前言
提示:这里可以添加本文要记录的大概内容:
例如:随着人工智能的不断发展,机器学习这门技术也越来越重要,很多人都开启了学习机器学习,本文就介绍了机器学习的基础内容。
一、基本语法
1.hello world
代码如下(示例):
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 单行注释用双斜杠,多行注释用 /* 注释 */
cout <<"hello world" << endl:
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.变量与常量
定义变量:
int a = 15
float f1 = 3.14f
double f2 = 3e2 //300
定义字符与字符串:
char ch = 'a' //单引号,只能放一个字符
(int)ch // 对用ASCII码 97 'A':65
char str1[] = "hello world"; //c风格
#include<string>
string str2 = "hello world"; //c++风格
定义bool:只要是非0值,都代表真
bool flag = true; //占1字节
标识符*(由字母、数字、下划线组成)*要避开关键字:
define 宏
int a = 15 //变量
//define 宏常量, 后续无法修改
#define Day 7
int main() {
cout <<"一周有:"<<Day<<"天"<<endl;
const
int main() {
const int a = 15 //后续无法修改
cout <<"一周有:"<<Day<<"天"<<endl;
3.转义字符
换行符 \n 反斜杠 \ \ 水平制表符\t
\t根据8字节对齐来设置空格数
4.键盘输入cin
int a = 0;
cout<<"请输入整形变量:"<<endl;
cin>>a;
cout<<a<<endl; //查看是否赋值成功
5.数组
定义
# ------方式1-----
int arr[5] ;
arr[0] = 10;
arr[1] = 20;
# ------方式2-----
int arr2[5] = {
10,20,30}; //后续自动补0
int arr3[] = {
10,20,30,40,50,60};
查看大小
sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) //数组元素个数
cout<<"数组首地址:"<<arr<<endl; //结果为16进制数
cout<<"数组首元素地址:"<<(int)&arr[0]<<endl; //结果为10进制数
二维数组
# ------方式1-----
int arr[2][3];
arr[0][0] = 1;
arr[0][1] = 2;
# ------方式2-----
int arr2[2][3] =
{
{
1,2,3},
{
4,5,6}
};
# ------方式3-----
int arr3[2][3] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6};
int arr3[][3] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6};
cout<<"二维数组行数:"<< sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;
cout<<"二维数组列数:"<< sizeof(arr[0]) / sizeof(arr[0][0]) << endl;
cout<<"第二行首地址:"<<(int)arr[1]) << endl;
cout<<"第一个元素首地址:"<<(int)&arr[0][0]) << endl;
6.函数sizeof
sizeof(short) //2 占用内存大小
sizeof(int) //4
sizeof(long) //4(windows) 8(linux64)
sizeof(long long) //8
7.运算符
算术运算符
赋值运算符
比较运算符
逻辑运算符
8.if、switch、while语句
int score = 0;
cout<<"请输入分数:"<<endl;
cin>>score;
if (score>600)
{
cout<<"恭喜是一本:"<<endl;
}
else if(score>700)
{
cout<<"清华
"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"是二本:"<<endl;
}
switch(score)
{
case 10:
cout<<"分数很高"<<endl;
break;
case 9:
cout<<"分数很高"<<endl;
break;
case 6:
cout<<"分数很高"<<endl;
break;
default:
cout<<"低分"<<endl;
break;
int main(){
int num = 0;
while(num < 10)
{
cout<<"num = "<<num<<endl;
num++;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
int num = 0;
do
{
cout<<num<<endl;
num++;
} while(num < 10)
system("pause");
return 0;
9.指针
1.空指针:指针变量指向内存中编号为0空间
0-255之间内存编号是系统占用,不可访问
int * p = NULL;
cout << *p << endl; //其内存不可访问: *p = 100 报错
野指针:指针变量指向非法内存空间
int * p = (int *)0x1100;
cout << *p << endl; //报错:没有访问权限
- const:常量指针与指针常量
# 1.const修饰指针,指向可改,指向的值不可改
const int * p1 = &a;
p1 = &b //正确
*p1 = 100 //报错
# 2.const修饰常量,指向不可改,指向的值可改
int * const p2 = &a;
p2 = &b //报错
*p2 = 100 //正确
# 3.const又修饰指针,又修饰常量
const int * const p3 = &a;
p3 = &b //报错
*p3 = 100 //报错
3.指针访问数组
int arr[] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}
int * p2 = arr;
for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << *p2 << endl;
p2++; //向后跳4个字节
}
4.指针函数
void swap1(int a ,int b){
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void swap2(int *p1 ,int *p2){
int temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;
}
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
swap1(a, b); //值传递不改变实参
swap2(&a, &b); //地址传递,改变实参
10.结构体
1.自定义数据类型:学生的姓名、年龄、分数等
# ------1.创建学生数据类型-------
struct Student
{
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
# ------2.创建具体学生-------
// 2.1 struct Student s1
#include <string>
struct Student s1; # struct 关键字可以省略
s1.name = "张三";
s1.age = 15;
s1.score = 100;
cout << "姓名:" << s1.name << "年龄:" << s1.age << endl;
// 2.2 struct Student s2 = {...}
