模型部署入门教程(八):如何添加 TensorRT 自定义算子 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
目录
在前面的模型入门系列文章中,我们介绍了部署一个 PyTorch 模型到推理后端,如 ONNXRuntime,这其中可能遇到很多工程性的问题。
有些可以通过创建 ONNX 节点来解决,该节点仍然使用后端原生的实现进行推理。而有些无法导出到后端的算法,可以通过重写代码改变算法的实现过程,同样可以导出到 ONNX ,达到一致的效果。以上两种方式一般可以处理绝大多数的部署问题,同时也不需要向推理框架引入新的内容,是我们进行模型部署时候的优先选择。
然而,仍然存在部分模型,模型中某些算子无法通过上述两种方式绕过问题,这时候,如何对特定后端实现对应代码就极为重要。这也是本文将介绍的第三种方式——自定义插件。
自定义插件是很多推理框架支持用户自定义算子的方式,以 MMDeploy 为例,它是一个支持多种推理后端的算法库。目前支持的后端有:
- ONNXRuntime
- TensorRT
- ncnn
- OpenVINO
- PPLNN
其中,前三种后端均实现了一些自定义的算子。例如 ONNXRuntime 中的调制可变性卷积,ncnn 中的topk 算子,TensorRT 中的 MultiLevelRoiAlign 。
介绍如何给后端自定义算子是一件相对复杂的事情,所以本文只针对其中一种后端 TensorRT,介绍自定义算子。如果读者对其他后端感兴趣,可以去他们的代码库查看,一般地,各个推理框架均有详细文档介绍如何添加客制化的算子实现。
在 MMDeploy 添加 TensorRT 插件
仍然以前面教程二中的超分辨模型 SRCNN 为例。在教程二中,我们用 ONNXRuntime 作为后端,通过 PyTorch 的 symbolic 函数导出了一个支持动态 scale 的 ONNX 模型,这个模型可以直接用 ONNXRuntime 运行,这是因为 NewInterpolate 类导出的节点 Resize 就是 ONNXRuntime 支持的节点。下面我们尝试直接将教程二导出的 srcnn3.onnx 转换到 TensorRT。
from mmdeploy.backend.tensorrt.utils import from_onnx
from_onnx(
'srcnn3.onnx',
'srcnn3',
input_shapes=dict(
input=dict(
min_shape=[1, 3, 256, 256],
opt_shape=[1, 3, 256, 256],
max_shape=[1, 3, 256, 256]),
factor=dict(
min_shape=[4],
opt_shape=[4],
max_shape=[4]))) 没有安装过 MMDeploy 的小伙伴可以先参考 build.md 进行安装,安装完成后执行上述脚本,会有如下报错:
RuntimeError: Failed to parse onnx, In node 1 (importResize): UNSUPPORTED_NODE: Assertion failed: mode != "cubic" && "This version of TensorRT does not support cubic interpolation!"
报错的原因有以下两方面:
'srcnn3.onnx'文件中的Resize是 ONNX 原生节点。其插值方式之一 bicubic 并不被 TensorRT 支持(TensorRT 的 Resize Layer仅支持 nearest 和 bilinear 两种插值方式)。日志的错误信息也明确提示了这点;- 但即便将 "bicubic" 模式改为 "bilinear" ,转换仍然失败:
RuntimeError: Failed to parse onnx, In node 1 (importResize): UNSUPPORTED_NODE: Assertion failed: scales.is_weights() && Resize scales must be initializer!"。这是因为 TensorRT 无法接受动态 scale 导致的。
创建 ONNX 节点
为解决上述问题,我们需要创建一个新的节点替换原生 Resize 节点,并且实现新节点对应的插件代码。
新改节点名称就叫 Test::DynamicTRTResize,这是种类 C++ 的写法,Test 为域名,主要用于区分不同来源下的同名的节点,比如 ONNX:: 和 Test::。当然了,ONNX 本身也不存在 DynamicTRTResize 的节点名。
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn.functional import interpolate
import torch.onnx
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os, requests
# Download checkpoint and test image
urls = ['https://download.openmmlab.com/mmediting/restorers/srcnn/srcnn_x4k915_1x16_1000k_div2k_20200608-4186f232.pth',
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/open-mmlab/mmediting/master/tests/data/face/000001.png']
names = ['srcnn.pth', 'face.png']
for url, name in zip(urls, names):
if not os.path.exists(name):
open(name, 'wb').write(requests.get(url).content)
class DynamicTRTResize(torch.autograd.Function):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
@staticmethod
def symbolic(g, input, size_tensor, align_corners = False):
"""Symbolic function for creating onnx op."""
