基于Spring Boot 版本:3.1
Java: 17
Spring Boot 的入口即为xxApplication类的main方法:
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class);
}
}
main方法内部再调用SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class);
SpringApplication.java ---- run 有两个重载方法:
/**
* 静态方法,使用默认设置从指定的源启动SpringApplication
* @param primarySource 载入的指定源
* @param args 应用程序参数 (通过从Main方法传递)
* @return 正在运行的ApplicationContext
*/
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] {
primarySource }, args);
}
/**
* 静态方法,使用默认设置从指定的源启动SpringApplication
* @param primarySources 载入的制定源,数组形式
* @param args 应用程序参数 (通过从Main方法传递),数组形式
* @return 正在运行的ApplicationContext
*/
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
应用程序初始化
经过两次调用run静态方法后,调用new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args)
首先new SpringApplication,调用链路如图
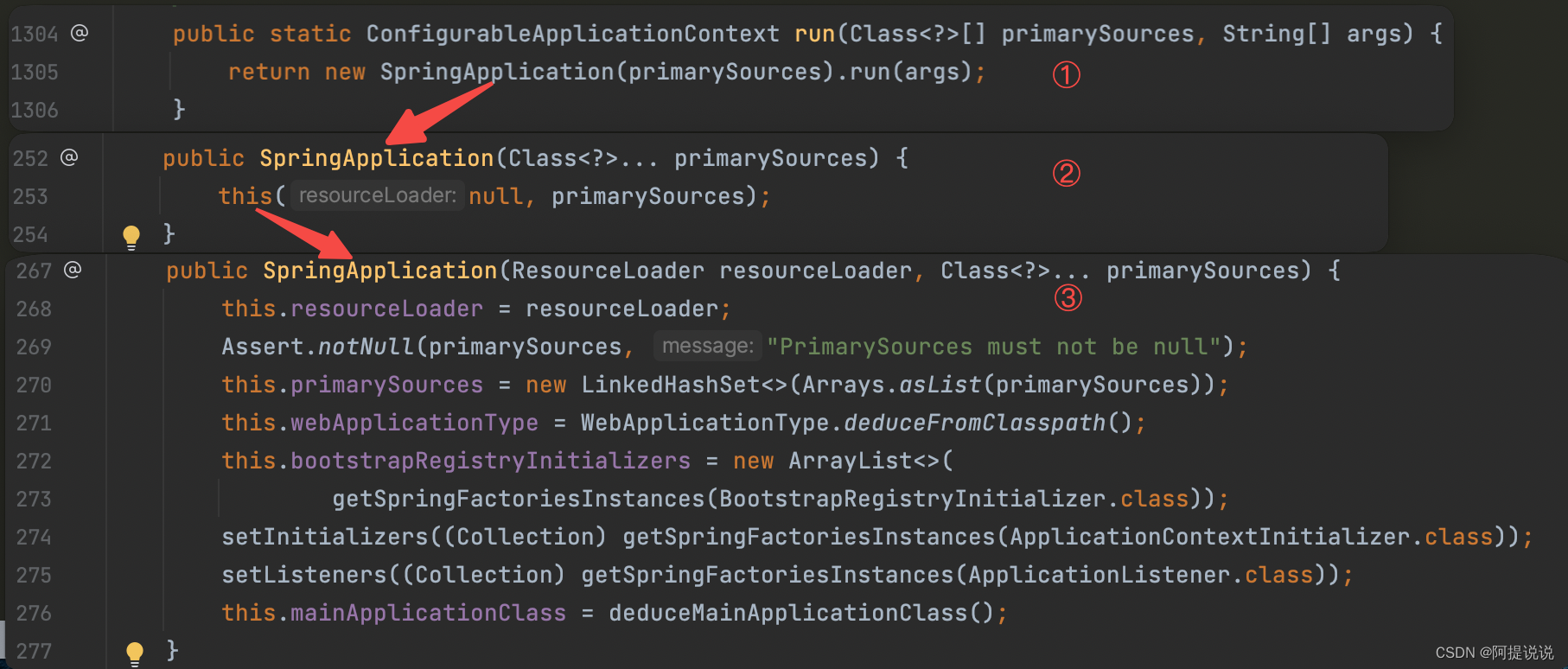
该处理的作用有:
1、创建一个SpringApplication实例,根据指定的源primarySources加载实例bean
2、将资源加载器类赋值给实例变量(此处为null)
3、将primarySources转为list并去重后赋值给实例变量
4、推断当前的Web应用程序环境(Reactive还是Servlet)
5、从META-INF/spring.factories加载BootstrapRegistryInitializer类实例
6、从META-INF/spring.factories加载ApplicationContextInitializer类实例
7、从META-INF/spring.factories加载ApplicationListener类实例
8、从堆栈中推断出主应用程序类
- BootstrapRegistryInitializer:该接口的作用是将一些默认的组件注册到BootstrapRegistry中,这些组件可以帮助Spring Boot实现自动配置和依赖注入等功能。通过实现BootstrapRegistryInitializer接口,开发人员可以向Spring Boot添加自定义组件,并在应用程序启动阶段进行初始化和注册,从而实现更具有个性化的应用程序配置和功能。
- ApplicationContextInitializer:该接口提供了一种灵活的机制,允许您在应用程序上下文创建之前自定义应用程序上下文的行为。该接口的实现类可以在应用程序上下文创建之前注册到SpringApplication实例中,并在应用程序上下文创建之前执行一些初始化操作,例如覆盖应用程序上下文中的默认bean定义、添加自定义属性源、激活特定的Spring配置文件等。通过实现该接口,可以实现一些在应用程序启动之前需要做的预处理操作,例如加载一些外部配置、初始化日志等。这样可以提高应用的灵活性和可配置性,使应用程序更加适应不同的环境和需求。建议实现Ordered接口,或者使用@Order注解
- ApplicationListener:该接口的实现类可以在Spring Boot应用程序中注册到ApplicationContext中,以便在应用程序生命周期内接收和处理特定的应用程序事件,例如启动、关闭、失败等事件。
通过实现该接口,可以在应用程序启动、关闭、失败等关键时刻进行一些自定义操作,例如初始化某些资源、注册特定的Bean、记录日志等。常见的Spring Boot应用程序事件包括ApplicationStartingEvent、ApplicationStartedEvent、ApplicationReadyEvent、ApplicationFailedEvent等。
应用程序启动
在new SpringApplication后,调用run方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//记录应用程序启动时间
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
//创建默认的引导上下文,循环调用BootstrapRegistryInitializer 中的 initialize
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
//配置headless,默认为true,不使用图形界面
configureHeadlessProperty();
//获取SpringApplicationRunListeners实例,从META-INF/spring.factories 和 SpringApplicationHook 中获取
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//启动SpringApplicationRunListeners实例,循环调用SpringApplicationRunListener实例的starting方法
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
//创建默认的ApplicationArguments实例,用于保存应用程序接收到的命令行参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//准备环境,准备完毕后调用SpringApplicationRunListener实例的environmentPrepared方法
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
