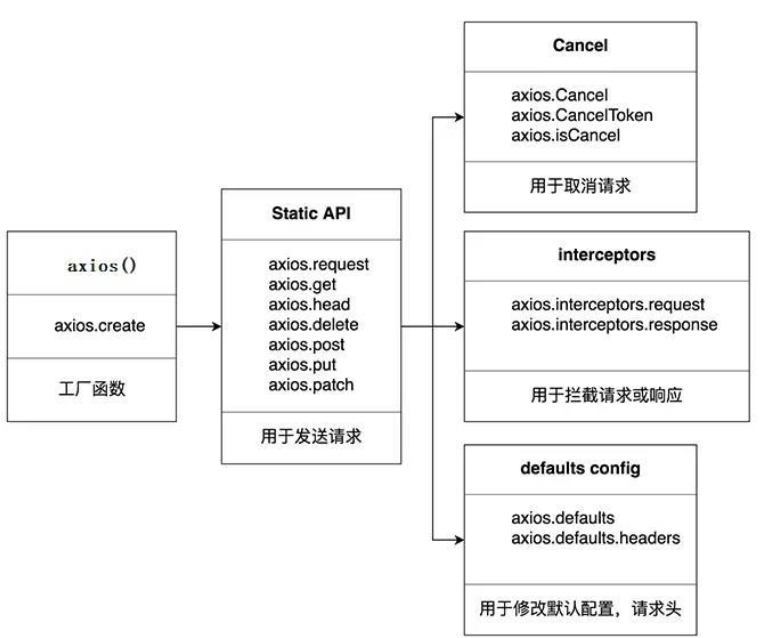
1.axios
1.1 axios 是什么?
- 前端最流行的 ajax请求库
- react/vue 官方都推荐使用 axios 发ajax 请求
- 文档:
https://github.com/axios/axiosopen
1.2 axios 特点
- 基于 xhr + promise 的异步 ajax请求库
- 浏览器端/node 端都可以使用
- 支持请求/响应拦截器
- 支持请求取消
- 请求/响应数据转换
- 批量发送多个请求
1.3 axios 常用语法
axios(config):通用/最本质的发任意类型请求的方式
axios(url[, config]): 可以只指定url发get请求
axios.request(config): 等同于axios(config)
axios.get(url[, config]): 发get请求
axios.delete(url[, config]): 发delete请求
axios.post(url[, data, config]): 发post 请求
axios.put(url[, data, config]): 发put 请求
axios.defaults.xxx:请求的默认全局配置(method\baseURL\params\timeout…)
axios.interceptors.request.use(): 添加请求拦截器
axios.interceptors.response.use(): 添加响应拦截器
axios.create([config]):创建一个新的axios(它没有下面的功能)
axios.Cancel():用于创建取消请求的错误对象
axios.CancelToken(): 用于创建取消请求的 token 对象
axios.isCancel(): 是否是一个取消请求的错误
axios.all(promises): 用于批量执行多个异步请求
axios.spread(): 用来指定接收所有成功数据的回调函数的方法
1.4 使用
配置对象常用的配置项
{
// 路径url
url: '/user',
// 请求方法,默认get
method: 'get',
//基础url,最终请求的url是 baseURL+url拼接,所以再全局设置默认,可以使得发送请求时的url变得简洁
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
//设置请求头
headers: {
'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'},
//设置请求url的query参数,可以使得url简洁。
//比如url是https://some-domain.com/api/user 然后params如下设置,那么最终的url是:
//https://some-domain.com/api/user?ID=12345&name=Jack
params: {
ID: 12345,
name:"Jack"
},
//设置请求体
data: {
firstName: 'Fred'
},
//设置请求的另外一种格式,不过这个是直接设置字符串的
data: 'Country=Brasil&City=Belo Horizonte',
//请求超时,单位毫秒,默认0,不超时。
timeout: 1000,
//响应数据类型,默认json
responseType: 'json',
//响应数据的编码规则,默认utf-8
responseEncoding: 'utf8',
//响应体的最大长度
maxContentLength: 2000,
// 请求体的最大长度
maxBodyLength: 2000,
//设置响应状态码为多少时是成功,调用resolve,否则调用reject失败
//默认是大于等于200,小于300
validateStatus: function (status) {
return status >= 200 && status < 300;
}
代码
<button id="btn1">发送get请求</button> <br><br>
<button id="btn2">发送post请求</button><br><br>
<button id="btn3">发送put请求</button><br><br>
<button id="btn4">发送delete请求</button>
<hr>
<div>其他发送请求的api:</div><br><br>
<button id="btn5">发送get请求1</button> <br><br>
<button id="btn6">发送post请求1</button><br><br>
<button id="btn7">发送put请求1</button><br><br>
