概览
Java I/O操作指的是数据的输入/输出操作。
Java的I/O操作类在java.io包中,主要分以下几种:
- 基于字节操作的I/O接口: InputStream和OutputStream
- 基于字符操作的I/O接口: Writer和Reader
- 基于磁盘操作的I/O接口: File
一、核心类介绍
- 基于字节的I/O操作,核心是操作字节数组byte[],可以操作任何类型的流数据
- 基于字符的I/O操作,核心是操作字符数组char[],只能操作字符类型的流数据,如果是非字符的流数据(如图片、视频等)会变成乱码
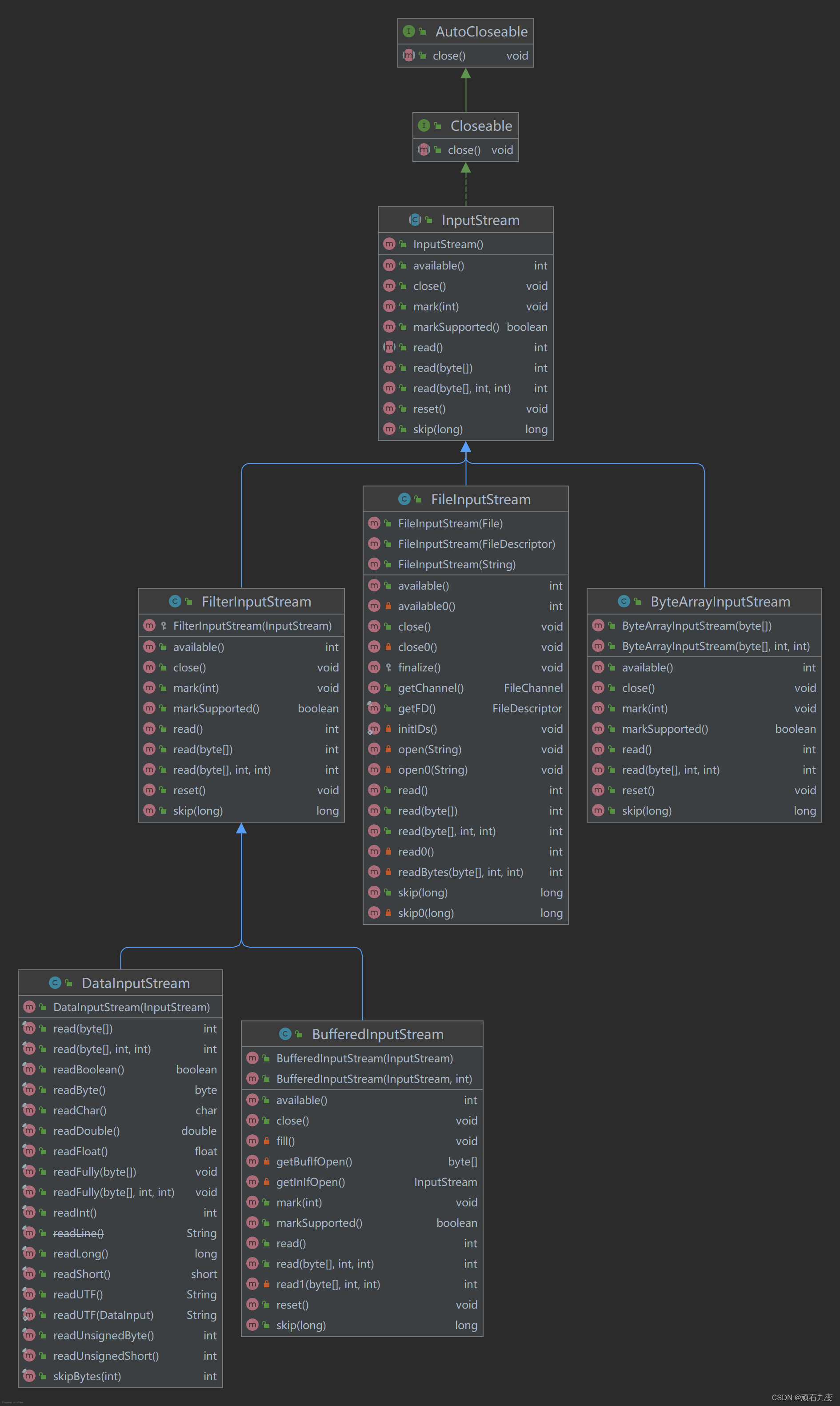
1、字节输入流
| 类 | 功能 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| ByteArrayInputStream | 将内存的缓冲区当做InputStream使用 | 将其与FilterInputStream对象相连,将字节流存入文件中 |
| FileInputStream | 从文件中读取信息 | 将文件对象File转换成输入流,以读取文件中数据 |
| FilterInputStream | 抽象类,作为装饰器的接口,为其他的InputStream类提供有用的功能 | |
| BufferedInputStream | 提供了缓冲区的操作,提高IO的性能;为传入的输入流添加缓冲功能 | FilterInputStream子类 |
| DataInputStream | 与DataOutputStream搭配使用,按照移植方式从流读取基本数据类型;包含用于读取基本数据类型的全部接口 | FilterInputStream子类 |
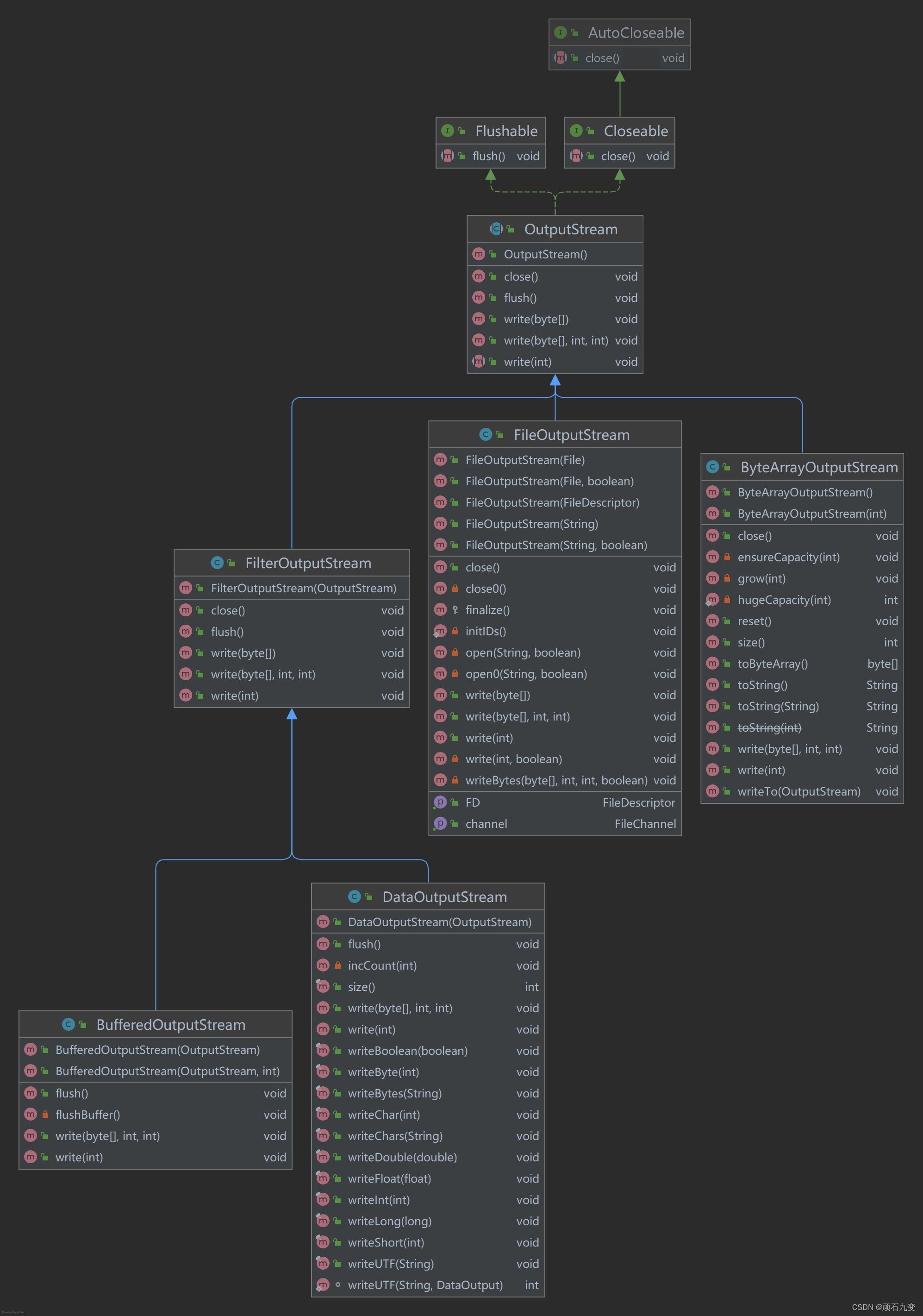
2、字节输出流
| 类 | 功能 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| ByteArrayOutputStream | 在内存中创建缓冲区。所有送往流的数据都要放置在此缓冲区 | 可以方便的将输入流转换成字节数组 |
| FileOutputStream | 用于将信息写入文件 | |
| FilterOutputStream | 抽象类,作为装饰器的接口,为其他OutputStream提供有用的功能 | |
| BufferedOutputStream | 提供了缓冲区的操作,提高IO的性能;为传入的输出流添加缓冲功能,可以调用flush()清空缓冲区 | FilterOutputStream子类 |
| DataOutputStream | 与DataInputStream搭配使用,可以按照移植方式向流中写入基本数据类型;包含用于写入基本数据类型的全部接口 | FilterOutputStream子类 |
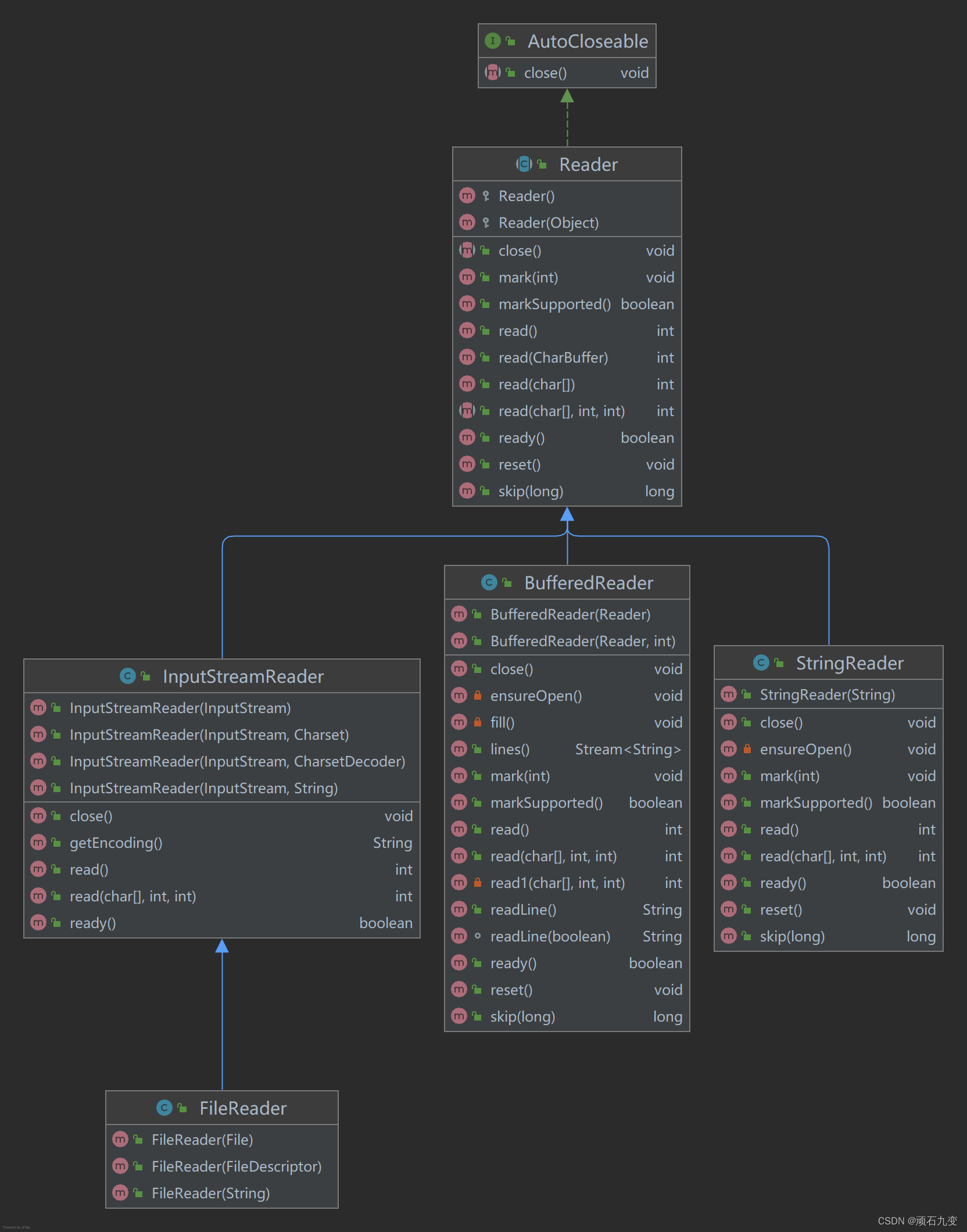
3、字符输入流
