题目链接:225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(Leetcode)
代码(CV复制黏贴)
老套路二话不说,先上代码 :
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail\n");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
QNode* head = pq->phead;
free(head);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
else
{
QNode* head = pq->phead;
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
free(head);
pq->size--;
}
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return(pq->phead->data);
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* tmp = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
if(tmp==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
QueueInit(&(tmp->q1));
QueueInit(&(tmp->q2));
return tmp;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){
QueuePush(&obj->q1, x);
}
else{
QueuePush(&obj->q2, x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* empty = &obj->q1;
Queue* noempty = &obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(empty))
{
empty = &obj->q2;
noempty=&obj->q1;
}
while(QueueSize(noempty)>1)
{
QueuePush(empty, QueueFront(noempty));
QueuePop(noempty);
}
int n = QueueFront(noempty);
QueuePop(noempty);
return n;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your MyStack struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = myStackCreate();
* myStackPush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myStackPop(obj);
* int param_3 = myStackTop(obj);
* bool param_4 = myStackEmpty(obj);
* myStackFree(obj);
*/
过啦!!!!!!!
思路以及题目分析
解题思路:
此题可以用两个队列去实现一个栈,每次始终保持一个队列为空, 入栈操作相当于给非空队列进行入队操作 出栈操作相当于非空队列的队尾元素出队,此时需要把非空队列除最后一个元素之外的其余元素入队到空队列,然后出队最后一个队尾元素。
首先他们各自的特点各位要明白
栈的特点是:先入后出
队列的特点是:先入先出
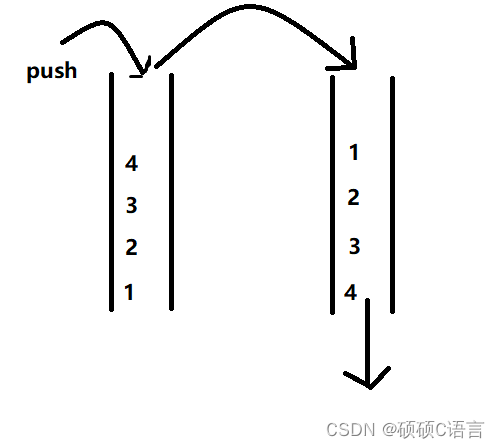
大概就是这样了