<button id="btn8">发送delete请求1</button>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
//发送get
document.getElementById("btn1").onclick = function(){
axios({
method:"GET",
url:"http://localhost:3000/posts/1"
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
//发送post
document.getElementById("btn2").onclick = function(){
axios({
method:"POST",
url:"http://localhost:3000/posts",
data:{
title:"axios学习",
author:"Yehaocong"
}
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
//发送put
document.getElementById("btn3").onclick = function(){
axios({
method:"PUT",
url:"http://localhost:3000/posts/2",
data:{
title:"axios学习",
author:"Liaoxiaoyan"
}
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
document.getElementById("btn4").onclick = function(){
axios({
method:"DELETE",
url:"http://localhost:3000/posts/2",
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
//其他发送请求的api
document.getElementById("btn5").onclick = function(){
//发送get,使用get,第一个参数时url,第二个参数时config配置对象
axios.get("http://localhost:3000/posts/1")
.then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
//发送post
document.getElementById("btn6").onclick = function(){
//发送post请求,第一个参数时url,第二个参数时请求体,第三个参数时config配置对象
axios.post("http://localhost:3000/posts",
{
title:"axios学习2",
author:"Yehaocong2"})
.then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
//发送put,
document.getElementById("btn7").onclick = function(){
//发送put,接收三个参数,url 请求体 、 config配置对象
axios.put("http://localhost:3000/posts/2",{
title:"axios学习",
author:"Liaoxiaoyan"})
.then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
document.getElementById("btn8").onclick = function(){
//发送delete请求,接收2个参数, url config配置对象
axios.delete("http://localhost:3000/posts/3")
.then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};

默认配置
可以设置全局默认配置,是为了避免多种重复配置在不同请求中重复,比如baseURL、timeout等,这里设置baseURL。
axios.defaults.baseURL="http://localhost:3000";
//因为上面配置了baseURL,所以我们之后的请求只需要配置url不用像之前那样的全路径
axios.get("/posts/1")
.then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
1.5 创建一个新的axios对象
根据指定配置创建一个新的 axios, 也就是每个新 axios 都有自己的配置 新 axios 只是没有取消请求和批量发请求的方法, 其它所有语法都是一致的 为什么要设计这个语法?