return g.op(
'Test::DynamicTRTResize',
input,
size_tensor,
align_corners_i=align_corners)
@staticmethod
def forward(g, input, size_tensor, align_corners = False):
"""Run forward."""
size = [size_tensor.size(-2), size_tensor.size(-1)]
return interpolate(
input, size=size, mode='bicubic', align_corners=align_corners)
class StrangeSuperResolutionNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=9, padding=4)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 32, kernel_size=1, padding=0)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 3, kernel_size=5, padding=2)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x, size_tensor):
x = DynamicTRTResize.apply(x, size_tensor)
out = self.relu(self.conv1(x))
out = self.relu(self.conv2(out))
out = self.conv3(out)
return out
def init_torch_model():
torch_model = StrangeSuperResolutionNet()
state_dict = torch.load('srcnn.pth')['state_dict']
# Adapt the checkpoint
for old_key in list(state_dict.keys()):
new_key = '.'.join(old_key.split('.')[1:])
state_dict[new_key] = state_dict.pop(old_key)
torch_model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
torch_model.eval()
return torch_model
model = init_torch_model()
factor = torch.rand([1, 1, 512, 512], dtype=torch.float)
input_img = cv2.imread('face.png').astype(np.float32)
# HWC to NCHW
input_img = np.transpose(input_img, [2, 0, 1])
input_img = np.expand_dims(input_img, 0)
# Inference
torch_output = model(torch.from_numpy(input_img), factor).detach().numpy()
# NCHW to HWC
torch_output = np.squeeze(torch_output, 0)
torch_output = np.clip(torch_output, 0, 255)
torch_output = np.transpose(torch_output, [1, 2, 0]).astype(np.uint8)
# Show image
cv2.imwrite("face_torch.png", torch_output)
x = torch.randn(1, 3, 256, 256)
dynamic_axes={
'input': {
0: 'batch',
2: 'height',
3: 'width'
},
'factor': {
0: 'batch1',
2: 'height1',
3: 'width1'
},
'output': {
0: 'batch2',
2: 'height2',
3: 'width2'
},
}
with torch.no_grad():
torch.onnx.export(
model, (x, factor),
"srcnn3.onnx",
opset_version=11,
input_names=['input', 'factor'],
output_names=['output'],
dynamic_axes=dynamic_axes)
执行上述脚本,我们成功导出了一个 ONNX 模型 srcnn.onnx。用 netron 打开这个模型可视化如下:
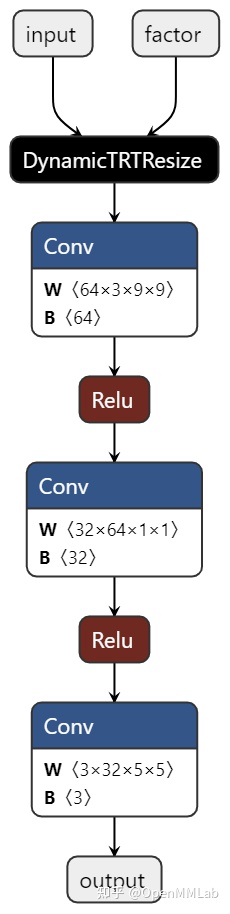
直接将该模型转换成 TensorRT 模型也是不可行的,这是因为 TensorRT 还无法解析 DynamicTRTResize 节点。而想要解析该节点,我们必须为 TensorRT 添加 c++ 代码,实现该插件。
C++ 实现
因为 MMDeploy 中已经实现了 Bicubic Interpolate 算子,所以我们可以复用其中的 CUDA 部分代码,只针对 TensorRT 实现支持动态 scale 的插件即可。对 CUDA 编程感兴趣的小伙伴可以参考 CUDA 的官方教程。
因为 csrc/backend_ops/tensorrt/bicubic_interpolate 中有我们需要的 CUDA 代码,所以我们可以直接在该文件夹加添加 TensorRT 相关的 trt_dynamic_resize.hpp 和 trt_dynamic_resize.cpp 文件,在这两个文件中分别声明和实现插件就可以了。我们也可以新建文件夹 csrc/backend_ops/tensorrt/dynamic_resize,将这两个文件直接放到这个文件夹下。
对 TensorRT 7+,要实现这样一个自定义插件,我们需要写两个类。
DynamicTRTResize,继承自 nvinfer1::IPluginV2DynamicExt,完成插件的具体实现。DynamicTRTResizeCreator,继承自 nvinfer1::IPluginCreator,是插件的工厂类,用于创建DynamicTRTResize插件的实例。
