文章目录
前言
本章重点是了解springMvc主流程做了什么,有些细节不是很详细,它源码也不是晦涩难懂的程度。
SpringMvc启动说明
Tomcat启动的一个过程(简单可能不准确,主要是了解Tomcat做了什么,其实springMvc的初始化是和Tomcat启动挂钩的,所以还是有必要了解的):
- Tomcat启动会解析server.xml,生成
servletContext(servlet上下文), - 解析web.xml,这时会将Tomcat的web.xml和应用的web.xml进行合并,然后将里面配置的
ContextLoaderListener和DispatcherServlet读取到容器里 - 后查找Tomcat下的jar包,查找
ServletContainerInitializer接口实现类,该接口是提供给应用程序进行初始化的,springMvc有实现该接口(springMVC是在classpath下存在META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer这样的一个文件),但并没有做其他操作,通过实现该接口,并且配置在/META-INF/services/下,就能被Tomcat读取得到,并执行,具体的加载逻辑是在WebappServiceLoader - 通过web.xml里的监听器
ContextLoaderListener进行spring容器的初始化 - 最后会通过
DisapatcherServlet初始化servlet容器,web.xml提供了默认的DefaultServlet``JspServlet也在这里执行
还有一个知识点:
servlet-mapping 的优先级如下:
/* > / > *.jsp
在Tomcat中有默认的web.xml,里面配置了两个处理器defaultServlet和JspServlet,分别是处理静态资源和jsp的,
这两个默认的作为缺省配置,当我们项目中没有配置时,Tomcat的默认配置会将其连接,
所以在项目中的配置,需要注意servlet-mapper不要配置成/和/*,因为我们项目中配置的是DispatcherServlet是处理controller那一类的请求,如果配置了/*,优先级高,会把默认的DefualtServlet的也拦截掉,
如下配置,拦截/*,在controller有RequestMapping("/index")

<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
页面请求 xxx/index 就都会走DispatcherServlet,当找不到资源时,它就不会走DefaultServlet,相当于少了一个默认的servlet,
而Tomcat还有一个servlet-mapping,是拦截后缀的,只要请求带上后缀,都会走,
所以,项目中一般配置都是配置*.html或是*.do作为区分,使独立
springMvc主流程
[SpringMVC流程架构图_gmvc图](https://blog.csdn.net/menglixiazhiweizhi/article/details/85318012?ops_request_misc=%7B%22request%5Fid%22%3A%22166495705016782417032134%22%2C%22scm%22%3A%2220140713.130102334…%22%7D&request_id=166495705016782417032134&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2allsobaiduend~default-2-85318012-null-null.142v51new_blog_pos_by_title,201v3control_1&utm_term=springmvc 图&spm=1018.2226.3001.4187)
如容器初始化
springMvc中有一个监听器ContextLoaderListenerTomcat会调用这个初始化容器initWebApplicationContext
位置:org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 1. 判断是否存在父容器,因为他需要初始化,当然已经存在父容器就是有问题的
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
} else {
// 记录日志
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
// 记录时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 创建父容器,也可以说是spring容器
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = this.createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
ApplicationContext parent = this.loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