//打印banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//创建ApplicationContext,根据WebApplicationType类型
context = createApplicationContext();
//设置启动期间的度量记录类
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
//准备应用程序上下文,这里会调用SpringApplicationRunListener实例的contextPrepared和contextLoaded方法
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//刷新应用程序上下文
refreshContext(context);
//刷新上下文后的操作,可以在子类实现
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
//计算启动需要的时间
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
//记录应用程序启动信息,默认是true
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
//调用SpringApplicationRunListener实例的started方法
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
//执行ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
//处理应用程序启动失败的情况,处理退出码,发送ExitCodeEvent事件,调用SpringApplicationRunListener的failed方法,向用户发送失败报告(可以实现FailureAnalysisReporter自定义),优雅关闭应用程序上下文
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
if (context.isRunning()) {
//准备完成时间
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
//最后调用SpringApplicationRunListener的ready方法
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
//返回应用程序上下文
return context;
}
这里完成处理有:
1、记录应用程序启动时间
2、创建默认的引导上下文,循环调用BootstrapRegistryInitializer 中的 initialize
3、配置headless,默认为true,不使用图形界面
4、获取SpringApplicationRunListeners实例,从META-INF/spring.factories 和 SpringApplicationHook 中获取,并启动SpringApplicationRunListeners实例,循环调用SpringApplicationRunListener实例的starting方法
5、创建默认的ApplicationArguments实例,用于保存应用程序接收到的命令行参数
6、准备环境,准备完毕后调用SpringApplicationRunListener实例的environmentPrepared方法
7、打印banner
8、创建ApplicationContext
9、设置启动期间的度量记录类
10、准备应用程序上下文
11、刷新应用程序上下文
12、计算启动需要的时间
13、如果需要,记录应用程序启动信息
14、调用SpringApplicationRunListener实例的started方法
15、执行ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner
16、最后调用SpringApplicationRunListener的ready方法
17、返回上下文
这样Spring Boot 整体的启动流程就完成了,后面详细看每一步都具体做了什么。
createBootstrapContext(),创建默认的引导上下文
private DefaultBootstrapContext createBootstrapContext() {
//创建默认的引导上下文
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = new DefaultBootstrapContext();
//循环调用initialize,可以在应用程序启动阶段进行初始化和注册,从而实现更具有个性化的应用程序配置和功能
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers.forEach((initializer) -> initializer.initialize(bootstrapContext));
return bootstrapContext;
}
configureHeadlessProperty(),配置headless
private void configureHeadlessProperty() {
//获取系统配置java.awt.headless的值,未配置使用默认值true
System.setProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS,
System.getProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS, Boolean.toString(this.headless)));
}
this.headless默认为true,表示不需要图形化界面,这样有利于提供性能
getRunListeners(args),获取SpringApplicationRunListeners实例
该方法会从META-INF/spring.factories 和 SpringApplicationHook 中获取,并启动SpringApplicationRunListeners实例,然后循环调用SpringApplicationRunListener实例的starting方法
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
//将应用程序接收到的命令行参数组合成一个参数解决器
