参考视频(编程不良人)
为什么要进行密码加密
如果密码直接存储到数据库不进行加密,一旦被黑客攻破就会导致用户的密码泄露。而且一般用户的密码是多个网站或者app用的同一个,这就导致了很大的安全隐患,所以一般数据库都不会直接存储用户的明文密码,都会对密码进行加密存储。
一般加密算法常见的有下面几种
- 单向Hash算法,等单向哈希算法,不可逆。
- 单向自适应函数:这种方式在单向自适应函数在进行计算的时候会占用大量的cpu资源,但是可以增大攻击者破解的难度。
ss中的默认密码加密
前面我们测试的密码前面都会存储一个{noop}代表是明文的意思,那么我们下面研究一下问什么这个会被理解成明文,ss底层是怎么做到。
我们从formLogin点下去
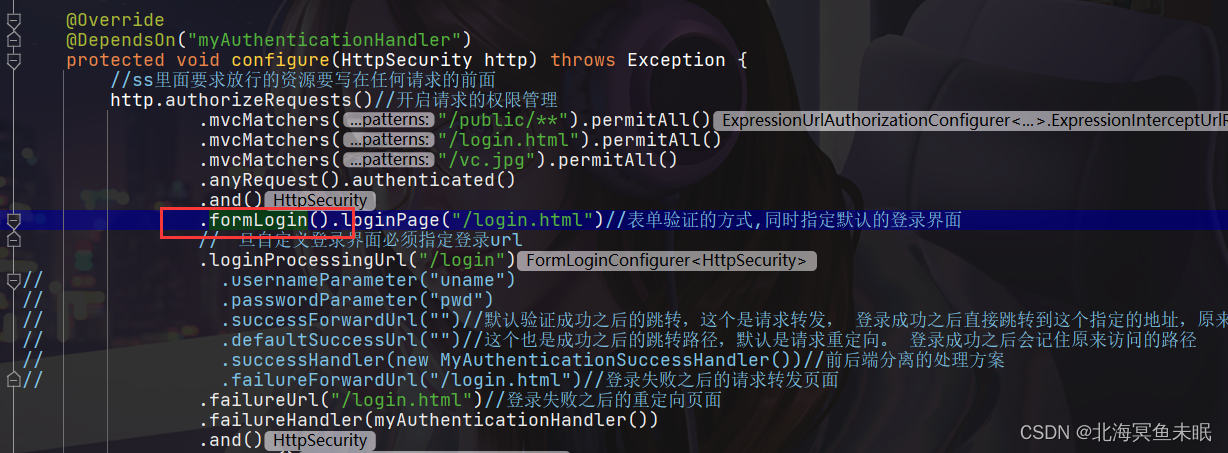
验证密码的在下面这个方法里面
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
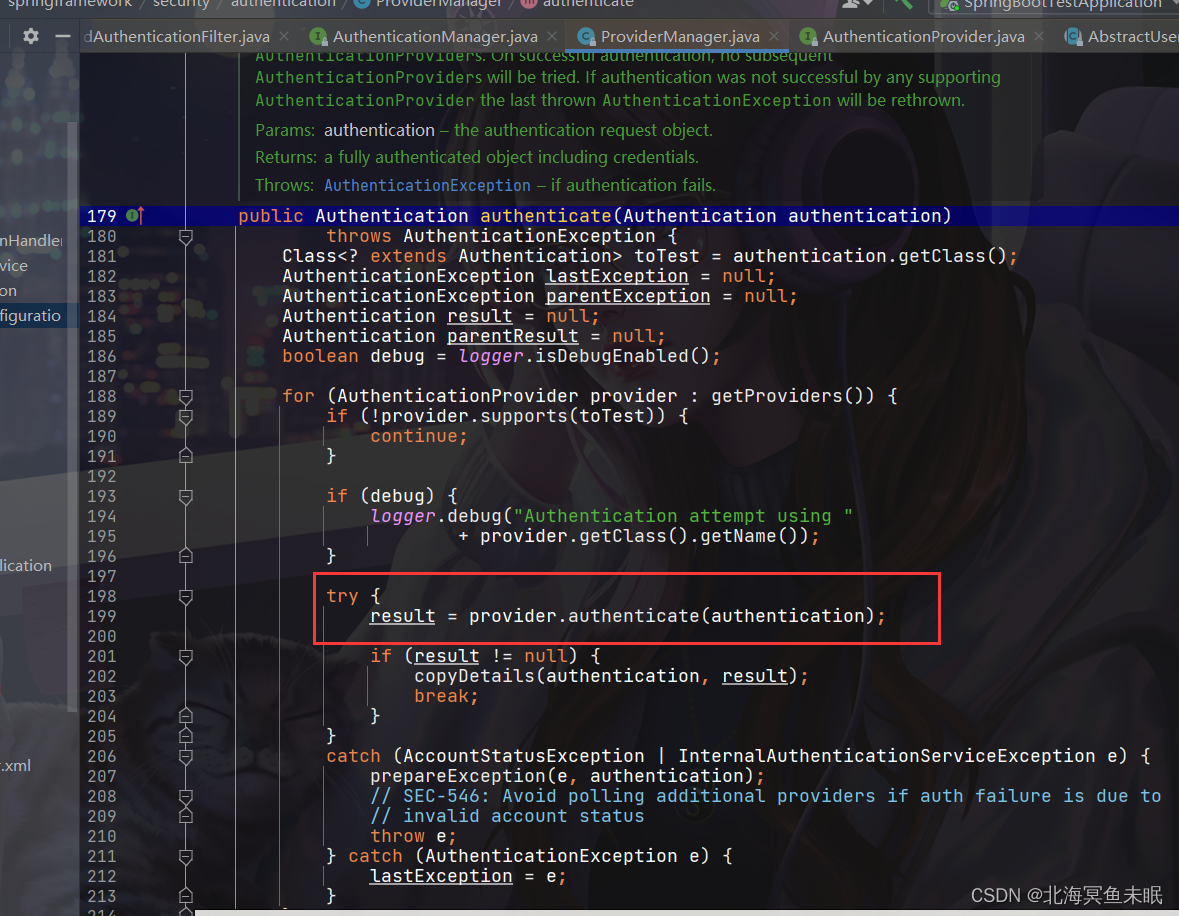
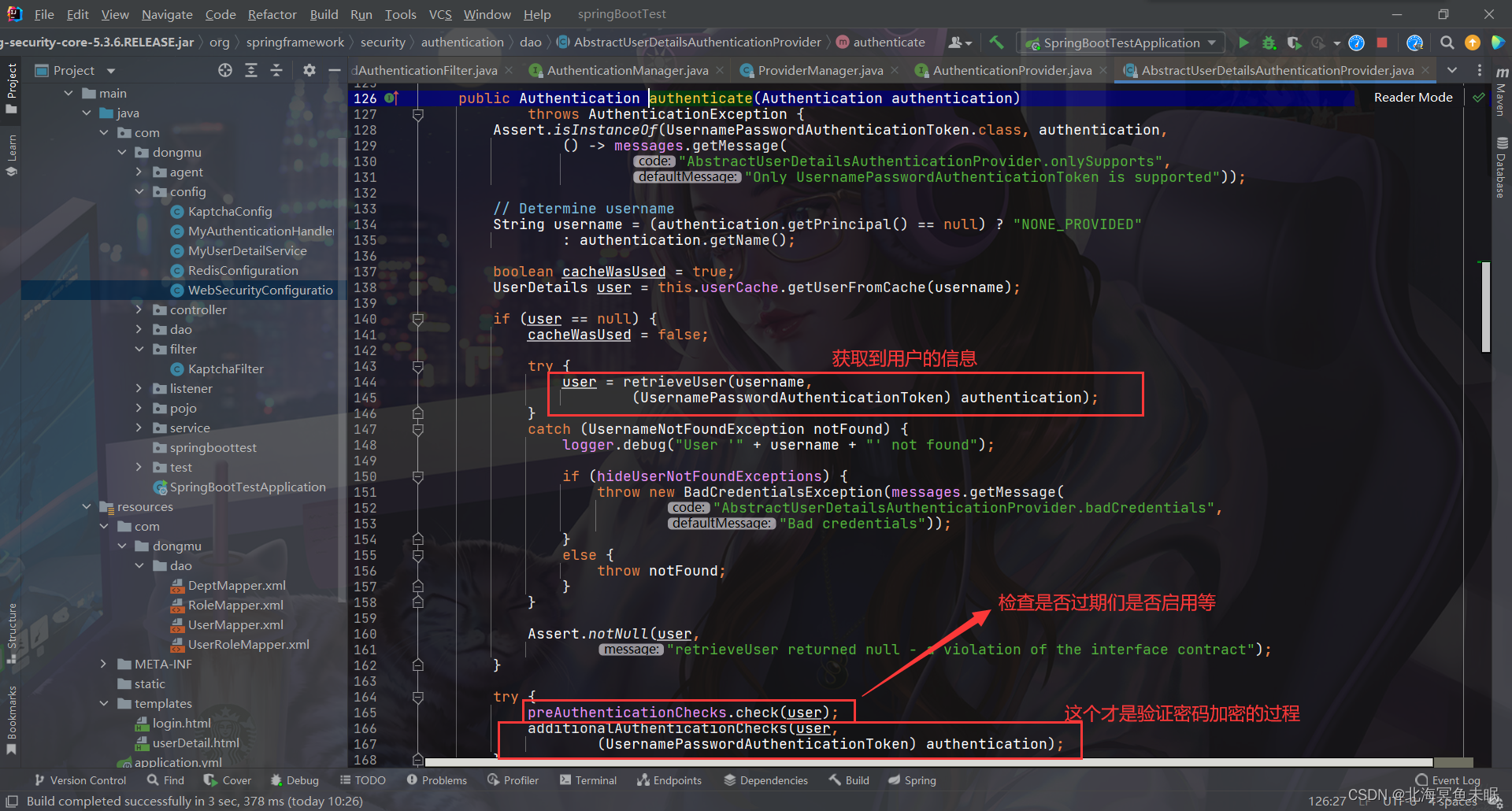
看一下这个check其实就是检查用户表其他几个字段的值
private class DefaultPreAuthenticationChecks implements UserDetailsChecker {
public void check(UserDetails user) {
if (!user.isAccountNonLocked()) {
logger.debug("User account is locked");
throw new LockedException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.locked",
"User account is locked"));
}
if (!user.isEnabled()) {
logger.debug("User account is disabled");
throw new DisabledException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.disabled",
"User is disabled"));
}
if (!user.isAccountNonExpired()) {
logger.debug("User account is expired");
throw new AccountExpiredException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.expired",
"User account has expired"));
}
}
}
密码加密验证源码
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
if (!passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
}
这里的passwordEncoder是一个成员变量,里面定义了几个方法
public interface PasswordEncoder {
/**
* Encode the raw password. Generally, a good encoding algorithm applies a SHA-1 or
* greater hash combined with an 8-byte or greater randomly generated salt.
*/
String encode(CharSequence rawPassword);
/**
* Verify the encoded password obtained from storage matches the submitted raw
* password after it too is encoded. Returns true if the passwords match, false if
* they do not. The stored password itself is never decoded.
*
* @param rawPassword the raw password to encode and match
* @param encodedPassword the encoded password from storage to compare with
* @return true if the raw password, after encoding, matches the encoded password from
* storage
*/
boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword);
/**
* Returns true if the encoded password should be encoded again for better security,
* else false. The default implementation always returns false.
* @param encodedPassword the encoded password to check
* @return true if the encoded password should be encoded again for better security,
* else false.
