
JenkinsFile详细使用教程
- 一、BlueOcean
- 二、Pipeline 简介
- 三、Jenkinsfile 语法简介
- 四、JenkinsFile语法参数post
- 五、JenkinsFile 语法参数 options
- 六、JenkinsFile 语法参数 parameters
- 七、JenkinsFile 语法参数 env_tools(有问题)
- 八、JenkinsFile 语法参数 if-else
- 九、JenkinsFile 语法参数 try-catch
- 十、JenkinsFile 语法参数 environment
- 十一、JenkinsFile 语法参数 triggers
- 十二、Pipeline 总结
一、BlueOcean
1、BlueOcean 概念
提供了一套可视化操作界面来帮助创建、编辑 Pipeline 任务
它为开发人员提供了更具乐趣的Jenkins使用方式
实现了一种全新的、现代风格的用户界面
有助于任何规模的团队实现持续交付
2、BlueOcean 特性
流水线编辑器:是一种直观并可视化的流水线编辑器
流水线的可视化:对流水线的可视化表示
流水线的诊断:即刻定位任务问题
个性化仪表盘:用户可以自定义仪表盘,只显示与自身相关的流水线
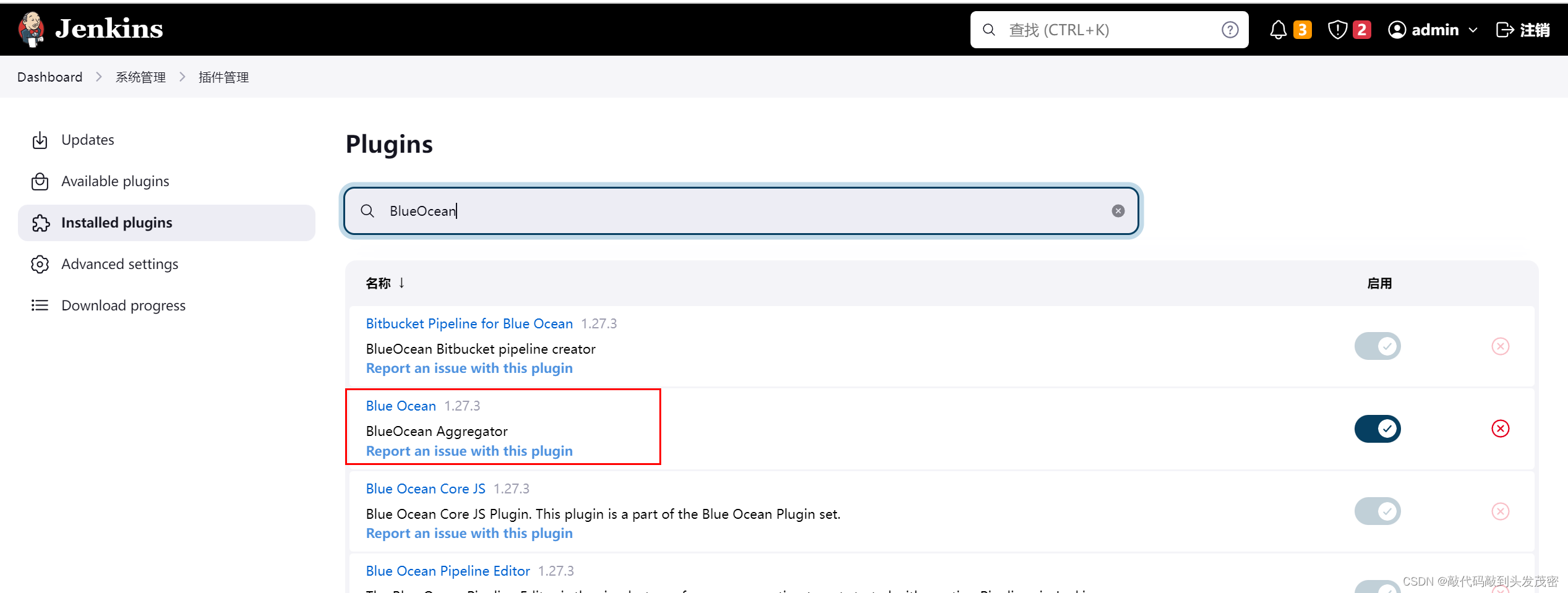
3、BlueOcean 安装
需要在 Jenkins plugin 中安装 BlueOcean
二、Pipeline 简介
1、Jenkins Pipeline 概念
a、借用Unix 中的Pipeline思路,一种高内聚低耦合的工具
b、Jenkins 2.0 以上才会有
c、一系列 Jenkins 插件将整个持续集成用解释性代码 Jenkinsfile 来描述
d、Jenkinsfile 使用方法:
Jenkins 任务页面输入
源代码工程中编辑
2、Jenkinsfile 语法类型:
Declarative pipeline
Scripts pipeline
3、采用Jenkins 任务页面输入
a. Jenkins中创建一个 pipeline 任务
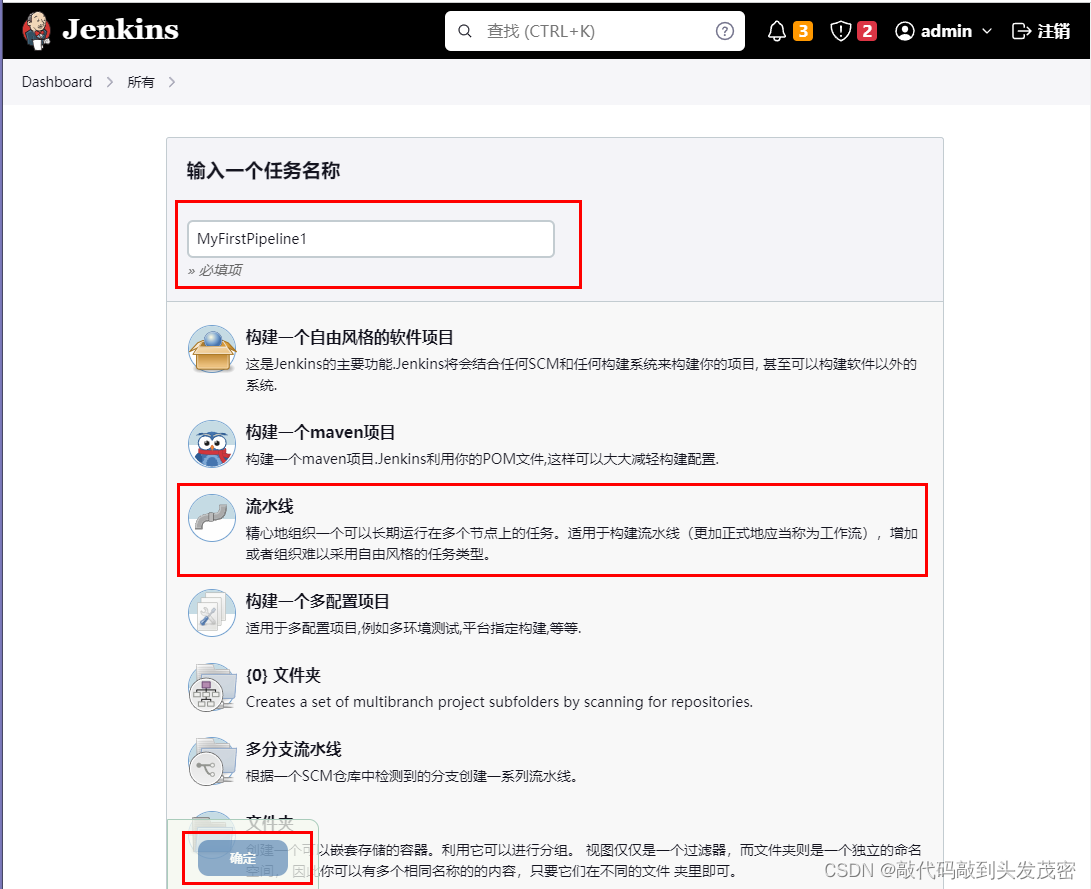
b. Definition 中选择 Pipeline Script
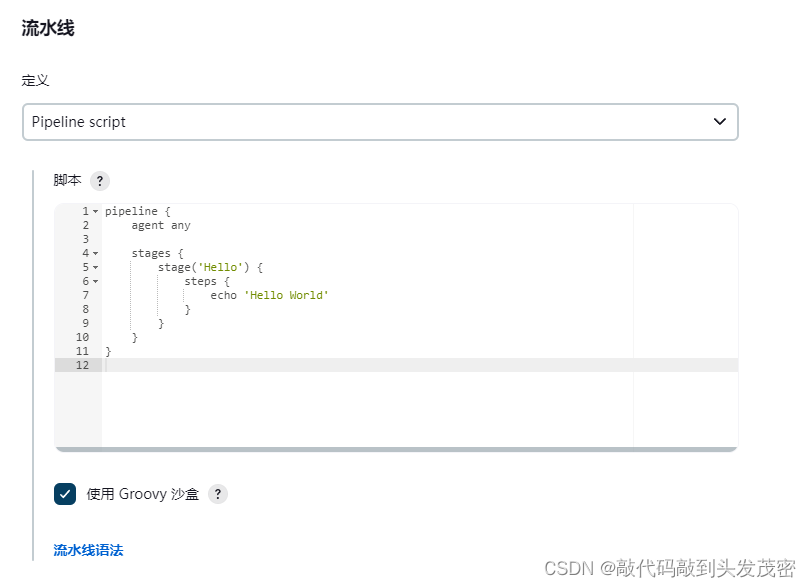
c. 在 Pipeline 模块添加Pipeline代码
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Hello') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
}
}
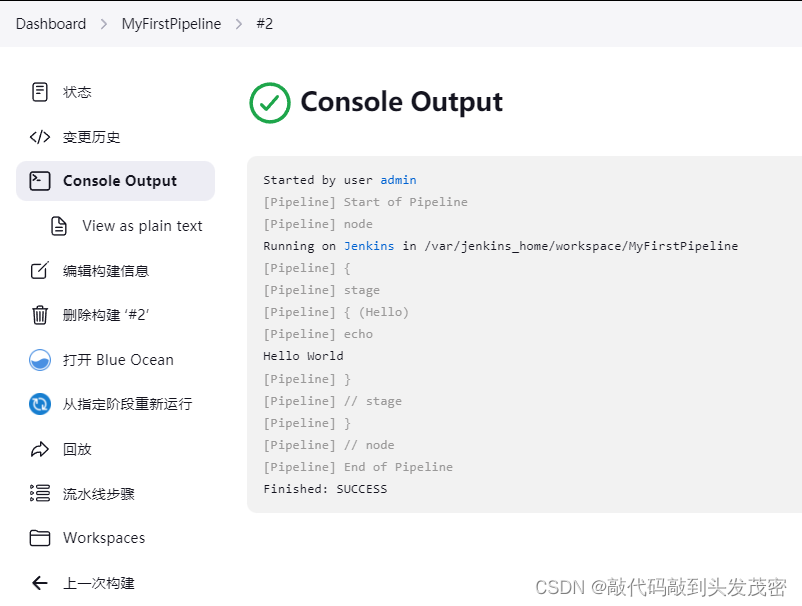
