一、什么是JDBC?
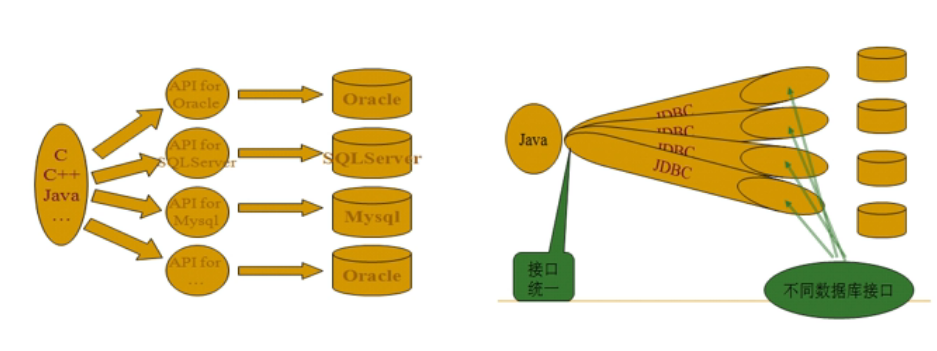
JDBC(Java Database Connection)为java开发者使用数据库提供了统一的编程接口,它由一组java类和接口组成。是java程序与数据库系统通信的标准API。JDBC API 使得开发人员可以使用纯java的方式连接数据库,并执行操作。
sun公司由于不知道各个主流商用数据库的程序代码,因此无法自己写代码连接各个数据库,因此,sun公司决定,自己提供一套api,凡是数据库想与java进行连接,数据库厂商自己必须实现JDBC这套接口。而数据库厂商的JDBC实现,我们就叫它是此数据库的驱动。
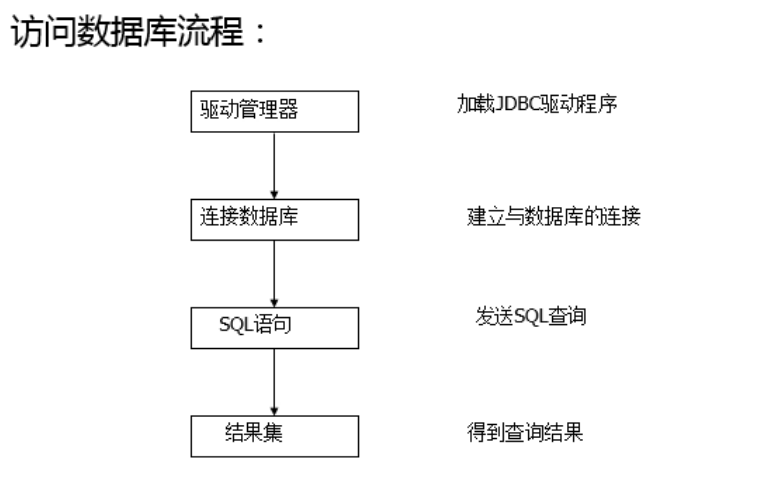
二、JDBC访问数据库流程:
三、JDBC的常用接口:
1.Driver接口
--Driver接口有数据库厂家提供,对于java开发者而言,只需要使用Driver接口就可以了.