// 接下来看这个方法,设置并初始化spring容器(bean扫描、实例化、后置处理器、国际化等)
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
// 将如容器设置到servlet上下文
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
} else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
} catch (Error | RuntimeException var8) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", var8);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, var8);
throw var8;
}
}
}
创建spring容器的方法createWebApplicationContext如下
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
// 读取容器类
Class<?> contextClass = this.determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
} else {
// 实例化
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
}
看看底层怎么读取容器类的
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 从servlet上下文获取容器类全名
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter("contextClass");
if (contextClassName != null) {
try
// 不等于空就反射
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var4) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", var4);
}
} else {
// 等于空,就从默认配置中获取
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var5) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", var5);
}
}
}
-
先是从spring容器中查找容器类,
-
如果有就反射获取
-
如果没有就从默认位置读取,看下面这句
java contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());它存在一个default,查找所以引用的地方,它是在
static块下,直接加载的,可以看到它是读取字节码文件目录下的ContextLoader.propertiesstatic { try { ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("ContextLoader.properties", ContextLoader.class); defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); } catch (IOException var1) { throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + var1.getMessage()); } currentContextPerThread = new ConcurrentHashMap(1); }
定位文件位置,还真有一个
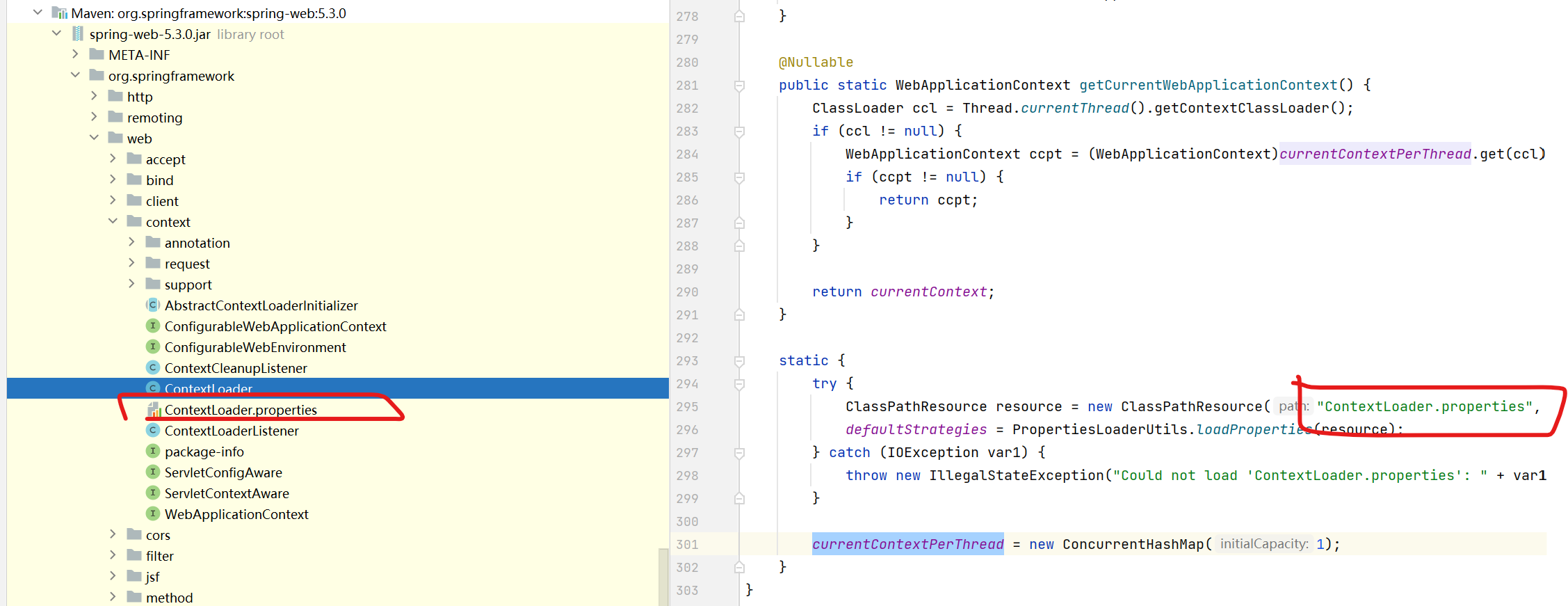
文件内容是:
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
该文件配置的类是XmlWebApplicationContext,我们直接定位过去
再回到org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
ApplicationContext parent = this.loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
// 接下来看这个方法,设置并初始化spring容器
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
String configLocationParam;
// 设置id
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter("contextId");
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setId(configLocationParam);
} else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX + ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
