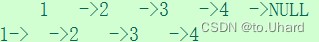题目描述
描述
给定一个链表,每个结点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任意结点或空结点,要求返回这个链表的深度拷贝。
我们用一个由n个结点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个结点用一个[val,random_index]表示:
val:一个表示Node.val的整数
random_index:随机指针指向的结点索引(范围从0到n-1),如果不指向任何结点,则为null
如:7(next->13,random->NULL) -> 13(next->11,random->7) -> 11(next->10,random->1) -> 10(next->1,random->11) -> 1(next->NULL,random->7)
注意:随机指针也可能指向自己。
示例1
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
7表示结点的val,null表示random返回的是指向的结点的索引
解题分析:
思路1:
一个一个的复制结点,并链接,而random的链接可以通过相对距离来确定链接指向。(时间复杂度为O(N^2))
先通过,原链表结点的random指向的位置,确定相对位置后,再确定拷贝结点的random指向的相对位置。
思路2:
第1步、依次拷贝结点,然后插入到对应原节点的后面
定义三个指针变量,cur、copy、next。
如果让cur指向copy则找不到原节点的下一个结点的地址,故需要先该copy指向下一个原结点,再cur指向复制的结点。否则需要定义next保存cur->next的地址,每个拷贝节点在每个原节点的后面,每个拷贝节点的random也在每个原节点的random的后面。
第2步、处理拷贝结点的random
拷贝的random的指向,是原结点的random的指向的next结点。
第3步、拆解出复制链表,并链接成一个新链表,且恢复原链表链接关系
定义三个指针变量,cur 、copy、next,让cur重新指向原节点的next,copy重新指向复制结点的next,cur、copy、next迭代往下走,依次恢复断点链表。
时间复杂度:O(N)
核心:复制结点的random的指向为,原结点的random的指向的next的指向。
代码实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
struct ListNode* random;
};
struct ListNode* copyRandom(struct ListNode* head)
{
if (head == NULL)//判断空链表,否则,导致cur->next空指针解引用
return NULL;
//第一步:
struct ListNode* cur = head;//不建议直接修改head
//拷贝原链表每个结点,插入到对应节点后面
while (cur != NULL)
{
//复制结点
struct ListNode* copy = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
copy->next = NULL;
copy->random = NULL;
copy->val = cur->val;
//插入copy结点
//不定义next,即以下两行代码不能颠倒
/*copy->next = cur->next;
cur->next = copy;*/
//或者定义next保存当前结点的下一个结点的地址,两个代码可以颠倒
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;//最后一个复制结点的next被置NULL
//cur、copy、(next)迭代
//不定义next
//cur = copy->next;
//定义next
cur = next;
//注意:copy是开辟的空间,next在保存下一个结点时,进入下一次循环copy、next开始迭代了
}
//第二步:
//根据原结点,处理拷贝结点的random
cur = head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
struct ListNode* copy = cur->next;
//拷贝结点的random是原结点的random的next
if (cur->random != NULL)//保证cur->random不能为空,否则导致空指针解引用
copy->random = cur->random->next;
else
copy->random = NULL;//这一行可以不用,因为copy->random在上一步已经初始化NULL了
//cur、copy迭代
cur = cur->next->next;//等价于cur = copy->next;
//注意:进入下一次循环copy开始迭代了
}
//注意:第二步可以放在第一步里面。
//第三步:
//拆解出复制结点,尾插链接
/*
//方法一:恢复原结点,链接复制结点
//定义next,方便迭代
cur = head;
struct ListNode* copyHead = head->next;//用于返回,防止复制的头结点找不到(迭代过程改变了)
while (cur != NULL)
{
struct ListNode* copy = cur->next;
struct ListNode* next = copy->next;
//先恢复原结点关系
cur->next = next;
//再链接复制结点
if (next != NULL)//保证next不能为空,否则next->next导致空指针解引用
copy->next = next->next;
else
copy->next = NULL;
//cur、copy、next迭代
cur = next;
//注意:进入下一次循环copy、next开始迭代了
}
*/
/*
//不定义next
cur = head;
struct ListNode* copyHead = head->next;//用于返回,防止头结点找不到(迭代过程改变了)
while (cur != NULL)
{
struct ListNode* copy = cur->next;
//断开原结点与复制结点的关系,并链接复制的链表。断掉链接是指将结点的next指针指向其他的结点
cur->next = copy->next;
if (copy->next != NULL)//保证copy->next不能为空,否则导致空指针解引用
copy->next = copy->next->next;
else
copy->next = NULL;
//迭代条件
cur = cur->next;
copy = copy->next;
}
*/
//方法二:取复制结点尾插,恢复原结点
//定义next
struct ListNode* copyHead = NULL,*copyTail = NULL;
cur = head;
//copyHead用于返回,防止头结点找不到(迭代过程改变了)copyTail保存尾结点,方便不需要找尾,直接尾插
while (cur != NULL)
{
struct ListNode* copy = cur->next;
struct ListNode* next = copy->next;//方便迭代
//取复制结点链接
if (copyTail == NULL)
{
//头插
copyHead = copyTail = copy;
}
else
{
//尾插
copyTail->next = copy;
copyTail = copy;//更新尾指针
}
//恢复原链表
cur->next = next;
//cur、copy、next迭代
cur = next;//copy、next,进入下一次循环开始迭代
}
//注意:链接复制结点后,原链表和复制链表最后一个结点的next都为NULL。分析的时候一定要细致。
return copyHead;
}
int main()
{
struct ListNode* n1 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
n1->val = 1;
struct ListNode* n2 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
n2->val = 2;
struct ListNode* n3 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
n3->val = 3;
struct ListNode* n4 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
n4->val = 4;
n1->next = n2;
n1->random = n3;
n2->next = n3;
n2->random = n1;
n3->next = n4;
n3->random = n3;
n4->next = NULL;
n4->random = NULL;
struct ListNode* copyHead = copyRandom(n1);
while (copyHead)
{
printf("%d -> ", copyHead->val);
copyHead = copyHead->next;
}
printf("NULL");
return 0;
}