d. 运行
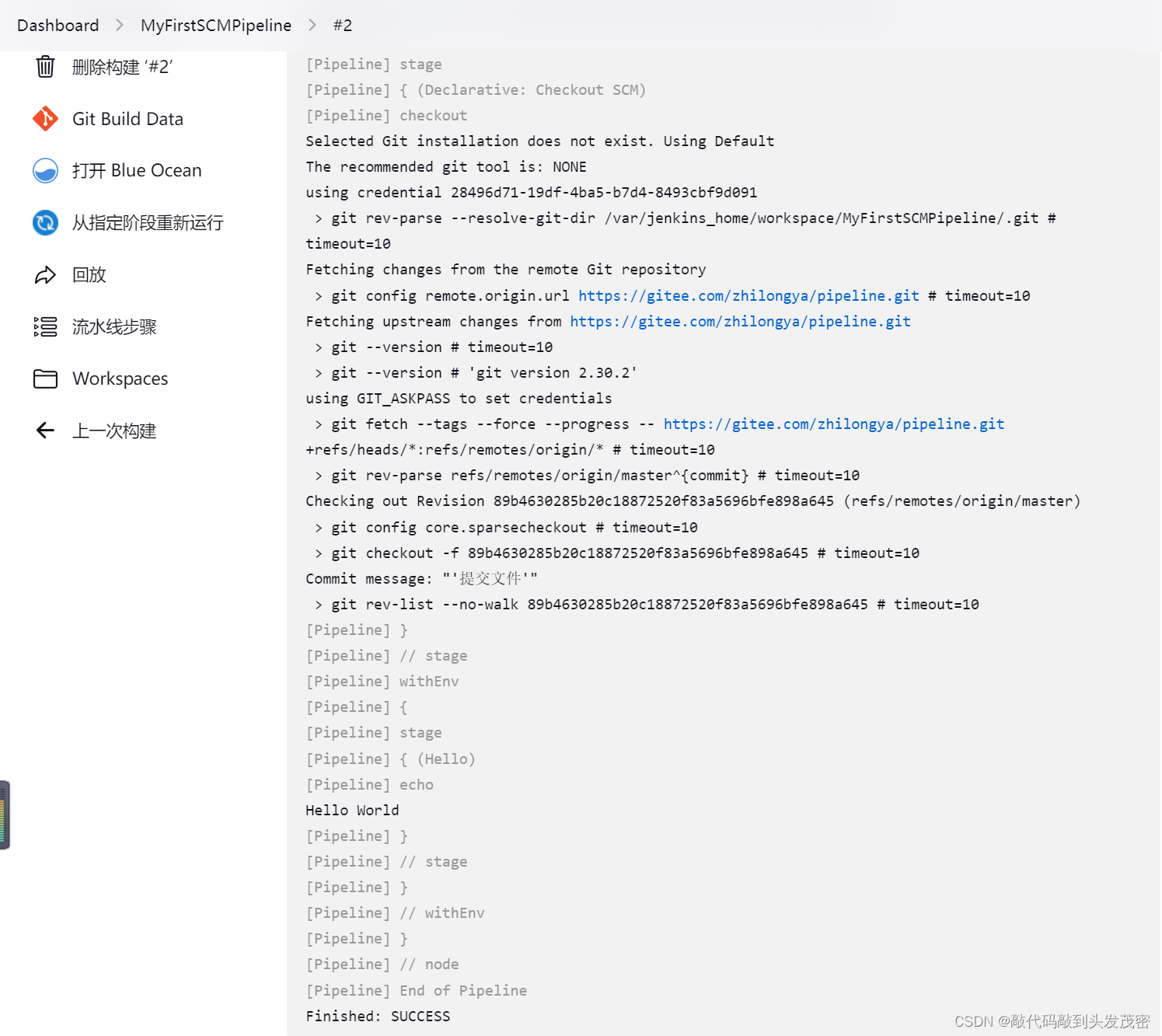
4、利用Git源码库导入 Jenkins Pipeline
a. 在Jenkins Pipeline 任务中选择 Pipeline script from SCM,
b. 然后添加 git 源码地址,
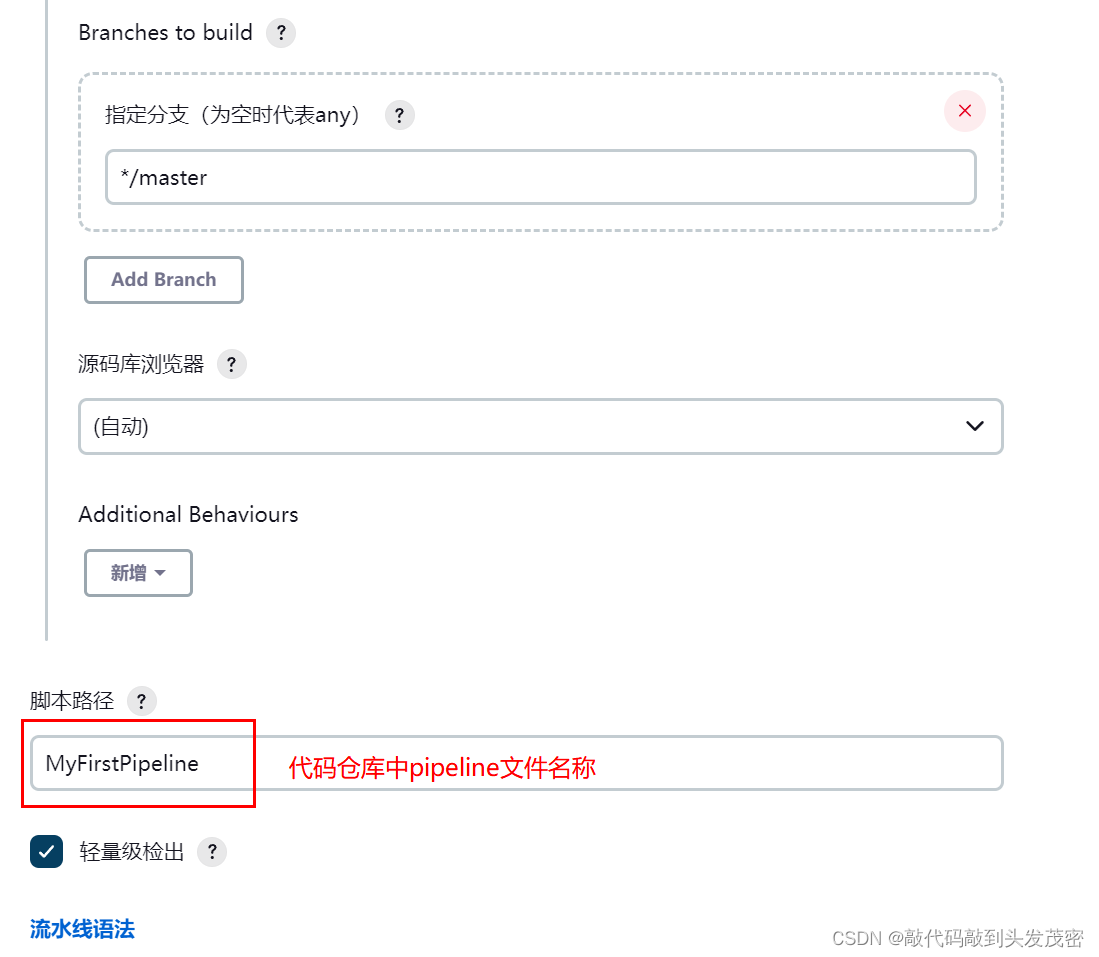
c. 在Script Path中填写需要运行的Jenkinsfile文件所在的地址
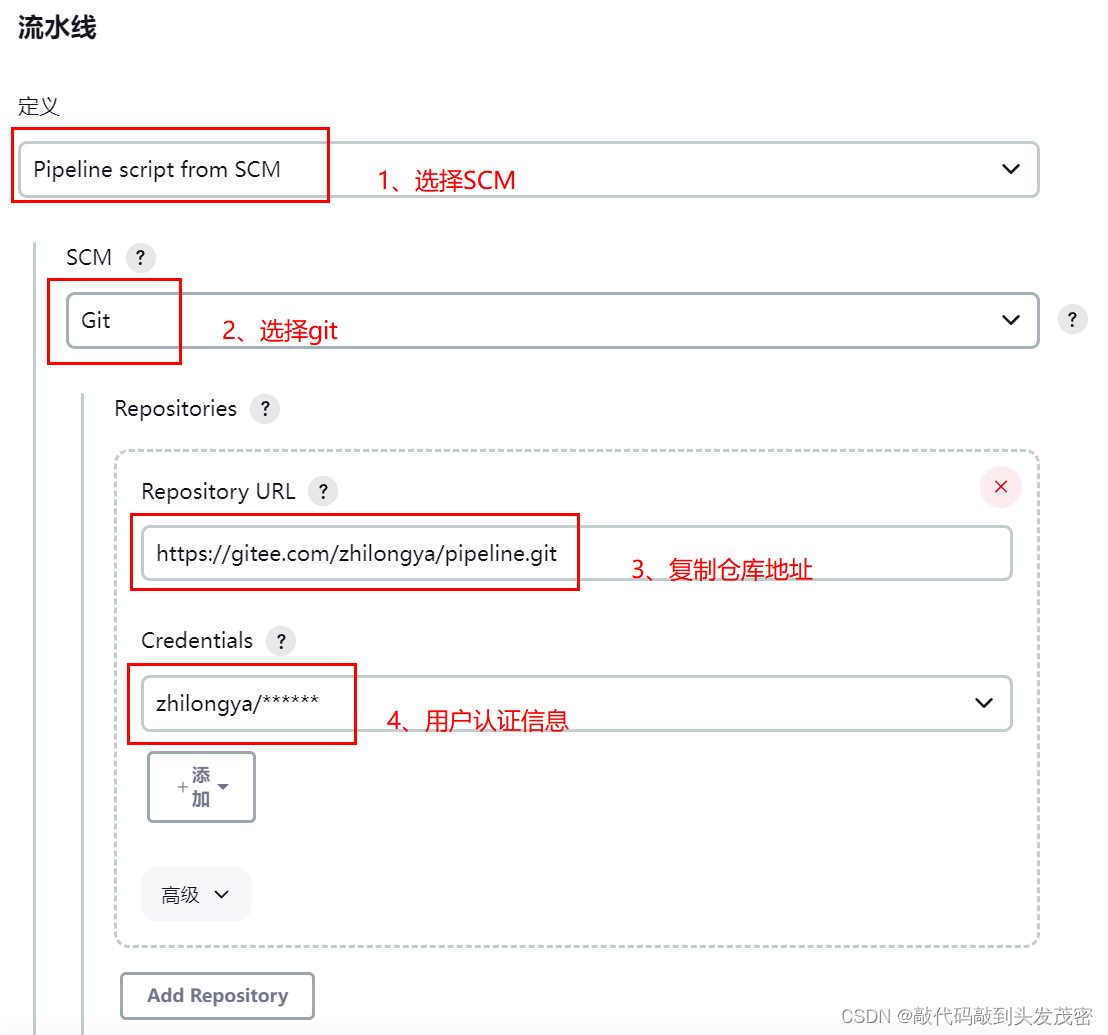
d. 运行
三、Jenkinsfile 语法简介
1、Jenkinsfile 支持两种语法形式 :
Declarative pipeline - v2.5之后引入,结构化方式
Scripts pipeline - 基于 groovy 的语法
2、Jenkinsfile 语法一:Declarative Pipeline
a.必须包含在一个pipeline块内,具体来说是:
pipeline {
}
b.基本的部分是“steps”,steps 告诉Jenkins要做什么
c.语句分类具体包含Sections, Steps,赋值等几大类
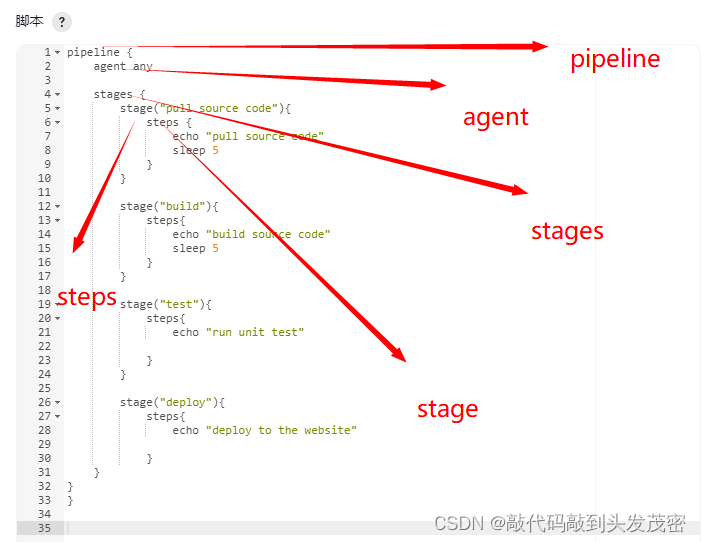
3、Declarative Pipeline - agent
agent :定义pipeline执行节点
必须出现的指令
参数
any:可以在任意agent上执行pipeline
none:pipeline将不分配全局agent, 每个stage分配自己的agent
label:指定运行节点的Label
node:自定义运行节点配置,指定 label
指定 customWorkspace
docker:控制目标节点上的docker运行相关内容
Declarative Pipeline - agent 代码举例
pipeline {
agent {
label 'master'
customWorkspace 'myWorkspace'
}
}
4、Declarative Pipeline - stages
必须出现的指令
无参数
包含一个或多个stage的序列,Pipeline的大部分工作在此执行;
每个Pipeline 代码区间中必须只有一个stages
5、Declarative Pipeline - stage
必须出现的指令
无参数
包含在stages中
Pipeline完成的所有实际工作都需要包含到stage中
需要定义stage的名字
6、Declarative Pipeline - steps
必须出现的指令
无参数
具体执行步骤,包含在 stage 代码区间中
7、Declarative Pipeline - stages, stage, steps 代码举例