ArgumentResolver argumentResolver = ArgumentResolver.of(SpringApplication.class, this);
argumentResolver = argumentResolver.and(String[].class, args);
//从META-INF/spring.factories 和 SpringApplicationHook 中获取,并启动SpringApplicationRunListeners实例
List<SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class,
argumentResolver);
//获取当前线程中的SpringApplicationHook,此处暂时有个疑问,没发现怎么设置这个SpringApplicationHook❓
SpringApplicationHook hook = applicationHook.get();
//如果hook 存在则将获取的SpringApplicationRunListener放入列表
SpringApplicationRunListener hookListener = (hook != null) ? hook.getRunListener(this) : null;
if (hookListener != null) {
listeners = new ArrayList<>(listeners);
listeners.add(hookListener);
}
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, listeners, this.applicationStartup);
}
prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments),准备环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
//创建并配置环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//配置环境,如果需要转换服务,添加ApplicationConversionService,另外委托给了configurePropertySources(属性源)和configureProfiles(配置文件),子类可以覆盖该方法或分别覆盖两者进行细粒度控制
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//将ConfigurationPropertySource支持附加到指定的环境
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
//调用environmentPrepared方法
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
//将defaultProperties属性源移动到指定配置环境的最后
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
//绑定环境到SpringApplication
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
//非自定义环境配置,就将其转换为标准类型
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
EnvironmentConverter environmentConverter = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader());
environment = environmentConverter.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
//重新将ConfigurationPropertySource支持附加到指定的环境
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
printBanner(environment) 打印banner
private Banner printBanner(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
//banner关闭,不打印
if (this.bannerMode == Banner.Mode.OFF) {
return null;
}
//获取资源加载器
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = (this.resourceLoader != null) ? this.resourceLoader
: new DefaultResourceLoader(null);
//banner打印器
SpringApplicationBannerPrinter bannerPrinter = new SpringApplicationBannerPrinter(resourceLoader, this.banner);
if (this.bannerMode == Mode.LOG) {
return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, logger);
}
return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, System.out);
}
createApplicationContext(),创建应用上下文
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
return this.applicationContextFactory.create(this.webApplicationType);
}
使用策略模式的创建应用程序上下文方法,支持显示设置applicationContextFactory,默认使用DefaultApplicationContextFactory
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup),设置启动期间的记录类