| 类 | 功能 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| InputStreamReader | 将字节输入流InputStream转换成字符输入流 | |
| FileReader | 将文件对象File转换成字符输入流 | InputStreamReader的子类 |
| BufferedReader | 提供缓冲区功能,提高字符输入流Reader的操作性能 | |
| StringReader | 将字符串转换成字符流操作 |
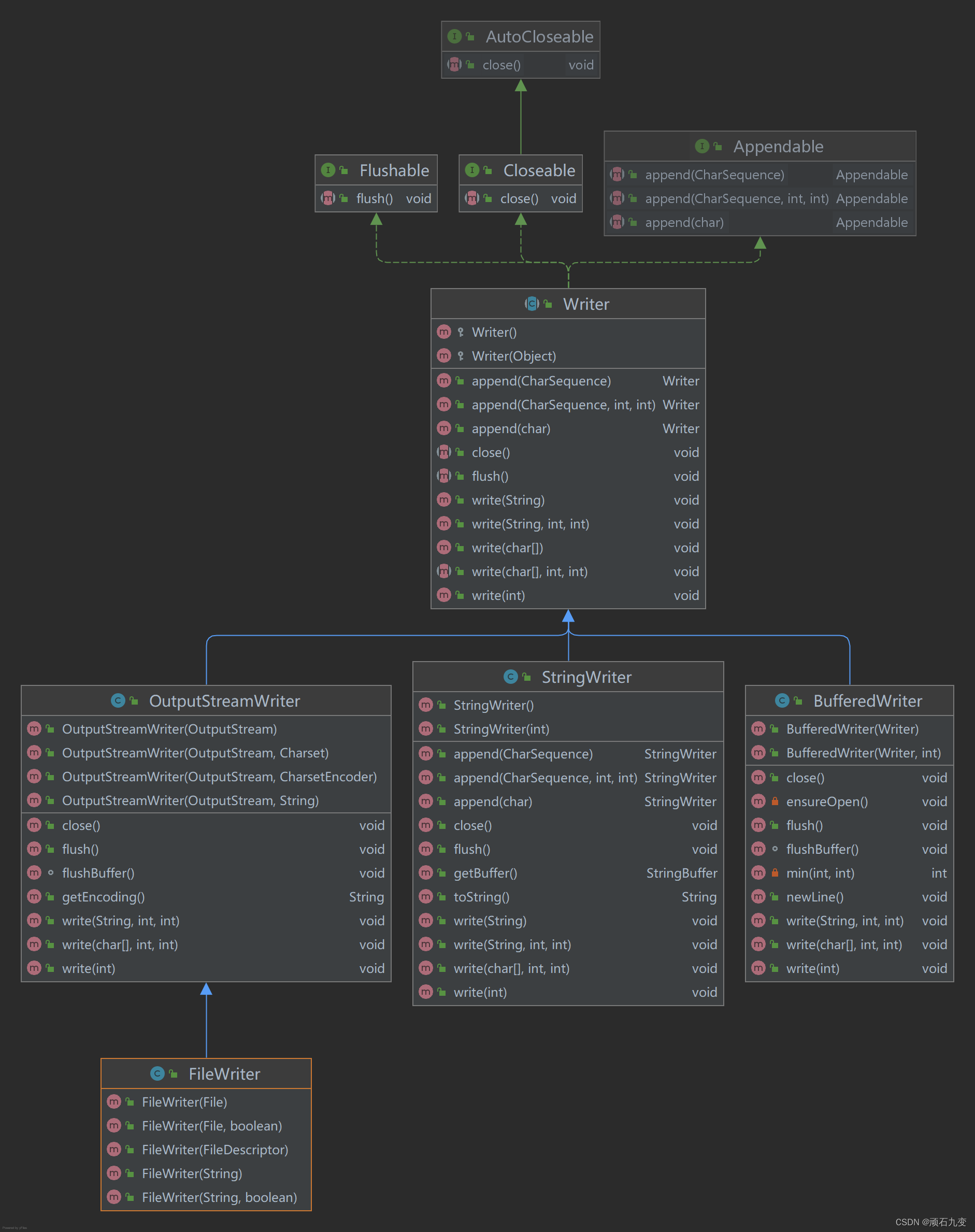
4、字符输出流
| 类 | 功能 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| OutputStreamWriter | 将字节输出流OutputStream转换成字符输出流 | |
| FileWriter | 将文件对象File转换成字符输出流 | OutputStreamWriter的子类 |
| BufferedWriter | 提供缓冲区功能,提高字符输出流Writer的操作性能 | |
| StringWriter | 将字符串转换成字符流操作 |
二、关键操作介绍
1、关闭流
所有数据流在操作完成后,都需要调用close方法关闭,在1.7及之后建议使用try-with-resources语句来使用流,这样可以避免显示的调用close()方法,减少一些重复代码,在操作完成后会自动调用close方法。
try-with-resources语句可以自动close所有实现接口java.io.Closeable的子类对象。
try (BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file))) {
bos.write(content.getBytes());
bos.flush();
}
2、刷新缓存
flush()方法用来强制要求OutputStream对象将暂存于内部缓冲区的数据立即进行实际的写入(一般情况下不需要手动的调用该方法,在内部缓冲区填充满了之后,会自动执行实际的写入操作,在调用close()方法时也会自动调用flush()方法)
3、序列化流和反序列化流
对象的序列化就是将对象转化为byte序列,反之叫做反序列化,ObjectOutputStream是序列化流,ObjectInputStream是反序列化流。
被操作的对象必须实现序列化接口Serializable,如果不想某个字段进行序列化,可以使用transient来修饰字段,使得该字段不进行序列化,也可以通过重写writeObjectOverride()和readObjectOverride()方法来进行手动序列化。
静态变量也不能进行序列化,因为所有的对象都共享同一份静态变量值
1)ObjectOutputStream序列化流
主要的方法是writeObject,存储对象的类、类的签名以及这个类及其父类中所有非静态和非瞬时的字段的值
public final void writeObject(Object obj) throws IOException {