stages {
stage('pull source code'){
steps {
echo 'pull source code'
sleep 5
}
}
}
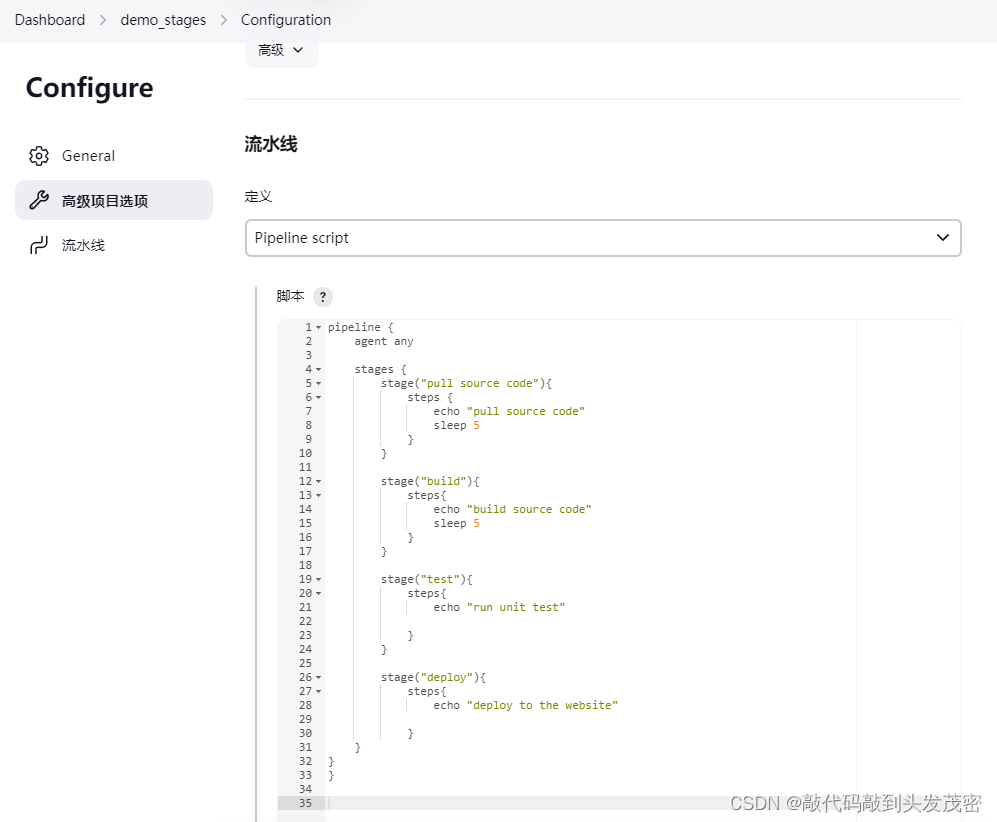
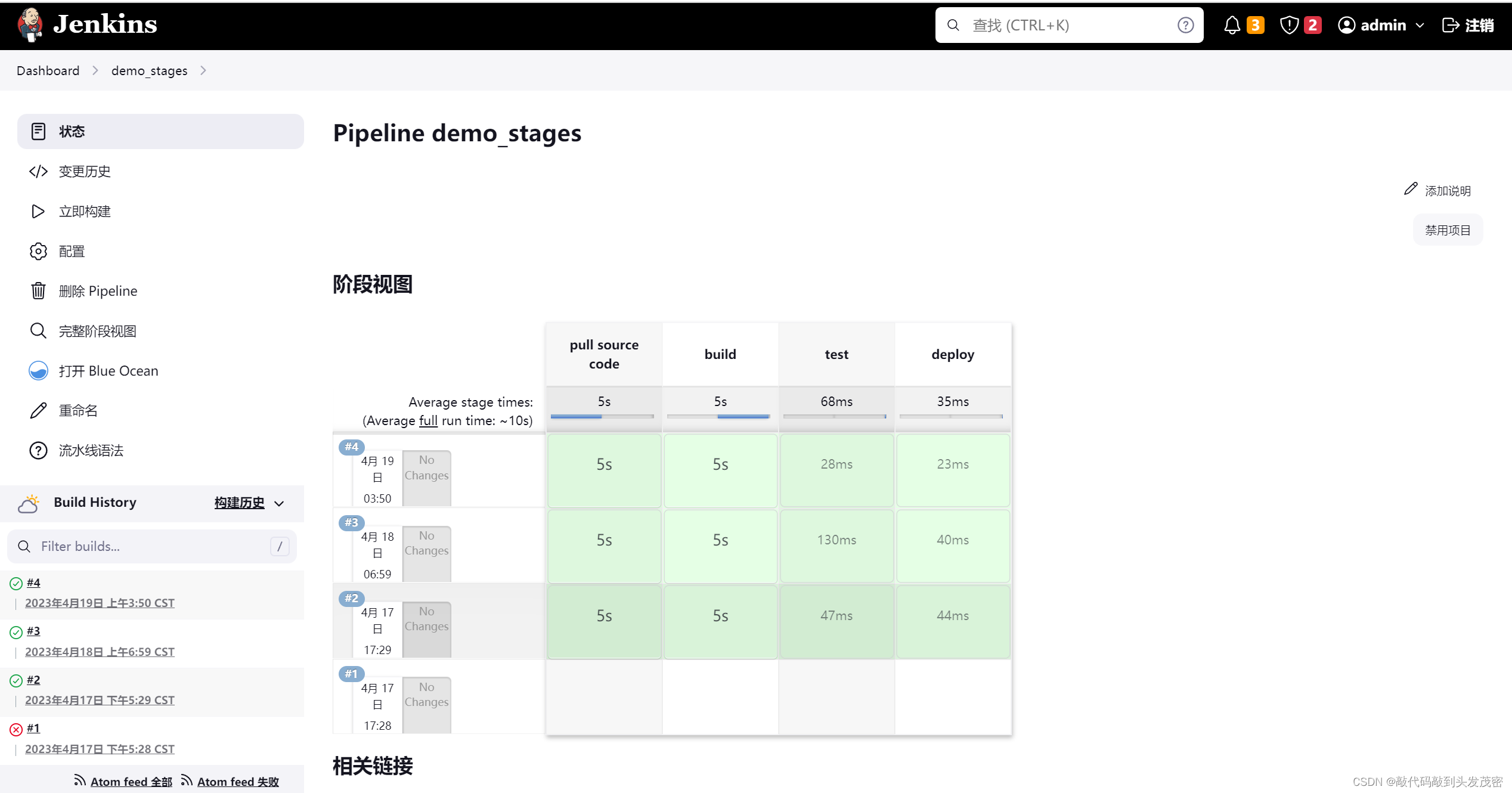
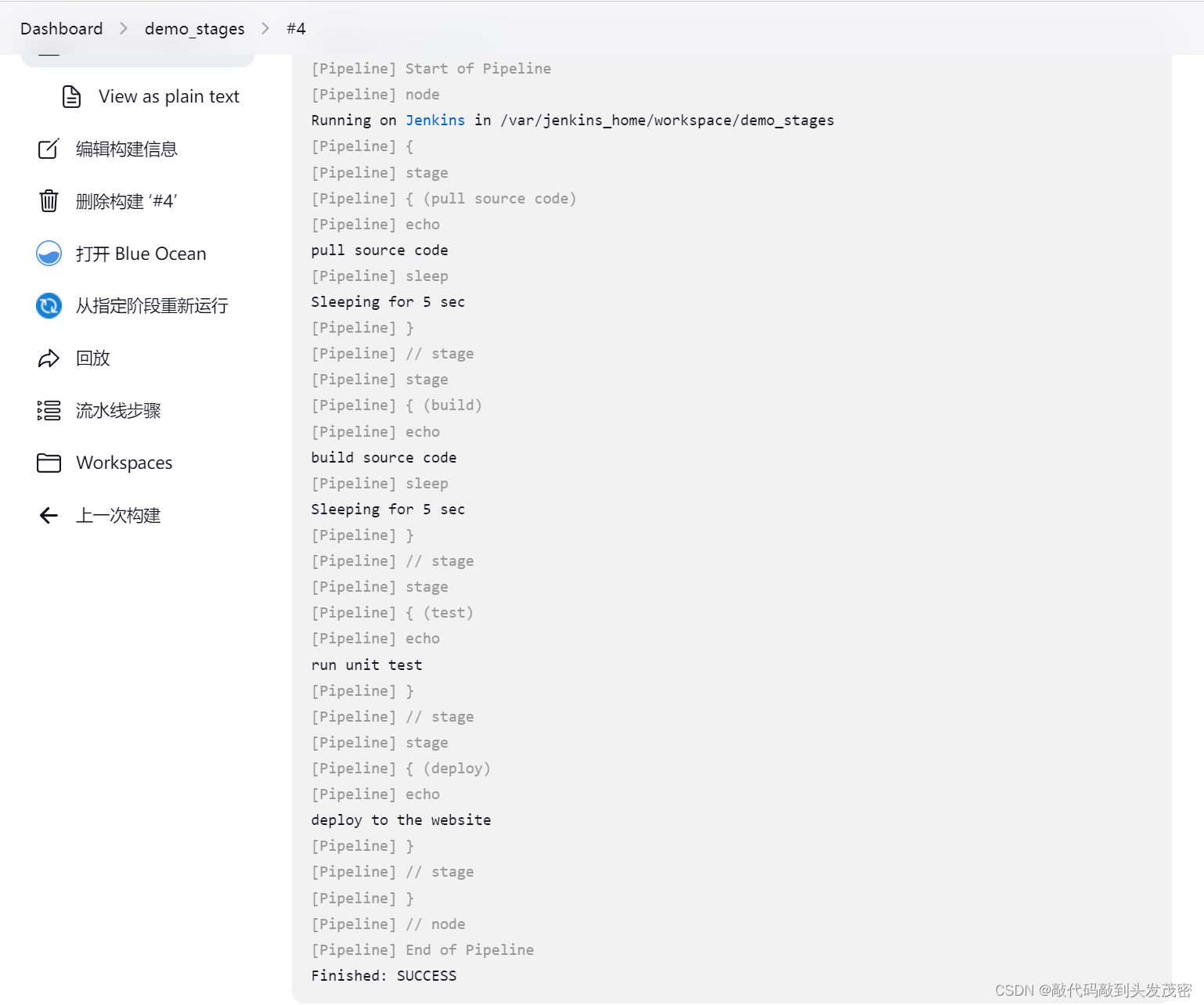
8、代码演示
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage("pull source code"){
steps {
echo "pull source code"
sleep 5
}
}
stage("build"){
steps{
echo "build source code"
sleep 5
}
}
stage("test"){
steps{
echo "run unit test"
}
}
stage("deploy"){
steps{
echo "deploy to the website"
}
}
}
}
四、JenkinsFile语法参数post
post :定义Pipeline或stage运行结束时的操作
不是必须出现的指令
参数:
always:无论Pipeline运行的完成状态如何都会运行
changed:只有当前Pipeline运行的状态与先前完成的Pipeline的状态不同时,才能运行
failure:仅当当前Pipeline处于“失败”状态时才运行
success :仅当当前Pipeline具有“成功”状态时才运行
unstable:只有当前Pipeline具有“不稳定”状态才能运行
aborted:只有当前Pipeline处于“中止”状态时才能运行
案例1-执行失败
pipeline{
agent any
stages {
stage('Test'){
steps{
echo "This is test code"
sleep 2
sh 'exit -1'
}
}
}
post{
always{
echo 'say goodby'
}
success{
echo 'This is success exit'
}
failure{
echo 'This is failure exit'
}
}
}
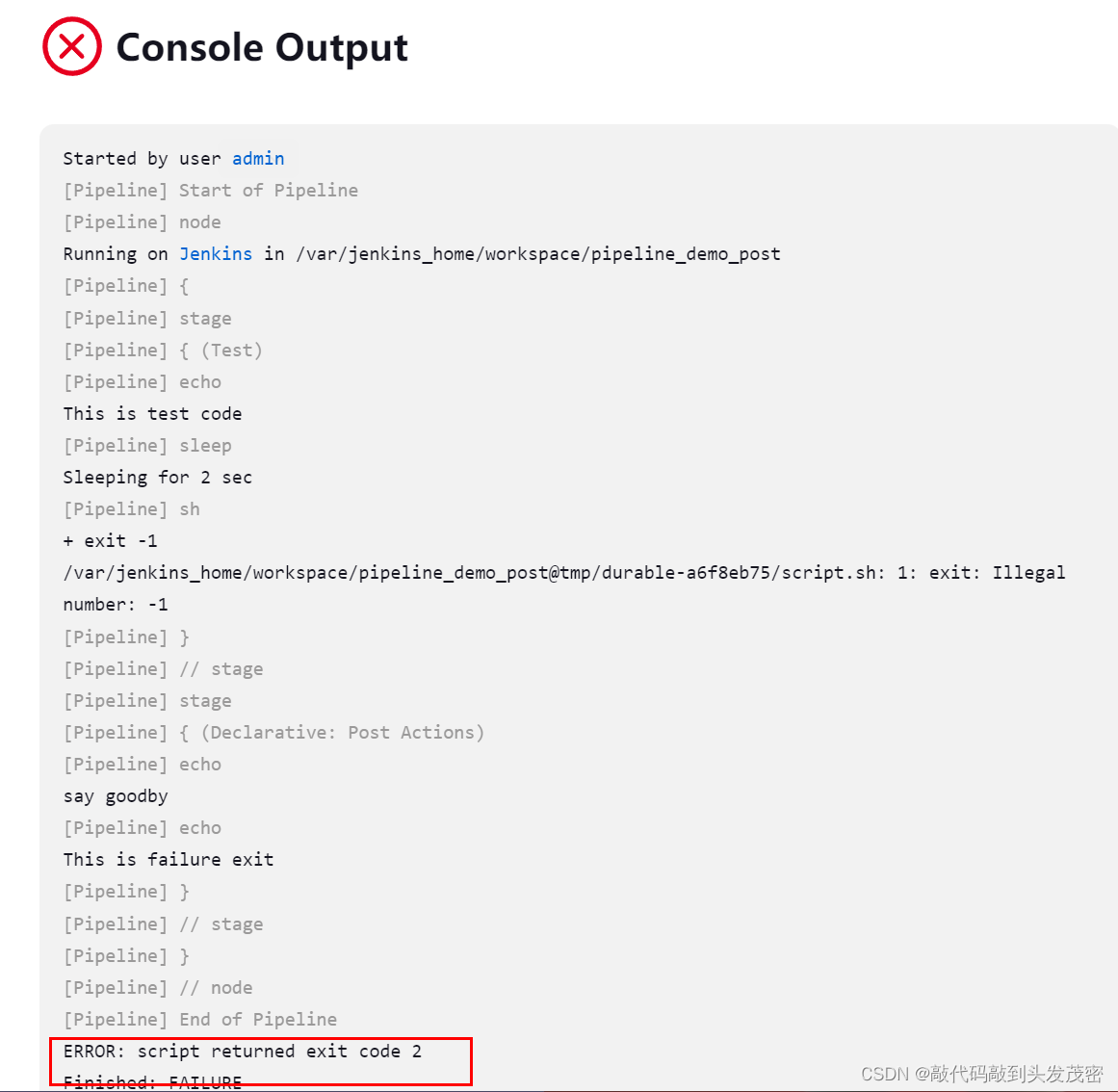
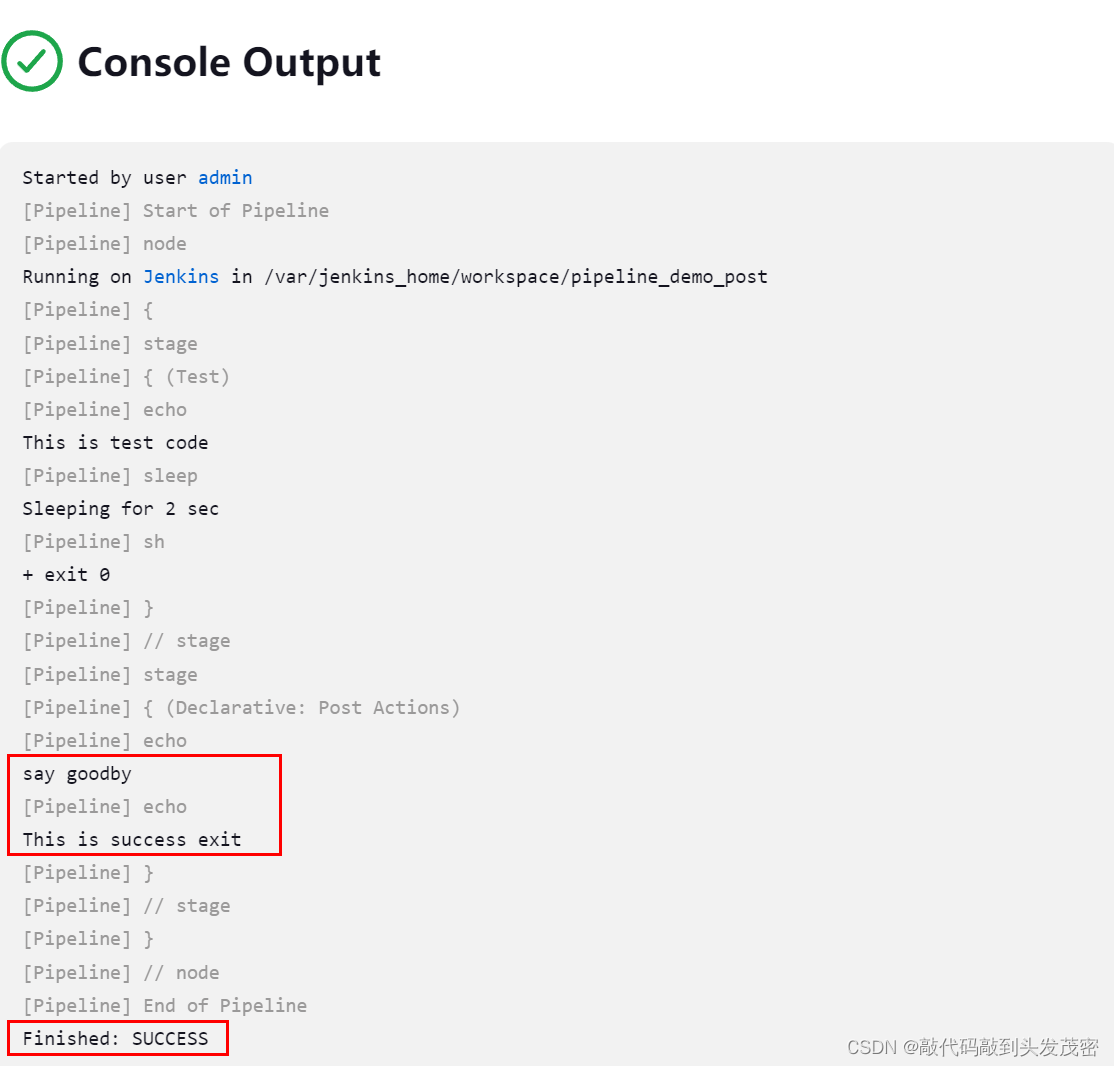
案例2-执行成功
pipeline{
agent any
stages {
stage('Test'){
steps{
echo "This is test code"
sleep 2
sh 'exit 0'
}
}
}
post{
always{