*/
default boolean upgradeEncoding(String encodedPassword) {
return false;
}
}
可以看一下matches的方法实现
它的默认实现是DelegatingPasswordEncoder
@Override
public boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String prefixEncodedPassword) {
if (rawPassword == null && prefixEncodedPassword == null) {
return true;
}
//获取加密算法,noop代表不做任何加密处理
String id = extractId(prefixEncodedPassword);
//private final Map<String, PasswordEncoder> idToPasswordEncoder;
PasswordEncoder delegate = this.idToPasswordEncoder.get(id);
if (delegate == null) {
return this.defaultPasswordEncoderForMatches
.matches(rawPassword, prefixEncodedPassword);
}
//获取取出{***}之后的部分
String encodedPassword = extractEncodedPassword(prefixEncodedPassword);
return delegate.matches(rawPassword, encodedPassword);
}
可以发现这个就是获取括号里面的内容,也就是{
noop}中的noop
private String extractId(String prefixEncodedPassword) {
if (prefixEncodedPassword == null) {
return null;
}
int start = prefixEncodedPassword.indexOf(PREFIX);
if (start != 0) {
return null;
}
int end = prefixEncodedPassword.indexOf(SUFFIX, start);
if (end < 0) {
return null;
}
return prefixEncodedPassword.substring(start + 1, end);
}
我们的noop对应的就是NoOpPasswordEncoder
@Deprecated
public final class NoOpPasswordEncoder implements PasswordEncoder {
public String encode(CharSequence rawPassword) {
return rawPassword.toString();
}
//可以看到这里面的实现就是equals。
public boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword) {
return rawPassword.toString().equals(encodedPassword);
}
/**
* Get the singleton {@link NoOpPasswordEncoder}.
*/
public static PasswordEncoder getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
private static final PasswordEncoder INSTANCE = new NoOpPasswordEncoder();
private NoOpPasswordEncoder() {
}
}
自定义加密算法
直接使用其他的密码加密方式
我们先把密码改成bcrypt加密
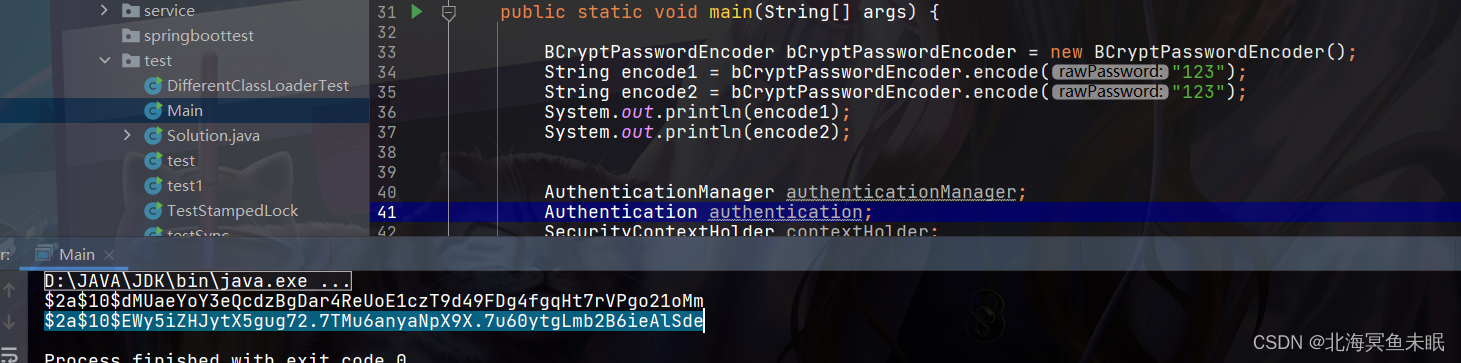
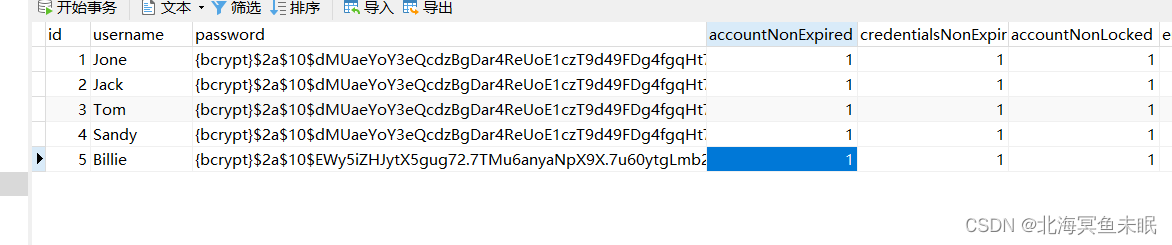
这个时候我们一样可以使用密码123登录
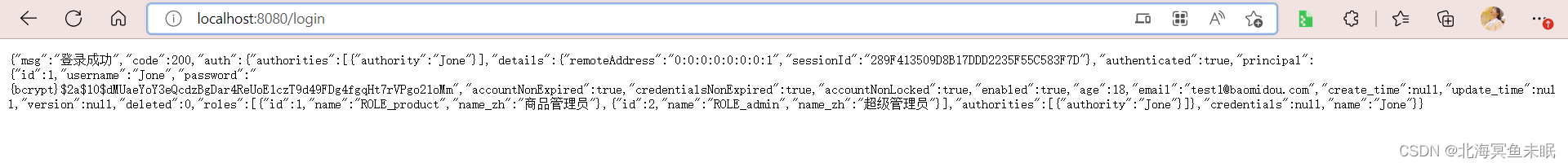

第二种密码加密方式
为什么我们前面说默认的是DelegatingPasswordEncoder?,这个是在配置里面配置的
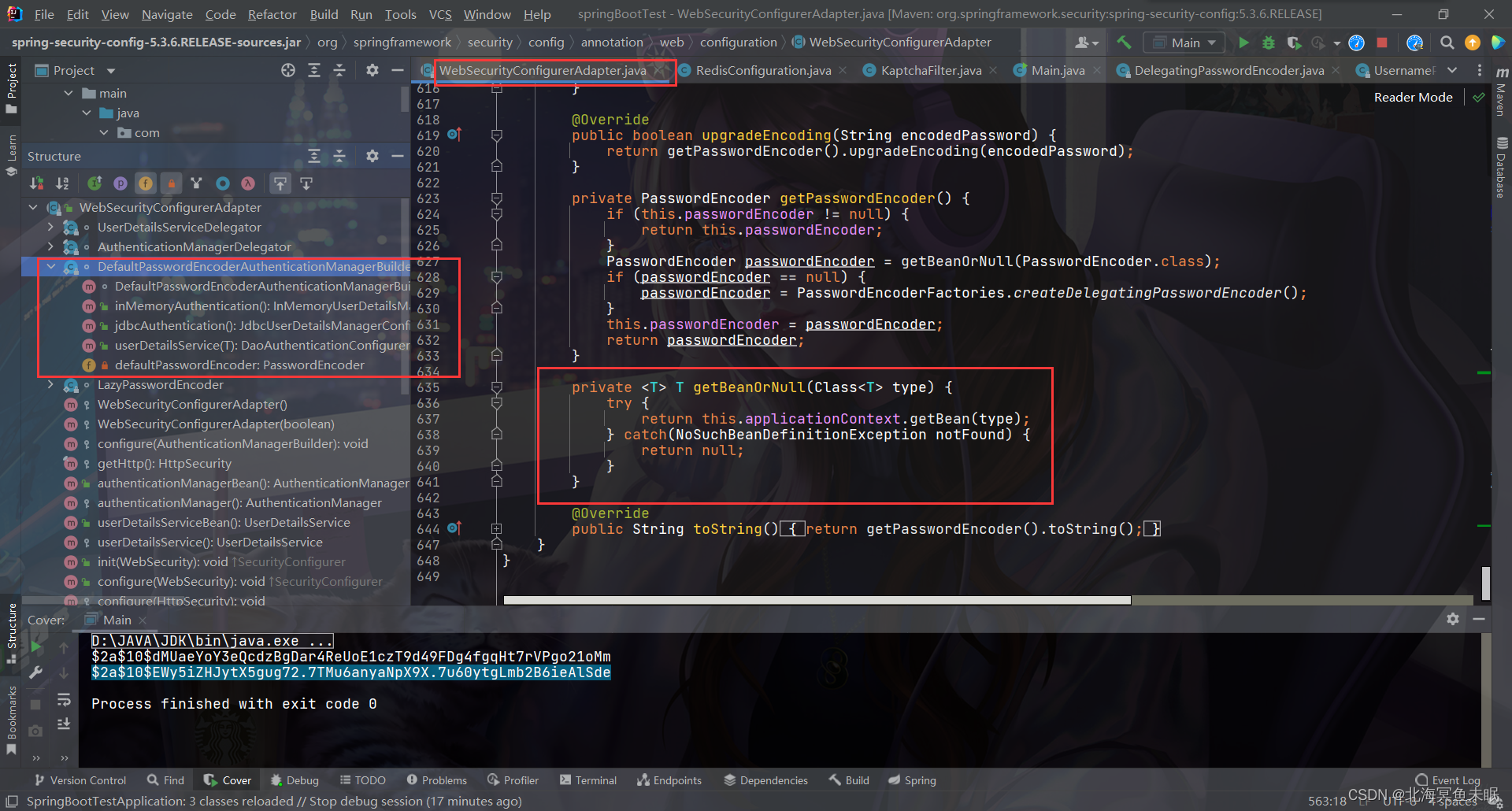
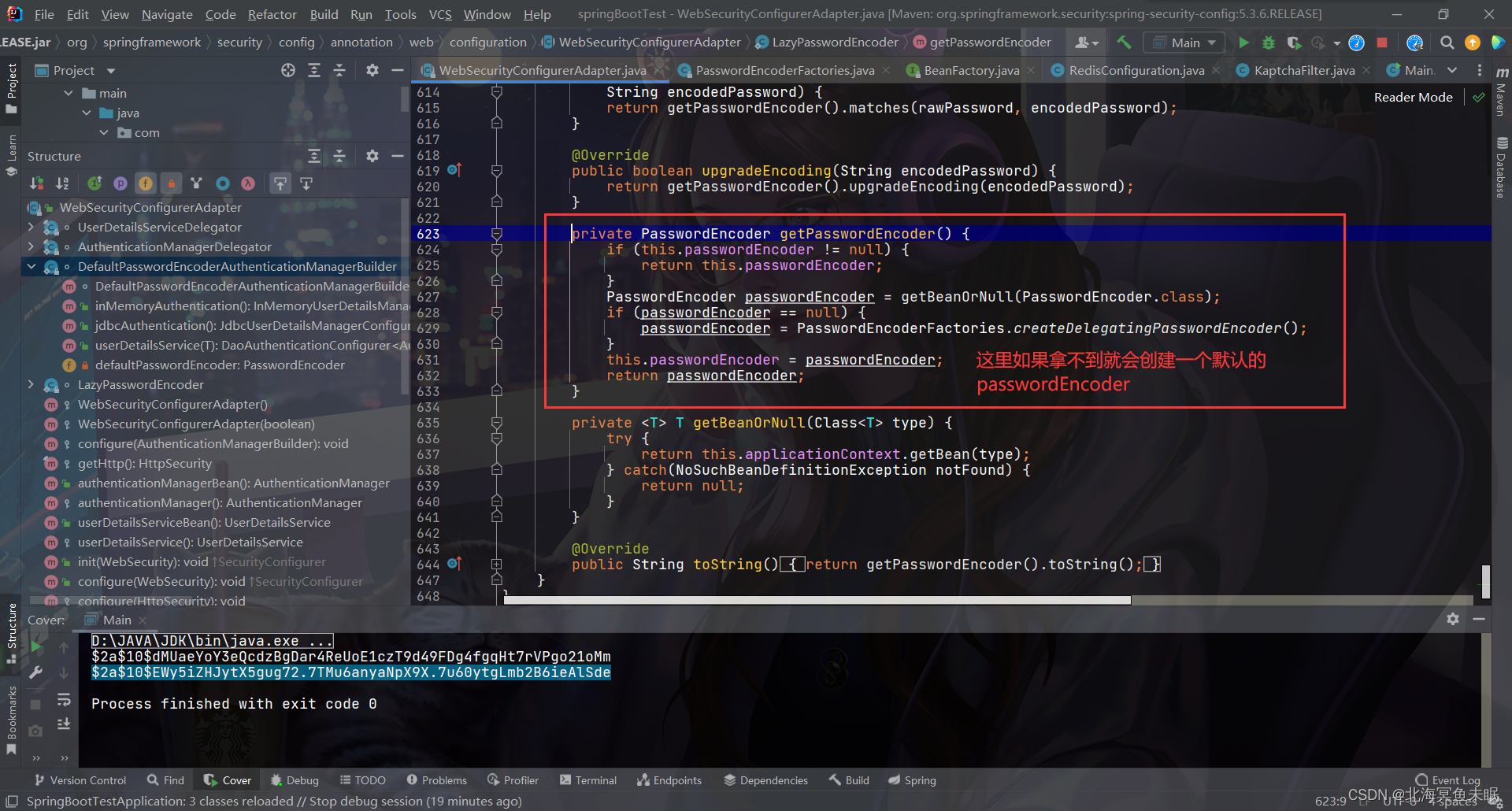
所以只要我们自己在容器中创建一个PasswordEncoder就可以实现使用自己的默认的编码方法。如果没有找到就会自己创建一个map,这个时候就要在密码字段前面加上指明加密方式。当然如果我们自定义了一个PasswordEncoder,这样我们数据库中的密码就不需要加上密码加密前缀。
public static PasswordEncoder createDelegatingPasswordEncoder() {
String encodingId = "bcrypt";
Map<String, PasswordEncoder> encoders = new HashMap<>();
encoders.put(encodingId, new BCryptPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("ldap", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.LdapShaPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("MD4", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.Md4PasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("MD5", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5"));
