标准模板库STL(Standard Template Library)是一组模板类和函数,包括
- 存储信息的容器
- 访问容器中存储信息的迭代器
- 操作容器内容的算法
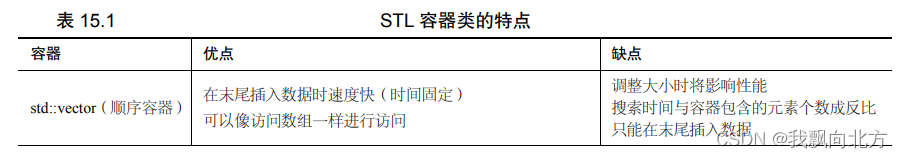
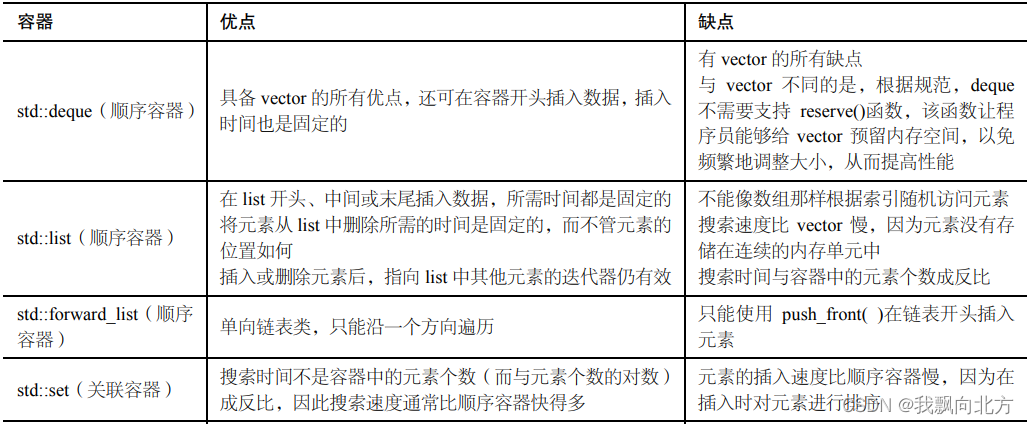
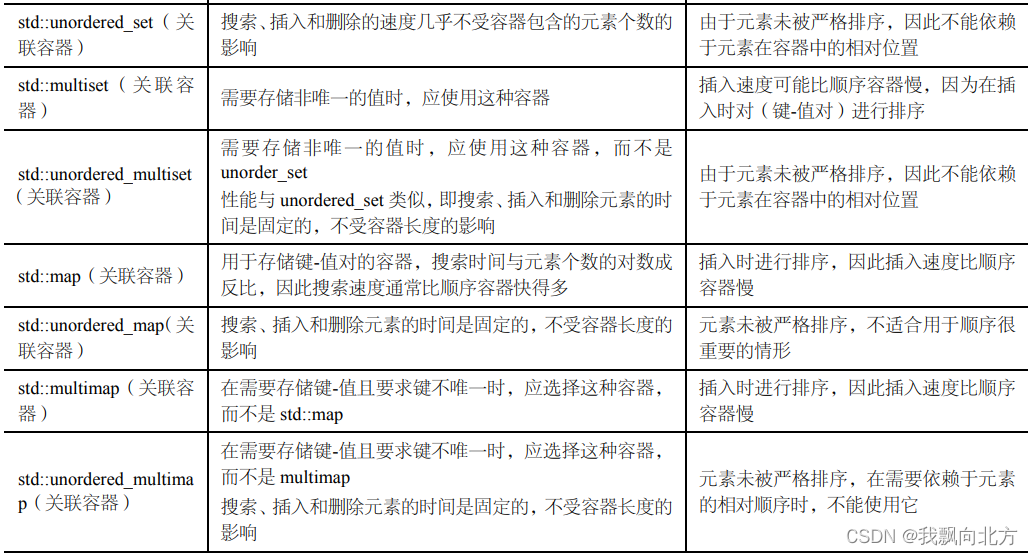
容器
包含两类:顺序容器、关联容器。在此基础之上还有容器适配器(Container Adapter)
- 顺序容器 -------> std::vector / std::deque / std::list / std::forward_list
- 关联容器 -------> std:: set / unordered_set / map / unordered_map / mutiset / unorder_multiset / multimap / unordered_multimap
- 容器适配器 -------> std:: stack / queue / priority_queue
迭代器
最简单的迭代器是指针。STL迭代器是模板类(某种程度上,可以说是泛型指针)
STL迭代器分为基本的两大类:
- 输入迭代器:通过对输入迭代器解除引用,它将引用对象,而对象可能位于集合中。最严格的输入迭代器确保只能以只读的方式访问对象。
- 输出迭代器:让程序员对集合执行写入操作。最严格的输出迭代器确保只能执行写入操作。
对上述两类基本迭代器不断细化,得到:
- 前向迭代器:允许输入和输出,用于单向链表。
- 双向迭代器:对前向迭代器细化,可执行递减操作从而向后移动,用于双向链表。
- 随机访问迭代器:对双向迭代器细化,可加减一个偏移量,还可将两个迭代器相减从而得到两个元素的相对距离,常用于数组。
STL算法
以下算法都是std命名空间的模板函数,必须包含头文件**<algorithm>**
std::find:在集合中查找值
find_if:根据用户指定的谓词在集合中查找值
reverse:反转集合中元素的排列顺序
remove_if:根据用户定义的谓词将元素从集合中删除
transform:使用用户定义的变换函数对容器中的元素进行变换
STL string类
std::string 和 std::wstring 实际上是同一个模板类 std::basic_string<T>的具体化
最常用的字符串函数包括:复制、连接、查找字符和子字符串、截短、配合STL算法实现字符串反转和大小写转换
使用string类,必须包含头文件**<string>**
实例化和复制
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const char* constCStyleString = "Hello string!";
cout << "Const string: " << constCStyleString << endl;
//方式1:使用C风格常量字符串初始化string对象(类似于:string str2 = constCStyleString;)
string strFromConst (constCStyleString);
cout << "strFromConst is: " << strFromConst << endl;
//方式2:构造器方式(类似于:string str2 = "Hello String!";)
string str2 ("Hello String!");
cout << "string str2: " << str2 << endl;
//复制:
string strCopy (str2);
cout << "strCopy: " << strCopy << endl;
//构造C风格字符串的前三个字符(传入的必须是const char*, 如果传入str2,就是其他重载函数)
string strPartialCopy (constCStyleString, 3);
cout << "strPartialCopy: " << strPartialCopy << endl;
//方式3:=复制构造string对象
string equalTestString = "abc";
cout << "equalTestString: " << equalTestString << endl;
//包含指定字符数量的string对象(10个a字符)
string strRepeatChar (10, 'a');
cout << "strReapeatChar: " << strRepeatChar << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
访问string字符内容
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
string strSTLString ("Hello String");
//方式1:通过string实现的下标运算符([])以类似数组的语法遍历string对象中的字符