需求:项目中有部分接口需要的配置与另一部分接口需要的配置不太一样, 如何处理(比如有多个baseURL需要指定)
解决:创建2 个新axios, 每个都有自己特有的配置, 分别应用到不同要求的接口请求中
const instance = axios.create({
// instance是函数类型
baseURL: 'http://localhost:3000'
})
// 使用instance发Ajax请求
instance({
url: '/posts'
})
instance.get('/posts')
1.6 拦截器
请求拦截器(在发送请求前,使用函数对请求的参数和内容进行处理和检测,若请求有问题可直接进行拦截->取消,后进先执行=则后面的请求拦截器先执行)
响应拦截器(对响应的结果预处理,先进先执行=前面的响应拦截器先执行)
1)请求拦截器:
- 在真正发送请求前执行的回调函数
- 可以对请求进行检查或配置进行特定处理
- 失败的回调函数,传递的默认是error
- 成功的回调函数,传递的默认是config(也必须是)
2)响应拦截器
- 在请求得到响应后执行的回调函数
- 可以对响应数据进行特定处理
- 成功的回调函数,传递的默认是response
- 失败的回调函数,传递的默认是error
3)请求转换器:对请求头和请求体数据进行特定处理的函数
响应转换器:将响应体json字符串解析为js对象或数组的函数
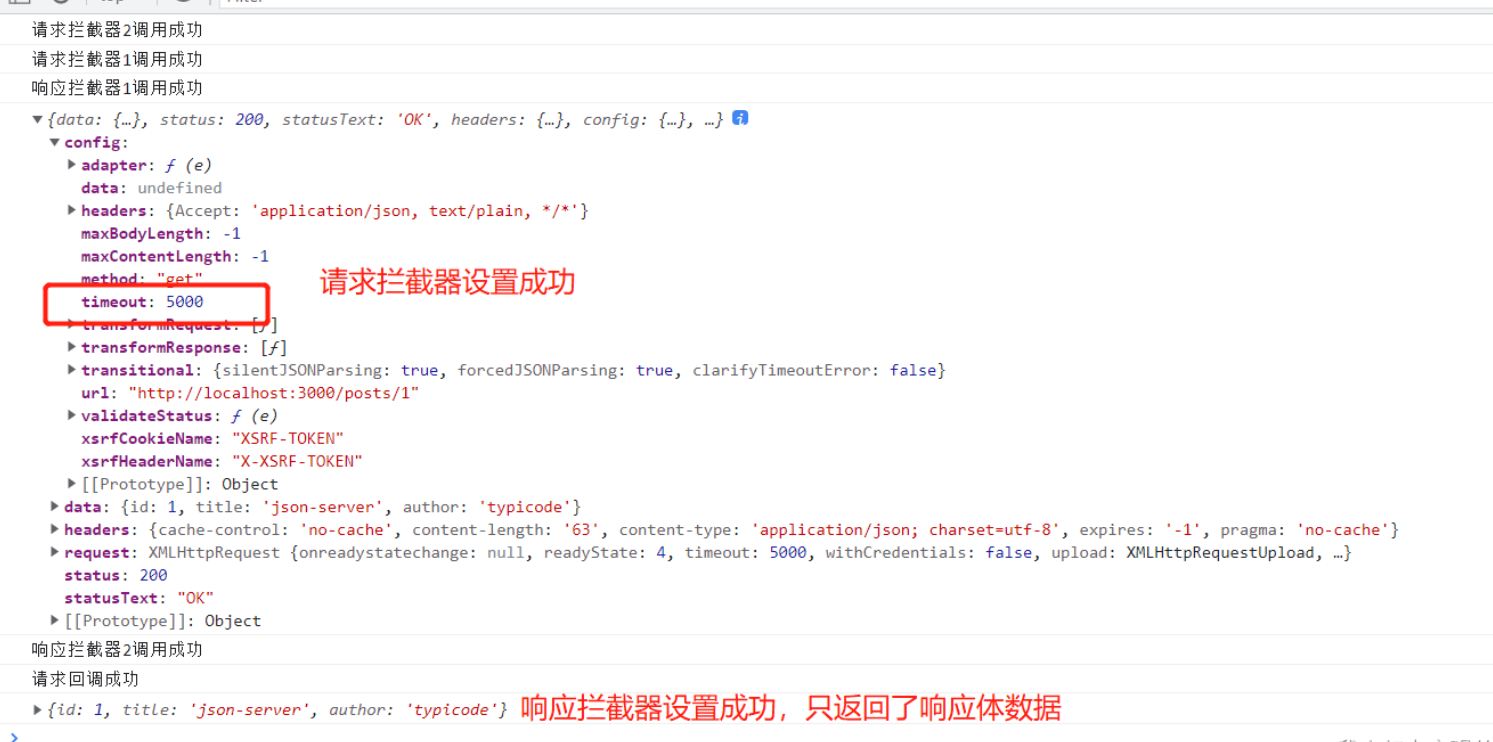
- 说明:调用axios()并不是立即发送ajax 请求, 而是需要经历一个较长的流程
- 流程:请求拦截器2 => 请求拦截器1 => 发ajax 请求 => 响应拦截器1 => 响应拦截器2 => 请求的回调
- 注意:此流程是通过 promise 串连起来的, 请求拦截器传递的是config, 响应拦截器传递的是response
代码
script>
//设置一个请求拦截器,在请求拦截器中可以对请求参数进行修改
//config:配置对象
axios.interceptors.request.use(
function (config) {
console.log("请求拦截器 成功 1号");
// config.headers.test = "I am only a header!";
//修改 config 中的参数
config.params = {
a: 100 };
return config;
},
error => {
console.log("请求拦截器 失败 1号");
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
axios.interceptors.request.use(
function (config) {
config.timeout = 5000;
console.log("请求拦截器 成功 2号");
// config.headers.test = "I am only a header!";
//修改 config 中的参数
config.timeout = 2000;
return config;
},
error => {
console.log("请求拦截器 失败 2号");
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
//设置一个响应拦截器,可以对响应结果做一些处理
axios.interceptors.response.use(
function (response) {
console.log("响应拦截器 成功 1号");
//返回到请求回调时,只要data数据
return response.data;
},
function (error) {
console.log("响应拦截器 失败 1号");
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
//设置一个响应拦截器
axios.interceptors.response.use(
function (response) {
console.log("响应拦截器 成功 2号");
