文章目录
系列文章目录
Netty核心源码分析(一),Netty的Server端启动过程源码分析
Netty核心源码分析(二),Netty的Server端接收请求过程源码分析
Netty核心源码分析(三)业务请求执行关键——ChannelPipeline、ChannelHandler、ChannelHandlerContext源码分析
Netty核心源码分析(四)心跳检测源码分析
Netty核心源码分析(五)核心组件EventLoop源码分析
一、EventLoop源码分析
之前我们简单分析过NioEventLoopGroup的源码。今天我们分析一下EventLoop执行的源码。
1、NioEventLoop源码
首先我们分析一下类继承关系图:
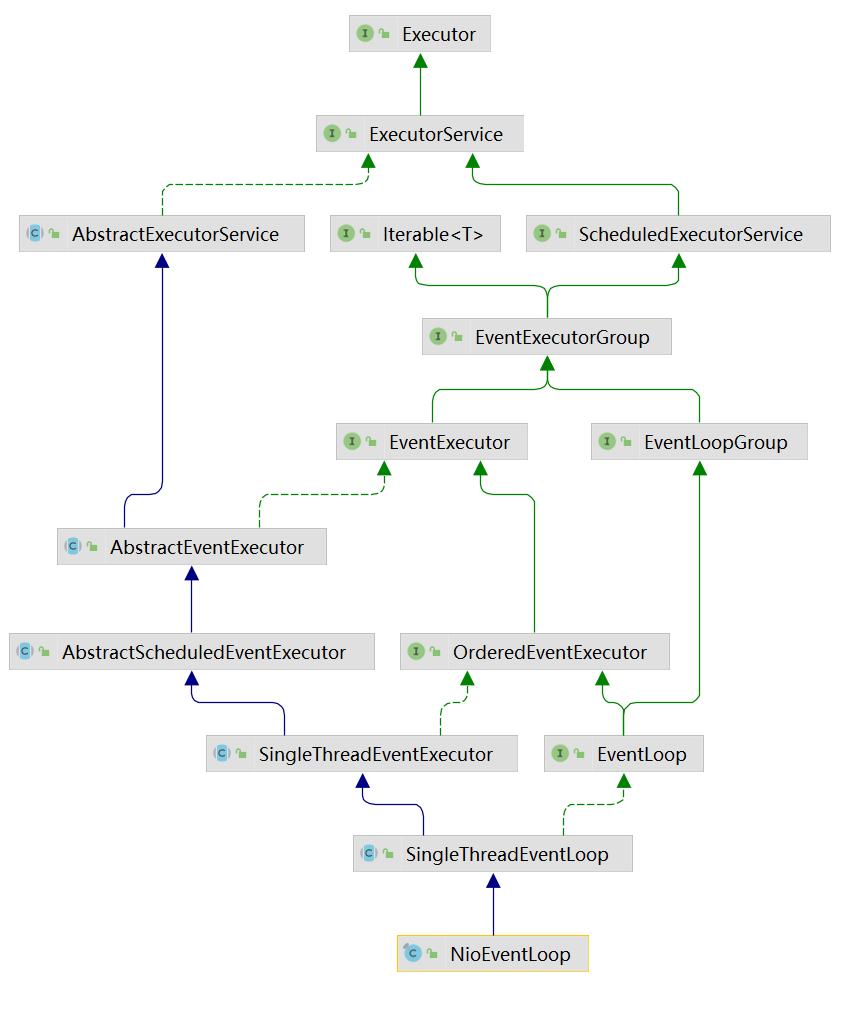
(1)ScheduledExecutorService接口表示是一个定时任务接口,EventLoop可以接受定时任务。
(2)EventLoop接口:一旦Channel注册了,就处理该Channel对应的所有IO操作。
(3)SingleThreadEventExecutor接口表示这是一个单线程的线程池。
(4)EventLoop是一个单例的线程池,里面含有一个死循环的线程不断地做着三件事情:监听端口、处理端口事件、处理队列事件。每个EventLoop都可以绑定多个Channel,而每个Channel始终只能由一个EventLoop来处理。
2、EventLoop的父接口SingleThreadEventExecutor
SingleThreadEventExecutor是一个单线程的线程池,其中包含着execute方法是EventLoop使用的源头:
// io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#execute
@Override
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
// 是否是当前线程
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
addTask(task);
if (!inEventLoop) {
// 如果该EventLoop的线程不是当前线程
startThread(); // 开启线程
if (isShutdown() && removeTask(task)) {
// 如果线程已经停止,并且删除任务失败,执行拒绝策略,默认是抛出异常RejectedExecutionException
reject();
}
}
// 如果addTaskWakesUp是false,并且任务不是NonWakeupRunnable类型的,尝试唤醒selector,这个时候,阻塞在selector的线程会立即返回
if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
(1)addTask方法
// io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#addTask
protected void addTask(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
if (!offerTask(task)) {
reject(task);
}
}
// io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#offerTask
final boolean offerTask(Runnable task) {
if (isShutdown()) {
reject();
}
return taskQueue.offer(task);
}
(2)startThread方法
首先判断是否启动过了,保证EventLoop只有一个线程,如果没有启动过,尝试使用CAS将state状态改为ST_STARTED,然后调用doStartThread启动
// io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#startThread
private void startThread() {
if (state == ST_NOT_STARTED) {
if (STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_NOT_STARTED, ST_STARTED)) {
try {
// 启动
doStartThread();
} catch (Throwable cause) {
// 异常回滚
STATE_UPDATER.set(this, ST_NOT_STARTED);
PlatformDependent.throwException(cause);
}
}
}
}
// io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor#doStartThread
private void doStartThread() {
assert thread == null;
// executor就是创建EventLoopGroup时创建的ThreadPerTaskExecutor类,将runnable包装秤Netty的FastThreadLocalThread