默认设置为DefaultApplicationStartup,是一个空操作的记录类,支持显示覆盖
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner),准备应用程序上下文
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
//将指定环境设置到应用程序上下文中
context.setEnvironment(environment);
//应用后置处理器
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
//如果需要,添加AOT生成的初始化器
addAotGeneratedInitializerIfNecessary(this.initializers);
//应用ApplicationContextInitializer
applyInitializers(context);
//通知侦听器应用程序上下文已经准备好
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
// 关闭引导上下文
bootstrapContext.close(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// 添加引导所必需的单例
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory autowireCapableBeanFactory) {
//设置循环引用
autowireCapableBeanFactory.setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory listableBeanFactory) {
//设置是否允许覆盖
listableBeanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
//设置延迟初始化
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
//设置一个PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor处理器
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor(context));
if (!AotDetector.useGeneratedArtifacts()) {
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
//将所有源bean加载到上下文中
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
}
//通知侦听器应用程序上下文已经加载完成
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
refreshContext(context) 刷新上下文
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
//如果需要,注册ShutdownHook以确保优雅关闭应用程序
shutdownHook.registerApplicationContext(context);
}
//调用Spring的刷新应用程序上下文
refresh(context);
}
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments) 刷新上下文后
protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
}
这是一个模版方法,子类实现
started方法
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
告知所有监听器应用程序启动完成
callRunners(context, applicationArguments) 执行ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner applicationRunner) {
callRunner(applicationRunner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner) {
callRunner(commandLineRunner, args);
}
}
}
用户自定义实现,会循环调用两个类的run,CommandLineRunner参数是数组,ApplicationRunner参数是ApplicationArguments类
调用ready
if (context.isRunning()) {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
最终调用监听器的ready方法,告知上下文刷新完成,并且调用了所有CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner
总结
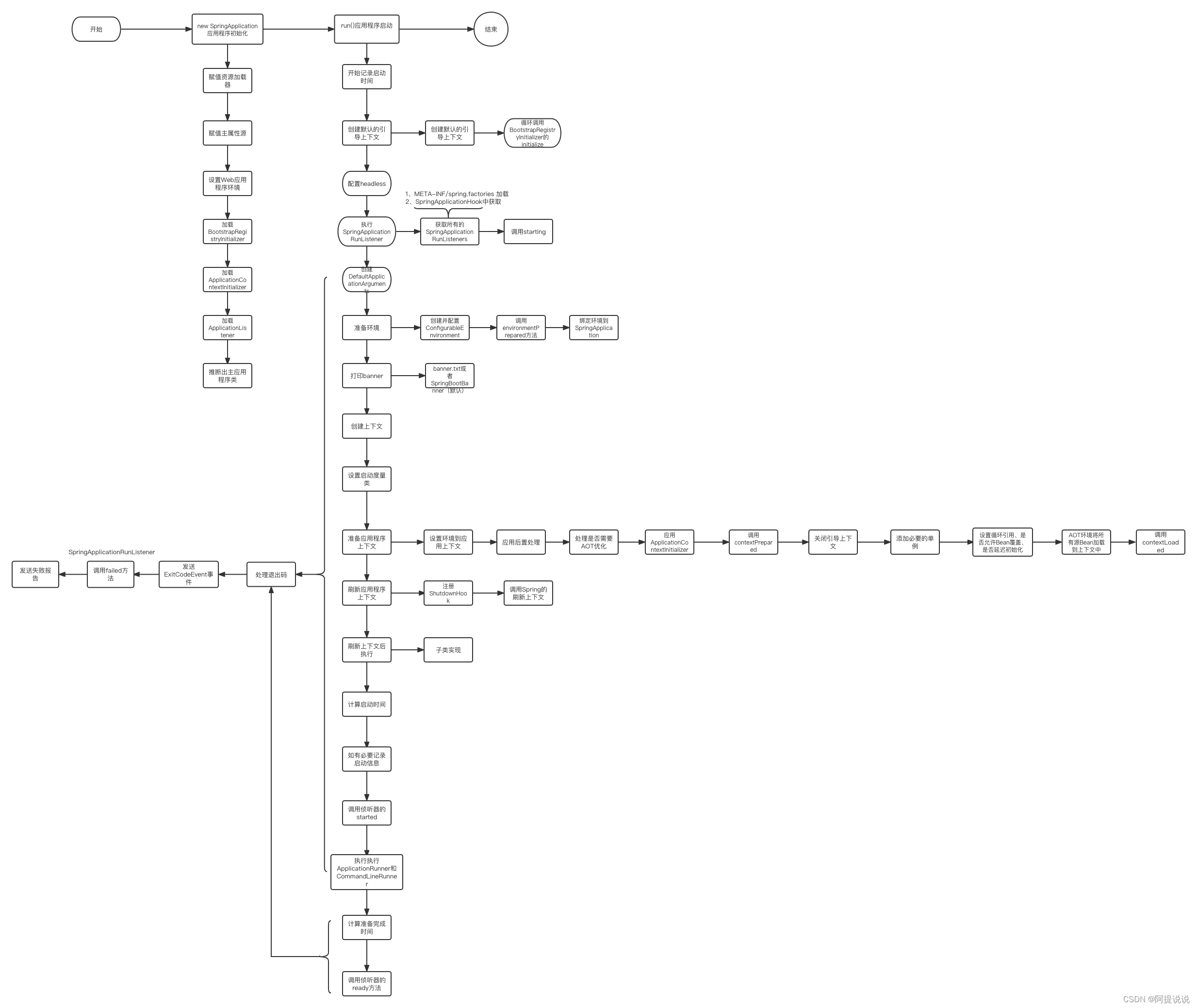
最后使用一张图来总结整个启动流程。
作者其他文章:
Spring Boot 3.x系列文章
- Spring Boot 2.7.8 中文参考指南(一)
- Spring Boot 2.7.8 中文参考指南(二)-Web
- Spring Boot 源码阅读初始化环境搭建
- Spring Boot 框架整体启动流程详解
Prometheus 系列文章
- Prometheus 的介绍和安装
- 直观感受PromQL及其数据类型
- PromQL之选择器和运算符
- PromQL之函数
- Prometheus 告警机制介绍及命令解读
- Prometheus 告警模块配置深度解析
- Prometheus 配置身份认证
- Prometheus 动态拉取监控服务
- Prometheus 监控云Mysql和自建Mysql
Grafana 系列文章,版本:OOS v9.3.1
- Grafana 的介绍和安装
- Grafana监控大屏配置参数介绍(一)
- Grafana监控大屏配置参数介绍(二)
- Grafana监控大屏可视化图表
- Grafana 查询数据和转换数据
- Grafana 告警模块介绍
- Grafana 告警接入飞书通知
Spring Boot Admin 系列