return response;
},
function (error) {
console.log("响应拦截器 失败 2号");
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
//发送请求
axios({
method: "GET",
url: "http://localhost:3000/posts",
})
.then((response) => {
console.log("自定义回调处理成功的结果");
//console.log(response);
})
.catch((reason) => {
console.log(reason);
});
</script>
1.7 取消请求
0.22版本之前可以使用,0.22开始被废弃
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1 class="page-header">axios取消请求</h1>
<button class="btn btn-primary">发送请求</button>
<button class="btn btn-warning">取消请求</button>
</div>
</body>
<script>
//获取按钮
const btns = document.querySelectorAll("button");
//2.声明一个全局变量
let cancel = null;
//发送请求
btns[0].onclick = () => {
//检测上一次请求是否已经完成
if (cancel !== null) {
//则代表上一次请求还未取消,故直接取消上一次请求
cancel();
}
axios({
method: "GET",
url: "http://localhost:3000/posts",
//1.添加配置对象的属性
cancelToken: new axios.CancelToken((c) => {
//3.将c的值赋值给cancel
cancel = c;
}),
}).then((response) => {
console.log(response);
//当请求执行完后 将cancel进行初始化设置
cancel = null;
});
};
//取消请求
btns[1].onclick = () => {
cancel();
};
</script>
0.22新方法
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/axios/0.27.2/axios.min.js"></script>
let btn = document.querySelectorAll('button');
const controller = new AbortController();
btn[0].onclick = function () {
axios( {
url:'https://api.uomg.com/api/get.kg?songurl=https://node.kg.qq.com/play?s=YaCv8EYfJunVWYcH',
signal: controller.signal
}).then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
});
}
btn[1].onclick = function () {
controller.abort()
}
1.8 在vue中封装axios
requests.js
//对于axios进行二次封装
import axios from 'axios';
//获取仓库:存储数据
import store from '@/store';
//axios.create方法执行,其实返回一个axios和request一样的
let requests = axios.create({
//基础路径,发请求URL携带api【发现:真实服务器接口都携带/api】
baseURL: '/api',
//超时的设置
timeout: 5000,
});
//请求拦截器:将来项目中【N个请求】,只要发请求,会触发请求拦截器!!!
