目录
一、改造哈希表
使用的代码是之前篇章哈希表的代码,改造后哈希表代码如下:
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <string>
//开散列(哈希桶)
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
T _data;
HashNode<T>* _next;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
//仿函数
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
//仿函数特化
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
{
hash *= 131;//BKDRHash算法
hash += ch;
}
return hash;
}
};
//声明HashTable,不声明__HTIerator的_ht变量找不到标识符
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
struct __HTIerator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef __HTIerator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, Hash, KeyOfT> Self;
typedef HashTable<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> HT;
//成员变量
Node* _node;
HT* _ht;
//构造函数
__HTIerator(Node* node, HT* ht)
:_node(node)
,_ht(ht)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)//当前桶没有走完,迭代遍历当前桶
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else//当前桶走完了,要找下一个桶的第一个
{
KeyOfT kot;
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();//找当前桶的哈希地址
++hashi;//找下一个桶
while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size())
{
if (_ht->_tables[hashi])//桶不为空
{
_node = _ht->_tables[hashi];
break;
}
else//桶为空,继续找下一个桶
{
++hashi;
}
//后面没有桶了,哈希表已经遍历完
if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size())
{
_node = nullptr;
}
}
}
return *this;
}
};
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
//要给__HTIerator类设置成友元,否则__HTIerator类无法访问HashTable的私有成员,ps;_ht->_tables.size()
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class Hash, class KeyOfT> friend struct __HTIerator;
public:
typedef __HTIerator<K, T, T&, T*, Hash, KeyOfT> iterator;
//构造
HashTable()
:_n(0)
{
_tables.resize(10);//默认开10个空间
}
//析构
~HashTable()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
//释放每一个桶
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}
iterator begin()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
if (_tables[i])
{
return iterator(_tables[i], this);
}
}
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
//插入
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
KeyOfT kot;
iterator it = Find(kot(data));
if (it != end())//查询插入的值是否已经存在
{
return make_pair(it, false);//存在插入失败
}
//大于标定负载因子,就需要扩容
//这里负载因子标定为 1
if (_tables.size() == _n)
{
//创建一个新的哈希表,新哈希表的大小设置为原哈希表的2倍
vector<Node*> newTables;
newTables.resize(_tables.size() * 2);
