1、computed函数使用
1.1、computed
在前面我们讲解过计算属性computed:当我们的某些属性是依赖其他状态时,我们可以使用计算属性来处理
- 在前面的Options API中,我们是使用computed选项来完成的;
- 在Composition API中,我们可以在 setup 函数中使用 computed 方法来编写一个计算属性;
如何使用computed呢?
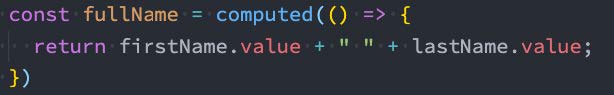
- 方式一:接收一个getter函数,并为 getter 函数返回的值,返回一个不变的 ref 对象;
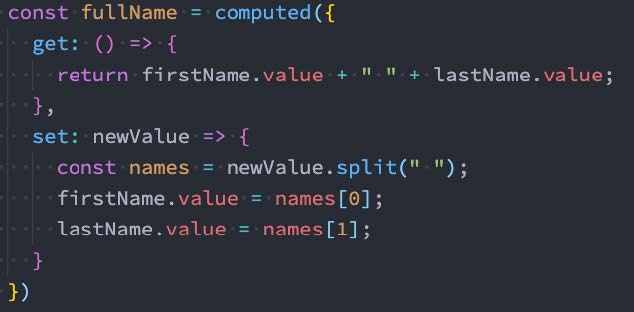
- 方式二:接收一个具有 get 和 set 的对象,返回一个可变的(可读写)ref 对象;
1.2、示例
App.vue
<template>
<h2>{
{ fullname }}</h2>
<button @click="setFullname">设置fullname</button>
<h2>{
{ scoreLevel }}</h2>
</template>
<script>
import {reactive, computed, ref} from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
// 1.定义数据
const names = reactive({
firstName: "kobe",
lastName: "bryant"
})
// const fullname = computed(() => {
// return names.firstName + " " + names.lastName
// })
const fullname = computed({
set: function (newValue) {
const tempNames = newValue.split(" ")
names.firstName = tempNames[0]
names.lastName = tempNames[1]
},
get: function () {
return names.firstName + " " + names.lastName
}
})
console.log(fullname) // 是一个ref对象
function setFullname() {
fullname.value = "coder why"
console.log(names)
}
// 2.定义score
const score = ref(89)
const scoreLevel = computed(() => {
return score.value >= 60 ? "及格" : "不及格"
})
return {
names,
fullname,
setFullname,
scoreLevel
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2、setup中使用ref
在setup中如何使用ref获取元素或者组件?
- 其实非常简单,我们只需要定义一个ref对象,绑定到元素或者组件的ref属性上即可;

示例:
ShowInfo.vue
<template>
<div>ShowInfo</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// methods: {
// showInfoFoo() {
// console.log("showInfo foo function")
// }
// }
setup() {
function showInfoFoo() {
console.log("showInfo foo function")
}
return {
showInfoFoo
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
App.vue
<template>
<!-- 1.获取元素 -->
<h2 ref="titleRef">我是标题</h2>
<button ref="btnRef">按钮</button>
<!-- 2.获取组件实例 -->
<show-info ref="showInfoRef"></show-info>
<button @click="getElements">获取元素</button>
</template>
<script>
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue'
import ShowInfo from './ShowInfo.vue'
export default {
components: {
ShowInfo
},
setup() {
const titleRef = ref()
const btnRef = ref()
const showInfoRef = ref()
// mounted的生命周期函数
onMounted(() => {
console.log(titleRef.value)
console.log(btnRef.value)
console.log(showInfoRef.value)
showInfoRef.value.showInfoFoo()
})
function getElements() {
console.log(titleRef.value)
}
return {
titleRef,
btnRef,
showInfoRef,
getElements
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>3、组件的生命周期函数
3.1、生命周期钩子
- 我们前面说过 setup 可以用来替代 data 、 methods 、 computed 等等这些选项,也可以替代 生命周期钩子。
- 那么setup中如何使用生命周期函数呢?