cout << "Displaying the elements in the string using array-syntax: " << endl;
for (size_t nCharCounter = 0;
nCharCounter < strSTLString.length()
; ++nCharCounter)
{
cout << "Character [" << nCharCounter << "] is: ";
cout << strSTLString [nCharCounter] << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//方式2:迭代器
cout << "Displaying the contents of the string using iterators: " << endl;
int charOffset = 0;
string::const_iterator iCharacterLocator;
for ( iCharacterLocator = strSTLString.begin()
; iCharacterLocator != strSTLString.end()
; ++iCharacterLocator)
{
cout << "Character [" << charOffset++ << "] is: " ;
cout << *iCharacterLocator << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "The char* represemtation of the string is: ";
cout << strSTLString.c_str() << endl;
return 0;
}
方式1:保证偏移量(nCharCounter)不超过string对象的长度( length() )
方式2:对迭代器解引用访问
拼接字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1 = "Hello";
string str2 = "world";
//方式1:运算符“+=”
str1 += str2;
cout << "after +=,str1: " << str1 << endl;
//方式2:append方法
string str3 = "Fun is not need to use pointers!";
str1.append(str3);
cout << "after append, str1: " << str1 << endl;
//append方法的重载:接收一个C风格字符串
const char* constCStyleString = "You however still can!";
str1.append(constCStyleString);
cout << str1 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
查找字符或子字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string strSample ("Good day String! Today is beautiful!");
cout << "The sample string is: " << endl;
cout << strSample << endl << endl;
//string类中的find方法,以下表示从索引20开始查找子字符串“day”
size_t charPos = strSample.find("day", 20);
if(charPos != string::npos) //npos是一个静态常量,如果相等代表访问完string对象所有元素仍未找到“day”
{
cout << "First instance of \"day\" was found at position " << charPos;
}
else
{
cout << "Substring not found." << endl;
}
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "Locating all instances of \"day\" " << endl;
size_t SubstringPos = strSample.find("day", 0);
while (SubstringPos != string::npos)
{
cout << "\"day\" was found at position " << SubstringPos << endl;
size_t nSearchPosition = SubstringPos + 1;
SubstringPos = strSample.find("day", nSearchPosition);
}
cout << endl;
//查找字符