在 MMDeploy 中,由于有若干插件需要实现,所以我们在 mmdeploy/csrc/backend_ops/tensorrt/common/trt_plugin_base.hpp 中实现了 TRTPluginBase 和 TRTPluginCreatorBase 两个类,用于管理一些所有插件共有的属性方法。
其中,TRTPluginBase 继承自 nvinfer1::IPluginV2DynamicExt,而 TRTPluginCreatorBase继承自nvinfer1::IPluginCreator。这样,用户实现插件时只需继承这两个新的类即可。所以我们只需在 dynamic_resize 文件夹下的 .hpp 文件中,引用 trt_plugin_base.hpp 头文件,继承逻辑如下:
class DynamicTRTResize : public TRTPluginBase{}
class DynamicTRTResizeCreator : public TRTPluginCreatorBase{}
在 trt_dynamic_resize.hpp 中,我们声明如下内容:
#ifndef TRT_DYNAMIC_RESIZE_HPP
#define TRT_DYNAMIC_RESIZE_HPP
#include <cublas_v2.h>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "trt_plugin_base.hpp"
namespace mmdeploy {
class DynamicTRTResize : public TRTPluginBase {
public:
DynamicTRTResize(const std::string &name, bool align_corners);
DynamicTRTResize(const std::string name, const void *data, size_t length);
DynamicTRTResize() = delete;
// IPluginV2DynamicExt Methods
nvinfer1::IPluginV2DynamicExt *clone() const TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
nvinfer1::DimsExprs getOutputDimensions(int outputIndex, const nvinfer1::DimsExprs *inputs,
int nbInputs, nvinfer1::IExprBuilder &exprBuilder)
TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
bool supportsFormatCombination(int pos, const nvinfer1::PluginTensorDesc *ioDesc, int nbInputs,
int nbOutputs) TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
void configurePlugin(const nvinfer1::DynamicPluginTensorDesc *in, int nbInputs,
const nvinfer1::DynamicPluginTensorDesc *out,
int nbOutputs) TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
size_t getWorkspaceSize(const nvinfer1::PluginTensorDesc *inputs, int nbInputs,
const nvinfer1::PluginTensorDesc *outputs,
int nbOutputs) const TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
int enqueue(const nvinfer1::PluginTensorDesc *inputDesc,
const nvinfer1::PluginTensorDesc *outputDesc, const void *const *inputs,
void *const *outputs, void *workspace, cudaStream_t stream) TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
// IPluginV2Ext Methods
nvinfer1::DataType getOutputDataType(int index, const nvinfer1::DataType *inputTypes,
int nbInputs) const TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
// IPluginV2 Methods
const char *getPluginType() const TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
const char *getPluginVersion() const TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
int getNbOutputs() const TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
size_t getSerializationSize() const TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
void serialize(void *buffer) const TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
private:
bool mAlignCorners;
};