- 可以使用直接导入的 onX 函数注册生命周期钩子;
| 选项式 API |
Hook inside setup |
| beforecreate |
无 |
| created |
无 |
| beforeMount |
onBeforeMount |
| mounted |
onMounted |
| beforeupdate |
onBeforeupdate |
| updated |
onUpdated |
| beforeUnmount |
onBeforeUnmount |
| unmounted |
onUnmounted |
| activated |
onActivated |
| deactivated |
onDeactivated |
Tip:因为 setup 是围绕 beforeCreate 和 created 生命周期钩子运行的,所以不需要显式地定义它们。换句话说,在这些钩子中缩写的任何代码都应该直接在 setup 函数中编写。

3.2、示例
App.vue
<template>
<div>AppContent</div>
</template>
<script>
import {onMounted, onUpdated, onUnmounted} from 'vue'
export default {
beforeCreate() {
},
// created() {
// },
// beforeMount() {
// },
// mounted() {
// },
// beforeUpdate() {
// },
// updated() {
// }
setup() {
// 在执行setup函数的过程中, 你需要注册别的生命周期函数
onMounted(() => {
console.log("onmounted")
})
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
4、Provide/Inject使用
4.1、Provide函数
- 事实上我们之前还学习过Provide和Inject,Composition API也可以替代之前的 Provide 和 Inject 的选项。
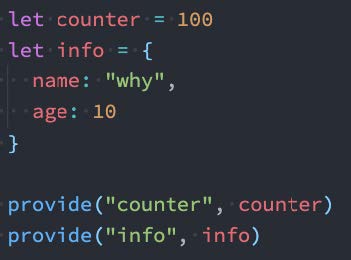
- 我们可以通过 provide来提供数据:
- 可以通过 provide 方法来定义每个 Property;
- provide可以传入两个参数:
- name:提供的属性名称;
- value:提供的属性值;
4.2、Inject函数
- 在 后代组件 中可以通过 inject 来注入需要的属性和对应的值:
- 可以通过 inject 来注入需要的内容;
- inject可以传入两个参数:
- 要 inject 的 property 的 name;
- 默认值;

4.3、数据的响应式
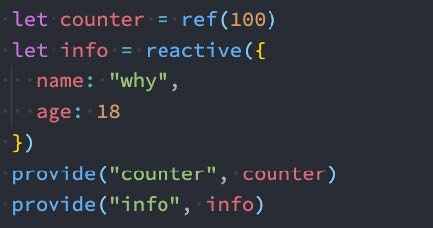
为了增加 provide 值和 inject 值之间的响应性,我们可以在 provide 值时使用 ref 和 reactive。
4.4、示例
ShowInfo.vue
<template>
<div>ShowInfo: {
{ name }}-{
{ age }}-{
{ height }}</div>
</template>
<script>
import {inject} from 'vue'
export default {
// inject的options api注入, 那么依然需要手动来解包
// inject: ["name", "age"],
setup() {
const name = inject("name")
const age = inject("age")
const height = inject("height", 1.88)
return {
name,
age,
height
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
App.vue
<template>
<div>AppContent: {
{ name }}</div>
<button @click="name = 'kobe'">app btn</button>
<show-info></show-info>
</template>
<script>
import { provide, ref } from 'vue'
import ShowInfo from './ShowInfo.vue'
export default {
components: {
ShowInfo
},
setup() {
const name = ref("why")
provide("name", name)
provide("age", 18)
return {
name
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
5、watch/watchEffect
5.1、侦听数据的变化