echo 'say goodby'
}
success{
echo 'This is success exit'
}
failure{
echo 'This is failure exit'
}
}
}
五、JenkinsFile 语法参数 options
options :定义pipeline 的专有属性
不是必须出现的指令
参数:
buildDiscarder:保持构建的最大个数(历史构建个数)
disableConcurrentBuilds:不允许并行执行pipeline任务
timeout:pipeline 超时时间
retry:失败后,重试整个Pipeline的次数
timestamps:预定义由Pipeline生成的所有控制台输出时间
skipStagesAfterUnstable:一旦构建状态进入了“Unstable”状态,就跳过此stage
1、正常情况
pipeline{
agent {
node{
label 'docker_node'
customWorkspace "pipelineWorkspace"
}
}
options {
timeout(time: 10,unit:"SECONDS") //构建超过10s,就会超时
buildDiscarder(logRotator(numToKeepStr:"2")) //最多保留2个最新的构建
retry(5) //失败后尝试运行5次
}
stages {
stage('begin'){
steps{
echo 'hello pipeline begin'
sleep 2
}
}
stage('running'){
steps{
echo 'hello pipeline running'
sleep 2
}
}
stage('finsh'){
steps{
echo 'hello pipeline finsh'
sleep 2
sh "exit 0"
}
}
}
post{
always{
echo 'say goodby'
}
success{
echo 'This is success exit'
}
failure{
echo 'This is failure exit'
}
}
}
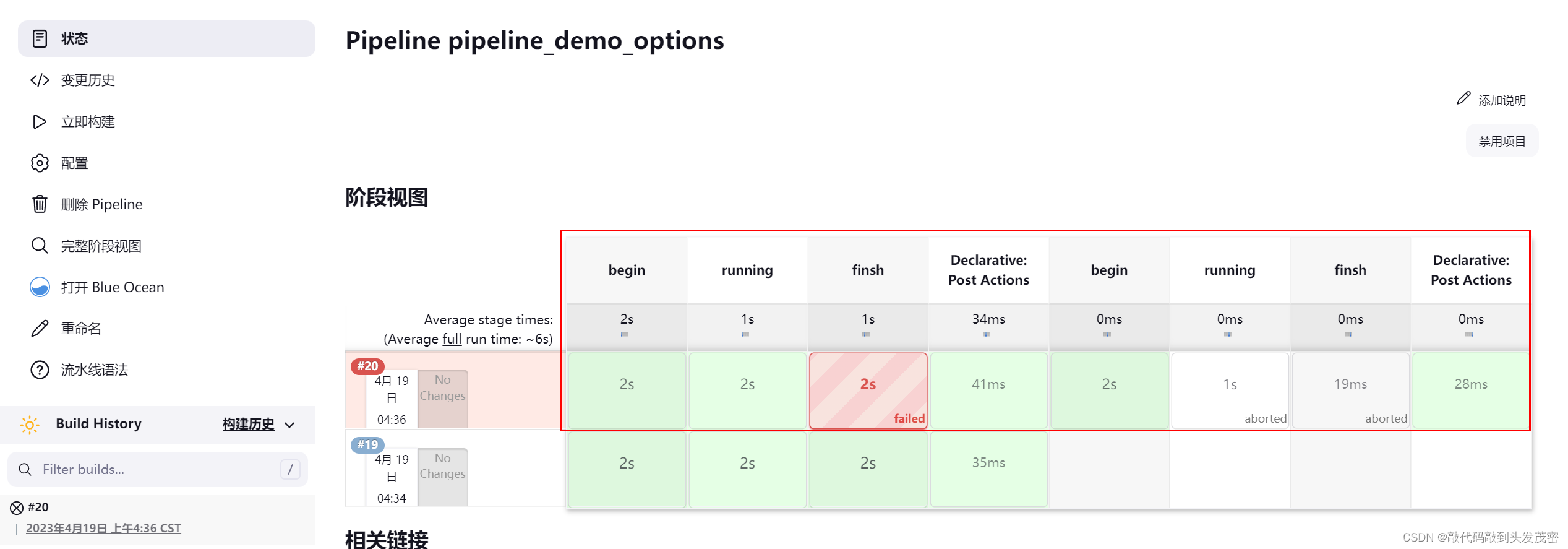
控制台输出
Started by user admin
[Pipeline] Start of Pipeline
[Pipeline] node
Running on docker_node in /root/jenkins_mulu/workspace/pipeline_demo_options
[Pipeline] {
[Pipeline] ws
Running in /root/jenkins_mulu/pipelineWorkspace
[Pipeline] {
