前言
本文介绍了顺序表的定义和常见操作并使用C语言代码对其进行实现。
1.顺序表的定义
顺序表是在计算机内存中 以数组的形式保存的线性表 ,线性表的顺序存储是指用一组地址连续的存储单元 依次存储线性表中的各个元素 、使得线性表中在逻辑结构上相邻的数据元素存储在相邻的物理存储单元中,即通过数据元素物理存储的相邻关系来反映数据元素之间逻辑上的相邻关系,采用顺序存储结构的线性表通常称为顺序表。
2.顺序表的存储结构
结构图:
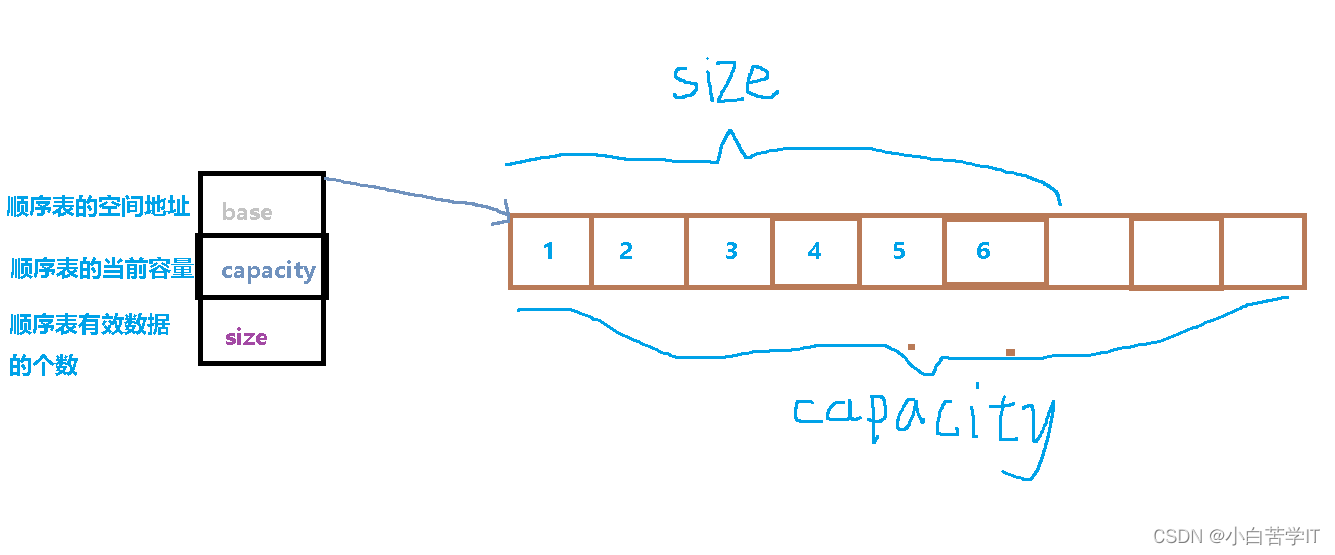
代码实现:
//增强程序可维护性
typedef int SQDataType;
//动态的
typedef struct SeqList
{
SQDataType* a;
int size; //有效数据的个数
int capacity;//容量
}SL;
3.顺序表的常用操作
3.1初始化
//初始化顺序表
void SeqListInit(SL* ps)
{
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
3.2检测容量
//检查容量是否足够
void SeqListCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->capacity == ps->size)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SQDataType *temp = (SQDataType* )realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(SQDataType));
if (temp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
ps->a = temp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
}
3.3 插入操作
//顺序表的插入
void SeqListInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SQDataType x)
{
assert(pos <= ps->size);
//检查容量
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);
//把pos这个位置的以后的数据往后移
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (pos <= end)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
end--;
}
//把这个值插入顺序表中
ps->a[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
3.3.1头插
//头部插入元素
void SeqListPushFront(SL* ps, SQDataType x)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, 0, x);
}
3.3.2尾插
//尾部插入元素
void SeqListPushBack(SL* ps, SQDataType x)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, ps->size, x);
}
3.4删除操作
//顺序表的删除操作
void SeqListErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(pos < ps->size);
int ret = SeqListFind(ps, ps->a[pos]);
if (ret == -1)
{
printf("你要删除的元素不存在!\n");
return;
}
int start = pos + 1;
//把要删除的元素后面的元素前移
while (start < ps->size)
{
ps->a[start-1] = ps->a[start];
start++;
}
ps->size--;
}
3.4.1头删
//头部删除元素
void SeqListPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps->size > 0);
SeqListErase(ps, 0);
}
3.4.2尾删
//尾部删除元素
void SeqListPopBack(SL* ps)
{
SeqListErase(ps,ps->size);
}
3.5查找
//查找顺序表中的元素
int SeqListFind(SL* ps, SQDataType x)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
//如果顺序表中没有该元素就返回-1
return -1;
}
3.6打印
//打印顺序表中的元素
void SeqListPrint(SL* ps)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
}
3.7销毁
//销毁顺序表
void SeqListDestroy(SL* ps)
{
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->size = 0;
}