文章目录
方案1:ServiceLoader
原理
通过将实现类的全类名写入特定路径的配置文件中, 生成APK会, 这些配置文件会进行合并. 读取配置文件中的类名, 使用类加载器获取Class对象, 用反射其实例化.
demo
1. 整体结构
新建工程, 新建common模块\impl1模块\impl2模块. 其中common是放置公用接口,imp1和2放置具体的实现类. 方案的依赖,如下图:
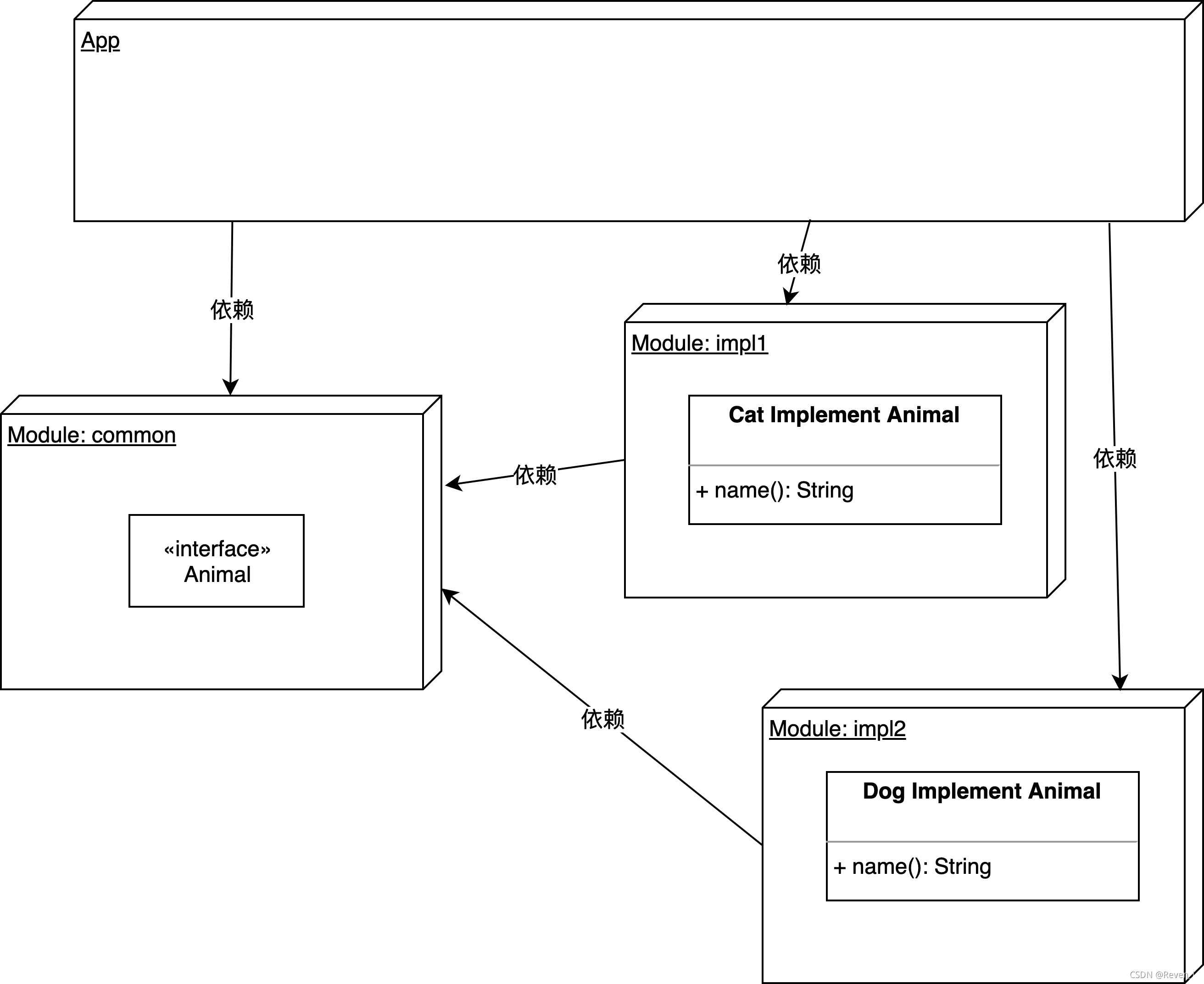
注:app中一定要依赖所有Module, 没有依赖的Module不会参与编译, 其中的类不能被找到.