requests.interceptors.request.use(config => {
//请求拦截器:请求头【header】,请求头能否给服务器携带参数
//请求拦截器:其实项目中还有一个重要的作用,给服务器携带请求们的公共的参数
if (store.state.detail.nanoid_token) config.headers.userTempId = store.state.detail.nanoid_token;
if (store.state.user.token) config.headers.token = store.state.user.token;
return config;
});
//响应拦截器:请求数据返回会执行
requests.interceptors.response.use(
res => {
//res:实质就是项目中发请求、服务器返回的数据
return res.data;
},
err => {
//温馨提示:某一天发请求,请求失败,请求失败的信息打印出来
alert(err.message);
//终止Promise链
return new Promise();
}
);
//最后需要暴露:暴露的是添加新的功能的axios,即为requests
export default requests;
使用
import requests from '@/api/requests';
//注册的接口
export const reqRegister = data =>
requests({
url: `/user/passport/register`, method: 'post', data });
2.fetch
2.1 XMLHttpRequest缺点
浏览器提供了原生的AJAX实现类XMLHttpRequest,基于该类实例,我们可以实现在网页上发送AJAX请求到服务端。
但是XMLHttpRequest的设计并不完美,主要体现在以下几个方面:
- HTTP请求,响应都被耦合在XMLHttpRequest实例上,结构不够简单明了
- 采用事件回调的方式获取HTTP响应,可能会产生回调地狱
- 如果HTTP响应数据过大,则会占用大量内存
- 最后一点就是,XMLHttpRequest实现AJAX的步骤太零碎了
2.2 fetch的优点
fetch和XMLHttpRequest一样,也是浏览器原生的,用于发送AJAX请求。

XMLHttpRequest之后诞生的,它旨在解决XMLHttpRequest的不足,所以XMLHttpRequest的缺点就是它的优点,具体优点如下
- 语法简单,结构清晰明了
- 支持Promise获取异步的HTTP响应
- HTTP响应支持流式获取,内存友好
fetch被设计为函数,通过fetch函数调用即可发起AJAX,而不需要像XMLHttpRequest那样创建实例,然后基于xhr实例发起AJAX。
fetch('http://localhost:3000/test') // fetch函数调用即发起AJAX
fetch函数返回一个Promise对象,而Promise对象的结果值就是HTTP响应
fetch('http://localhost:3000/test').then(response => {
// fetch函数返回值是一个Promise类型对象
console.log(response) // 该Promise对象的结果值response就是HTTP响应
fetch函数返回的Promise对象的结果值HTTP响应是流式获取,即使HTTP响应数据很大,也不会占用过多的内存。
2.3 fetch的请求和响应
2.3.1 Request
fetch(url,options).then((response)=>{
//处理http响应
},(error)=>{
//处理错误
})
url :是发送网络请求的地址。