encoders.put("noop", org.springframework.security.crypto.password.NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance());
encoders.put("pbkdf2", new Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("scrypt", new SCryptPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("SHA-1", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-1"));
encoders.put("SHA-256", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-256"));
encoders.put("sha256", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.StandardPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("argon2", new Argon2PasswordEncoder());
return new DelegatingPasswordEncoder(encodingId, encoders);
}
密码的升级
如果我们的系统进行升级,原来的密码加密的方式由于已经过时,需要对原来的密码进行升级版本的加密,我们可以这样做
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
这个方法中调用了
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
@Override
protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal,
Authentication authentication, UserDetails user) {
boolean upgradeEncoding = this.userDetailsPasswordService != null
&& this.passwordEncoder.upgradeEncoding(user.getPassword());
if (upgradeEncoding) {
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
String newPassword = this.passwordEncoder.encode(presentedPassword);
user = this.userDetailsPasswordService.updatePassword(user, newPassword);
}
return super.createSuccessAuthentication(principal, authentication, user);
}
这也就说明只要我们在AuthenticationProvider设置了userDetailsPasswordService ,那么就会对密码进行升级的操作。
下面我们对MyUserDetailService 进行修改如下
@Component
public class MyUserDetailService implements UserDetailsService, UserDetailsPasswordService {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
UserRoleMapper userRoleMapper;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userMapper.selectByUserName(username);
if (user==null) throw new RuntimeException("用户名不存在。");
//查询用户的权限信息
List<Long> longs = userRoleMapper.selectUserRoleIdsByUserId(user.getId());
if (longs!=null&&longs.size()>0){
List<Role> roles = userRoleMapper.selectUserRolesByUserId(user.getId());
user.setRoles(roles);
}else {
user.setRoles(new ArrayList<>());
}
return user;
}
@Override
public UserDetails updatePassword(UserDetails user, String newPassword) {
// pbkdf2
//这种方式默认的newPassword采用的加密方式是相对于这个版本来说
//最安全的加密方式
User user1 = userMapper.selectByUserName(user.getUsername());
user1.setPassword(newPassword);
int i = userMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(user1);
if (i==1){
((User) user).setPassword(newPassword);
}
return user;
}
}
这里要注意updatePassword默认使用相对来说最安全的加密方式,而相对于当前版本最安全的加密方式是bcrypt,所以如果此时我把密码改成{noop}123,当我登录之后就会自动修改为{bcrypt}$2a$10$Z0bmSC1x/nuWjQLPe3uBr.7PWXFwBwDmER7e.Zr1Dxpfl3mzm5GD.这种。
至于相对当前版本最安全的加密方式是怎么确定的呢?