//将原哈希表当中的结点插入到新哈希表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)//桶不为空
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = Hash()(kot(cur->_data)) % newTables.size();
//节点头插到新表
cur->_next = newTables[hashi];
newTables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;//取该桶的下一个节点
}
//该桶取完后将该桶置空
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
//交换这两个哈希表
_tables.swap(newTables);
}
//不需要扩容,进行插入
size_t hashi = Hash()(kot(data)) % _tables.size();
//头插
Node* newNode = new Node(data);
newNode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newNode;
//有效数据+1
++_n;
return make_pair(iterator(newNode, this), true);
}
//查找
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = Hash()(key) % _tables.size();//计算key的哈希地址
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
//遍历这个桶进行查找
while (cur)
{
if (KeyOfT()(cur->_data) == key)//查找成功
{
return iterator(cur, this);
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
//该桶遍历完,查找失败
return end();
}
//删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = Hash()(key) % _tables.size();//计算key的哈希地址
Node* prev = nullptr;//用于记录 cur的前一个节点
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (KeyOfT()(cur->_data) == key)//找到需要删除的节点
{
if (cur == _tables[hashi])//头删
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else//中间删除
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
--_n;
return true;
}
else//迭代遍历
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
//删除失败
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;//指针数组, 哈希表
size_t _n;//用于记录表中有效数据的个数
};
哈希表模板参数的控制:unordered_set是K模型的容器,而unordered_map是KV模型的容器
HashTable类的模板参数介绍:
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>模板参数K(key)用于查找和删除数据,模板参数T用于存储数据,如果上层是unordered_set,T则是key,如果上层是unordered_map,T则是键值对pair
- 上层容器是unordered_set时,传入的T是键值,哈希结点中存储的就是Key
- 上层容器是unordered_map时,传入的T是键值对,哈希结点中存储的就是键值对
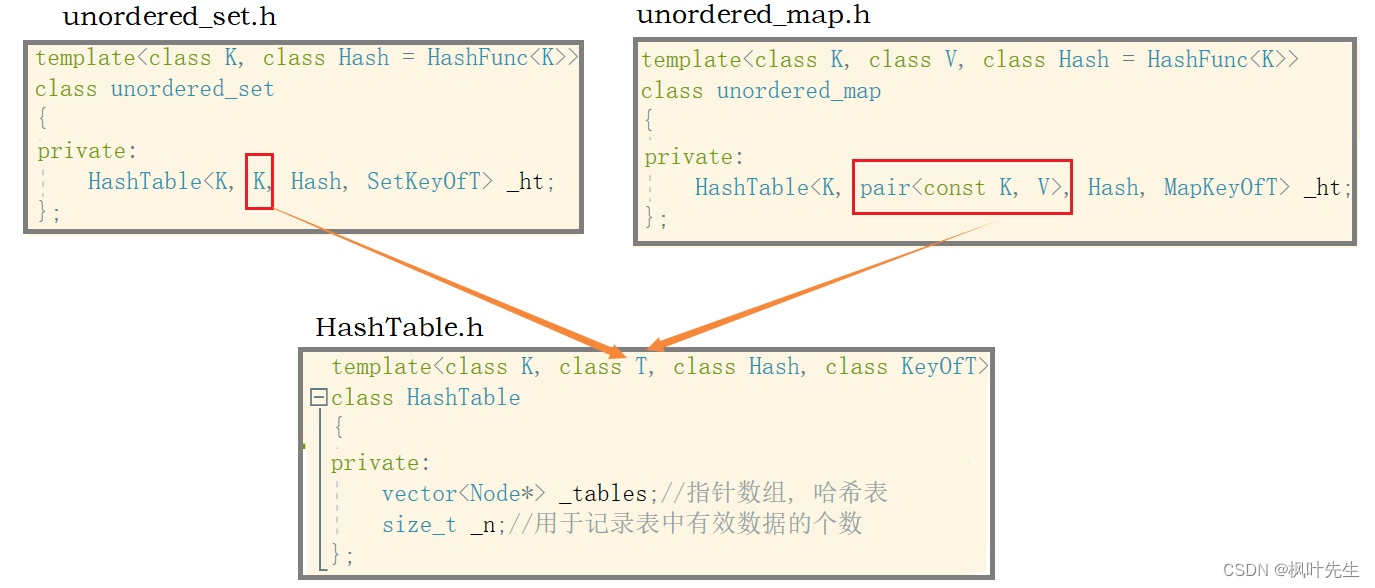
模板参数Hash是一个哈希函数,在哈希表已经有过详细解释

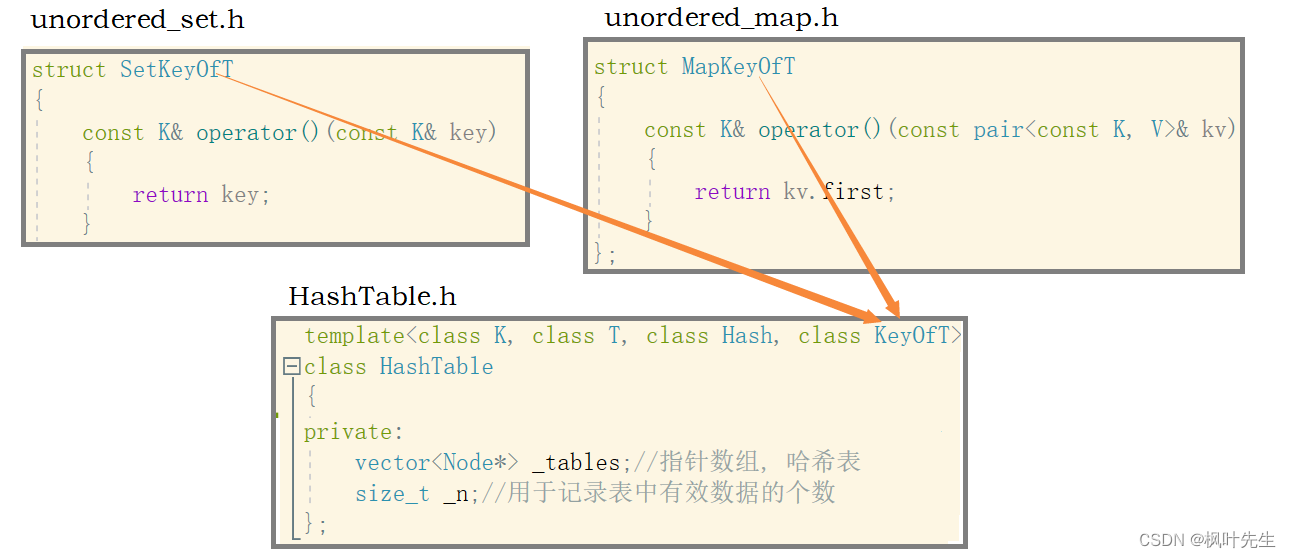
模板参数KeyOfT 是一个仿函数,用于获取数据,由上层的 unordered_set 和 unordered_map 独立实现
1.1 节点定义
数据类型是泛型,由上层传入才确定是Key 或键值对pair
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
T _data;
HashNode<T>* _next;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};1.2 哈希表迭代器相关
迭代器模板参数如下
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class Hash, class KeyOfT>哈希表的迭代器与其他容器的迭代器有所不同,哈希表的迭代器增加了一个 HashTable 的指针,不增加这个变量是无法完成哈希表的迭代器的,这也意味着 const 版本的迭代器需要重新写在另一个类,不能复用普通迭代器的代码完成const 迭代器

构造迭代器时,不仅需要对应哈希结点的指针,还需要该哈希结点所在哈希表的地址