struct Student s2 = {
"李四" , 19 , 80};
// 2.3 创建结构体时顺便创建结构体变量
struct Student
{
string name;
int age;
}s3;
# ------3.创建结构体数组-------
# 先定义结构体,步骤如1.然后执行以下:
struct Student stuArray[3] =
{
{
"李四" , 19 ,80},
{
"王五" , 16, 80},
{
"赵四" , 20 ,80}
};
# 重新或更改内容:
stuArray[2].name = "赵六";
2.结构体指针
# 1.先定义结构体
# 2.创建结构体变量:
student s = {
"李四" , 19 ,80};
# 3.指针 指向结构体变量:
student *p = &s;
# 4.通过指针访问结构体:
cout << "姓名:" << p->name <<"年龄:" << p->age << endl;
3.结构体嵌套结构体
# 1.定义学生结构体
struct Student
{
string name;
int age;
};
# 2.定义老师结构体:
struct teacher
{
int id:
string name;
int age;
struct student stu; //辅导的学生
};
# 3.创建老师:
teacher t;
t.id = 5685;
t.name = "老王";
t.stu.name = "小王";
t.stu.score = 60;
cout << t.stu.score;
4.结构体中 const 使用
# 1.定义结构体
# 2.const使用场景
void PrintStudent(const student *stu) //加const防止函数体中,修改结构体内容
{
cout << "姓名" << stu-> name << endl;
}
int main() {
student stu = {
"小明", 18, 100};
PrintStudent(&stu);
system("pause");
二、小项目
1.猜数字
生成随机数;猜数字;判断大小
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <ctime>
int main() {
// 利用系统时间,生成随机数,防止每次都一样
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
//1.生成系统随机数(1-100之间)
int num = rand() % 100 + 1;
//2.玩家猜测
int val = 0;
while(1)
{
cin>>val;
if (val>num)
{
cout<<"猜测过大"<<endl;
}
else if (val<num)
{
cout<<"猜测过小"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"猜对"<<endl;
break;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.找水仙花数
在100-999之中,找到个位、十位、百位数的三次幂之和是这个数
int main() {
int num = 100; //打印所有三位数字
do
{
int a = 0; //个位
int b = 0; //十位
int c = 0; //百位
a = num % 10;
b = num / 10 % 10;
c = num / 100;
if (a*a*a + b*b*b + c*c*c = num)
{
cout<<num<<endl;
}
num++
} while (num < 1000)
3.乘法口诀表
int main() {
for (int i = 1;i <= 9; i++) //打印行数
{
for(int j=1; j <=i;j++)
{
cout<<j<<"*"<<i<<"="<<j*i<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
4.冒泡排序
int main() {
int arr[9] = {
4,2,5,8,9,3,1,7,6};
for (int i = 0; i < 9-1; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j < 9-1-i; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j+ 1] ) //如果前一个数大于后面,交换
{
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
利用指针做冒泡排序:
void bubbleSort(int *arr, int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j < len- 1 -i; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j+ 1] ) //如果前一个数大于后面,交换
{
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
void printArray(int *arr, int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout <<arr[i] << endl;
}
}
int main() {
int arr[10] = {
4,2,5,8,9,3,1,7,6,10};
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bubbleSort(arr, len);
printArray(arr, len);
5.结构体例题
- 设计学生和老师的结构体:在3名老师的结构体中,有姓名和一个存放5名学生的数组作为成员;
学生的成员有姓名、考试分数,创建数组存放3名老师,通过函数给每个老师及所带的学生赋值
最终打印出老师数据以及老师所带的学生数据。
struct Student
{
string name;
int score;
};
struct Teacher
{
string name;
Student sArray[5];
};
void allocateSpace(Teacher tArray[] , int len)
{
string tName = "教师";
string sName = "学生";
string nameSeed = "ABCDE";
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
tArray[i].name = tName + nameSeed[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
tArray[i].sArray[j].name = sName + nameSeed[j];
tArray[i].sArray[j].score = rand() % 61 + 40;
}
}
}
void printTeachers(Teacher tArray[], int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << tArray[i].name << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
cout << "\t姓名:" << tArray[i].sArray[j].name << " 分数:" << tArray[i].sArray[j].score << endl;
}
}
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); //随机数种子 头文件 #include <ctime>
Teacher tArray[3]; //老师数组
int len = sizeof(tArray) / sizeof(Teacher);
allocateSpace(tArray, len); //创建数据
printTeachers(tArray, len); //打印数据
