文章目录
方法
● maxBy:获取流中最大元素;minBy:获取流中最小元素
● joining:合并,将流中的元素,以字符串的形式拼接起来
● summingInt:把流中的元素映射成int类型的元素,求和
● averagingInt:把流中的元素映射成int类型的元素,求平均值
● summarizingInt:把流中的元素映射成int类型的元素,获取描述信息
实践说明
一、前提条件
Person类
package com.example;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @BelongsProject: StreamOperate
* @BelongsPackage: com.example
* @CreateTime: 2023-05-01 11:18
* @Description: Person实体类
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class Person implements Comparable<Person>{
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Person setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public Person setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
return this;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public Person setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
return this;
}
private String name;
private int age;
private int score;
public Person(String name, int age, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public Person() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
//地址相同,为true
if (this == o) return true;
//为null,并且类型不一样,为false
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
//向下转型,再去比较属性值
Person person = (Person) o;
//如果属性值相同,最后的结果为true
return age == person.age && score == person.score && Objects.equals(name, person.name);
//return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age, score);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return this.getScore()-o.getScore();
}
}
Data类
package com.example;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @BelongsProject: StreamOperate
* @BelongsPackage: com.example
* @CreateTime: 2023-05-01 11:08
* @Description: Data类
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class Data {
public static ArrayList<Person> getData() {
ArrayList<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();
personList.add(new Person("张三", 18, 90));
personList.add(new Person("李四", 19, 100));
personList.add(new Person("王五", 17, 60));
personList.add(new Person("赵六", 18, 89));
personList.add(new Person("孙七", 20, 96));
personList.add(new Person("郑十", 20, 46));
personList.add(new Person("周八", 20, 96));
personList.add(new Person("周八", 20, 96));
personList.add(new Person("吴九", 20, 45));
personList.add(new Person("邓十一", 20, 35));
personList.add(new Person("刘十二", 20, 99));
personList.add(new Person("小十三", 20, 56));
personList.add(new Person("小十三", 20, 56));
return personList;
}
}
二、操作
maxBy:获取流中最大元素;minBy:获取流中最小元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> stream = Data.getData().stream();
//maxBy:获取流中最大元素;minBy:获取流中最小元素
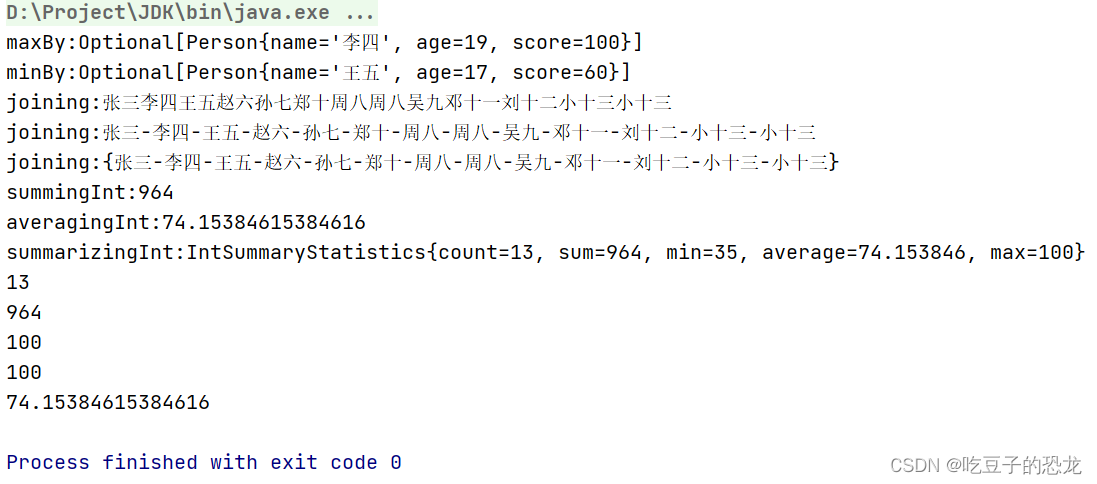
System.out.println(Data.getData().stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy((ele1, ele2) -> ele1.getScore() - ele2.getScore())));
System.out.println(Data.getData().stream().collect(Collectors.minBy((ele1, ele2) -> ele1.getAge() - ele2.getAge())));
}
joining:合并,将流中的元素,以字符串的形式拼接起来
去public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> stream = Data.getData().stream();
//joining:合并,将流中的元素,以字符串的形式拼接起来
//将集合中person对象的姓名拼接成一个字符串
System.out.println(Data.getData().stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.joining()));
System.out.println(Data.getData().stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("-")));
System.out.println(Data.getData().stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("-", "{", "}")));
}
summingInt:把流中的元素映射成int类型的元素,求和
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> stream = Data.getData().stream();
//summingInt:把流中的元素映射成int类型的元素,求和
System.out.println(Data.getData().stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(Person::getScore)));
}
averagingInt:把流中的元素映射成int类型的元素,求平均值
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> stream = Data.getData().stream();
//averagingInt:把流中的元素映射成int类型的元素,求平均值
System.out.println(Data.getData().stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Person::getScore)));
}
summarizingInt:把流中的元素映射成int类型的元素,获取描述信息
需求:将流中分数大于等于80的Person对象替换成他们的姓名
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> stream = Data.getData().stream();
//summarizingInt:把流中的元素映射成int类型的元素,获取描述信息
IntSummaryStatistics collect = Data.getData().stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Person::getScore));
System.out.println(collect);
System.out.println(collect.getCount());
System.out.println(collect.getSum());
System.out.println(collect.getMax());
System.out.println(collect.getMax());
System.out.println(collect.getAverage());
输出结果:
如果有想要交流的内容欢迎在评论区进行留言,如果这篇文档受到了您的喜欢那就留下你点赞+收藏+评论脚印支持一下博主~