class DynamicTRTResizeCreator : public TRTPluginCreatorBase {
public:
DynamicTRTResizeCreator();
const char *getPluginName() const TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
const char *getPluginVersion() const TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
nvinfer1::IPluginV2 *createPlugin(const char *name, const nvinfer1::PluginFieldCollection *fc)
TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
nvinfer1::IPluginV2 *deserializePlugin(const char *name, const void *serialData,
size_t serialLength) TRT_NOEXCEPT override;
};
} // namespace mmdeploy
#endif // TRT_DYNAMIC_RESIZE_HPP
在这样一份头文件中,DynamicTRTResize 类进行了如下的套娃继承:
从上面的图片和代码中我们发现,在插件类 DynamicTRTResize 中,我们定义了私有变量 mAlignCorners,该变量表示是否 align corners。此外只要实现构造函数、析构函数和 TensoRT 中三个基类的方法即可。其中构造函数有二,分别用于创建插件和反序列化插件。而基类方法中:
- 基类
IPluginV2DynamicExt的方法较为值得关注,getOutputDimensions获取输出张量的形状,enqueue真正负责执行我们的算法,内部一般会调用 CUDA 核函数。本文实现的插件直接调用 MMDeploy 已定义在csrc/backend_ops/tensorrt/bicubic_interpolate的核函数bicubic_interpolate。 - 基类
IPluginV2Ext的方法,我们只要实现获取输出数据类型的getOutputDataType即可。 - 基类
IPluginV2则是些获取插件类型和版本号的方法,此外则是序列化输入插件的参数的函数serialize和计算该参数的序列化后buffer大小的函数getSerializationSize,以及获取输出张量个数的方法getNbOutputs。还有部分公共方法被定义在TRTPluginBase类内了。
在插件工厂类 DynamicTRTResizeCreator 中,我们需要声明获取插件名称和版本的方法 getPluginName 和 getPluginVersion。同时我们还需要声明创建插件和反序列化插件的方法 createPlugin 和 deserializePlugin,前者调用 DynamicTRTResize 中创建插件的方法,后者调用反序列化插件的方法。
接下来,我们就实现上述声明吧。在 .cpp 文件中我们实现的代码如下:
// Copyright (c) OpenMMLab. All rights reserved
#include "trt_dynamic_resize.hpp"
#include <assert.h>
#include <chrono>
#include "trt_plugin_helper.hpp"
#include "trt_serialize.hpp"
// to get the reference to kernel function bicubic_interpolate,which will be used in enqueue
#include "../bicubic_interpolate/trt_bicubic_interpolate_kernel.hpp"
using namespace nvinfer1;
namespace mmdeploy {
namespace {
static const char *PLUGIN_VERSION{"1"};
static const char *PLUGIN_NAME{"DynamicTRTResize"};//plagin name == ONNX node name,triggered in building engine
} // namespace
DynamicTRTResize::DynamicTRTResize(const std::string &name, bool align_corners)
: TRTPluginBase(name), mAlignCorners(align_corners) {}
DynamicTRTResize::DynamicTRTResize(const std::string name, const void *data,
size_t length)
: TRTPluginBase(name) {
deserialize_value(&data, &length, &mAlignCorners);
}
nvinfer1::IPluginV2DynamicExt *DynamicTRTResize::clone() const TRT_NOEXCEPT {
DynamicTRTResize *plugin =
new DynamicTRTResize(mLayerName, mAlignCorners);
plugin->setPluginNamespace(getPluginNamespace());
return plugin;
}
nvinfer1::DimsExprs DynamicTRTResize::getOutputDimensions(
int outputIndex, const nvinfer1::DimsExprs *inputs, int nbInputs,
nvinfer1::IExprBuilder &exprBuilder) TRT_NOEXCEPT {
nvinfer1::DimsExprs ret;
ret.nbDims = 4;
// input two tensors: input and size_tensor, the later is for shape inference only