options:发送请求参数,
-
body - http请求参数
-
mode - 请求的模式
cors:默认值,允许跨域请求。same-origin:只允许同源请求。no-cors:请求方法只限于 GET、POST 和 HEAD,并且只能使用有限的几个简单标头,不能添加跨域的复杂标头,相当于提交表单所能发出的请求。
-
cache - 用户指定缓存。
-
method - 请求方法,默认GET
-
signal - 用于取消 fetch
-
headers - http请求头设置
-
keepalive - 用于页面卸载时,告诉浏览器在后台保持连接,继续发送数据。
-
credentials -是否发送 Cookie
same-origin:默认值,同源请求时发送 Cookie,跨域请求时不发送。include:不管同源请求,还是跨域请求,一律发送 Cookie。omit:一律不发送。
-
referrer- 用于设定
fetch()请求的referer标头 -
referrerPolicy- 用于设定
Referer标头的规则
- no-referrer-when-downgrade:默认值,总是发送Referer标头,除非从 HTTPS 页面请求 HTTP 资源时不发送。
- no-referrer:不发送Referer标头。
- origin:Referer标头只包含域名,不包含完整的路径。
- origin-when-cross-origin:同源请求Referer标头包含完整的路径,跨域请求只包含域名。
- same-origin:跨域请求不发送Referer,同源请求发送。
- strict-origin:Referer标头只包含域名,HTTPS 页面请求 HTTP 资源时不发送Referer标头。
- strict-origin-when-cross-origin:同源请求时Referer标头包含完整路径,跨域请求时只包含域名,
- HTTPS 页面请求 HTTP 资源时不发送该标头。
- unsafe-url:不管什么情况,总是发送Referer标头。
fetch('http://localhost:3000/test',{
method: 'post',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
name: 'qfc',
age: 18
})
}).then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
其中需要注意的是Request对象的body属性,该属性值支持
- 查询参数字符串,如’name=qfc&age=18’
- 文本字符串,如’{“name”:“qfc”, “age”: 18}’
- FormData对象
- Blob对象
- ReadableStream对象
- BufferSource对象
2.3.2 Response
fetch 请求成功后,响应 response 对象如图:
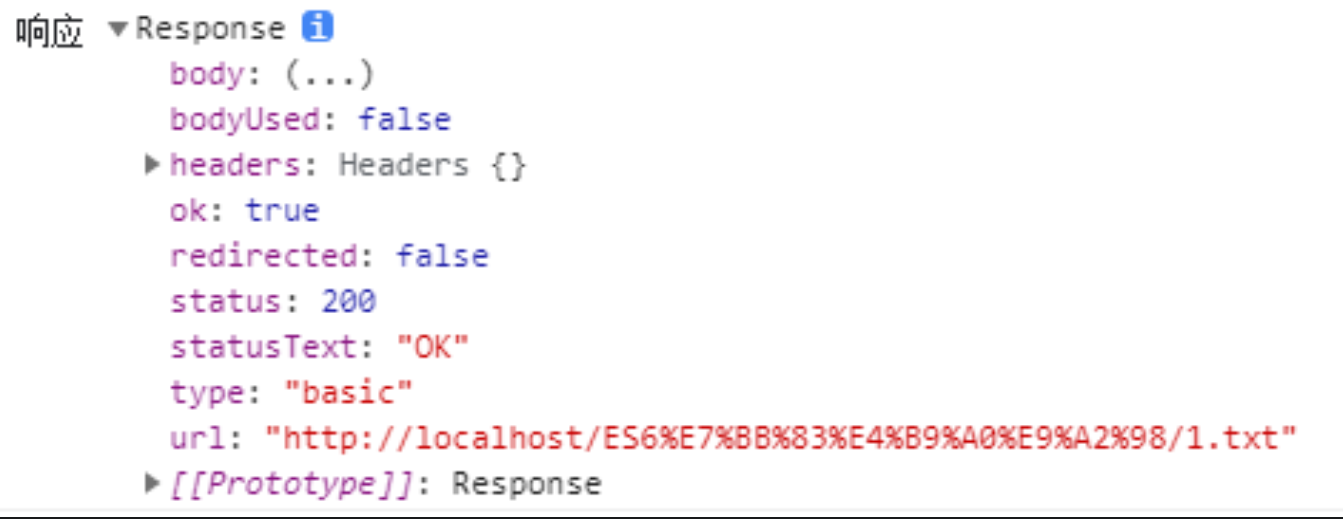
- status - http状态码,范围在100-599之间
- statusText - 服务器返回状态文字描述
- ok - 返回布尔值,如果状态码2开头的,则true,反之false
- headers - 响应头
- body - 响应体。响应体内的数据,根据类型各自处理。
- type - 返回请求类型。
- basic: 标准值, 同源响应, 带有所有的头部信息除了“Set-Cookie” 和 “Set-Cookie2″.
- cors: Response 接收到一个有效的跨域请求.
- error: 网络错误. 没有有用的描述错误的信息。响应的状态为0,header为空且不可变。从 Response.error()中获得的响应的类型.
- opaque: 响应 “no-cors” 的跨域请求.