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
thread = Thread.currentThread();
// 判断中断状态
if (interrupted) {
thread.interrupt();
}
boolean success = false;
// 设置最后一次的执行时间
updateLastExecutionTime();
try {
// this就是NioEventLoop,执行NioEventLoop的run方法,这个方法是个死循环,也是整个EventLoop的核心!
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();
success = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception from an event executor: ", t);
} finally {
// 使用CAS不断修改state状态,改成ST_SHUTTING_DOWN
for (;;) {
int oldState = state;
if (oldState >= ST_SHUTTING_DOWN || STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, oldState, ST_SHUTTING_DOWN)) {
break;
}
}
// Check if confirmShutdown() was called at the end of the loop.
if (success && gracefulShutdownStartTime == 0) {
logger.error("Buggy " + EventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + " implementation; " +
SingleThreadEventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + ".confirmShutdown() must be called " +
"before run() implementation terminates.");
}
try {
// Run all remaining tasks and shutdown hooks.
for (;;) {
if (confirmShutdown()) {
break;
}
}
} finally {
try {
// cheanup
cleanup();
} finally {
// 修改状态ST_TERMINATED
STATE_UPDATER.set(SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, ST_TERMINATED);
threadLock.release();
if (!taskQueue.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn(
"An event executor terminated with " +
"non-empty task queue (" + taskQueue.size() + ')');
}
// 回调terminationFuture方法
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
}
}
}
}
});
}
3、NioEventLoop的run方法(核心!)
该方法是一个死循环,也是整个NioEventLoop的核心!
从源码我们可以看出,run方法总共做了三件事:
(1)select获取感兴趣的事件。
(2)processSelectedKeys处理事件。
(3)runAllTasks执行队列中的任务。
// io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop#run
@Override
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
try {
switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
// select
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));
// 'wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)' is always evaluated
// before calling 'selector.wakeup()' to reduce the wake-up
// overhead. (Selector.wakeup() is an expensive operation.)
//
// However, there is a race condition in this approach.
// The race condition is triggered when 'wakenUp' is set to
// true too early.