system("pause");
return 0;
}
- 创建有5个英雄的结构体,包括姓名,年龄,性别;
通过冒泡排序的算法,将数组中的英雄按照年龄进行升序排序,最终打印排序后的结果。
//英雄结构体
struct hero
{
string name;
int age;
string sex;
};
//冒泡排序
void bubbleSort(hero arr[] , int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (arr[j].age > arr[j + 1].age)
{
hero temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
//打印数组
void printHeros(hero arr[], int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << "姓名: " << arr[i].name << " 性别: " << arr[i].sex << " 年龄: " << arr[i].age << endl;
}
}
int main() {
struct hero arr[5] =
{
{
"刘备",23,"男"},
{
"关羽",22,"男"},
{
"张飞",20,"男"},
{
"赵云",21,"男"},
{
"貂蝉",19,"女"},
};
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(hero); //获取数组元素个数
bubbleSort(arr, len); //排序
printHeros(arr, len); //打印
system("pause");
return 0;
}
6.通讯录管理系统
通讯录是一个可以记录亲人、好友信息的工具
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
# --------------------1.菜单界面------------------
void showMenu()
{
cout << "***************************" << endl;
cout << "***** 1、添加联系人 *****" << endl;
cout << "***** 2、显示联系人 *****" << endl;
cout << "***** 3、删除联系人 *****" << endl;
cout << "***** 4、查找联系人 *****" << endl;
cout << "***** 5、修改联系人 *****" << endl;
cout << "***** 6、清空联系人 *****" << endl;
cout << "***** 0、退出通讯录 *****" << endl;
cout << "***************************" << endl;
}
int main() {
showMenu();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
# ---------------------------2.退出功能--------------------------
int main() {
int select = 0;
while (true)
{
showMenu();
cin >> select;
switch (select)
{
case 1: //添加联系人
break;
case 2: //显示联系人
break;
case 3: //删除联系人
break;
case 4: //查找联系人
break;
case 5: //修改联系人
break;
case 6: //清空联系人
break;
case 0: //退出通讯录
cout << "欢迎下次使用" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
# ---------------------------3.添加联系人---------------------------
struct Person
{
string m_Name; //姓名
int m_Sex; //性别:1男 2女
int m_Age; //年龄
string m_Phone; //电话
string m_Addr; //住址
};
#define MAX 1000 //最大人数
//通讯录结构体
struct Addressbooks
{
struct Person personArray[MAX]; //通讯录中保存的联系人数组
int m_Size; //通讯录中人员个数
};
int main() {
//创建通讯录
Addressbooks abs;
//初始化通讯录中人数
abs.m_Size = 0;
void addPerson(Addressbooks *abs)
{
//判断电话本是否满了
if (abs->m_Size == MAX)
{
cout << "通讯录已满,无法添加" << endl;
return;
}
else
{
//姓名
string name;
cout << "请输入姓名:" << endl;
cin >> name;
abs->personArray[abs->m_Size].m_Name = name;
cout << "请输入性别:" << endl;
cout << "1 -- 男" << endl;
cout << "2 -- 女" << endl;
//性别
int sex = 0;
while (true)
{
cin >> sex;
if (sex == 1 || sex == 2)
{
abs->personArray[abs->m_Size].m_Sex = sex;
break;
}
cout << "输入有误,请重新输入";
}
//年龄
cout << "请输入年龄:" << endl;
int age = 0;
cin >> age;
abs->personArray[abs->m_Size].m_Age = age;
//联系电话
cout << "请输入联系电话:" << endl;
string phone = "";
cin >> phone;
abs->personArray[abs->m_Size].m_Phone = phone;
//家庭住址
cout << "请输入家庭住址:" << endl;
string address;
cin >> address;
abs->personArray[abs->m_Size].m_Addr = address;
//更新通讯录人数
abs->m_Size++;
cout << "添加成功" << endl;
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
}
# ---------------------4.显示所有联系人--------------------
void showPerson(Addressbooks * abs)
{
if (abs->m_Size == 0)
{
cout << "当前记录为空" << endl;
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < abs->m_Size; i++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << abs->personArray[i].m_Name << "\t";
cout << "性别:" << (abs->personArray[i].m_Sex == 1 ? "男" : "女") << "\t";
cout << "年龄:" << abs->personArray[i].m_Age << "\t";
cout << "电话:" << abs->personArray[i].m_Phone << "\t";
cout << "住址:" << abs->personArray[i].m_Addr << endl;
}
}
# ----------------------5.检测联系人是否存--------------------
int isExist(Addressbooks * abs, string name)