ret.d[0] = inputs[0].d[0];
ret.d[1] = inputs[0].d[1];
ret.d[2] = inputs[1].d[2];
ret.d[3] = inputs[1].d[3];
return ret;
}
bool DynamicTRTResize::supportsFormatCombination(int pos,
const nvinfer1::PluginTensorDesc *ioDesc,
int nbInputs, int nbOutputs) TRT_NOEXCEPT {
if (pos == 0) {
return (ioDesc[pos].type == nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT &&
ioDesc[pos].format == nvinfer1::TensorFormat::kLINEAR);
} else {
return ioDesc[pos].type == ioDesc[0].type && ioDesc[pos].format == ioDesc[0].format;
}
}
void DynamicTRTResize::configurePlugin(const nvinfer1::DynamicPluginTensorDesc *inputs,
int nbInputs,
const nvinfer1::DynamicPluginTensorDesc *outputs,
int nbOutputs) TRT_NOEXCEPT {}
size_t DynamicTRTResize::getWorkspaceSize(const nvinfer1::PluginTensorDesc *inputs,
int nbInputs,
const nvinfer1::PluginTensorDesc *outputs,
int nbOutputs) const TRT_NOEXCEPT {
return 0;
}
int DynamicTRTResize::enqueue(const nvinfer1::PluginTensorDesc *inputDesc,
const nvinfer1::PluginTensorDesc *outputDesc,
const void *const *inputs, void *const *outputs, void *workSpace,
cudaStream_t stream) TRT_NOEXCEPT {
int batch = inputDesc[0].dims.d[0];
int channels = inputDesc[0].dims.d[1];
int height = inputDesc[0].dims.d[2];
int width = inputDesc[0].dims.d[3];
int height_out = outputDesc[0].dims.d[2];
int width_out = outputDesc[0].dims.d[3];
const void *x = inputs[0];
void *output = outputs[0];
// TODO: add fp16 support
auto data_type = inputDesc[0].type;
switch (data_type) {
case nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT:
bicubic_interpolate<float>((float *)x, (float *)output, batch, channels, height, width,
height_out, width_out, mAlignCorners, stream);
break;
default:
return 1;
break;
}
return 0;
}
nvinfer1::DataType DynamicTRTResize::getOutputDataType(int index,
const nvinfer1::DataType *inputTypes,
int nbInputs) const TRT_NOEXCEPT {
return inputTypes[0];
}
// IPluginV2 Methods
const char *DynamicTRTResize::getPluginType() const TRT_NOEXCEPT { return PLUGIN_NAME; }
const char *DynamicTRTResize::getPluginVersion() const TRT_NOEXCEPT { return PLUGIN_VERSION; }
int DynamicTRTResize::getNbOutputs() const TRT_NOEXCEPT { return 1; }
size_t DynamicTRTResize::getSerializationSize() const TRT_NOEXCEPT {
return serialized_size(mAlignCorners);
}
void DynamicTRTResize::serialize(void *buffer) const TRT_NOEXCEPT {
serialize_value(&buffer, mAlignCorners);
}
// creator /
DynamicTRTResizeCreator::DynamicTRTResizeCreator() {
mPluginAttributes.clear();
mPluginAttributes.emplace_back(nvinfer1::PluginField("align_corners"));
mFC.nbFields = mPluginAttributes.size();
mFC.fields = mPluginAttributes.data();
}
const char *DynamicTRTResizeCreator::getPluginName() const TRT_NOEXCEPT { return PLUGIN_NAME; }