- 在前面的Options API中,我们可以通过watch选项来侦听data或者props的数据变化,当数据变化时执行某一些操作。
- 在Composition API中,我们可以使用watchEffect和watch来完成响应式数据的侦听;
- watchEffect:用于自动收集响应式数据的依赖;
- watch:需要手动指定侦听的数据源;
5.2、Watch的使用
watch的API完全等同于组件watch选项的Property:
- watch需要侦听特定的数据源,并且执行其回调函数;
- 默认情况下它是惰性的,只有当被侦听的源发生变化时才会执行回调;

5.3、侦听多个数据源
侦听器还可以使用数组同时侦听多个源:
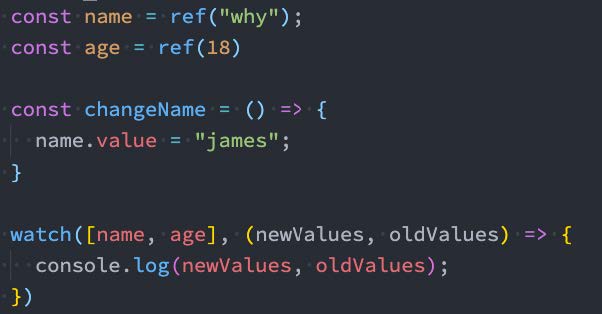
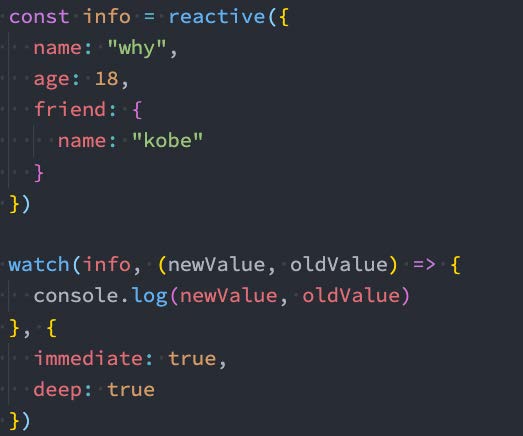
5.4、watch的选项
如果我们希望侦听一个深层的侦听,那么依然需要设置 deep 为true:也可以传入 immediate 立即执行;
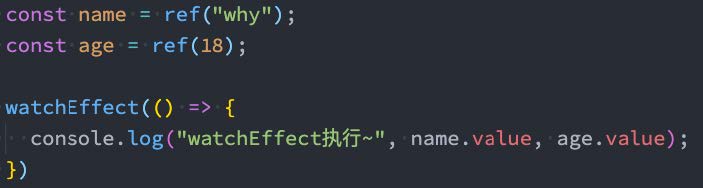
5.5、watchEffect
- 当侦听到某些响应式数据变化时,我们希望执行某些操作,这个时候可以使用 watchEffect。
- 我们来看一个案例:
- 首先,watchEffect传入的函数会被立即执行一次,并且在执行的过程中会收集依赖;
- 其次,只有收集的依赖发生变化时,watchEffect传入的函数才会再次执行;
5.6、watchEffect的停止侦听
- 如果在发生某些情况下,我们希望停止侦听,这个时候我们可以获取watchEffect的返回值函数,调用该函数即可。
- 比如在上面的案例中,我们age达到20的时候就停止侦听:

5.7、示例
App-watch.vue
<template>
<div>AppContent</div>
<button @click="message = '你好啊,李银河!'">修改message</button>
<button @click="info.friend.name = 'james'">修改info</button>
</template>
<script>
import {reactive, ref, watch} from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
// 1.定义数据
const message = ref("Hello World")
const info = reactive({
name: "why",
age: 18,
friend: {
name: "kobe"
}
})
// 2.侦听数据的变化
watch(message, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
})
watch(info, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
console.log(newValue === oldValue) // true,两者为同一个对象(浅拷贝)
}, {
// 这个属性作用就是,加载后默认就会执行一次这个console.log回调方法
immediate: true
})
// 3.监听reactive数据变化后, 获取普通对象
watch(() => ({...info}), (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
}, {
immediate: true,
deep: true
})
return {
message,
info
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>当前计数: {
{ counter }}</h2>
<button @click="counter++">+1</button>
<button @click="name = 'kobe'">修改name</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { watchEffect, watch, ref } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
const counter = ref(0)
const name = ref("why")
// watch(counter, (newValue, oldValue) => {})
// 1.watchEffect传入的函数默认会直接被执行
// 2.在执行的过程中, 会自动的收集依赖(依赖哪些响应式的数据)
const stopWatch = watchEffect(() => {
console.log("-------", counter.value, name.value)
// 判断counter.value > 10
if (counter.value >= 10) {
// 停止监听
stopWatch()
}
})
return {
counter,