{
for (int i = 0; i < abs->m_Size; i++)
{
if (abs->personArray[i].m_Name == name)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
# ----------------------6.删除指定联系人---------------------
void deletePerson(Addressbooks * abs)
{
cout << "请输入您要删除的联系人" << endl;
string name;
cin >> name;
int ret = isExist(abs, name);
if (ret != -1)
{
for (int i = ret; i < abs->m_Size; i++)
{
abs->personArray[i] = abs->personArray[i + 1];
}
abs->m_Size--;
cout << "删除成功" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "查无此人" << endl;
}
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
## ---------------------7.查找联系人--------------------
void findPerson(Addressbooks * abs)
{
cout << "请输入您要查找的联系人" << endl;
string name;
cin >> name;
int ret = isExist(abs, name);
if (ret != -1)
{
cout << "姓名:" << abs->personArray[ret].m_Name << "\t";
cout << "性别:" << abs->personArray[ret].m_Sex << "\t";
cout << "年龄:" << abs->personArray[ret].m_Age << "\t";
cout << "电话:" << abs->personArray[ret].m_Phone << "\t";
cout << "住址:" << abs->personArray[ret].m_Addr << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "查无此人" << endl;
}
## ---------------------8.修改联系人--------------------
void modifyPerson(Addressbooks * abs)
{
cout << "请输入您要修改的联系人" << endl;
string name;
cin >> name;
int ret = isExist(abs, name);
if (ret != -1)
{
//姓名
string name;
cout << "请输入姓名:" << endl;
cin >> name;
abs->personArray[ret].m_Name = name;
cout << "请输入性别:" << endl;
cout << "1 -- 男" << endl;
cout << "2 -- 女" << endl;
//性别
int sex = 0;
while (true)
{
cin >> sex;
if (sex == 1 || sex == 2)
{
abs->personArray[ret].m_Sex = sex;
break;
}
cout << "输入有误,请重新输入";
}
//年龄
cout << "请输入年龄:" << endl;
int age = 0;
cin >> age;
abs->personArray[ret].m_Age = age;
//联系电话
cout << "请输入联系电话:" << endl;
string phone = "";
cin >> phone;
abs->personArray[ret].m_Phone = phone;
//家庭住址
cout << "请输入家庭住址:" << endl;
string address;
cin >> address;
abs->personArray[ret].m_Addr = address;
cout << "修改成功" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "查无此人" << endl;
}
## ---------------------9.清空联系人--------------------
void cleanPerson(Addressbooks * abs)
{
abs->m_Size = 0;
cout << "通讯录已清空" << endl;
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
7.设计立方体类
求出立方体的面积和体积
分别用全局函数和成员函数判断两个立方体是否相等
//1.创建立方体类
//2.设计属性
//3.设计行为 获取面积、体积
//4.分别用 全局函数 与成员函数 ,判断两立方体是否相等
class Cube
{
public:
//设置长
void setL(int l)
{
m_L = l;
}
//获取长
int getL()
{
return m_L;
}
//设置宽、高
//获取面积
ing calculateS()
{
return 2*m_L*m_W + 2*m_W*m_H + 2*m_L*m_H ;
}
//获取体积
ing calculateV()
{
return m_L*m_W *m_H;
}
//类内:利用成员函数判断
bool isSameByClass(Cube &c)
{
if(m_L==c.getL() && m_H==c.getH())
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
private:
int m_L; //长
int m_W; //宽
int m_H; //高
# 利用全局函数判断:是否相等:
bool isSame(Cube &c1 , Cube &c2)
{
if(c1.getL()==c2.getL() && c1.getH()==c2.getH())
{
return true;
}
return false;
int main() {
Cube c1; Cube c2;
c1.setL(10)
c1.setH(10)
cout << "c1的面积为:" << c1.calculateS() << endl;
# 1.利用全局函数判断
bool ret = isSame(c1, c2);
# 2.利用成员函数判断
bool ret = isSameByClass(c2);
if (ret)
{
cout << "c1和c2是相等的" << endl;
}
else
{
cout<< <<endl;
}
system("pause");
system("cls");
8.点和圆的关系(类)
设计一个圆形类(Circle),和一个点类(Point),计算点和圆的关系。
# -------------------------1.点类
class Point
{
public:
//设置x
void setx(int x)
{
m_X = x;
}
//获取x
int getx()
{
return m_X;
}
//设置y
private:
int m_x;
int m_y;
}
# -----------------------2.圆类
class Circle
{
public:
//设置半径
void setR(int r)
{
m_R = r;
}
//获取半径
int getR()
{
return m_R ; }
//设置圆心
void setCenter(Point center)
{
m_Center = center;
}
//获取圆心
Point getCenter()
{
return m_Center ;}
private:
int m_R; //半径
Point m_Center; //圆心
}