if (enableOverride) {
writeObjectOverride(obj);
return;
}
try {
writeObject0(obj, false);
} catch (IOException ex) {
if (depth == 0) {
writeFatalException(ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
2)ObjectInputStream反序列化流
主要的方法是readObject,读回对象的类、类的签名以及这个类及其父类中所有非静态和非瞬时的字段的值
public final Object readObject()
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
if (enableOverride) {
return readObjectOverride();
}
// if nested read, passHandle contains handle of enclosing object
int outerHandle = passHandle;
try {
Object obj = readObject0(false);
handles.markDependency(outerHandle, passHandle);
ClassNotFoundException ex = handles.lookupException(passHandle);
if (ex != null) {
throw ex;
}
if (depth == 0) {
vlist.doCallbacks();
}
return obj;
} finally {
passHandle = outerHandle;
if (closed && depth == 0) {
clear();
}
}
}
三、代码示例
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
import java.io.*;
public class FileUtilTest {
/**
* 复制文件
*/
public static void copyFile(String fromFileName, String toFileName) throws Exception {
File fromFile = new File(fromFileName);
File toFile = new File(toFileName);
StopWatch watch = new StopWatch("fileTest");
watch.start("copy");
if (!fromFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("源文件不存在");
System.exit(1);
}
if (!toFile.getParentFile().exists()) {
toFile.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream(fromFile);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(toFile)) {
int temp = 0;
byte[] data = new byte[4096];
while ((temp = is.read(data)) != -1) {
os.write(data, 0, temp);
}
watch.stop();
System.out.println(watch.prettyPrint());
}
}
/**
* 通过字符流将字符串写入到文件中
*/
public static void write(String fileName, String content) throws IOException {
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) {
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
try (Writer out = new FileWriter(file)) {
out.write(content);
out.flush();
}
}
/**
* 通过字节流将字符串写入到文件中,增加缓冲区功能
*/
public static void writeBuffer(String fileName, String content) throws IOException {
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) {
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
try (BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file))) {
bos.write(content.getBytes());
bos.flush();
}
}
/**
* 通过字符流将字符串写入到文件中,增加缓冲区功能
*/
public static void writeBufferedWriter(String fileName, String content) {
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) {
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
try (BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file))) {
bw.write(content);
bw.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 通过字符流,从文件中读取字符串内容