//
// 'wakenUp' is set to true too early if:
// 1) Selector is waken up between 'wakenUp.set(false)' and
// 'selector.select(...)'. (BAD)
// 2) Selector is waken up between 'selector.select(...)' and
// 'if (wakenUp.get()) { ... }'. (OK)
//
// In the first case, 'wakenUp' is set to true and the
// following 'selector.select(...)' will wake up immediately.
// Until 'wakenUp' is set to false again in the next round,
// 'wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)' will fail, and therefore
// any attempt to wake up the Selector will fail, too, causing
// the following 'selector.select(...)' call to block
// unnecessarily.
//
// To fix this problem, we wake up the selector again if wakenUp
// is true immediately after selector.select(...).
// It is inefficient in that it wakes up the selector for both
// the first case (BAD - wake-up required) and the second case
// (OK - no wake-up required).
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
// fall through
default:
}
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
// 处理select keys
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
runAllTasks();
}
} else {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
// Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception.
try {
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
(1)select
大致的逻辑就是:调用NIO的selector的select方法,默认阻塞一秒钟,如果有定时任务,则在定时任务剩余时间的基础上再加上0.5秒进行阻塞。当执行execute方法的时候,也就是添加任务的时候,会唤醒selector,防止selector阻塞时间过长。
// io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop#select
private void select(boolean oldWakenUp) throws IOException {
Selector selector = this.selector;
try {
int selectCnt = 0;
long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();
long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);
for (;;) {
long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
if (selectCnt == 0) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
}
break;
}
// If a task was submitted when wakenUp value was true, the task didn't get a chance to call
// Selector#wakeup. So we need to check task queue again before executing select operation.
// If we don't, the task might be pended until select operation was timed out.
// It might be pended until idle timeout if IdleStateHandler existed in pipeline.
if (hasTasks() && wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
// 阻塞给定时间,默认一秒
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
selectCnt ++;
// 如果有返回值||select被用户唤醒||任务队列有任务||有定时任务即将被执行,则跳出循环
if (selectedKeys != 0 || oldWakenUp || wakenUp.get() || hasTasks() || hasScheduledTasks()) {
// - Selected something,
// - waken up by user, or
// - the task queue has a pending task.
// - a scheduled task is ready for processing
break;
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
// Thread was interrupted so reset selected keys and break so we not run into a busy loop.
// As this is most likely a bug in the handler of the user or it's client library we will
// also log it.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2426
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely because " +
"Thread.currentThread().interrupt() was called. Use " +
"NioEventLoop.shutdownGracefully() to shutdown the NioEventLoop.");
}
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
long time = System.nanoTime();
if (time - TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeoutMillis) >= currentTimeNanos) {
// timeoutMillis elapsed without anything selected.
selectCnt = 1;
} else if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 &&
selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) {
// The selector returned prematurely many times in a row.
// Rebuild the selector to work around the problem.
logger.warn(
"Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row; rebuilding Selector {}.",
selectCnt, selector);
rebuildSelector();
selector = this.selector;
// Select again to populate selectedKeys.