dependencies {
...
implementation project(path: ':common')
implementation project(path: ':impl1')
implementation project(path: ':impl2')
}
2. 接口和实现类
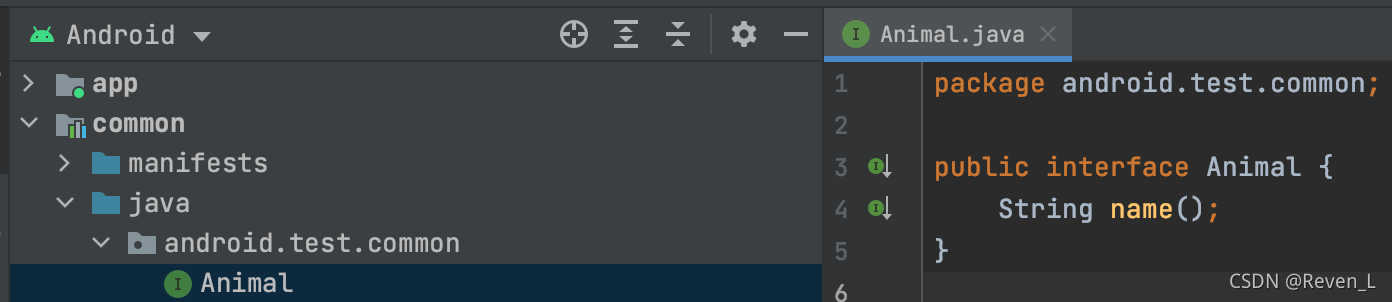
common中的Animal接口:
impl中的实现:
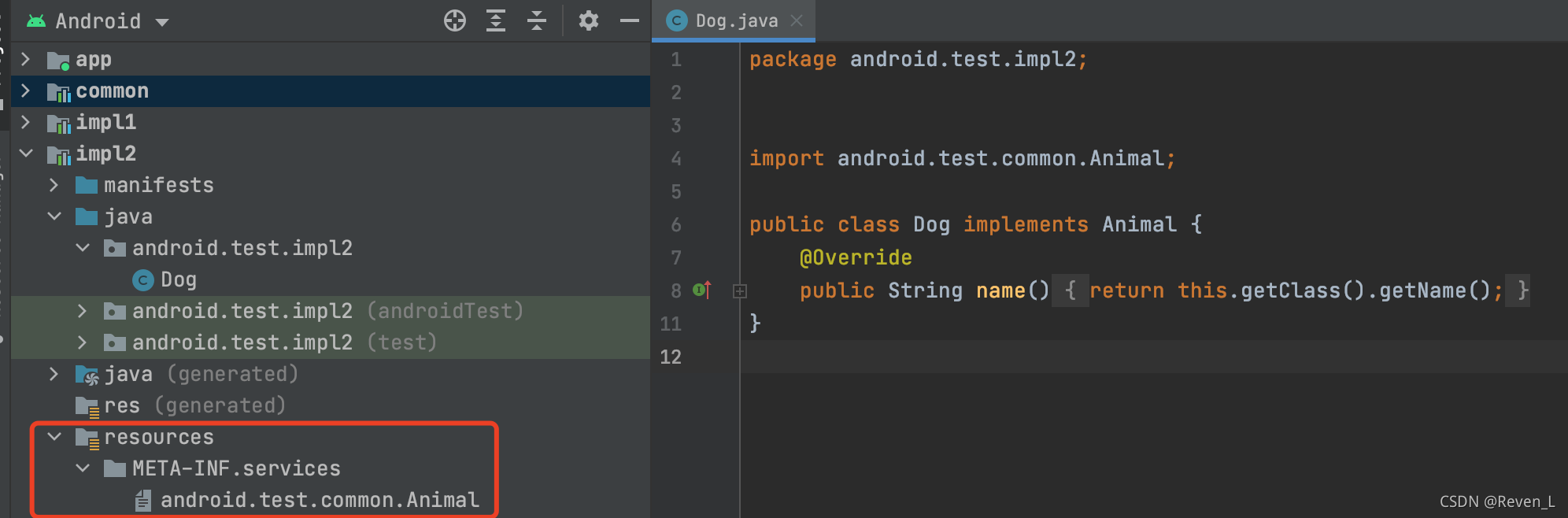
生成配置文件:
一定要在与java同级的文件夹建立/resources/META-INF/services目录(不是在res目录下),在该目录下创建以实现的接口的全名(包名+类名)为名字的文本文件, 里面是该Module中实现类的全名.