*/
public static void readChar(String fileName) {
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.exists()) {
return;
}
try (Reader in = new FileReader(file)) {
char[] data = new char[4096];
int len;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while ((len = in.read(data)) != -1) {
sb.append(new String(data, 0, len));
}
in.close();
System.out.println(sb);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 通过字节流,从文件中读取字符串内容
*/
public static void readByte(String fileName) throws IOException {
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.exists()) {
return;
}
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file)) {
byte[] data = new byte[4096];
int len;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while ((len = in.read(data)) != -1) {
sb.append(new String(data, 0, len));
}
System.out.println(sb);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 通过字符流,从文件中读取字符串内容,增加缓冲区功能
*/
public static void readBufferReader(String fileName) throws Exception {
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.exists()) {
return;
}
try (BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file))) {
String line;
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
}
}
/**
* 通过字节流,从文件中读取字符串内容,增加缓冲区功能
*/
public static void readBuffer(String fileName) throws Exception {
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.exists()) {
return;
}
try (BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file))) {
int len;
byte[] data = new byte[4096];
while ((len = bis.read(data)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(data, 0, len));
}
}
}
/**
* 将文件内容转换成字节数组
*/
public static byte[] file2OutStream(String fileName) throws Exception {
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.exists()) {
return null;
}
try (BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
int len;
byte[] data = new byte[4096];
while ((len = bis.read(data)) != -1) {
bos.write(data, 0, len);
}
return bos.toByteArray();
}
}
/**
* 将Java对象序列化存储在到文件中
*/
public static void objWrite(String fileName) {
File file = new File(fileName);
try (ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file))) {
oos.writeObject("Hello ,World");
oos.writeBoolean(false);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 从序列化文件中反序列化出Java对象
*/
public static void objRead(String fileName) {
File file = new File(fileName);
try (ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file))) {
Object o = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(o.getClass());
System.out.println("o = " + o);
System.out.println("ois.readBoolean() = " + ois.readBoolean());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}