// 将spring容器作为父容器,将servlet容器作为子容器设置
wac.setServletContext(sc);
// 这里的`contextConfigLocation`就是web.xml配置里的那个`contextConfigLocation`,下面给了截图
configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation");
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// 初始化spring容器的配置到servlet容器
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment)env).initPropertySources(sc, (ServletConfig)null);
}
// 初始化操作
this.customizeContext(sc, wac);
// spring 的启动时调用的初始方法,这个在spring篇章讲过的AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类里
// 就是做了扫描bean,创建bean,postProcesser,国际化等操作
wac.refresh();
}

子容器初始化
DispatcherServlet继承HttpServletBean,容器初始化由init()方法完成。
位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean#init
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// 这里是将servlet的配置信息设置的pvs,往细的看扯到了Tomcat的过程, ̄□ ̄||,之后在仔细看Tomcat
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(this.getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
// beanWrapper包装该类
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
// 创建servlet资源加载器
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(this.getServletContext());
// 根据名字看是一个编辑器,在这里的作用是将变量替换,环境加载等操作
// ResourceEditor 资源编辑器,它是对如:file:E:/xxx/xxx,classpaht:xxxx, ${xxx}等这样的资源进行处理
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, this.getEnvironment()));
// 这里并没有实现
this.initBeanWrapper(bw);
// 这里的方法在spring中也有,就是将属性值设置进去
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
} catch (BeansException var4) {
if (this.logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
this.logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'", var4);
}
throw var4;
}
}
// 初始化改servletBean 重点看这个方法,这个是让子类去实现的
this.initServletBean();
}
initServletBean()实现,也就是FrameworkServlet
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
// 打日志
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// 时间记录
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 初始化web容器,也就是servlet容器,上文我说的是servlet容器,一样的
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
// 这里是空实现
initFrameworkServlet();
}
// 下面就是日志一堆
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initWebApplicationContext
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 查找当前servlet上下文对应的跟容器(spring容器)
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
// 暂定servlet容器对象为wac