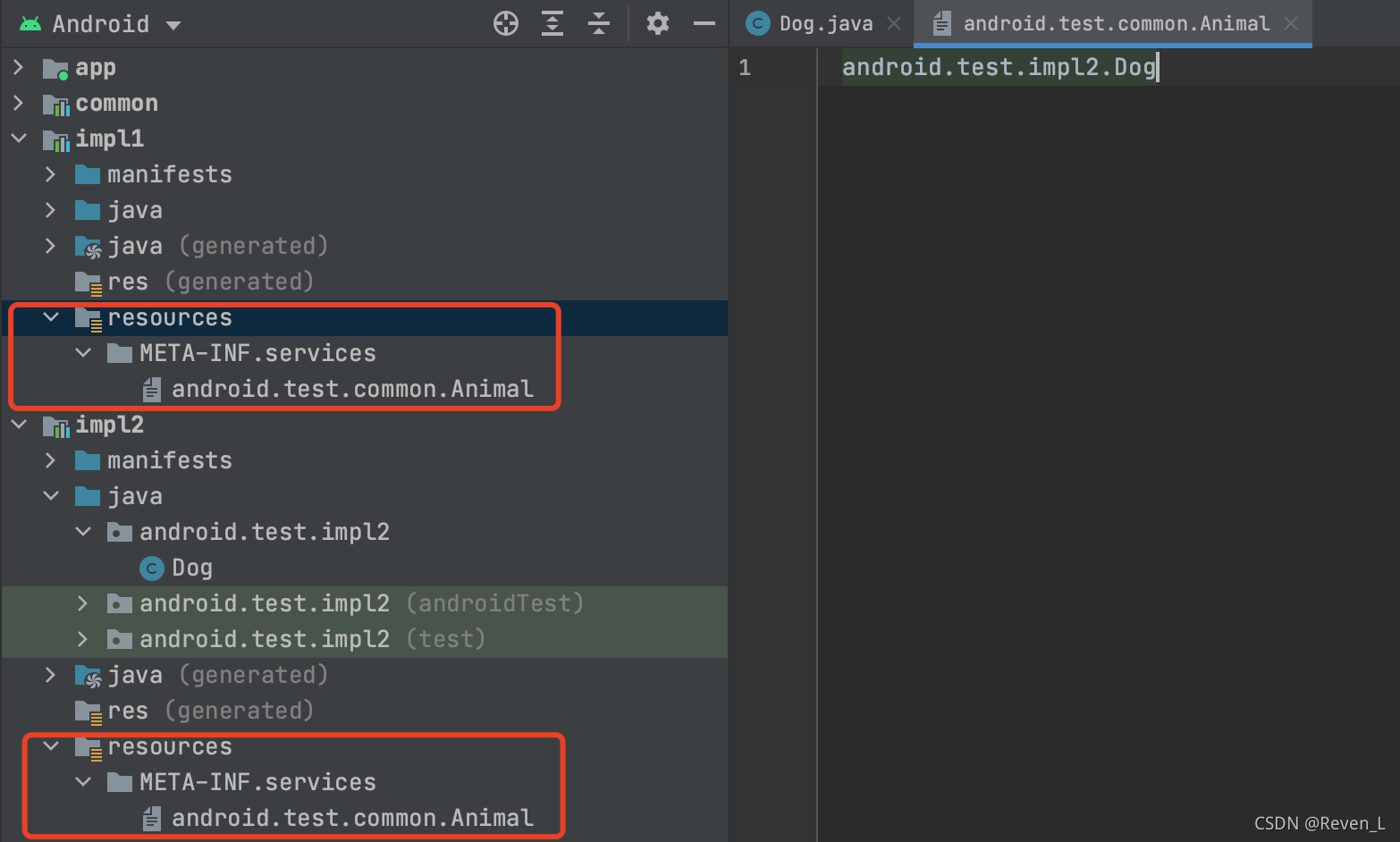
3. 查找实现类
- 将ServiceLoader封装成了一个工具类:
/**
* 接口实现类工厂
*
* @param <I> 要被寻找实现类的接口
*/
public class ImplClassFactory<I> implements Iterator<I> {
private final Iterator<I> mIterator;
private final ServiceLoader<I> mLoader;
public ImplClassFactory(Class<I> interfaceClass) {
this(interfaceClass, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
}
public ImplClassFactory(Class<I> interfaceClass, ClassLoader loader) {
if (interfaceClass == null || !interfaceClass.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interfaceClass must be a Interface!");
}
mLoader = ServiceLoader.load(interfaceClass, loader);
mIterator = mLoader.iterator();
}
public void reload() {
mLoader.reload();
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return mIterator.hasNext();
}
@Override
public I next() {
return mIterator.next();
}
}
- 在Activity的onCreate中遍历:
Iterator<Animal> it = new ImplClassFactory<>(Animal.class);
while (it.hasNext()) {
Log.e("animal: ", it.next().name());
}
Log输出:
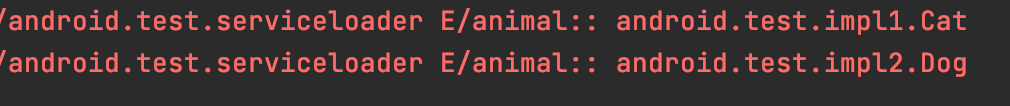
可见获取了实现类的实例.
AutoService
上面的方案, 要手动生成配置文件, 非常不方便.
于是Google给了我们一个解决方案: 通过给实现类加注解, 编译时自动生成配置文件, 简化这个过程.
1. 添加依赖
// 依赖 autoService 库
implementation 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc7'
annotationProcessor 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc7'
- 需要加implementation,不然找不到AutoService注解
2. 为实现类添加注解
import android.test.common.Animal;
import com.google.auto.service.AutoService;
//添加注解,参数是实现的接口类
@AutoService(Animal.class)