const char *DynamicTRTResizeCreator::getPluginVersion() const TRT_NOEXCEPT {
return PLUGIN_VERSION;
}
nvinfer1::IPluginV2 *DynamicTRTResizeCreator::createPlugin(
const char *name, const nvinfer1::PluginFieldCollection *fc) TRT_NOEXCEPT {
nvinfer1::Dims size{2, {1, 1}};
bool align_corners = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < fc->nbFields; i++) {
if (fc->fields[i].data == nullptr) {
continue;
}
std::string field_name(fc->fields[i].name);
if (field_name.compare("align_corners") == 0) {
align_corners = static_cast<const int *>(fc->fields[i].data)[0];
}
}
// create the instance of DynamicTRTResize
DynamicTRTResize *plugin = new DynamicTRTResize(name, align_corners);
plugin->setPluginNamespace(getPluginNamespace());
return plugin;
}
nvinfer1::IPluginV2 *DynamicTRTResizeCreator::deserializePlugin(
const char *name, const void *serialData, size_t serialLength) TRT_NOEXCEPT {
auto plugin = new DynamicTRTResize(name, serialData, serialLength);
plugin->setPluginNamespace(getPluginNamespace());
return plugin;
}
REGISTER_TENSORRT_PLUGIN(DynamicTRTResizeCreator);//register the plugin
} // namespace mmdeploy
然后,我们就对 MMDeploy 重新 build 一次 TensorRT 的动态库 build/lib/libmmdeploy_tensorrt_ops.so。一般编译成功就表示已经注册算子了,但是我们需要进行一些测试以保证结果正确。
测试
我们用 TensorRT 的 python api 查看一下目前的插件列表:
import tensorrt as trt
from mmdeploy.backend.tensorrt import load_tensorrt_plugin
load_tensorrt_plugin()
def get_plugin_names():
return [pc.name for pc in trt.get_plugin_registry().plugin_creator_list]
print(get_plugin_names()) 可以发现 'DynamicTRTResize' 在插件列表中。然后我们对这个插件进行功能测试,看推理结果是否和 PyTroch 结果一致,并且是否可以动态控制输出尺寸。
from mmdeploy.backend.tensorrt import create_trt_engine, save_trt_engine
engine = create_trt_engine(
'srcnn3.onnx',
input_shapes=dict(input = dict(
min_shape=[1, 3, 256, 256],
opt_shape=[1, 3, 256, 256],
max_shape=[1, 3, 256, 256]),
factor = dict(min_shape = [1, 1, 256, 256], opt_shape = [1, 1, 512, 512], max_shape = [1, 1, 1024, 1024])))
save_trt_engine(engine, 'srcnn3.engine')
from mmdeploy.backend.tensorrt import TRTWrapper
trt_model = TRTWrapper('srcnn3.engine', ['output'])
factor = torch.rand([1, 1, 768, 768], dtype=torch.float)
trt_output = trt_model.forward(dict(input = x.cuda(), factor = factor.cuda()))
torch_output = model.forward(x, factor)
assert np.allclose(trt_output['output'].cpu().numpy(), torch_output.cpu().detach(), rtol = 1e-3, atol = 1e-5) 对比 TensorRT 的输出结果和 PyTorch 的输出结果是否一致,程序如果不报错即可说明推理正确。此外,测试时我们使用和导出时不一样的尺寸,结果也和 PyTorch 一致,说明可以支持动态的尺寸。
总结
本篇教程我们主要讲述如何在 MMDeploy 代码库中添加一个自定义的 TensorRT 插件,整个过程不涉及太多更复杂的 CUDA 编程,相信小伙伴们学完可以自己实现想要的插件。
https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdeploygithub.com/open-mmlab/mmdeploy
至此,我们的模型部署入门系列教程已经更新了八期,那到这里可能就先暂时告一段落啦!感谢小伙伴的支持和喜爱,后续我们也将继续推出模型部署进阶教程,请大家敬请期待哦!所有跟模型部署相关的内容,都整理在这个专栏啦,欢迎大家关注~
模型部署那些事www.zhihu.com/column/c_1497987564452114432正在上传…重新上传取消