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// 走这里是构造器实例化就已经传入的
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// 这里它有一个标志 active 这个标志着实例化完,并设置好了web容器需要的环境及工具
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// 如果目前获取到的servlet容器是没有父容器的,那么就把刚刚获取到的设置进去
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
// 开始刷新(设置各种容器环境:bean的扫描、注册、国际化等)
// 注意,这里在刷新完(设置完)会发布一个`ContextRefreshedEvent`事件
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// 构造器没有传入,它就会到servlet 上下文中找,然后返回
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// 如果到这里还没有,就自己创建一个,并刷新(设置容器环境)
// 注意,这里在刷新完(设置各种容器环境:bean的扫描、注册、国际化等)会发布一个`ContextRefreshedEvent`事件
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// 这里判断如果没有刷新,就会在刷新一次,这里再刷新,和`ContextRefreshedEvent`事件监听器里的一样,都是调用子类`DispatcherServlet`的实现方法
// 事件监听器位置在:org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.ContextRefreshListener#onApplicationEvent
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
onRefresh(wac);实际执行是下面这段代码
位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#initStrategies
可以看到它初始化了很多解析器:多文件上传、国际化、动态样式、映射处理器、映射处理器适配器、异常处理器、视图解析器…
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
在上面的demo中我们模拟了HandlerMappings和handlerAdapters,我们着重看一下。
请求流程
当请求过来时,tomcat会之间调用DispatcherServlet来处理,位置在:org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain#internalDoFilter
也就对应的是:javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet#service(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest, javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse)
它这个方法代码就没必要贴出来了,它这个具体的作用就是,请求校验分发的,get的方法调用doGet,post调用doPost这样
映射处理器
在springMvc流程图中,可以知道,HandlerAdapter是根据请求获取到对应的映射处理器,可是它是一个接口,
创建一个请求处理器
在springMvc中,接口处理器:
- @Controller @RequestMapping
- Controller 接口
- HttpRequestHandler
创建servlet请求
方式一:继承HttpServlet,重写doGet或者doPost以处理请求,不过这个是直接用的Tomcat的servlet,所以需要在web.xml中配置servlet-mapping
public class IndexController2 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2964194399437247271L;
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("in httpServlet");
super.doGet(req, resp);
}
}
<servlet>
<servlet-name>indexController2</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.liry.controller.IndexController2</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>indexController2</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/index2.html</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