# -----------------------3.判断点和圆的关系
void isIncircle(Circle &c, Point &p)
{
//计算两点之间距离 的平方
int distance =
(c.getCenter().getx() - p.getx()) * (c.getCenter().getx() - p.getx()) +
(c.getCenter().gety() - p.gety()) * (c.getCenter().gety() - p.gety());
//计算半径 的平方
int rdistance = c.getR() * c.getR();
//判断关系
if(distance == rdistance)
{
cout << "点在圆上" <<endl;
}
elseif(distance > rdistance)
{
}
else(distance < rdistance)
{
}
}
# -----------------------4.main函数
int main() {
//创建圆
Circlr c;
c.setR(10);
Point center;
center.setx(10);
center.sety(0);
c.setCenter(center);
//创建圆
Point p;
p.setx(10);
p.sety(10);
//判断
isIncircle(c , p);
8.1 分文件编写
分为5个文件:
point的头文件与源文件、circle的头文件与源文件、主文件
# -------------1.point.h(声明)-----------
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
//设置x
void setx(int x);
//获取x
int getx();
//设置y
void sety(int y);
private:
int m_x;
int m_y;
}
# -------------2.point.cpp(定义)-----------
#include "point.h"
// 只留下函数实现
//设置x
void Point::setx(int x)
{
m_X = x;
}
//获取x
int Point::getx()
{
return m_X;
}
//设置y
}
# -------------3.circle.h(声明)-----------
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "point.h"
class Circle
{
public:
//设置半径
void setR(int r);
//获取半径
int getR() ;
//设置圆心
void setCenter(Point center);
//获取圆心
Point getCenter();
private:
int m_R; //半径
Point m_Center; //圆心
}
# -------------4.circle.cpp(定义)-----------
include "circle.h"
//设置半径
void Circle::setR(int r)
{
m_R = r;
}
//获取半径
int Circle::getR()
{
return m_R ; }
//设置圆心
void Circle::setCenter(Point center)
{
m_Center = center;
}
//获取圆心
Point Circle::getCenter()
{
return m_Center ;}
# -------------5.main.cpp(同上)-----------
三、进阶
1.分文件编写
1.创建 .h 的头文件
2.创建 .cpp 的源文件
3.在头文件中写函数声明
4.在源文件中写函数定义
*另一个文件中调用
swap.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//函数声明
void swap(int a, int b);
swap.cpp
#include "swap.h"
//函数定义
void swap(int a, int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
}
分文件编写.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "swap.h"
int main(){
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
swap(a,b);
system('pause');
return 0;}
2.内存四区
1.代码区:exe中的二进制文件
2.全局区:全局变量、静态变量(static)、常量、字符串常量、const修饰全局变量
3.栈区:局部变量、const修饰局部变量等,由编译器维护
4.堆区:程序员自己开辟
//全局变量
int g_a = 10;
int g_b = 10;
//全局常量
const int c_g_a = 10;
const int c_g_b = 10;
int main() {
//局部变量
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
//打印地址
cout << "局部变量a地址为: " << (int)&a << endl; # 9697232
cout << "全局变量g_a地址为: " << (int)&g_a << endl; # 3461120
//静态变量
static int s_a = 10;
cout << "静态变量s_a地址为: " << (int)&s_a << endl; # 3461128
cout << "字符串常量地址为: " << (int)&"hello world" << endl; # 3451880
cout << "全局常量c_g_a地址为: " << (int)&c_g_a << endl; # 3452096
const int c_l_a = 10;
cout << "局部常量c_l_a地址为: " << (int)&c_l_a << endl; # 9697208
system("pause");
return 0;
}
- 栈区:局部变量不能取地址
int * func(int b) //形参数据也会放在栈
{
int a = 10;
return &a; //返回局部变量地址
}
int main() {
int *p = func(); # 返回地址不稳定
cout << *p << endl; # 10:第一次正确:编译器做了保留
cout << *p << endl; # 693132 第二次不再保留
- 堆区:数据由程序员管理开辟和释放; 利用new关键字进行开辟内存
int* func()
{
int* a = new int(10); # 返回的是堆区上地址 指针(局部变量)在栈上;数据在堆区
return a;
}
int* func2()
{
int* arr = new int[10]; # 返回的是堆区上地址 指针(局部变量)在栈上;数据在堆区
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
arr[i] = i + 100 ; }
# 释放堆区数组
delete[] arr;
}
int main() {
int *p = func();
cout << *p << endl; # 打印正确
cout << *p << endl; # 打印正确
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.引用
本质:在c++内部实现是一个指针常量。指向同一个地址:
int a = 10;
int &b = a; //自动转换为 int* const b = &a
- 引用必须初始化
- 引用舒适化后,不可改变
//全局变量
int a = 10;
int c = 20;
int &b ; # 报错
int &b = a;
b = c #赋值操作,不是更改引用 c++内部是 *b = 20;
- 引用传递,相当于地址传递
//2. 地址传递
void mySwap02(int* a, int* b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