public class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public String name() {
return this.getClass().getName();
}
}
- 这样, AutoService就会自动生成配置文件, 不需要我们自己创建目录添加配置文件.
使用fat-aar不打包配置文件的解决方案
- 问题: 使用
embed引入的包的META-INF文件夹不会合并到主工程的aar. - 但打包出来的aar还是包含有主工程的
META-INF文件夹的.
解决方案
- 思路: 将引入的包的配置文件手动合并放到主工程的
META-INF文件夹中, 从而打包进aar.
- 在子工程(被
embed引入的工程)中的build.gradle中新增任务:
afterEvaluate {
assembleRelease.doLast {
copy {
from "build/outputs/aar/"
into "主工程目录/libs/"
}
//合并配置文件
//AutoServer生成的文件在build目录
FileTree srcDir = fileTree(dir: 'build/intermediates/javac/release/compileReleaseJavaWithJavac/classes/META-INF/services')
//如果手动填写文件, 使用下面这个路径
// FileTree srcDir = fileTree(dir: 'src/main/resources/META-INF/services')
FileTree desDir = fileTree(dir: "主工程目录/src/main/resources/META-INF/services")
Iterator<File> iterator = desDir.dir.listFiles().iterator()
for (File srcFile : srcDir.dir.listFiles()) {
boolean isWritten = false
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
File nowFile = iterator.next()
if (nowFile.name == srcFile.name) {
//添加到已有文件的末端
//Set去重,避免多次打包时出现重复
Set toWriteLines = srcFile.readLines() - nowFile.readLines()
if (!toWriteLines.isEmpty()) {
BufferedWriter writer = nowFile.newWriter(true)
for (String line : toWriteLines) {
writer.newLine()
writer.append(line)
}
writer.flush()
writer.close()
}
iterator.remove()
isWritten = true
break
}
}
if (isWritten) continue
//复制
copy {
from srcFile.path
into desDir.dir.path
}
}
}
}
- 在主工程的依赖中引入aar:
dependencies {
...