方式二:实现Controller接口
public class IndexController3 implements Controller {
@Override
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
System.out.println("in controller");
ModelAndView result = new ModelAndView();
result.setViewName("index");
return result;
}
}
然后配置映射
配置映射也是两种方式:
@Component("/index3.html"):注解方式定义beanName未url<bean id="/index3.html" class="com.liry.controller.IndexController3"/>这种方式是经典的xml方式配置
虽说是两种,其实就是一种,两个是一样的,将controller作为一个bean存起来
方式三:@Controller@RequestMapping
最常用也是最方便的方式就是使用注解的方式,一个类里可以处理多个请求
HandlerMapping
SpringMvc流程里,是这样的请求 -> DisaptcherServlet -> HandlerAdapter -> HandlerMapping -> hander
不难看出走到DispatcherServlet后,或通过HandlerAdapter适配对应HandlerMapping,然后使用HandlerMapping处理请求,这里HandlerMapping可以看作是controller,所以,我们可以通过Adapter反推。
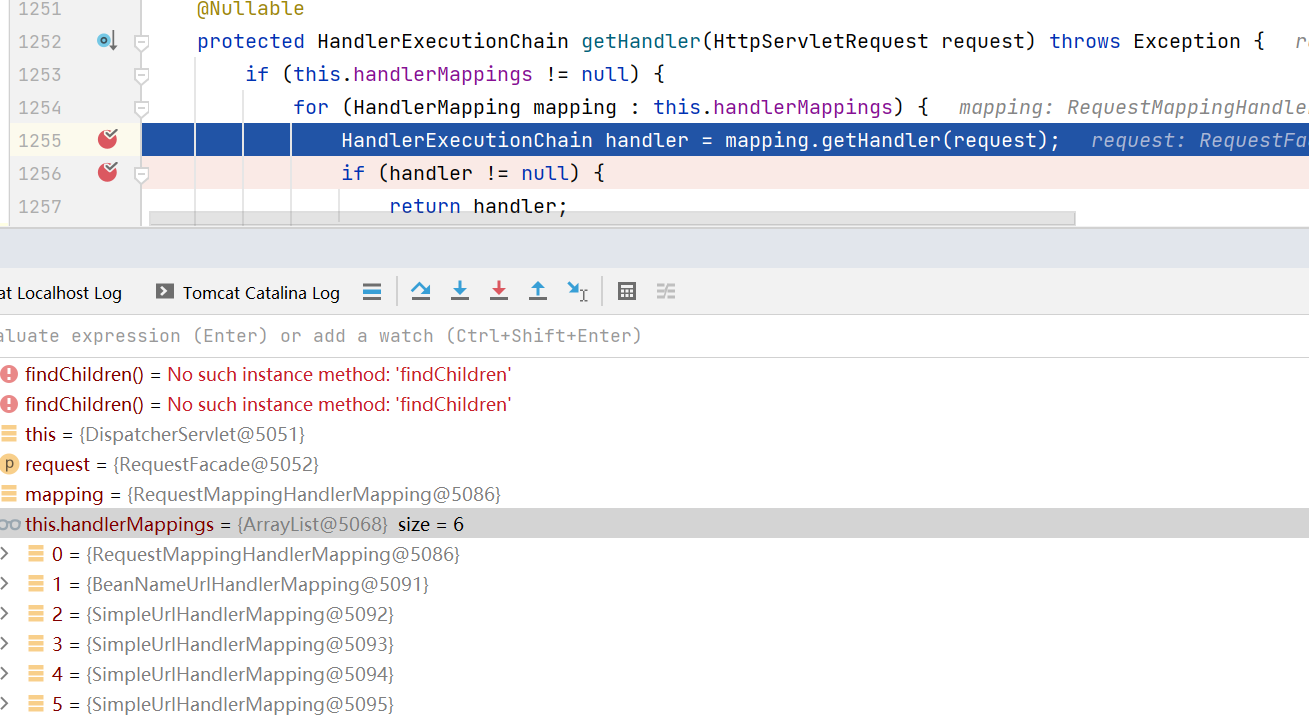
从图中可以看到它获取到了3种类型的HandlerMapping:
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping
- BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
- SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
RequestMappingHandlerMapping
当我们使用@Controller是,就会被它进行扫描到。
当启动应用时,初始化spring容器,会走到回调函数:
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping#afterPropertiesSet
然后走到父类:
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#initHandlerMethods
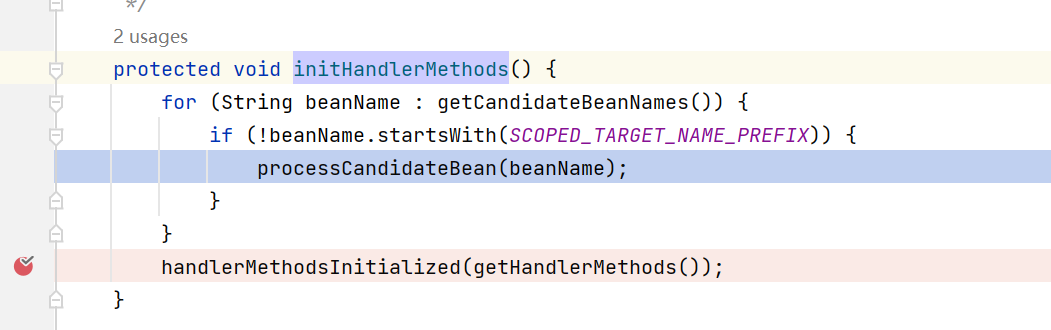
getCandidateBeanNames()该方法会获取到IOC容器中的beanName,然后通过processCandidateBean(beanName)对controller进行解析,看一下内部方法:
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
// 获取class
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
// 这个是判断是否是一个Controller
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
判断条件就是存在:@Controller@RequestMapping,这里要注意,下面判断是 ||前提是标注有@RequestMapping的bean是能被spring扫描到的,@Controller是本时包和一个@Component所以之间判断是没有问题的。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-VkzN9wCB-1665802757031)(E:/ALI/Documents/%E5%BE%85%E5%8F%91%E5%B8%83%E6%96%87%E7%AB%A0/Typora/typora/images/image-20221014000036670.png)]
然后看一下解析处理器的过程:
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
// 匿名函数,处理指定class和method对象
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
查找RequestMapping标注的方法的逻辑如下:
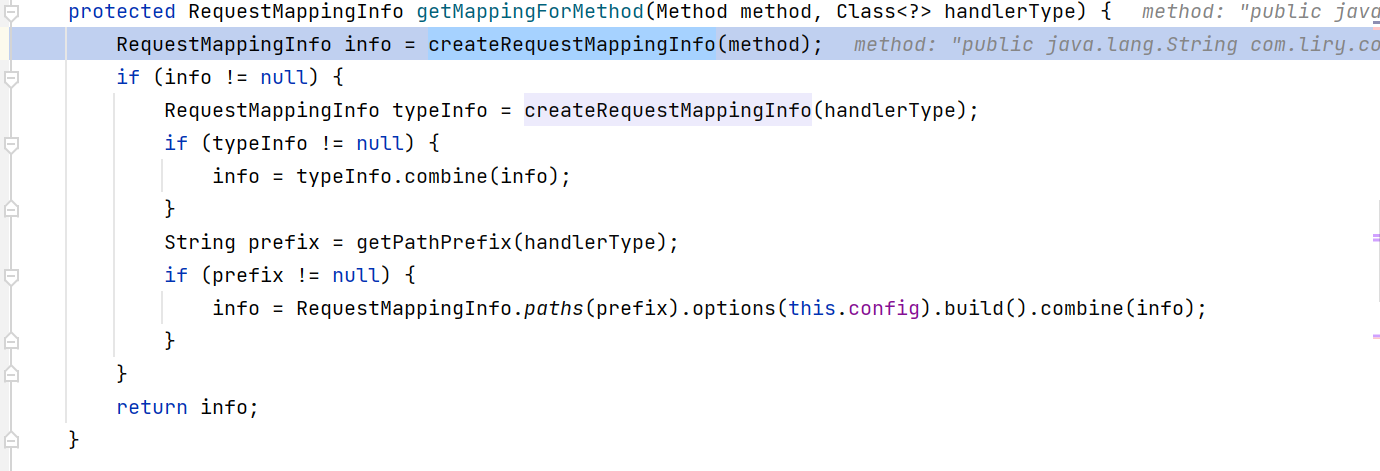
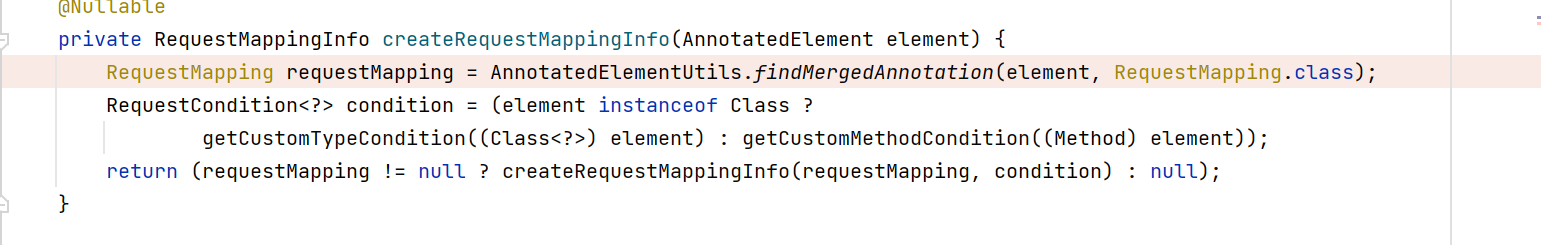
它最终找的是RequestMapping,可是,我们也用了GetMapping, PostMapping, DeleteMapping这些注解,难道还有其他方法来查找吗?