//3. 引用传递
void mySwap03(int& a, int& b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
mySwap02(&a, &b);
cout << "a:" << a << " b:" << b << endl;
mySwap03(a, b);
cout << "a:" << a << " b:" << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
- 引用做函数返回值
注意:不要返回局部变量引用
用法:函数调用作为左值
//返回局部变量引用
int& test01() {
int a = 10; //局部变量:栈区
return a;
}
//返回静态变量引用
int& test02() {
static int a = 20; // 静态变量:全局区,在程序结束后系统释放
return a;
}
int main() {
//不能返回局部变量的引用
int& ref = test01();
cout << "ref = " << ref << endl; //第一次正确:编译器做了保留
cout << "ref = " << ref << endl; //第二次错误:内存释放
//如果函数做左值,那么必须返回引用
int& ref2 = test02();
cout << "ref2 = " << ref2 << endl;
cout << "ref2 = " << ref2 << endl;
test02() = 1000; # 函数返回值是引用时:函数调用可作为左值
cout << "ref2 = " << ref2 << endl; //1000
cout << "ref2 = " << ref2 << endl; //1000
system("pause");
return 0;
}
- 常量引用
int& ref = 10; 报错:常量引用,不是合法的内存空间。
//加入const就可以了,编译器优化代码,int temp = 10; const int& ref = temp;
const int& ref = 10;
- 引用做函数参数
void showValue(const int& v) {
//v += 10; # 不可改变
cout << v << endl;
}
int main() {
int a = 10;
showValue(a);
system("pause");
4.函数高级
1.默认参数
- 如果某个位置参数有默认值,那么从这个位置往后,从左向右,必须都要有默认值
- 如果函数声明有默认值,函数实现的时候就不能有默认参数
int func(int a, int b = 10, int c = 10) {
return a + b + c;
}
int func2(int a = 10, int b = 10);
int func2(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
int main() {
cout << "ret = " << func(20, 20) << endl;
cout << "ret = " << func(100) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2 函数占位参数
函数的形参列表里可以有占位参数,用来做占位,调用函数时必须填补该位置(暂时用不上)
void func(int a, int) {
cout << "this is func" << endl;
}
int main() {
func(10,10); //占位参数必须填补
3 函数重载
函数重载满足条件: 调用时,会选择唯一满足的函数,来进入执行
- 同一个作用域下(全局域等)
- 函数名称相同
- 函数参数类型不同 或者 个数不同 或者 顺序不同
//函数重载需要函数都在同一个作用域下
void func()
{
cout << "func 的调用!" << endl;
}
void func(int a)
{
cout << "func (int a) 的调用!" << endl;
}
void func(double a)
{
cout << "func (double a)的调用!" << endl;
}
void func(int a ,double b)
{
cout << "func (int a ,double b) 的调用!" << endl;
}
void func(double a ,int b)
{
cout << "func (double a ,int b)的调用!" << endl;
}
int main() {
func();
func(10);
func(3.14);
func(10,3.14);
func(3.14 , 10);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
函数重载注意事项
- 引用作为重载条件
- 函数重载碰到函数默认参数
//1、引用作为重载条件
void func(int &a)
{
cout << "需要输入一个变量(int &a) 调用 " << endl;
}
void func(const int &a)
{
cout << "需要输入常量 (const int &a) 调用 " << endl;
}
//2、函数重载碰到函数默认参数
void func2(int a, int b = 10)
{
cout << "func2(int a, int b = 10) 调用" << endl;
}
void func2(int a)
{
cout << "func2(int a) 调用" << endl;
}
int main() {
int a = 10;
func(a); //调用无const
func(10);//调用有const
func2(10); //碰到默认参数,产生歧义,报错
func2(10,20); //正常执行
system("pause");
return 0;
}
四、类和对象
c++面向对象的三大特性: 封装、继承、多态
1.封装
1.封装的意义:
- 将属性和行为作为一个整体,表现生活中的事物
- 将属性和行为加以权限控制
示例1:封装一个圆类,求圆的周长
const double PI = 3.14;
class Circle
{
public: //访问权限 公共的权限
//属性
int m_r;//半径
//行为
//获取到圆的周长
double calculateZC()
{
//2 * pi * r
//获取圆的周长
return 2 * PI * m_r;
}
};
int main() {
## 通过类,创建对象: c1就是一个具体的圆
Circle c1;
c1.m_r = 10; //给圆对象的半径 进行赋值操作
cout << "圆的周长为: " << c1.calculateZC() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
示例2:设计一个学生类,属性有姓名和学号(可赋值,可显示)
class Student {
public:
void setName(string name) {
m_name = name;
}
void setID(int id) {
m_id = id;
}
void showStudent() {
cout << "name:" << m_name << " ID:" << m_id << endl;
}
public:
string m_name;
int m_id;
};
int main() {
Student stu;
stu.setName("德玛西亚");
stu.setID(250);
stu.showStudent();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.三种权限:
- 公共权限 public 类内可以访问 类外可以访问
- 保护权限 protected 类内可以访问 类外不可以访问
- 私有权限 private 类内可以访问 类外不可以访问
class Person
{
public:
string m_Name; //姓名 公共权限
protected:
string m_Car; //汽车 保护权限