name
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
6、script setup语法糖
6.1、script setup语法
- <script setup> 是在单文件组件 (SFC) 中使用组合式 API 的编译时语法糖,当同时使用 SFC 与组合式 API 时则推荐该语法。
- 更少的样板内容,更简洁的代码;
- 能够使用纯 Typescript 声明 prop 和抛出事件;
- 更好的运行时性能 ;
- 更好的 IDE 类型推断性能 ;
- 使用这个语法,需要将 setup attribute 添加到 <script> 代码块上:

- 里面的代码会被编译成组件 setup() 函数的内容:
- 这意味着与普通的 <script> 只在组件被首次引入的时候执行一次不同;
- <script setup> 中的代码会在每次组件实例被创建的时候执行。
6.2、顶层的绑定会被暴露给模板
当使用 <script setup> 的时候,任何在 <script setup> 声明的顶层的绑定 (包括变量,函数声明,以及 import 引入的内容)都能在模板中直接使用:
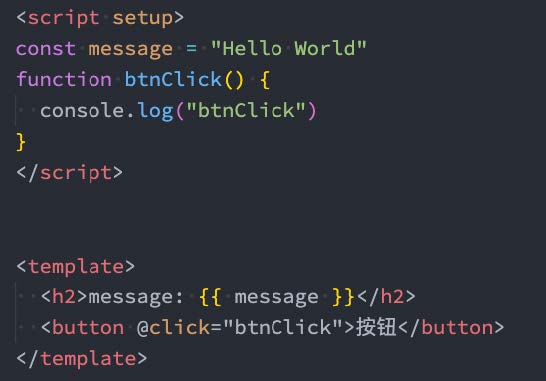
响应式数据需要通过ref、reactive来创建。
6.3、导入的组件直接使用
<script setup> 范围里的值也能被直接作为自定义组件的标签名使用:
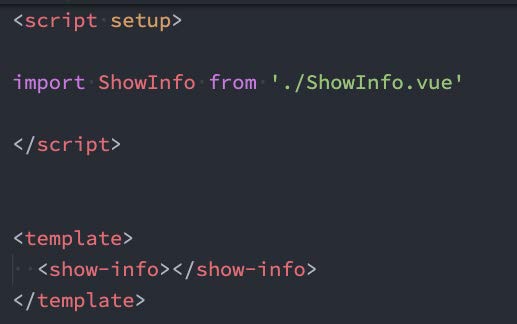
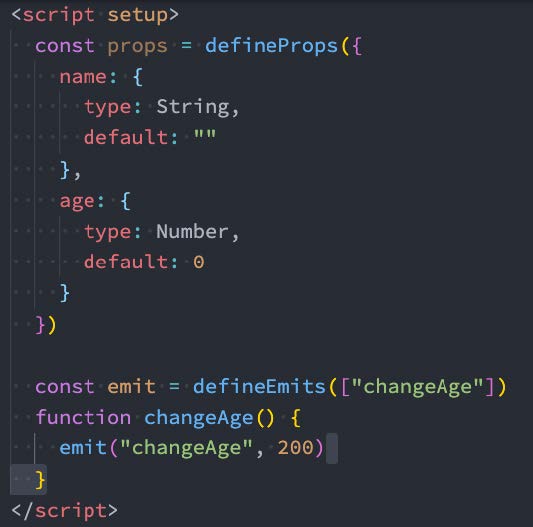
6.4、defineProps() 和 defineEmits()
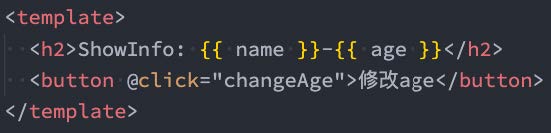
为了在声明 props 和 emits 选项时获得完整的类型推断支持,我们可以使用 defineProps 和 defineEmits API,它们将自动地在 <script setup> 中可用:
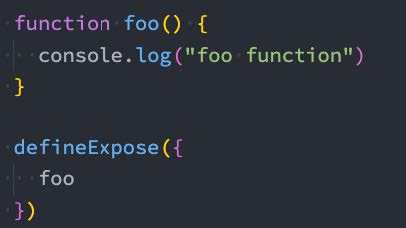
6.5、defineExpose()
- 使用 <script setup> 的组件是默认关闭的:
- 通过模板 ref 或者 $parent 链获取到的组件的公开实例,不会暴露任何在 <script setup> 中声明的绑定;
- 通过 defineExpose 编译器宏来显式指定在 <script setup> 组件中要暴露出去的 property:
6.6、示例
ShowInfo.vue
<template>
<div>ShowInfo: {
{ name }}-{
{ age }}</div>
<button @click="showInfoBtnClick">showInfoButton</button>
</template>
<script setup>
// 定义props
const props = defineProps({
name: {
type: String,
default: "默认值"
},
age: {
type: Number,
default: 0
}
})
// 绑定函数, 并且发出事件
const emits = defineEmits(["infoBtnClick"])
function showInfoBtnClick() {
emits("infoBtnClick", "showInfo内部发生了点击")
}
// 定义foo的函数
function foo() {
console.log("foo function")
}
// 暴露实例
defineExpose({
foo
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
App.vue
<template>
<div>AppContent: {
{ message }}</div>
<button @click="changeMessage">修改message</button>
<show-info name="why"
:age="18"
@info-btn-click="infoBtnClick"
ref="showInfoRef">
</show-info>
<show-info></show-info>
<show-info></show-info>
</template>
<script setup>
// 1.所有编写在顶层中的代码, 都是默认暴露给template可以使用
import {ref, onMounted} from 'vue'
// 组件不在需要注册,直接导入使用即可
import ShowInfo from './ShowInfo.vue'
// 2.定义响应式数据
const message = ref("Hello World")
console.log(message.value)
// 3.定义绑定的函数
function changeMessage() {
message.value = "你好啊, 李银河!"