可惜不是,查看GetMapping注解定义,GetMapping被RequestMapping标注,那么相当于标注了GetMapping的方法也标注了RequestMapping,而且GetMapping的属性都通过@AliasFor注解进行关联,所以这就是使用GetMapping和使用RequestMapping一样效果的原因了。
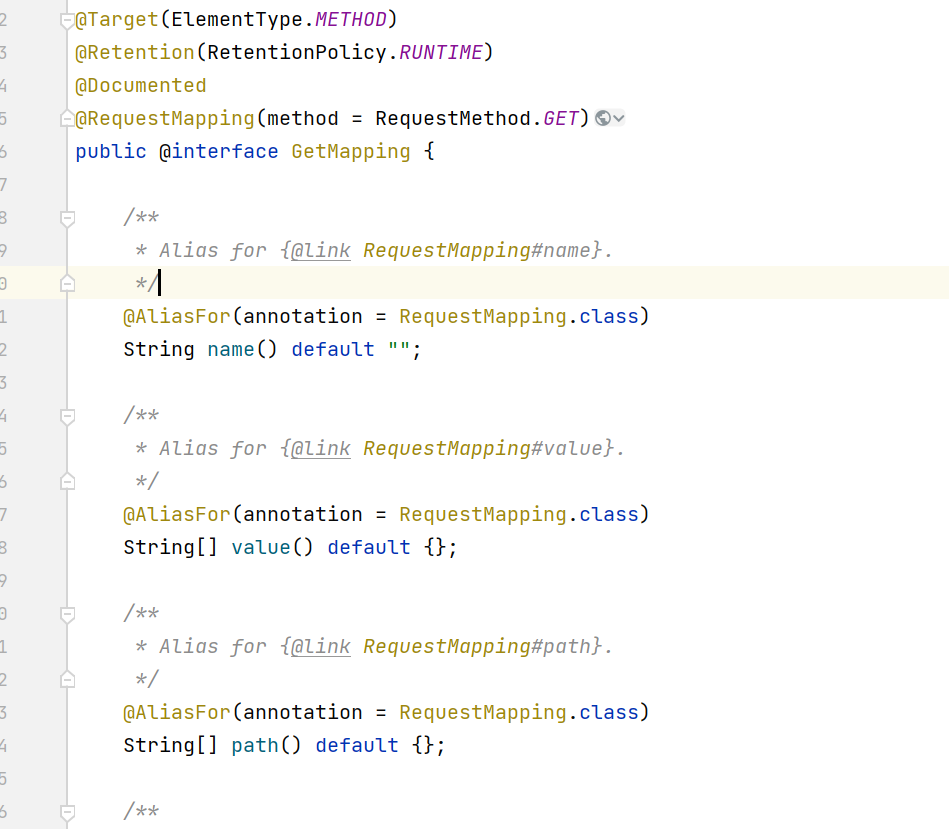
还是可以看一下它内部的方法逻辑,它是将方法解析出来的对象RequestMappingInfo作为value,method作为key,存入map中,
public static <T> Map<Method, T> selectMethods(Class<?> targetType, final MetadataLookup<T> metadataLookup) {
final Map<Method, T> methodMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
Set<Class<?>> handlerTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
Class<?> specificHandlerType = null;
// 判断是否是代理类
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetType)) {
specificHandlerType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetType);
handlerTypes.add(specificHandlerType);
}
// 获取所有的接口的class
handlerTypes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetType));
for (Class<?> currentHandlerType : handlerTypes) {
// 这里还不太懂,代理对象要这样处理
final Class<?> targetClass = (specificHandlerType != null ? specificHandlerType : currentHandlerType);
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(currentHandlerType, method -> {
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);
if (result != null) {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {
methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);
}
}
}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
}
return methodMap;
}
最有以mapping(url) 为key,注册到mapperRegistry里,内部由分了pathLookup, nameLookup, corsLookup,只有的获取handler是之间从pathLookUp中获取

SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