[Pipeline] timeout
Timeout set to expire in 10 sec
[Pipeline] {
[Pipeline] retry
[Pipeline] {
[Pipeline] stage
[Pipeline] {
(begin)
[Pipeline] echo
hello pipeline begin
[Pipeline] sleep
Sleeping for 2 sec
[Pipeline] }
[Pipeline] // stage
[Pipeline] stage
[Pipeline] {
(running)
[Pipeline] echo
hello pipeline running
[Pipeline] sleep
Sleeping for 2 sec
[Pipeline] }
[Pipeline] // stage
[Pipeline] stage
[Pipeline] {
(finsh)
[Pipeline] echo
hello pipeline finsh
[Pipeline] sleep
Sleeping for 2 sec
[Pipeline] sh
+ exit 0
[Pipeline] }
[Pipeline] // stage
[Pipeline] stage
[Pipeline] {
(Declarative: Post Actions)
[Pipeline] echo
say goodby
[Pipeline] echo
This is success exit
[Pipeline] }
[Pipeline] // stage
[Pipeline] }
[Pipeline] // retry
[Pipeline] }
[Pipeline] // timeout
[Pipeline] }
[Pipeline] // ws
[Pipeline] }
[Pipeline] // node
[Pipeline] End of Pipeline
Finished: SUCCESS
2、异常情况
pipeline{
agent {
node{
label 'docker_node'
customWorkspace "pipelineWorkspace"
}
}
options {
timeout(time: 10,unit:"SECONDS") //构建超过10s,就会超时
buildDiscarder(logRotator(numToKeepStr:"2")) //最多保留2个最新的构建
retry(5) //失败后尝试运行5次
}
stages {
stage('begin'){
steps{
echo 'hello pipeline begin'
sleep 2
}
}
stage('running'){
steps{
echo 'hello pipeline running'