private:
int m_Password; //银行卡密码 私有权限
public:
void func()
{
m_Name = "张三";
m_Car = "拖拉机";
m_Password = 123456;
}
};
int main() {
Person p;
p.m_Name = "李四";
//p.m_Car = "奔驰"; //保护权限类外访问不到
//p.m_Password = 123; //私有权限类外访问不到
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.struct 和 class 区别:
唯一的区别就在于 默认的访问权限不同
class C1
{
int m_A; //默认是私有权限
};
struct C2
{
int m_A; //默认是公共权限
};
int main() {
C1 c1;
c1.m_A = 10; //错误,访问权限是私有
C2 c2;
c2.m_A = 10; //正确,访问权限是公共
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4.成员属性设置为私有
- 优点1:将所有成员属性设置为私有,可以自己控制读写权限
- 优点2:对于写权限,我们可以检测数据的有效性
class Person {
public:
//姓名设置可读可写
void setName(string name) {
m_Name = name;
}
string getName()
{
return m_Name;
}
//获取年龄
int getAge() {
return m_Age;
}
//设置年龄
void setAge(int age) {
if (age < 0 || age > 150) {
cout << "你个老妖精!" << endl;
return;
}
m_Age = age;
}
//情人设置为只写
void setLover(string lover) {
m_Lover = lover;
}
private:
string m_Name; //可读可写 姓名
int m_Age; //只读 年龄
string m_Lover; //只写 情人
};
int main() {
Person p;
//姓名设置
p.setName("张三");
cout << "姓名: " << p.getName() << endl;
//年龄设置
p.setAge(50);
cout << "年龄: " << p.getAge() << endl;
//情人设置
p.setLover("苍井");
//cout << "情人: " << p.m_Lover << endl; //只写属性,不可以读取
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.构造、析构函数
对象的初始化和清理:这两个函数将会被编译器自动调用,完成对象初始化和清理工作。
对象的初始化和清理工作是编译器强制要我们做的事情,因此如果我们不提供构造和析构,编译器会提供。编译器提供的构造函数和析构函数是空实现。
- 构造函数:主要作用在于创建对象时为对象的成员属性赋值,构造函数由编译器自动调用,无须手动调用。
- 构造函数,没有返回值也不写void
- 函数名称与类名相同
- 构造函数可以有参数,因此可以发生重载
- 程序在调用对象时候会自动调用构造,无须手动调用,而且只会调用一次
- 析构函数:主要作用在于对象销毁前系统自动调用,执行一些清理工作。
- 析构函数,没有返回值也不写void
- 函数名称与类名相同,在名称前加上符号 ~
- 析构函数不可以有参数,因此不可以发生重载
- 程序在对象销毁前会自动调用析构,无须手动调用,而且只会调用一次
class Person
{
public:
//构造函数
Person()
{
cout << "Person的构造函数调用" << endl;
}
//析构函数
~Person()
{
cout << "Person的析构函数调用" << endl;
}
};
void test01()
{
Person p; //保存在栈上。退出test01(),会自动调用析构函数
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
构造函数的分类(2种)
- 按参数分为: 有参构造和无参(默认构造
- 按类型分为: 普通构造和拷贝构造
三种调用方式:括号法、 显示法、 隐式转换法
class Person {
public:
//无参(默认)构造函数
Person() {
cout << "无参构造函数!" << endl;
}
//有参构造函数
Person(int a) {
age = a;
cout << "有参构造函数!" << endl;
}
//拷贝构造函数
Person(const Person& p) {
age = p.age;
cout << "拷贝构造函数!" << endl;
}
//析构函数
~Person() {
cout << "析构函数!" << endl;
}
public:
int age;
};
//2、构造函数的调用
//调用无参构造函数
void test01() {
Person p; //调用无参构造函数
}
//调用有参的构造函数
void test02() {
# ----------------1. 括号法,常用---------------------
Person p1(10);
//注意1:调用无参构造函数不能加括号,如果加了编译器认为这是一个函数声明
//Person p2();
# -----------------2. 显式法----------------
Person p2 = Person(10);
Person p3 = Person(p2);
//Person(10)单独写就是匿名对象 当前行结束之后,马上析构
# -----------------3. 隐式转换法-----------------
Person p4 = 10; // Person p4 = Person(10);
Person p5 = p4; // Person p5 = Person(p4);
//注意2:不能利用 拷贝构造函数 初始化匿名对象 编译器认为是对象声明
//Person p5(p4);
}
int main() {
test01();
//test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
拷贝构造函数,调用时机
# -------1.使用一个已经创建完毕的对象来初始化一个新对象--------- void test01() { Person p1(20); Person p2(p1); # 调用了拷贝函数 } # ----------------2.值传递的方式给函数参数传值---------------- void doWork(Person p1) { p1.age = 1000 # 不影响实参 } void test02() { Person p; //无参构造函数 doWork(p); # 形参传给实参,相互不影响 } -------------------3. 以值方式返回局部对象------------------ Person doWork2() { Person p1; cout << (int *)&p1 << endl; return p1; # 此时会拷贝新的对象返回 } void test3() { Person p = dowork2() cout << (int *)&p1<< endl; }
构造函数调用规则:
默认情况下,c++编译器至少给一个类添加3个函数
-
如果用户定义有参构造函数,c++不在提供默认无参构造,但是会提供默认拷贝构造
-
如果用户定义拷贝构造函数,c++不会再提供其他构造函数
class Person {
public:
//无参(默认)构造函数
Person() {
}
Person(int a) {
}
Person(const Person& p) {
}
~Person() {
}
public:
int age;
};
void test01()
{
Person p1(18);
//如果不写拷贝构造,编译器会自动添加拷贝构造,并且做浅拷贝操作
Person p2(p1);