if(file('libs/subProject.aar').exists()) {
embed(name: 'subProject', ext: 'aar')
}
}
...
}
- 创建一个依次打包的脚本作为总调用:
//build.sh
# reset bin
rm -rf ../bin
mkdir -p ../bin
# clean build file
sh gradlew clean
rm -rf 主工程目录/libs
# build sub module arr
sh gradlew :subProject::assembleRelease
# build main module aar
sh gradlew :mainProject::assembleRelease
# mv result
cp ./../../../../主工程目录/build/outputs/aar/moyuSDK2-release.aar ../bin/MoyuSDK.aar
cd ../bin
- 该脚本作用是依次调用子工程的构建, 将配置文件合并入主工程文件下, 最后调用主工程的构建, 从而打包出完整配置文件的aar. 再将其复制到bin目录方便管理.
可优化点
- 方案1中每次都需要读取配置文件进行实例化, 但其实编译完成后, 配置文件其实是不会变的, 所以我们没必要每次都读取.
- 可以通过gradle插件, 利用注解生成新的java文件,这个文件中包含了具体的实现类. 这样程序在运行时,就已经知道了所有的具体服务类, 避免了IO读取类名和反射获取类的开销.
方案2:遍历Dex(不推荐)
问题分解
1. 获取所有的类
Android App所有Java类都是封装到Dex文件中, 让虚拟机执行, 所以我们可以通过DexFile.entries();来获取指定DexFile中所封装的所有完整类名, 然后通过反射就可以获取类了.
如何获取DexFile
A. 直接创建DexFile对象
DexFile df = new DexFile(context.getPackageCodePath());
但这种方法不适用于多个dex的情况, 而且其构造方法将在API26被弃用
B. 通过类加载器获取DexFile
查看BaseDexClassLoader的源码 可知, 其私有对象pathList是DexFile的容器, 所以我们可以通过反射来获取这个容器中所有的DexFile.
同时, 也可以找到多个Dex文件.
注: 由于DexFile的API在26版本对外弃用了, 但在DexFile源码 可知,其内部的核心方法还是可用的. 在高于26版本继续通过反射进行调用.
2. 筛选出实现指定接口的类
在通过反射利用类名得到Class对象A后, 我们需要判断其是否实现了指定接口B,通过B.isAssignableFrom(A)可以分辨, 当其返回true,则说明B是A的实现类或子接口.