这里还要提一点,开篇我们对tomcat进行了简单的说明:Tomcat 启动会读取web.xml,先是读取应用的web.xml,然后将Tomcat的web.xml进行合并,而Tomcat的web.xml中配置了两个Servlet,一个是DefaultServlet,一个是JspServlt,两个分别处理静态资源和jsp页面的。
而这里SimpleUrlHandlerMapping就是处理静态资源的,这里由4个,分别是:
/css/**/js/**/image/**/
前三个是对应问哦们spring-mvc.xml里配置的静态资源映射:
<!--静态资源映射-->
<!--本项目把静态资源放在了webapp的statics目录下,资源映射如下-->
<mvc:resources mapping="/css/**" location="/statics/css/"/>
<mvc:resources mapping="/js/**" location="/statics/js/"/>
<mvc:resources mapping="/image/**" location="/statics/images/"/>
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/> <!--这句要加上,要不然可能会访问不到静态资源,具体作用自行百度-->
而最后一个是tomcat里的web.xml里配置的DefaultServlet拦截,作为最后一道拦截。
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
顾名思义,这个是将beanName作为url映射的处理器,在上面创建处理器的配置方式,已经可以理解,它是将beanName作为url拦截地址。
SimpleURLHandlerMapping和BeanNameURLHandlerMapping的父类都是org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping
他们都是属于通过url地址进行匹配处理器的方式,只是最后处理的对象不同,导致了出现了不同的实现
总结
HandlerMapping可以归为两种方式,
- 扫描指定的注解作为请求处理器的标识
- 扫描bean,然后将beanName以
/开头的bean作为处理器
HandlerAdapter
以HandlerMapping相对应的它也有3个Adapter
-
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
-
HttpRequestHandlerAdapter
-
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter
位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#getHandlerAdapter
它会遍历Adapter,然后通过调用adapter.supports()来判断该Adapter是否支持handler,supports方法已经没用悬念了。
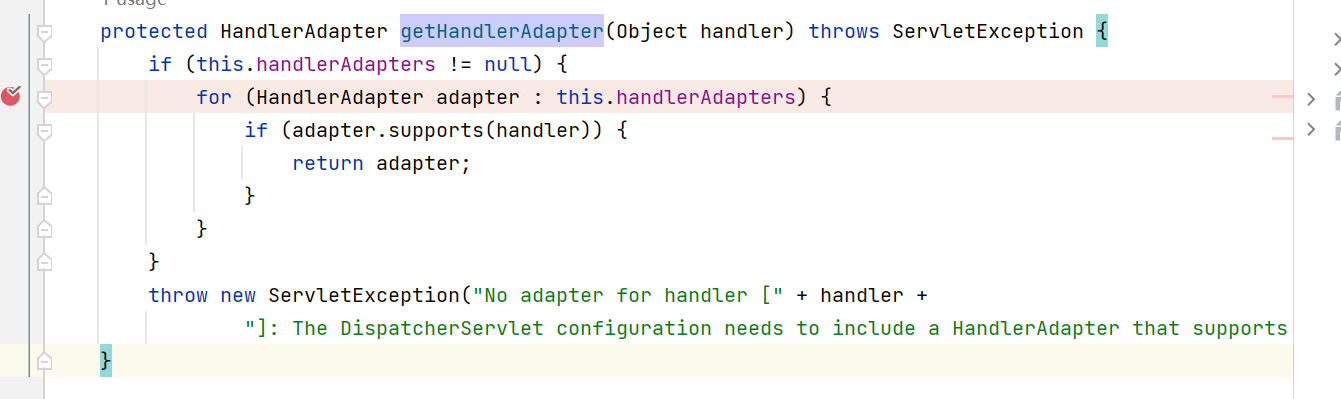
之后就是调用HandlerAdatper.handler反射执行,这就是它的一个主要流程。
demo - 模拟SpringMvc主流程
针对上面我们所了解的,根据spring容器+Tomcat写一个springMvc,只是尝试一下