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
currentTimeNanos = time;
}
if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.",
selectCnt - 1, selector);
}
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?",
selector, e);
}
// Harmless exception - log anyway
}
}
4、小结
每次执行 ececute 方法都是向队列中添加任务。当第一次添加时就启动线程,执行 run 方法,而 run 方法是整个 EventLoop 的核心,就像 EventLoop 的名字一样,Loop Loop ,不停的 Loop ,Loop 做什么呢?做3件事情。
- 调用 selector 的 select 方法,默认阳塞一秒钟,如果有定时任务,则在定时任务剩余时间的基础上在加上0.5秒进行阻塞。当执行 execute 方法的时候,也就是添加任务的时候,唤醒 selecor,防止 selector 阻塞时间过大。
- 当 selector 返回的时候,会调用 processSelectedKeys 方法对 selectKey 进行处理。
- 当 processSelectedKeys 方法执行结束后,则按照 ioRatio 的比例执行 runAlITasks 方法,默认是 IO 任务时间和非IO 任务时间是相同的,你也可以根据你的应用特点进行调优 。比如 非IO任务比较多,那么你就将ioRatio 调小一点,这样非 IO 任务就能执行的长一点。防止队列积攒过多的任务。
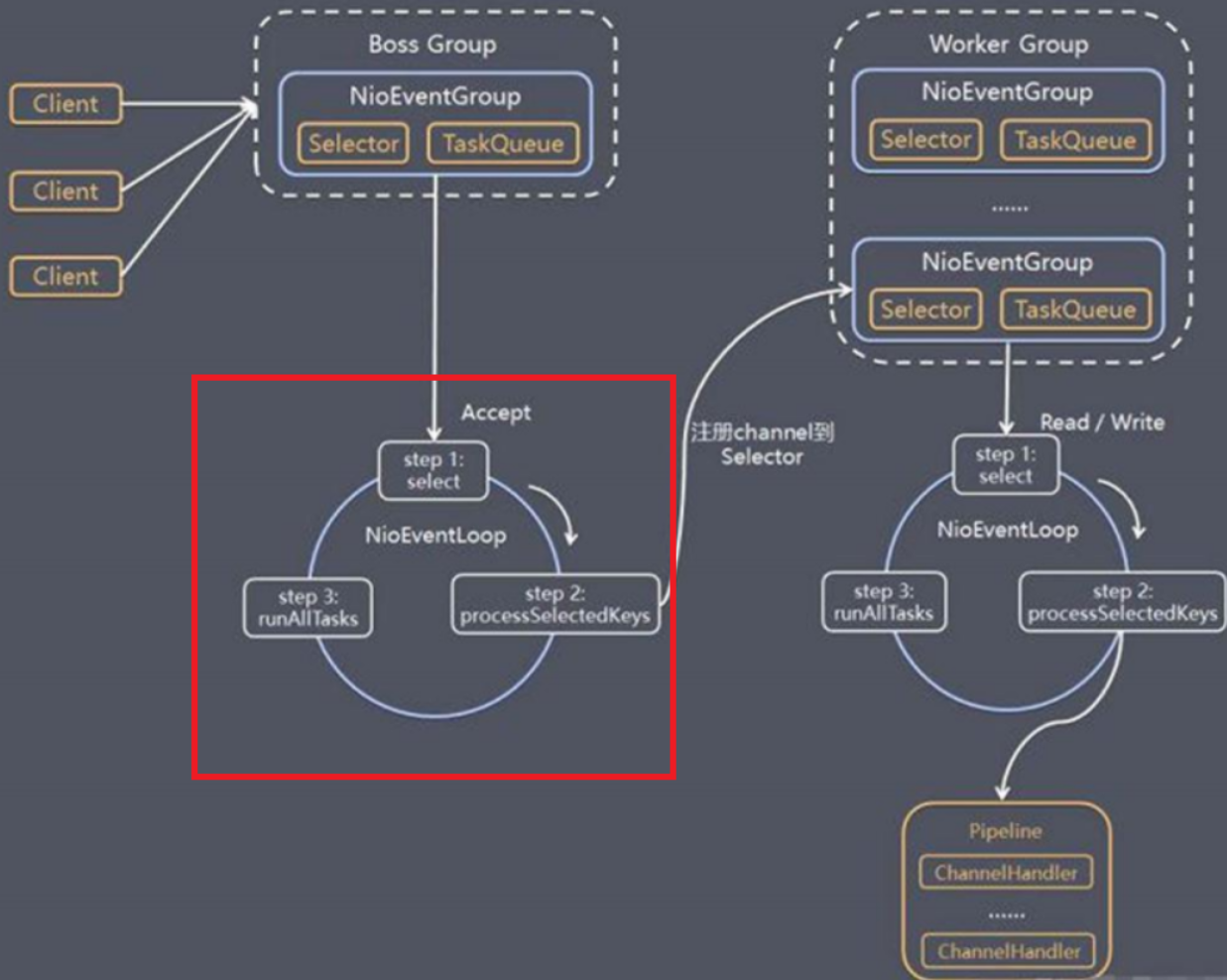
此时,下图红圈部分源码我们分析完毕。