- redirected - 返回布尔值,表示该 Response 是否来自一个重定向,如果是的话,它的 URL 列表将会有多个条目。
- url:HTTP请求URL
其中,我们需要注意的是body属性值是一个可读流,所以我们无法直接获取body内容,需要从可读流中读取内容,而读取可读流中内容也是一个异步操作,Response贴心的为我们提供了如下实例方法去异步地获取body可读流中的内容
- json() 读取body内容为JSON对象
- text() 读取body内容为普通文本字符串
- formData() 读取body内容为FormData对象
- blob() 读取body内容为Blob对象
- arrayBuffer() 读取body内容为ArrayBuffer对象
以上方法都返回一个Promise对象,且Promise对象的结果值为它们读取到并转换为对应格式的数据。
fetch('http://127.0.0.1:8000/fetch-server?vip=10', {
//请求方法
method: 'POST',
//请求头
headers: {
name:'atguigu'
},
//请求体
body: 'username=admin&password=admin'
}).then(response => {
// return response.text();
return response.json();
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
});
通过以上代码测试发现,当response.json()返回的Promise的结果值确实是body实际内容,并且自动被转化为JSON对象。
2.4 GET和POST
2.1.1 GET
fetch(`http://localhost:80/fetch.html?user=${user.value}&pas=${pas.value}`,{
method:'GET'
}).then(response=>{
console.log('响应',response)
})
2.1.2 POST
fetch(`http://localhost:80/fetch`,{
method:'POST',
headers:{
'Content-Type':'application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8'
},
body:`user=${
user.value}&pas=${
pas.value}`
}).then(response=>{
console.log('响应',response)
})
如果是提交json数据时,需要把json转换成字符串。如
fetch(`http://localhost:80/fetch`,{
method:'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
name: 'qfc',
age: 18
}).then(response=>{
console.log('响应',response)
})
如果提交的是表单数据,使用 formData转化下,如:
body:new FormData(form)
上传文件,可以包含在整个表单里一起提交,如:
const input = document.querySelector('input[type="file"]');
const data = new FormData();
data.append('file', input.files[0]);
data.append('user', 'foo');
fetch('/avatars', {
method: 'POST',
body: data
});
2.5 fetch默认不带cookie
传递cookie时,必须在参数内加上 credentials:'include',才会像 xhr 将当前cookie 带有请求中。
2.6 异常处理
fetch 不同于 xhr ,xhr 自带取消、错误等方法,所以服务器返回 4xx 或 5xx 时,是不会抛出错误的,需要手动处理,通过 response 中的 status 字段来判断。
3.跨域
3.1 同源策略
- 同源策略(Same-Origin Policy)最早由Netscape 公司提出,是浏览器的一种安全策略
- 同源: 协议、域名、端口号必须完全相同
- 跨域: 违背同源策略就是跨域
3.2 如何解决跨域
3.2.1 JSONP
jsonp 只支持get请求不支持post请求
1) JSONP 是什么
JSONP(JSON with Padding),是一个非官方的跨域解决方案,纯粹凭借程序员的聪明 才智开发出来,只支持get 请求。
2) JSONP 怎么工作的?
在网页有一些标签天生具有跨域能力,比如:img link iframe script。 JSONP 就是利用script 标签的跨域能力来发送请求的。
3) JSONP 的使用
html代码
//1. 创建 script 标签
const script = document.createElement('script');
//2. 设置标签的 src 属性
script.src = 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/check-username?callback=abc';
//3. 将script 添加到body 中
document.body.appendChild(script);
function abc(data) {
alert(data.name);
};
后端代码
app.get("/check-username" , function (req , res) {
var callback = req.query.callback;
const data = {
name: '孙悟空'
};
//将数据转化为字符串
let str = JSON.stringify(data);
//返回结果(一段可执行的JavaScript代码)
response.end(`handle(${
str})`);
});
3.2.2 CORS
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/HTTP/Access_control_CORS
- CORS 是什么? CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing),跨域资源共享。CORS 是官方的跨域解决方 案,它的特点是不需要在客户端做任何特殊的操作,完全在服务器中进行处理,支持 get 和post 请求。跨域资源共享标准新增了一组HTTP 首部字段,允许服务器声明哪些 源站通过浏览器有权限访问哪些资源
- CORS 怎么工作的? CORS 是通过设置一个响应头来告诉浏览器,该请求允许跨域,浏览器收到该响应 以后就会对响应放行。
- CORS 的使用 主要是服务器端的设置:
router.get("/testAJAX" , function (req , res) {
//通过res 来设置响应头,来允许跨域请求
//res.set("Access-Control-Allow-Origin","http://127.0.0.1:3000");
res.set("Access-Control-Allow-Origin","*");//允许所有来源访问
res.send("testAJAX 返回的响应");
});