sleep 2
}
}
stage('finsh'){
steps{
echo 'hello pipeline finsh'
sleep 2
sh "exit -1"
}
}
}
post{
always{
echo 'say goodby'
}
success{
echo 'This is success exit'
}
failure{
echo 'This is failure exit'
}
}
}
六、JenkinsFile 语法参数 parameters
parameters :定义pipeline 的专有参数列表
不是必须出现的指令
参数:
支持数据类型:booleanParam, choice, credentials, file, text, password, run, string
类似参数化构建的选项
1、Declarative Pipeline - parameters 代码举例
parameters {
string(name: 'PERSON', defaultValue: 'Jenkins', description: '输入的文本参数')
choice(name: 'CHOICE', choices: ['One', 'Two', 'Three'], description: 'Pick something')
}
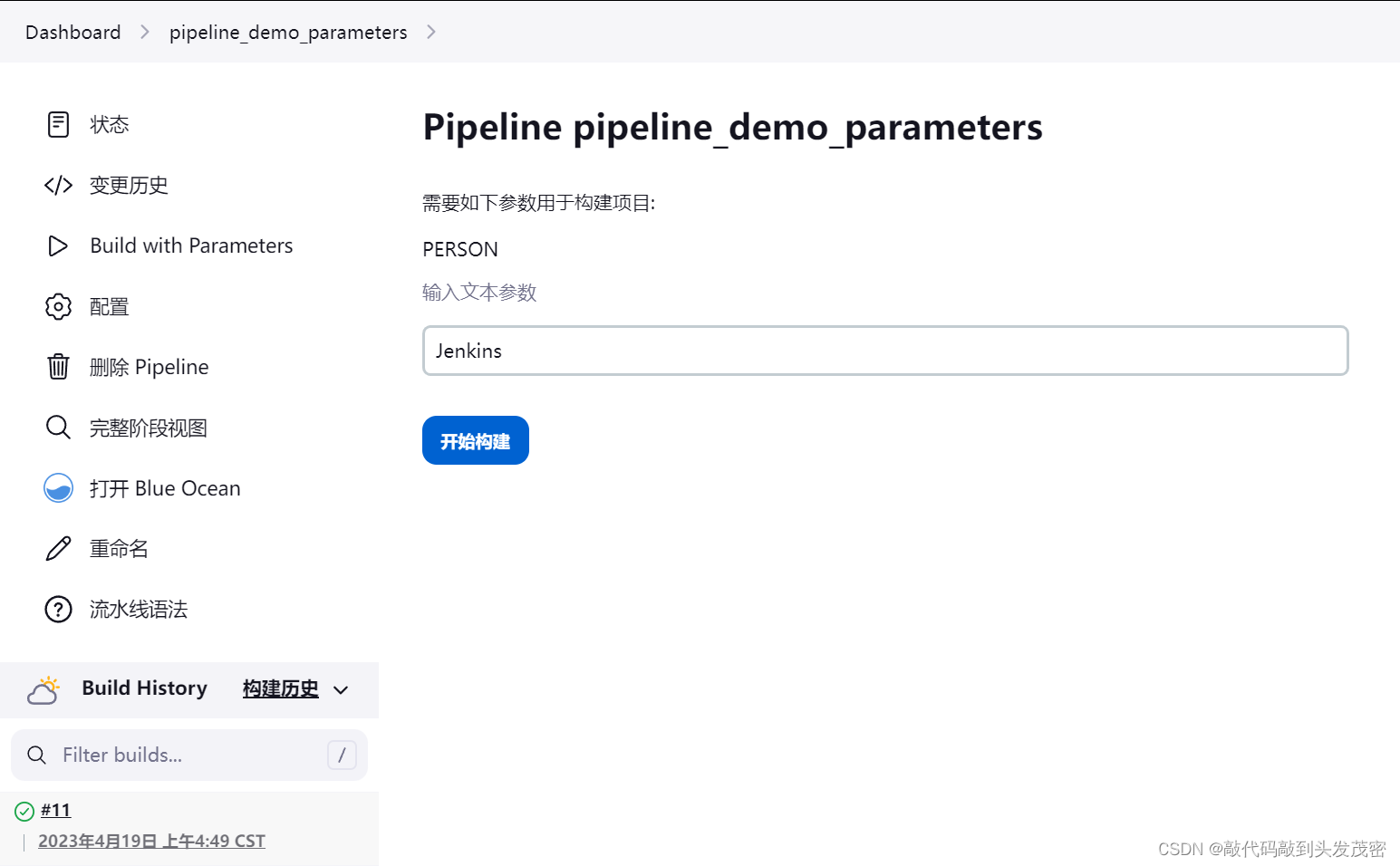
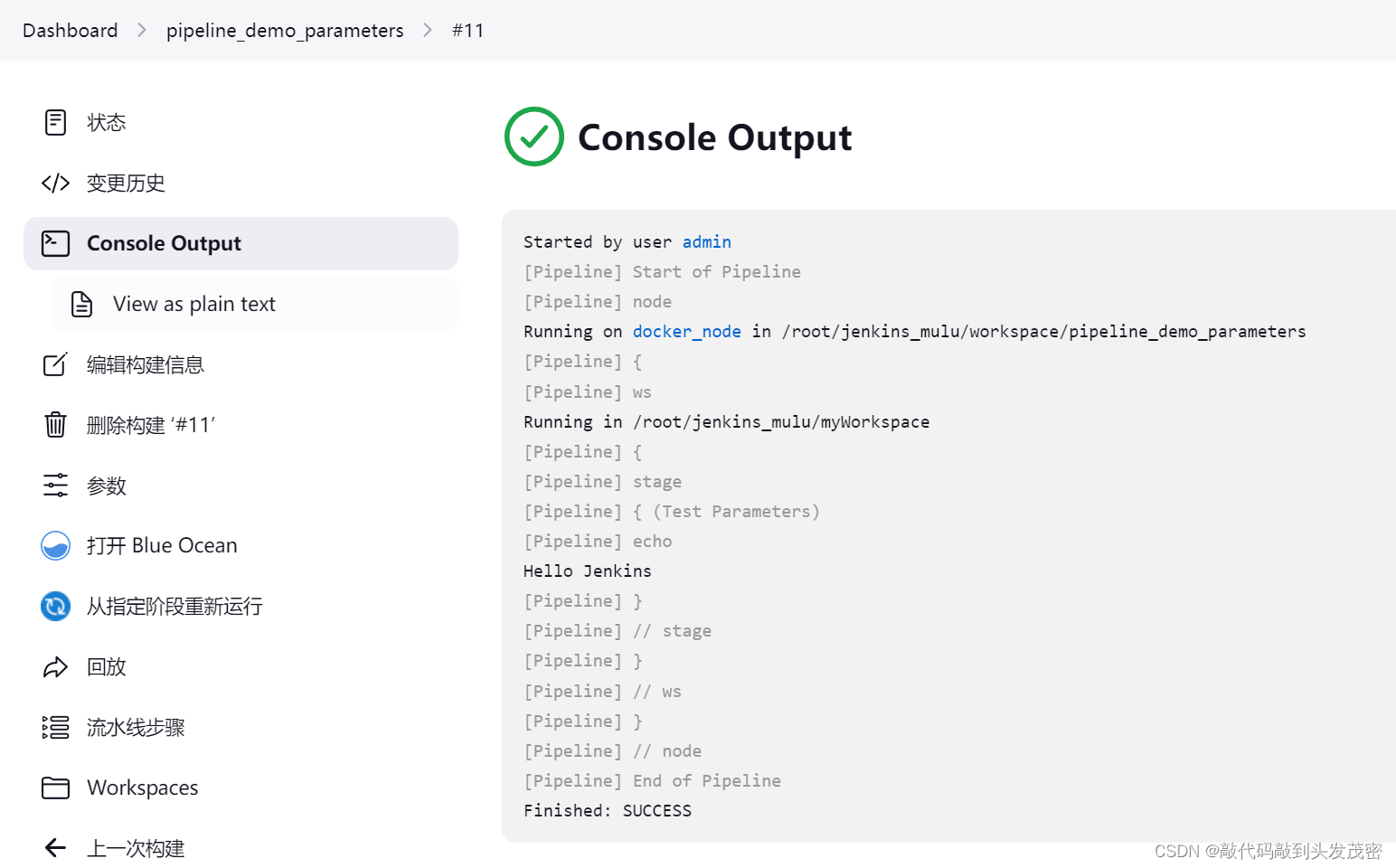
2、案例:以默认值构建
pipeline {
agent{
node{
label 'docker_node'
customWorkspace "myWorkspace"
}
}
parameters{
string(name:'PERSON',defaultValue:'Jenkins',description:'输入文本参数')
}
stages{
stage('Test Parameters'){
steps{
echo "Hello ${PERSON}"
}
}
}
}
3、案例:非默认值构建
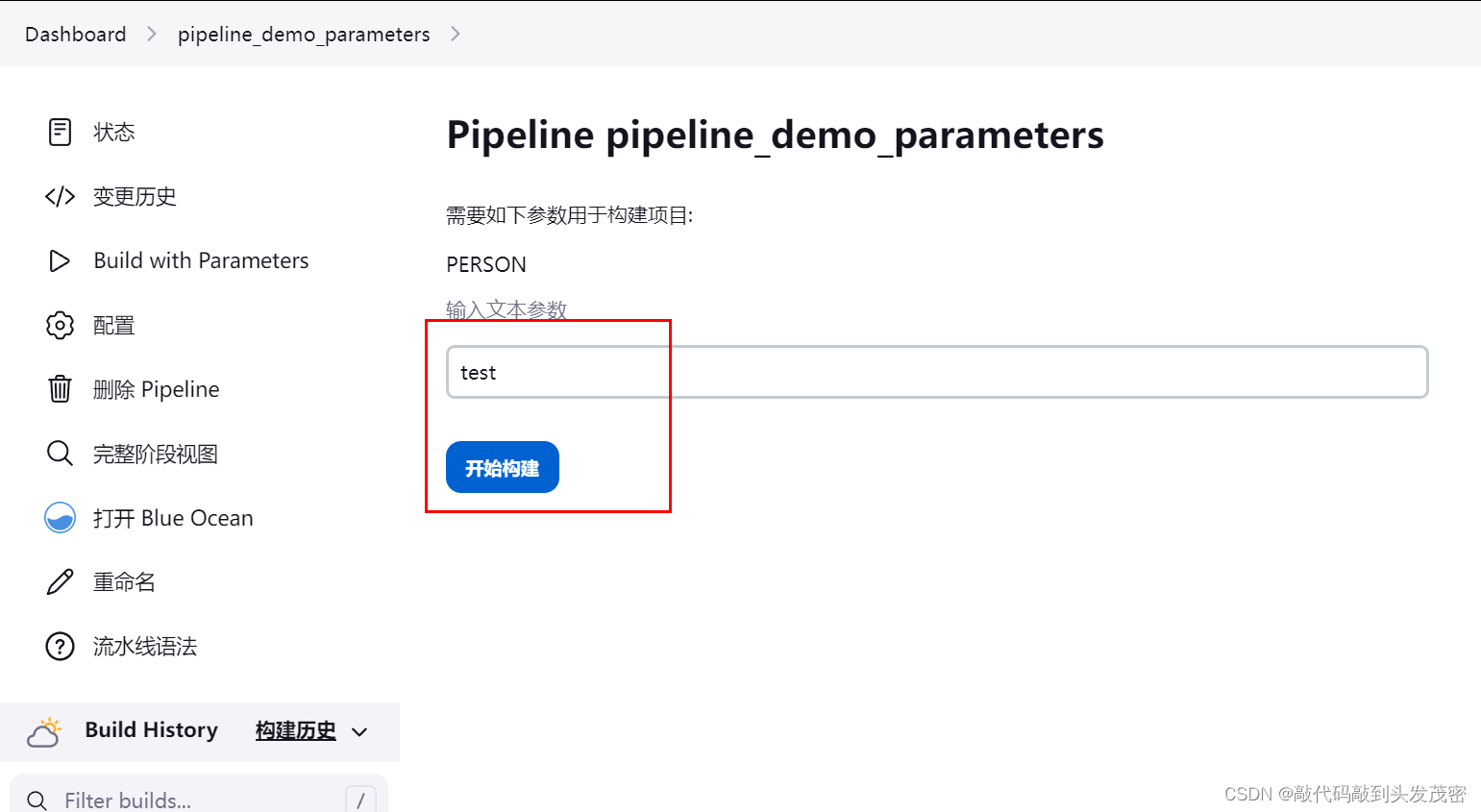
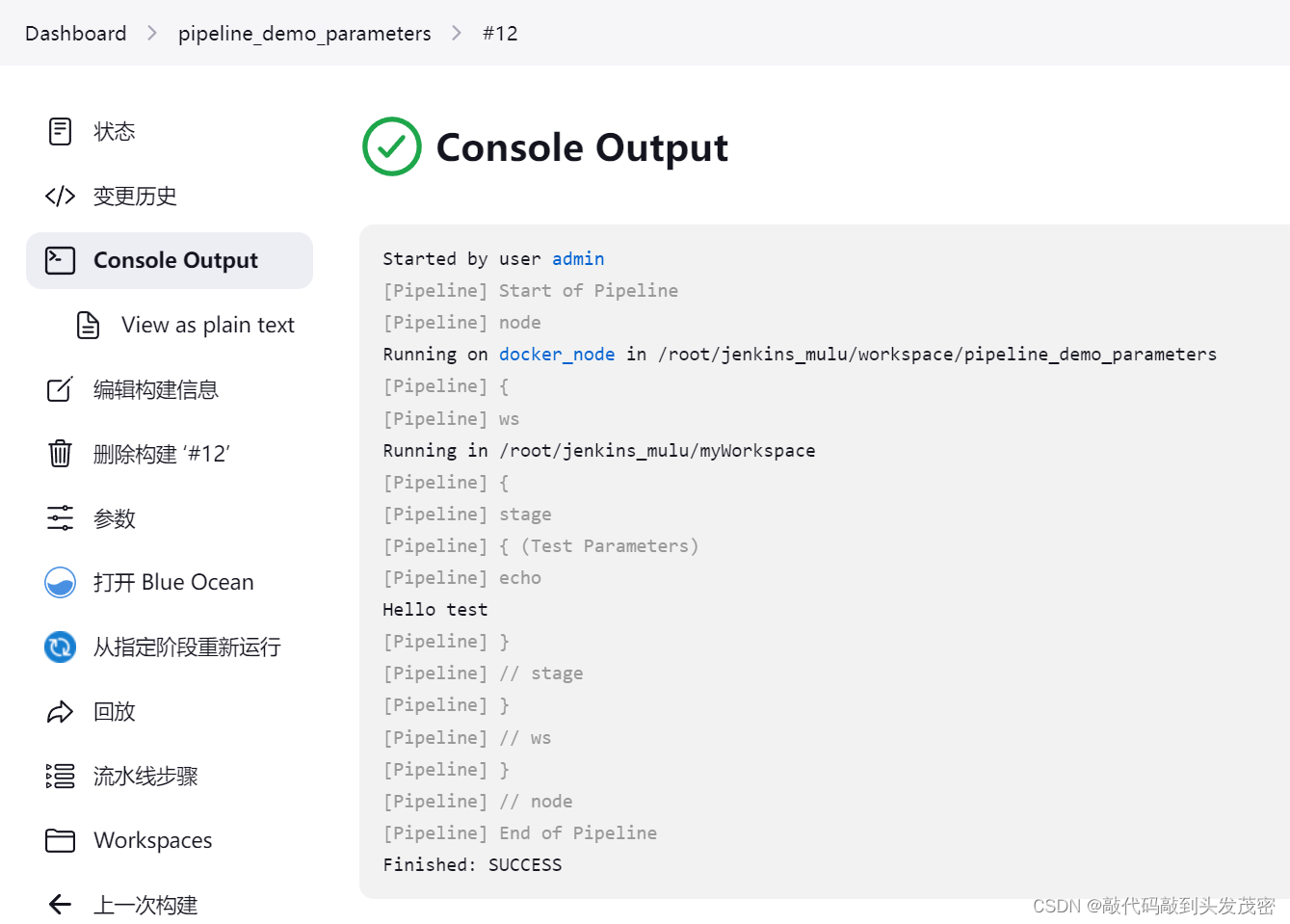
3、解决第一次运行失败的问题
pipeline {
agent{
node{
label 'docker_node'
customWorkspace "myWorkspace"
}
}
parameters{
string(name:'PERSON',defaultValue:'Jenkins',description:'输入文本参数')
}
environment{
PERSON ="$params.PERSON"
}
stages{