cout << "Locating all instances of character 'a'" << endl;
const char charToSearch = 'a';
charPos = strSample.find(charToSearch, 0);
while (charPos != string::npos)
{
/* code */
cout << "'" << charToSearch << "' is found" ;
cout << " at position: " << charPos << endl;
size_t charSearchPos = charPos + 1;
charPos = strSample.find(charToSearch, charSearchPos);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
截短
/*
string类提供erase函数,可用于:
• 在给定偏移位置和字符数时删除指定数目的字符。
string sampleStr ("Hello String! Wake up to a beautiful day!");
sampleStr.erase (13, 28); // 13是起始位置,28是要删除的字符串长度。结果为:Hello String!
• 在给定指向字符的迭代器时删除该字符。
sampleStr.erase (iCharS); // iterator points to a specific character
• 在给定由两个迭代器指定的范围时删除该范围内的字符。
sampleStr.erase (sampleStr.begin (), sampleStr.end ());
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str ("Hello String! Wake up to a beautiful day!");
cout << "原始字符串为:" << str << endl;
cout << "删除指定数目的字符(13-28):" << endl;
str.erase(13, 28);
cout << str << endl;
//
cout << "删除指定字符(S):" << endl;
auto iCharS = find ( str.begin (), str.end (), 'S' );
if(iCharS != str.end())
{
cout << "删除成功,str:" ;
str.erase(iCharS);
cout << str << endl;
}
cout << str << endl;
//左闭右开
cout << "另一种截断方式:" << endl;
str.erase(str.begin(), str.end());
if (str.length() == 0)
{
cout << "这个字符串为空" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
反转
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string strSample("Hello String! We will reverse you!");
cout << "Orignal string is: ";
cout << strSample << endl;
//使用泛型算法std::reverse
cout << "reverse:";
reverse(strSample.begin(), strSample.end());
cout << strSample << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
大小写转换
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
int main ()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "Please enter a string for case-convertion:" << endl;
cout << "> ";
string inStr;
getline (cin, inStr);
cout << endl;
//使用transform
transform(inStr.begin(), inStr.end(), inStr.begin(), ::toupper);
cout << "The string converted to upper case is: " << endl;
cout << inStr << endl << endl;
transform(inStr.begin(), inStr.end(), inStr.begin(), ::tolower);
cout << "The string converted to lower case is: " << endl;
cout << inStr << endl << endl;
return 0;
}