}
function infoBtnClick(payload) {
console.log("监听到showInfo内部的点击:", payload)
}
// 4.获取组件实例
const showInfoRef = ref()
onMounted(() => {
showInfoRef.value.foo()
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
7、自定义Hook练习
useCounter.js
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue'
export default function useCounter() {
const counter = ref(0)
function increment() {
counter.value++
}
function decrement() {
counter.value--
}
onMounted(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
counter.value = 989
}, 1000);
})
return {
counter,
increment,
decrement
}
}
useScrollPosition.js
import { reactive } from 'vue'
export default function useScrollPosition() {
// 1.使用reative记录位置
const scrollPosition = reactive({
x: 0,
y: 0
})
// 2.监听滚动
document.addEventListener("scroll", () => {
scrollPosition.x = window.scrollX
scrollPosition.y = window.scrollY
})
return {
scrollPosition
}
}useTitle.js
import { ref, watch } from "vue";
export default function useTitle(titleValue) {
// document.title = title
// 定义ref的引入数据
const title = ref(titleValue)
// 监听title的改变
watch(title, (newValue) => {
document.title = newValue
}, {
immediate: true
})
// 返回ref值
return {
title
}
}
About.vue
<template>
<h2>About计数: {
{ counter }}</h2>
<button @click="increment">+1</button>
<button @clcik="decrement">-1</button>
</template>
<script>
import { onActivated } from 'vue'
import useCounter from '../hooks/useCounter'
import useTitle from '../hooks/useTitle'
export default {
setup() {
// 切换标题
useTitle("关于")
return {
...useCounter()
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
Home.vue
<template>
<h2>Home计数: {
{ counter }}</h2>
<button @click="increment">+1</button>
<button @click="decrement">-1</button>
<button @click="popularClick">首页-流行</button>
<button @click="hotClick">首页-热门</button>
<button @click="songClick">首页-歌单</button>
<div class="scroll">
<h2>x: {
{ scrollPosition.x }}</h2>
<h2>y: {
{ scrollPosition.y }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { onMounted, ref } from 'vue'
import useCounter from '../hooks/useCounter'
import useTitle from '../hooks/useTitle'
import useScrollPosition from '../hooks/useScrollPosition'
export default {
setup() {
// 1.counter逻辑
const { counter, increment, decrement } = useCounter()
// 2.修改标题
const { title } = useTitle("首页")
// 3.监听按钮的点击
function popularClick() {
title.value = "首页-流行"
}
function hotClick() {
title.value = "首页-热门"
}
function songClick() {
title.value = "首页-歌单"
}
// 4.获取滚动位置
const { scrollPosition } = useScrollPosition()
console.log(scrollPosition)
return {
counter,
increment,
decrement,
popularClick,
hotClick,
songClick,
scrollPosition
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
App.vue
<template>
<div>AppContent</div>
<button @click="changeTitle">修改title</button>
<!-- 1.计数器 -->
<!-- <hr>
<home></home>
<hr>
<about></about> -->
<!-- 2.home和about页面的切换 -->
<button @click="currentPage = 'home'">home</button>
<button @click="currentPage = 'about'">about</button>
<component :is="currentPage"></component>
<div class="content"></div>
<br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import Home from './views/Home.vue'
import About from './views/About.vue'
import useTitle from './hooks/useTitle'
export default {
components: {
Home,
About
},
setup() {
const currentPage = ref("home")
function changeTitle() {
useTitle("app title")
}
return {
changeTitle,
currentPage
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.content {
width: 3000px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
注意:这个案例只是展示了setup中其他函数的搭配使用方式。