看下面源码
/*
* Copyright 2002-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.security.crypto.factory;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.argon2.Argon2PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.DelegatingPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.scrypt.SCryptPasswordEncoder;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Used for creating {@link PasswordEncoder} instances
* @author Rob Winch
* @since 5.0
*/
public class PasswordEncoderFactories {
/**
* Creates a {@link DelegatingPasswordEncoder} with default mappings. Additional
* mappings may be added and the encoding will be updated to conform with best
* practices. However, due to the nature of {@link DelegatingPasswordEncoder} the
* updates should not impact users. The mappings current are:
*
* <ul>
* <li>bcrypt - {@link BCryptPasswordEncoder} (Also used for encoding)</li>
* <li>ldap - {@link org.springframework.security.crypto.password.LdapShaPasswordEncoder}</li>
* <li>MD4 - {@link org.springframework.security.crypto.password.Md4PasswordEncoder}</li>
* <li>MD5 - {@code new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5")}</li>
* <li>noop - {@link org.springframework.security.crypto.password.NoOpPasswordEncoder}</li>
* <li>pbkdf2 - {@link Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder}</li>
* <li>scrypt - {@link SCryptPasswordEncoder}</li>
* <li>SHA-1 - {@code new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-1")}</li>
* <li>SHA-256 - {@code new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-256")}</li>
* <li>sha256 - {@link org.springframework.security.crypto.password.StandardPasswordEncoder}</li>
* <li>argon2 - {@link Argon2PasswordEncoder}</li>
* </ul>
*
* @return the {@link PasswordEncoder} to use
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static PasswordEncoder createDelegatingPasswordEncoder() {
String encodingId = "bcrypt";
Map<String, PasswordEncoder> encoders = new HashMap<>();
encoders.put(encodingId, new BCryptPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("ldap", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.LdapShaPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("MD4", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.Md4PasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("MD5", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5"));
encoders.put("noop", org.springframework.security.crypto.password.NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance());
encoders.put("pbkdf2", new Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("scrypt", new SCryptPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("SHA-1", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-1"));
encoders.put("SHA-256", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-256"));
encoders.put("sha256", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.StandardPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("argon2", new Argon2PasswordEncoder());
return new DelegatingPasswordEncoder(encodingId, encoders);
}
private PasswordEncoderFactories() {
}
}
WebSecurityAdapter的静态内部类LazyPasswordEncoder 中用到的时候就会创建上面的对象,返回以一个定死的bcrypt的加密方式。
static class LazyPasswordEncoder implements PasswordEncoder {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
LazyPasswordEncoder(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Override
public String encode(CharSequence rawPassword) {
return getPasswordEncoder().encode(rawPassword);
}
@Override
public boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword,
String encodedPassword) {
return getPasswordEncoder().matches(rawPassword, encodedPassword);
}
@Override
public boolean upgradeEncoding(String encodedPassword) {
return getPasswordEncoder().upgradeEncoding(encodedPassword);
}
private PasswordEncoder getPasswordEncoder() {
if (this.passwordEncoder != null) {
return this.passwordEncoder;
}
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = getBeanOrNull(PasswordEncoder.class);
if (passwordEncoder == null) {
passwordEncoder = PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
}
this.passwordEncoder = passwordEncoder;
return passwordEncoder;
}
private <T> T getBeanOrNull(Class<T> type) {
try {
return this.applicationContext.getBean(type);
} catch(NoSuchBeanDefinitionException notFound) {
return null;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return getPasswordEncoder().toString();
}
}