//构造函数
__HTIerator(Node* node, HT* ht)
:_node(node)
,_ht(ht)
{}前置++
- 若当前结点不是当前哈希桶中的最后一个结点,则++后走到当前哈希桶的下一个结点
- 若当前结点是当前哈希桶的最后一个结点,则++后走到下一个非空哈希桶的第一个结点
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)//当前桶没有走完,迭代遍历当前桶
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else//当前桶走完了,要找下一个桶的第一个
{
KeyOfT kot;
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();//找当前桶的哈希地址
++hashi;//找下一个桶
while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size())
{
if (_ht->_tables[hashi])//桶不为空
{
_node = _ht->_tables[hashi];
break;
}
else//桶为空,继续找下一个桶
{
++hashi;
}
//后面没有桶了,哈希表已经遍历完
if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size())
{
_node = nullptr;
}
}
}
return *this;
}
};其他都与之前一致,就不解释了
1.3 哈希表接口相关
详细介绍在哈希表篇章,这里不解释了,这里只是对它的进口进行了封装
二、unordered_set模拟实现代码
都是调用哈希表接口,不解释了
#include "HashTable.h"
namespace fy
{
template<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
//没有实例化,没办法到HashTable里面找iterator,所以typename就是告诉编译器这里是一个类型,实例化以后再去取
typedef typename HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
//typedef typename HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
/*const_iterator begin()const
{
return
}*/
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Insert(key);
}
private:
HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfT> _ht;
};
void Test_unorderSet()
{
unordered_set<int> us;
us.insert(4);
us.insert(14);
us.insert(8);
us.insert(2);
us.insert(18);
us.insert(2);
us.insert(234);
us.insert(24);
us.insert(11);
us.insert(666);
unordered_set<int>::iterator it = us.begin();
while (it != us.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
us.insert(5);
us.insert(16);
us.erase(4);
us.erase(4);
us.erase(2);
us.erase(11);
us.erase(666);
us.erase(234);
}
}
三、unordered_map模拟实现代码
都是调用哈希表接口,不解释了
#include "HashTable.h"
namespace fy
{
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& data)
{
return _ht.Insert(data);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));//无法直接返回,要使用变量进行接收再返回
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfT> _ht;
};
void Test_unorderedMap()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "香蕉", "草莓", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
unordered_map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& e : arr)
{
countMap[e]++;
}
for (const auto& kv : countMap)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
}
}
文章内容都是炒旧饭,没啥介绍的,文章就到这
----------------我是分割线---------------
文章到这里就结束了,下一篇即将更新