cout << "p2的年龄为: " << p2.age << endl;
}
void test02()
{
//如果用户提供有参构造,编译器不会提供默认构造,会提供拷贝构造
Person p1; //此时如果用户自己没有提供默认构造,会出错
Person p2(10); //用户提供的有参
Person p3(p2); //此时如果用户没有提供拷贝构造,编译器会提供
//如果用户提供拷贝构造,编译器不会提供其他构造函数
Person p4; //此时如果用户自己没有提供默认构造,会出错
Person p5(10); //此时如果用户自己没有提供有参,会出错
Person p6(p5); //用户自己提供拷贝构造
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.深拷贝 浅拷贝
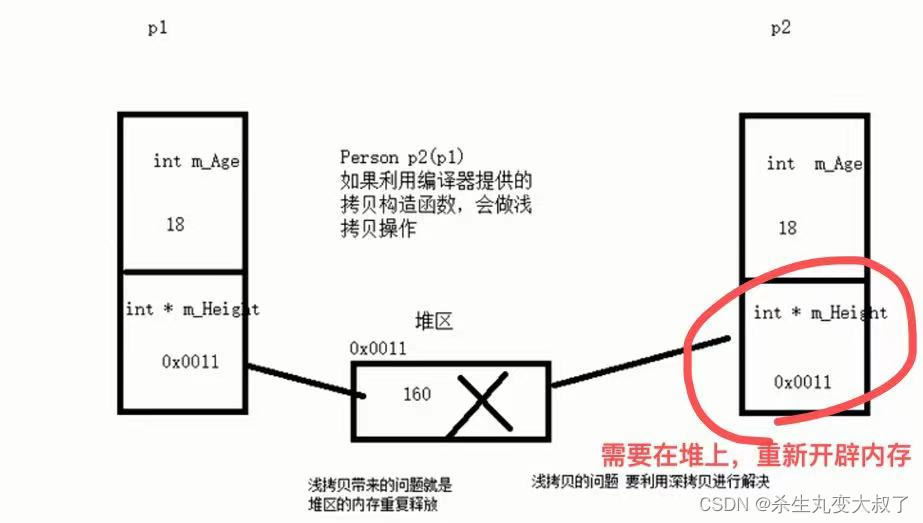
深拷贝(在堆区重新申请空间,进行拷贝操作)与浅拷贝
涉及到堆区开辟的属性,由于浅拷贝(拷贝函数),在栈区释放时会重复释放,导致出错。如图:
class Person {
public:
//无参(默认)构造函数
Person() {
cout << "无参构造函数!" << endl;
}
//有参构造函数
Person(int age ,int height) {
cout << "有参构造函数!" << endl;
m_age = age;
m_height = new int(height);
}
//拷贝构造函数
Person(const Person& p) {
cout << "拷贝构造函数!" << endl;
//如果不利用深拷贝在堆区创建新内存,会导致浅拷贝带来的重复释放堆区问题
m_age = p.m_age;
m_height = p.m_height # 报错:编译器默认实现代码,导致堆区数据重复释放
m_height = new int(*p.m_height);
}
//析构函数
~Person() {
cout << "析构函数!" << endl;
if (m_height != NULL)
{
delete m_height;
}
}
public:
int m_age;
int* m_height;
};
void test01()
{
Person p1(18, 180);
Person p2(p1);
cout << "p1的年龄: " << p1.m_age << " 身高: " << *p1.m_height << endl;
cout << "p2的年龄: " << p2.m_age << " 身高: " << *p2.m_height << endl;
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
涉及到拷贝函数,释放时会重复,必须替代浅拷贝
2.初始化列表
作用:用来初始化属性
语法:构造函数():属性1(值1),属性2(值2)... {}
class Person {
public:
传统方式初始化
//Person(int a, int b, int c) {
// m_A = a;
// m_B = b;
// m_C = c;
//}
//初始化列表方式初始化
Person(int a, int b, int c) :m_A(a), m_B(b), m_C(c) {
}
void PrintPerson() {
cout << "mA:" << m_A << endl;
cout << "mB:" << m_B << endl;
}
private:
int m_A;
int m_B;
int m_C;
};
int main() {
Person p(1, 2, 3);
p.PrintPerson();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.类对象作为类成员
类中的成员可以是另一个类的对象,我们称该成员为 对象成员:
class A {}
class B
{
A a;
}
B类中有对象A作为成员,A为对象成员。先创建A,创建B,析构B,析构A。
class Phone
{
public:
Phone(string name)
{
m_PhoneName = name;
cout << "Phone构造" << endl;
}
~Phone()
{
cout << "Phone析构" << endl;}
string m_PhoneName;
};
class Person
{
public:
//初始化列表可以告诉编译器调用哪一个构造函数
Person(string name, string pName) :m_Name(name), m_Phone(pName)
{
cout << "Person构造" << endl;}
~Person()
{
cout << "Person析构" << endl;}
void playGame()
{
cout << m_Name << " 使用" << m_Phone.m_PhoneName << " 牌手机! " << endl;
}
string m_Name;
Phone m_Phone;
};
void test01()
{
//当类中成员是其他类对象时,我们称该成员为 对象成员
//构造的顺序是 :先调用对象成员的构造,再调用本类构造
//析构顺序与构造相反
Person p("张三" , "苹果X");
p.playGame();
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.静态成员
在成员变量和成员函数前加上关键字static,称为静态成员。分为:
- 静态成员变量
- 所有对象共享同一份数据
- 在编译阶段分配内存
- 类内声明,类外初始化
class Person
{
public:
static int m_A; //静态成员变量
private:
static int m_B; //静态成员变量也是有访问权限的
};
int Person::m_A = 10; # 类外初始化
int Person::m_B = 10; # 类外初始化
void test01()
{
//静态成员变量两种访问方式
#------------------------1、通过对象-----------
Person p1;
p1.m_A = 100;
cout << "p1.m_A = " << p1.m_A << endl;
Person p2;
p2.m_A = 200;
cout << "p1.m_A = " << p1.m_A << endl; //共享同一份数据:200
cout << "p2.m_A = " << p2.m_A << endl; //200
# ----------------------2、通过类名----------
cout << "m_A = " << Person::m_A << endl;
//cout << "m_B = " << Person::m_B << endl; //私有权限访问不到
}
- 静态成员函数
- 所有对象共享同一个函数
- 静态成员函数只能访问静态成员变量
class Person
{
public:
static void func()
{
cout << "func调用" << endl;
m_A = 100;
//m_B = 100; //错误,不可以访问非静态成员变量
}
static int m_A; //静态成员变量
int m_B; //
private:
//静态成员函数也是有访问权限的
static void func2()
{
cout << "func2调用" << endl;
}
};
int Person::m_A = 10;
void test01()
{
//静态成员变量两种访问方式
#----------------1、通过对象------------
Person p1;
p1.func();
#----------------2、通过类名------------
Person::func();
//Person::func2(); //私有权限访问不到
}
总结
提示:这里对文章进行总结:
例如:以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了pandas的使用,而pandas提供了大量能使我们快速便捷地处理数据的函数和方法。