请输入要释放的作业序号 : ";
cin >> i;
if (i >= running_job_num || i < 0)
{
cout << "\n\n输入序号有误,请按任意键重新输入" << endl;
show_running_job();
}
else
{
release_memory(i);
show_message();
}
}
void release_job() //释放作业
{
show_running_job();
}
void menu() //选项菜单
{
char choice;
while (1)
{
system("cls");
cout << " 1: 输入作业" << endl;
cout << " 2: 释放作业" << endl;
cout << " 3: 离开" << endl;
cout << "\n\n\n请输入选择: " << endl;
choice = _getch();
if (choice == '1')
input_job();
else if (choice == '2')
release_job();
else if (choice == '3')
exit(0);
else
{
cout << "输入有误,请按任意键继续" << endl;
_getch();
}
}
}
int main()
{
Init();
menu();
return 0;
}输入内存大小640KB,起始地址0

作业1申请130KB后

作业2申请60KB后

作业3申请100KB后

作业2释放60KB后
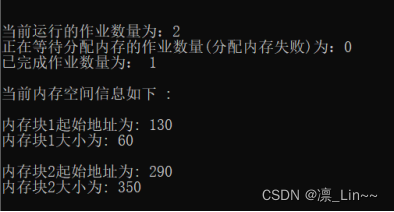
作业4申请200KB后

作业3释放100KB后

作业1释放130KB后
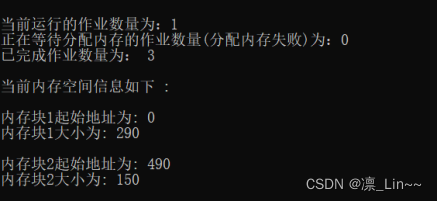
作业5申请140KB后
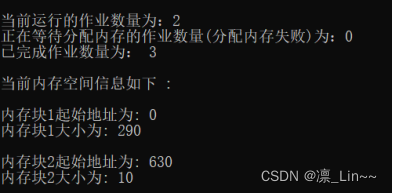
作业6申请60KB后
作业7申请50KB后

作业8申请60KB后