工具类
public class ClassUtils {
private static BaseDexClassLoader mClassLoader = (BaseDexClassLoader) Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
private static SoftReference<Set<String>> mAllClassNamesBuffer;
/**
* 默认情况下有可能ClassLoader获取失败
* 调用该函数确保ClassLoader能获取到
*/
public static void setClassLoader(Context context) {
if (mClassLoader == null) {
mClassLoader = (BaseDexClassLoader) context.getClassLoader();
}
}
public static void setClassLoader(BaseDexClassLoader classLoader) {
if (classLoader != null) {
mClassLoader = classLoader;
}
}
/**
* @return 返回与接口同包名的所有实现类
*/
public static <C> List<Class<C>> getAllClassByInterface(Class<C> interfaceClass) {
Package pkg = interfaceClass.getPackage();
String pkgName = pkg != null ? pkg.getName() : "";
return getAllClassByInterface(interfaceClass, pkgName);
}
/**
* @param packageName 指定返回的类的包名前缀,设为空则不限制
* @return 返回这个interfaceClass的所有实现类及子接口, 不包括interfaceClass本身
*/
public static <C> List<Class<C>> getAllClassByInterface(Class<C> interfaceClass, String packageName) {
if (!interfaceClass.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interfaceClass must be a Interface!");
}
List<Class<C>> returnClassList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Class<?>> allClass = getClasses(packageName);
//排除本身
allClass.remove(interfaceClass);
for (Class<?> c : allClass) {
if (interfaceClass.isAssignableFrom(c)) {
returnClassList.add((Class<C>) c);
}
}
return returnClassList;
}
/**
* @param packageName 指定返回的包名前缀,设为空则不限制
* @return 返回以包名前缀与参数相同的类
*/
private static List<Class<?>> getClasses(String packageName) {
ArrayList<Class<?>> classes = new ArrayList<>();
for (String str : getAllClassesName(packageName)) {
try {
classes.add(getClass(str));
} catch (Throwable ignored) {
}
}
return classes;
}
/**
* @param packageName 指定返回的包名前缀,设为空则不限制
* @return 返回以包名前缀与参数packageName相同的类的全地址(包名 + 类名)
*/
private static Set<String> getAllClassesName(String packageName) {
if (mAllClassNamesBuffer != null) {
Set<String> ref = mAllClassNamesBuffer.get();
if (ref != null) {
return ref;
}
}
Set<String> classNames = new LinkedHashSet<>();
try {
Field f_pathList = getField("pathList", dalvik.system.BaseDexClassLoader.class);
Field f_dexElements = getField("dexElements", getClass("dalvik.system.DexPathList"));
Field f_dexFile = getField("dexFile", getClass("dalvik.system.DexPathList$Element"));
Object pathList = getObjectFromField(f_pathList, mClassLoader);
Object[] list = (Object[]) getObjectFromField(f_dexElements, pathList);
if (list == null) {
return classNames;
}
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
//DexFile在API26版本被弃用
for (Object o : list) {
DexFile d = (DexFile) getObjectFromField(f_dexFile, o);
if (d != null) {
Enumeration<String> enumeration = d.entries();
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
String className = enumeration.nextElement();
if (packageName.isEmpty() || className.startsWith(packageName)) {
classNames.add(className);
}
}
}
}
} else {
Class<?> c_DexFile = getClass("dalvik.system.DexFile");
Field f_mCookie = getField("mCookie", c_DexFile);
Method m_getClassNameList = getMethod("getClassNameList", c_DexFile, Object.class);
try {
if (m_getClassNameList == null) {
return classNames;
}
for (Object o : list) {
Object o_DexFile = getObjectFromField(f_dexFile, o);
Object o_mCookie = getObjectFromField(f_mCookie, o_DexFile);
if (o_mCookie == null) {
continue;
}
String[] classList = (String[]) m_getClassNameList.invoke(o_DexFile, o_mCookie);
if (classList != null) {
Collections.addAll(classNames, classList);
}
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
mAllClassNamesBuffer = new SoftReference<>(classNames);
return classNames;
}
public static Field getField(String field, Class<?> Class) {
try {
return Class.getDeclaredField(field);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static Method getMethod(String method, Class<?> Class, Class<?>... parameterTypes) {
try {
Method res = Class.getDeclaredMethod(method, parameterTypes);
res.setAccessible(true);
return res;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static Class<?> getClass(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return mClassLoader.loadClass(className);
}
public static Object getObjectFromField(Field field, Object arg) {
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
return field.get(arg);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
方案比较
比较代码:
int time = 1;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < time; i++) {
Iterator<Animal> it = new ImplClassFactory<>(Animal.class);
while (it.hasNext()) {
it.next().name();
}
}
Log.e("Main", "1耗时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < time; i++) {
for (Class<Animal> c : ClassUtils.getAllClassByInterface(Animal.class)) {
try {
c.newInstance().name();
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Log.e("Main", "2耗时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
测试结果:
| 次数 | 1 | 10 | 100 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 方案1耗时(ms) | 4 | 28 | 264 |
| 方案2 耗时(ms) | 213 | 696 | 3330 |
可见方案2耗时比方案1高十几倍甚至几十倍, 所以优先使用方案1.