stage('Test Parameters'){
steps{
echo "Hello ${PERSON}"
}
}
}
}
七、JenkinsFile 语法参数 env_tools(有问题)
1、Scripts pipeline: 环境变量定义与引用
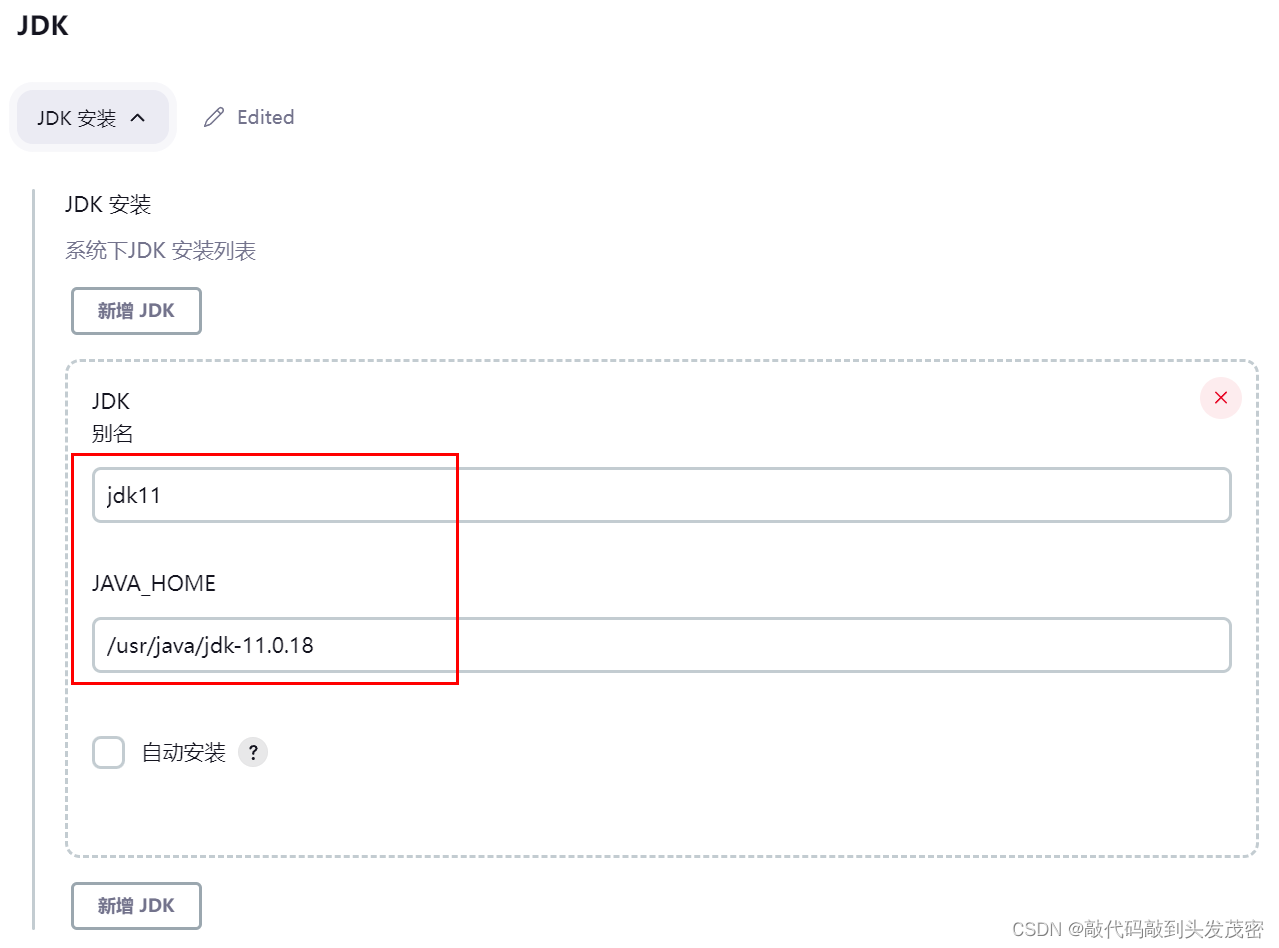
环境工具变量的定义
设置位置: “Manage Jenkins”——> “Global Tool Configuration”
1.1、环境变量定义1: JDK Home的定义
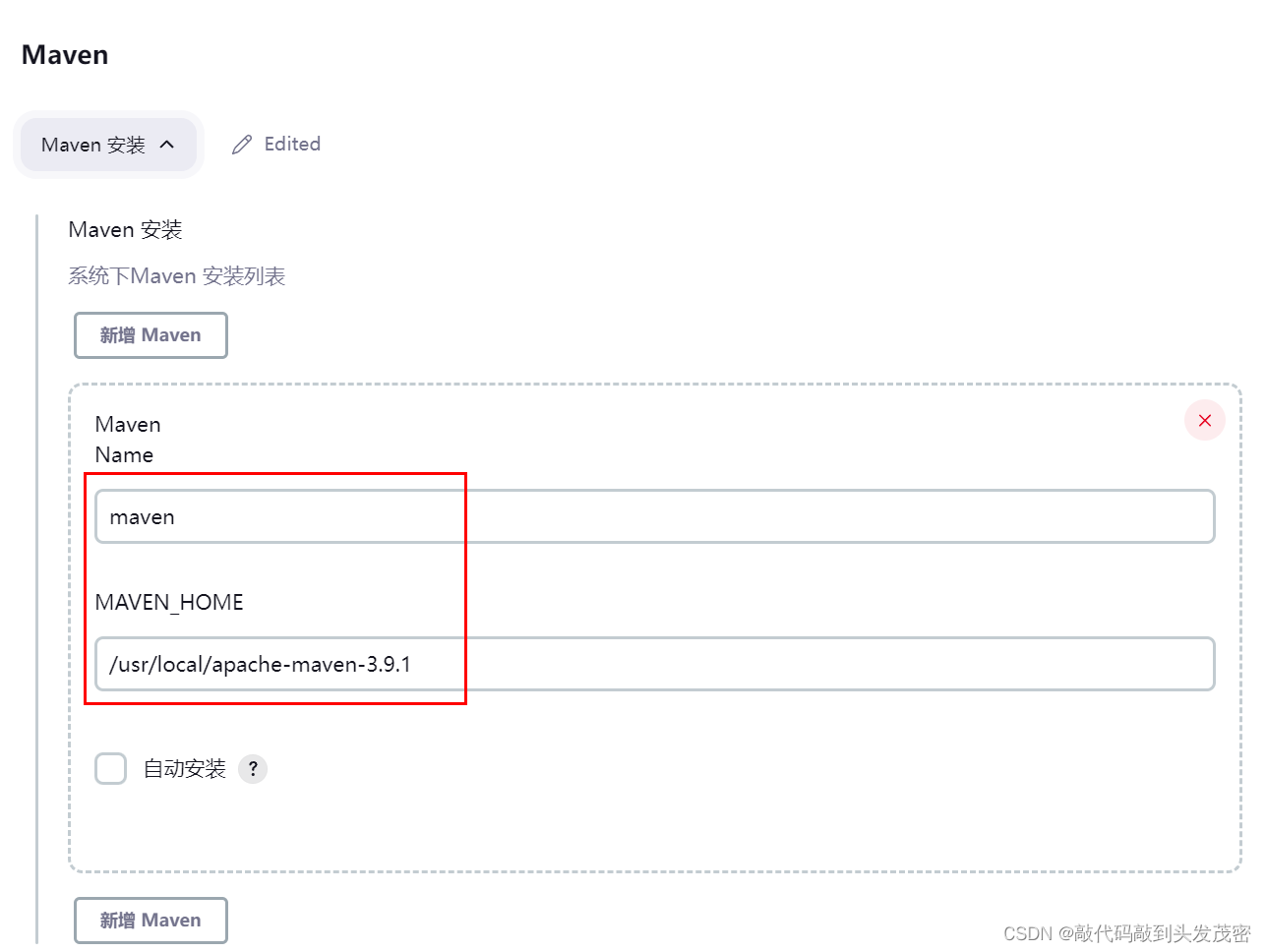
1.2、环境变量定义2: Maven Home的定义
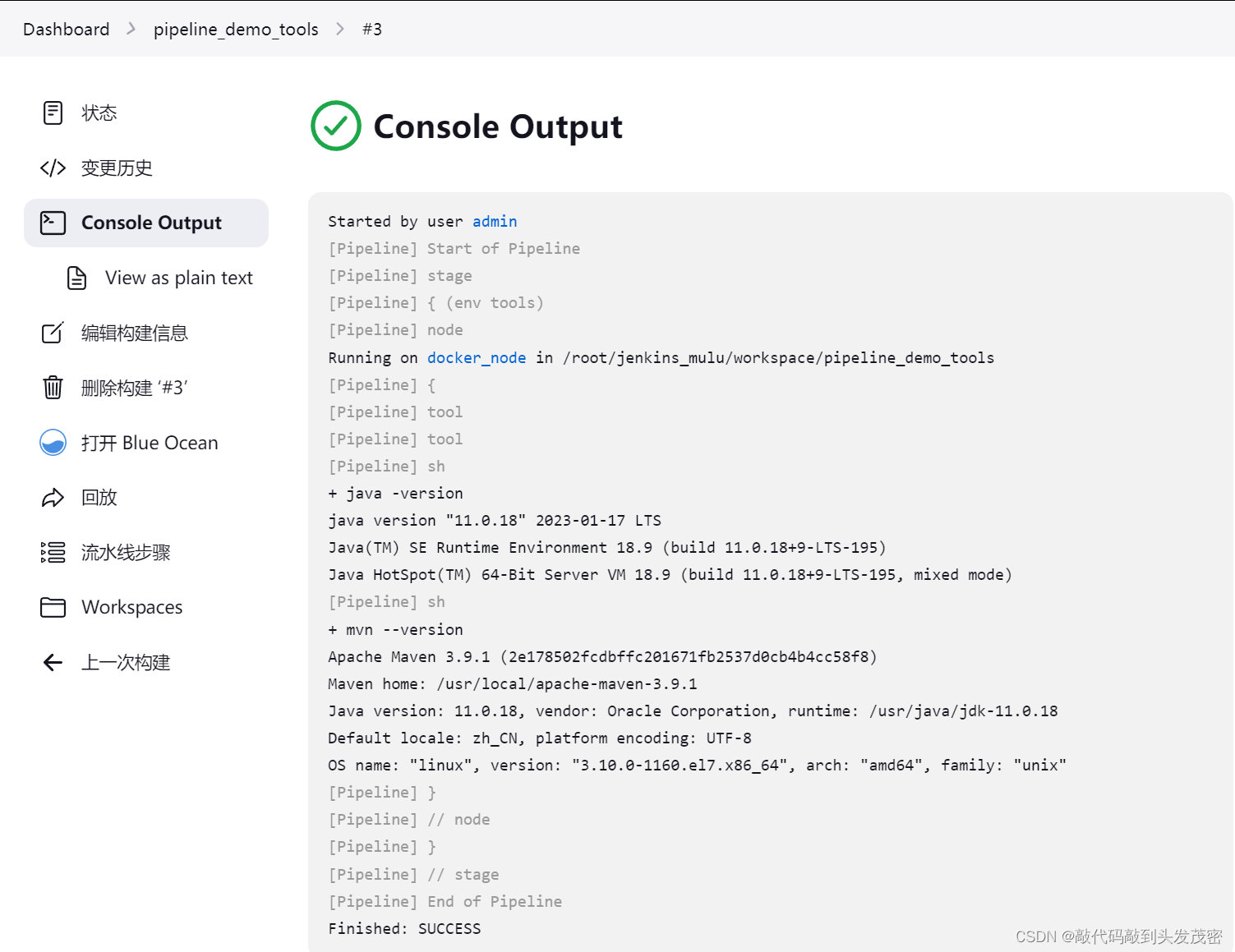
2、Script 代码中引用环境变量,调用java、maven工具
stage('env tools') {
node('docker_node'){
//定义maven java环境
def mvnHome = tool 'maven'
def jdkHome = tool 'jdk11'
//引用环境变量,配置PATH变量
env.PATH = "${mvnHome}/bin:${env.PATH}"
env.PATH = "${jdkHome}/bin:${env.PATH}"
//调用java mvn 工具
sh "java -version"
sh "mvn --version"
}
}
运行结果
八、JenkinsFile 语法参数 if-else
1、Jenkinsfile 语法二:Scripts pipeline
基于 groovy 语法定制的一种DSL语言
灵活性更高
可扩展性更好
Script pipeline 与 Declarative pipeline 程序构成方式有雷同之处,基本语句也有相似之处
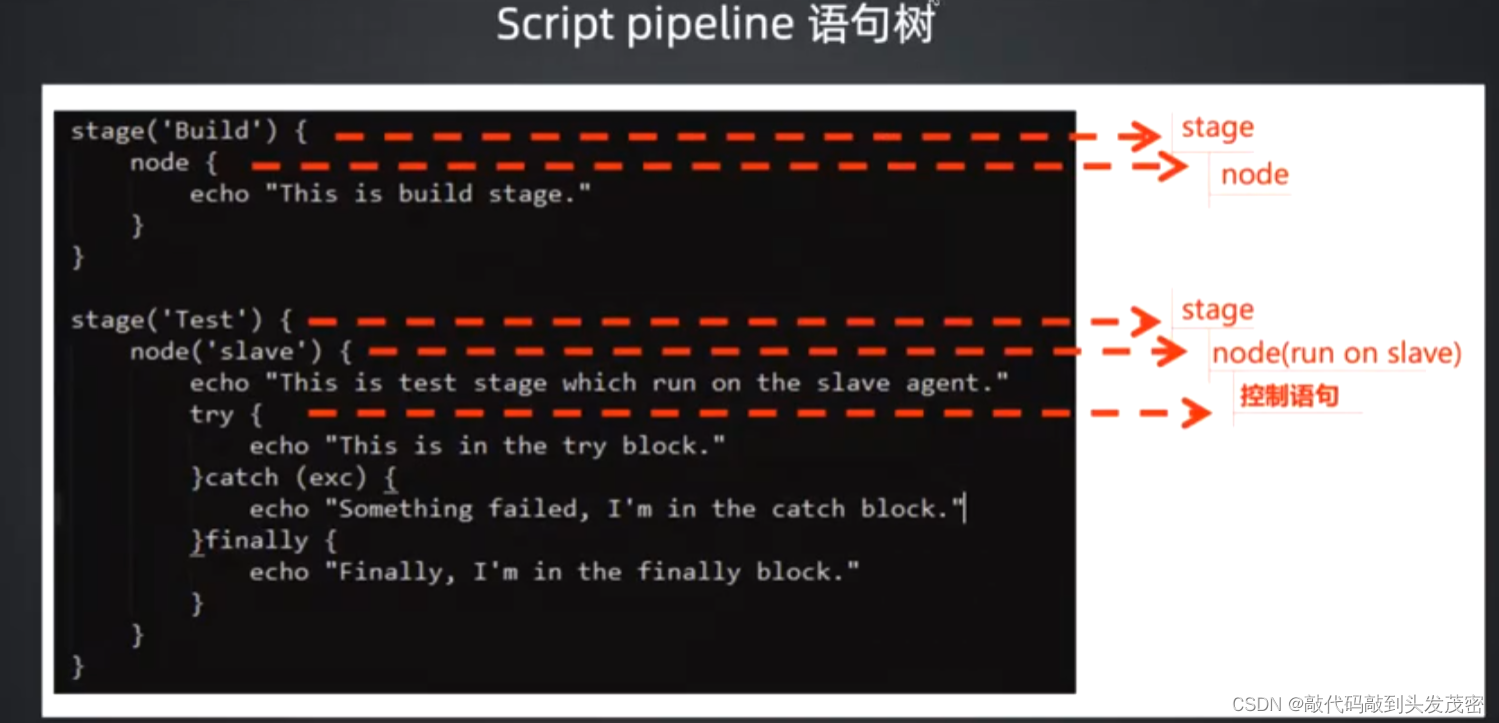
2、Scripts pipeline: 流程控制之 – if/else
node {
stage('Example') {
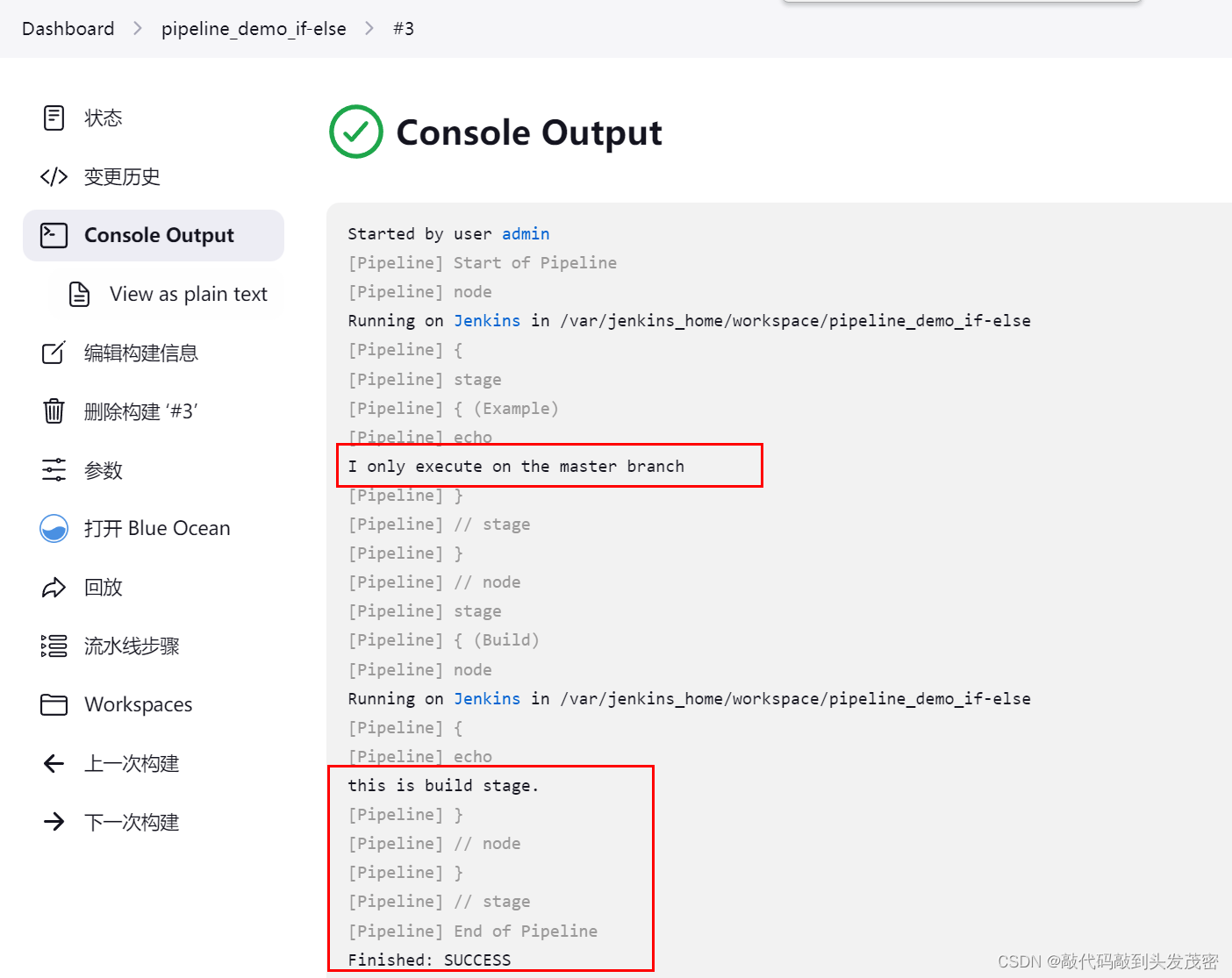
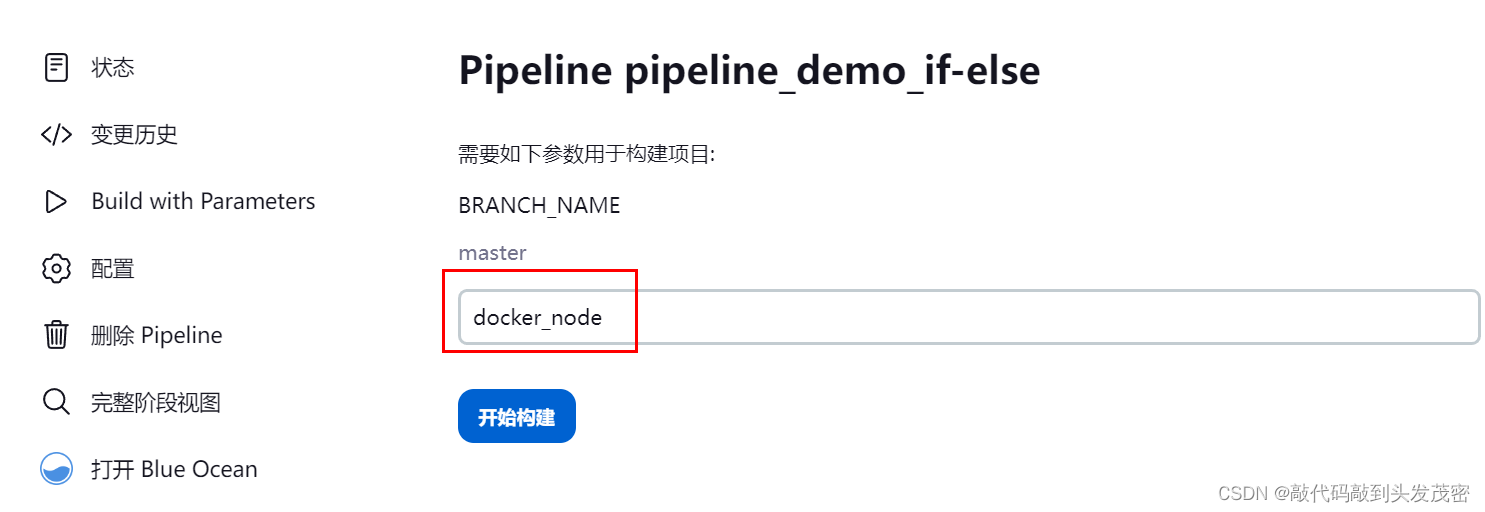
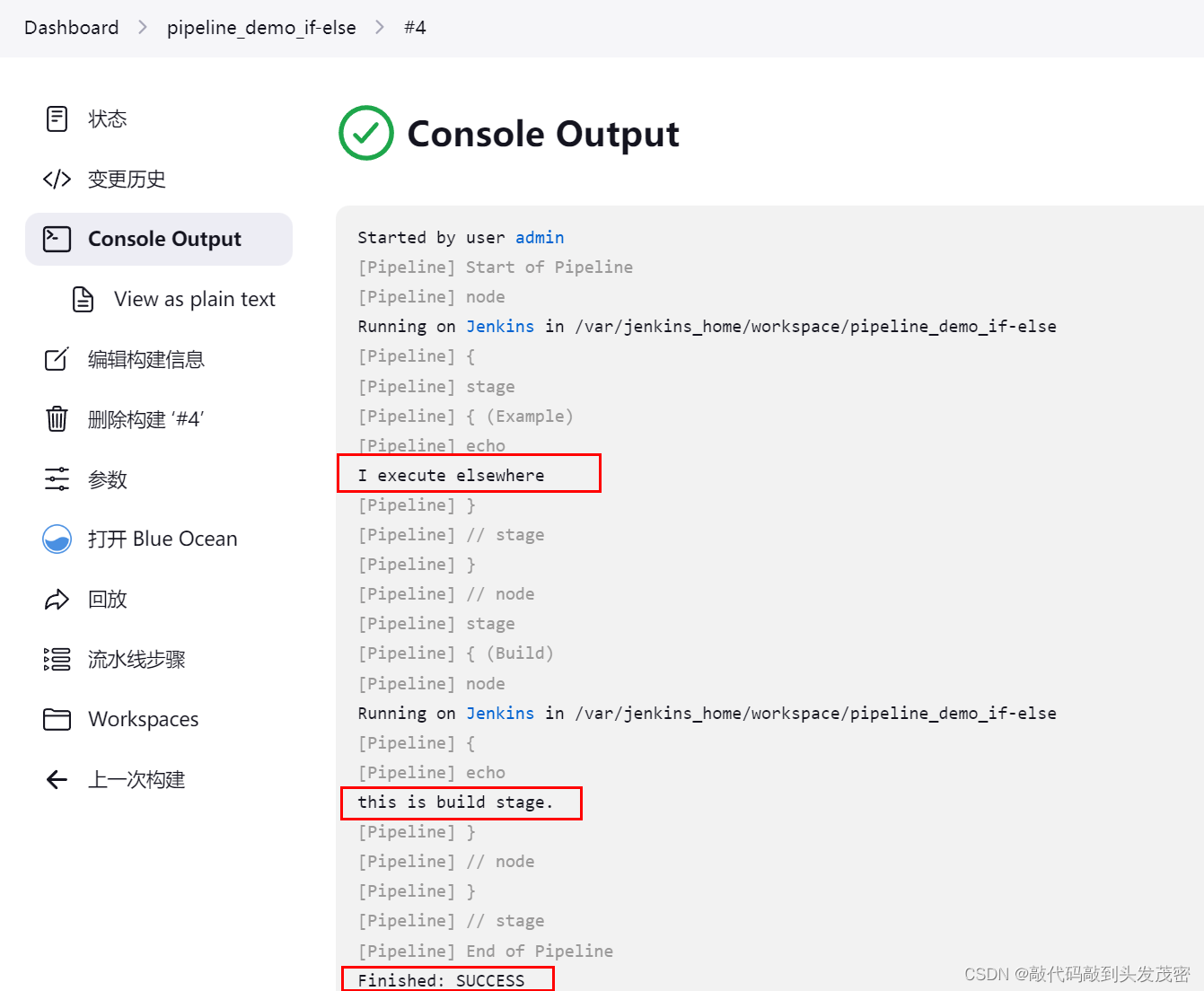
if (env.BRANCH_NAME == 'master') {
echo 'I only execute on the master branch'
} else {
echo 'I execute elsewhere'
}
}
}
stage('Build'){
node {
echo 'this is build stage.'
}
}
3、采用master构建
4、采用非master构建
九、JenkinsFile 语法参数 try-catch
1、Scripts pipeline: 流程控制之 – try/catch
场景:异常处理,在运行程序的时候,不希望代码的错误,导致程序的退出
使用try进行捕获,使用catch对异常的代码进行处理
2、演示出现异常
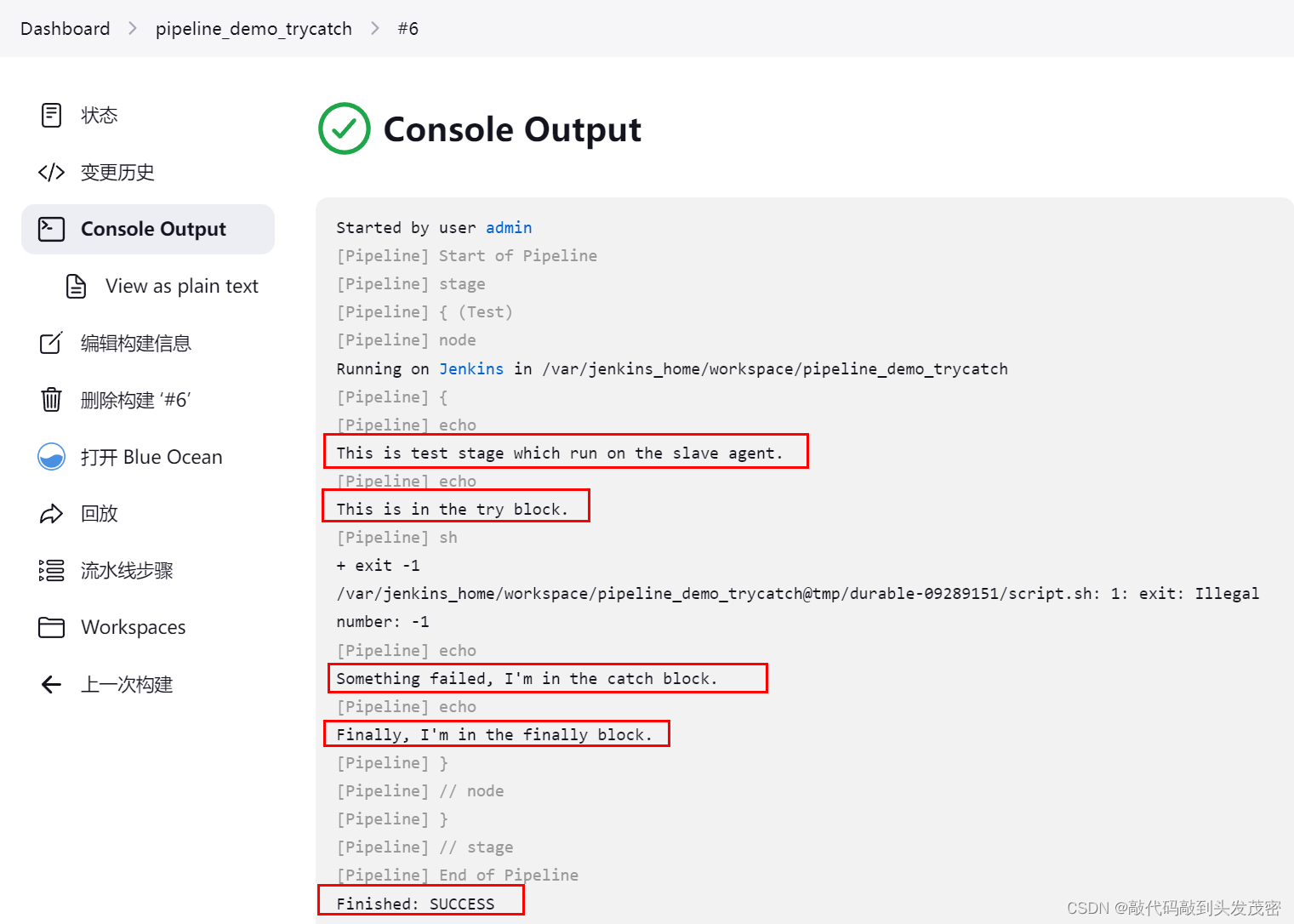
stage('Test') {
node{
echo "This is test stage which run on the slave agent."
try {
echo "This is in the try block."
sh 'exit 1'
}catch (exc) {
echo "Something failed, I'm in the catch block."
}finally {
echo "Finally, I'm in the finally block."
}
}
}
3、演示正常
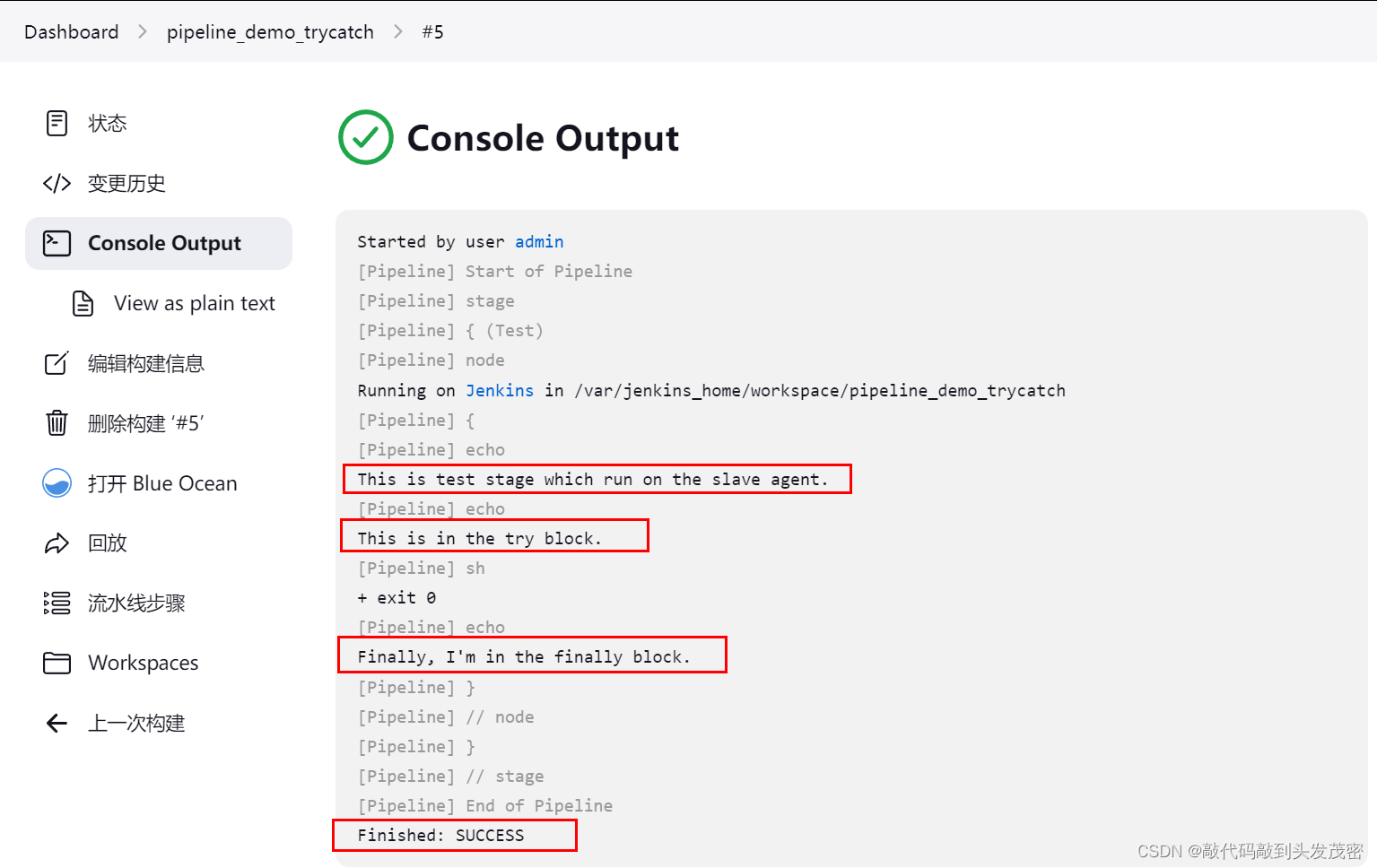
stage('Test') {
node{
echo "This is test stage which run on the slave agent."
try {
echo "This is in the try block."
sh 'exit 0'
}catch (exc) {
echo "Something failed, I'm in the catch block."
}finally {
echo "Finally, I'm in the finally block."
}
}
}
十、JenkinsFile 语法参数 environment
1、Declarative Pipeline - environment
environment: 定义Pipeline或stage运行时的环境变量
不是必须出现的指令
无参数
2、Declarative Pipeline - environment代码举例
environment {
hlw = 'hello world'
}
3、environment 运行演示
pipeline {
agent {
node{
label 'docker_node'
customWorkspace "myWorkspace"
}
}
environment {
hlw = 'hello world'
}
stages {
stage('Print environment_1'){
steps {
echo hlw
sleep 1
}
}
stage('Print environment_2'){
steps {
sh 'echo ${hlw}'
sleep 1
}
}
}
post {
success {
echo 'goodbye pipeline success!'
sleep 5
}
failure {
echo 'ops!!! pipeline failed....'
sleep 5
}
always {
echo 'always say goodbye'
}
}
}
运行结果

十一、JenkinsFile 语法参数 triggers
1、Declarative Pipeline - triggers
triggers:定义了Pipeline自动化触发的方式
不是必须出现的指令
参数:
cron:接受一个cron风格的字符串来定义Pipeline触发的常规间隔
pollSCM:接受一个cron风格的字符串来定义 Jenkins 检查SCM源更改的常规间隔;如果存在新的更改,则Pipeline将被重新触发。
2、Declarative Pipeline - triggers 代码举例
triggers {
cron('H/2 * * * *')
}
3、triggers 运行演示
pipeline {
agent{
node{
label 'docker_node'
customWorkspace "myWorkspace"
}
}
triggers {
cron('H/2 * * * *')
}
stages{
stage('Test Parameters'){
steps{
echo "Hello"
}
}
}
}
十二、Pipeline 总结
Pipeline 是 Jenkins 2.0之后推出的高阶工具
有了Pipeline之后,Jenkins任务可以实现从简单持续集成到全面CI/CD流水线升级的转变
可以选择在Jenkins 任务中填写Pipeline script
也可以选择利用源码库对Pipeline script进行管理
两种Jenkinsfile语法:Declarative Pipeline 与 Script Pipeline
语句上有相似之处,可扩展性不同,灵活性也不同