--在编程中要连接数据库,必须先装载特定厂商的数据库驱动程序。不同的数据库有不同的装载方法
--驱动:就是各个数据库厂商实现的sun公司提出的JDBC接口。即对Connnection等接口的实现类的jar文件
--装载Mysql驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
--装载Oracle驱动
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
2.DriverManager接口
--DriverManager是JDBC的管理层,作用于用户和驱动程序之间
--DriverManager跟踪可用的驱动程序,并在数据和相应的驱动程序之间建立连接
3.Connection接口
--Connection与特定数据库的连接(会话),在连接上下文中执行SQL语句并返回结果
--DriverManager的getConnection()方法建立在JDBC URL中定义的数据库Connection连接上
--连接Mysql数据库
Connection con = DriverManager.grtConnection("jdbc:mysql://host:port/database","user","password");
--连接Oracle数据库
Connection con = DriverManager.grtConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@host:port/database","user","password");
/* * 测试跟数据库建立连接 * */ public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; try { //加载驱动类 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); //建立连接(连接对象内部其实包含了Socket对象,是一个远程连接。比较耗时,这是Connection管理对象的一个要点!) // 真正开发中,为了提高效率,都会使用连接池来管理连接对象! conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library", "root", "123456"); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(conn); System.out.println("建立连接,耗时:" + (end - start)+"ms毫秒"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); ///关闭连接 } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
4.Statement接口
--用于执行静态SQL语句并返回它所生成结果的对象。
--三种Statement类
1)Statement:
由createStatement创建,用于发送简单的SQL语句。(不带参数的)
/* * 测试用Statement接口执行SQl语句 * */ public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement statement = null; try { //加载驱动类 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true", "root", "123456"); statement = conn.createStatement(); /* String name = "张三"; String sql = "insert into testjdbc values(3,'"+name+"',now())"; statement.execute(sql);*/ //测试SQL注入 String id = "3 or 1 =1"; String sql = "delete from testjdbc where id="+id; statement.execute(sql); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if (statement != null) { try { statement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); ///关闭连接 } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
2)PreparedStatement:
继承自Statement接口,由PreparedStatement创建,用于发送含有一个或多个输入参数的SQL语句。PreparedStatement对象比Statement的效率更高,并且可以防止SQL注入。我们一般都用PreparedStatement。
/* * 测试PreparedStatement的基本用法 * */ public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { //加载驱动类 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //建立连接(连接对象内部其实包含了Socket对象,是一个远程连接。比较耗时,这是Connection管理对象的一个要点!) // 真正开发中,为了提高效率,都会使用连接池来管理连接对象! conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true", "root", "123456"); String sql = "insert into testjdbc (name,registerTime)values (?,?)";//占位符,可以防止SQL注入 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //两种方式 ps.setString(1, "小4"); //参数从1开始,而不是0 ps.setDate(2, new Date(System.currentTimeMillis())); ps.setObject(1, "小3"); ps.setObject(2, new java.sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis())); ps.execute(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if (ps != null) { try { ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
3)CallableStatement:
继承自PreparedStatement。由方法preParedCall创建,用于调用存储过程
--常用的Statement方法:
1)execute():运行语句,返回是否有结果集,有结果集为true,没有则为false
2)executeQuery():运行select语句,返回ResultSet结果集
3)executeUpdate():运行insert/update/delete操作,返回更新的行数
5.ResultSet接口:
--Statement执行SQL语句时返回ResultSet结果集。
--ResultSet提供的检索不同类型字段的方法,常用的有:
1)getString():获得在数据库里的varchar,char等数据类型的对象。
2)getFloat():获得在数据库里是Float类型的对象。
3)getDate():获得在数据库里是Date类型的数据。
4)getBoolean():获得在数据库里是Bolean类型的数据。
依次关闭使用之对象及连接:
- ResultSet-->Starement-->Connection
/* * 测试ResultSet的基本用法 * */ public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //加载驱动类 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //建立连接(连接对象内部其实包含了Socket对象,是一个远程连接。比较耗时,这是Connection管理对象的一个要点!) // 真正开发中,为了提高效率,都会使用连接池来管理连接对象! conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true", "root", "123456"); String sql = "select * from testjdbc where id>?";//占位符,可以防止SQL注入 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setObject(1, 2); rs = ps.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getInt(1) + "-->" + rs.getString(2)+"-->"+rs.getDate(3)); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if (rs != null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (ps != null) { try { ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
四、JDBC详细操作
1)灵活指定SQL语句中的变量
-- PreparedStatement
2)对存储过程进行调用
--CallableStatement
3)运用事务处理
--Transaction
4)批处理
--Batch
--对于大量的批处理,建议使用Statement,因为PreparedStatement的预编译空间有限,当数据量特别大时,会发生异常。
/* * 测试JDBC批处理 * */ public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement statement = null; try { //加载驱动类 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //建立连接(连接对象内部其实包含了Socket对象,是一个远程连接。比较耗时,这是Connection管理对象的一个要点!) // 真正开发中,为了提高效率,都会使用连接池来管理连接对象! conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true", "root", "123456"); conn.setAutoCommit(false); //事务默认为自动提交,现在设为手动提交 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); statement = conn.createStatement(); for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) { statement.addBatch("insert into testjdbc (name,registerTime) values ('小"+i+"',now())"); } statement.executeBatch(); conn.commit(); //提交事务 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("插入20000条数据,总耗时(毫秒数):"+(end-start)); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if (statement != null) { try { statement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
五、事务
1.基本概念:一组要么同时执行成功,要么同时执行失败的SQL语句。是数据库操作的一个执行单元!
2.事务开始于:
1>连接到数据库上,并执行一条DML语句(INSERT、UPDATE、SELECT、DELETE)
2>前一个事务结束后,又输入另一条DML语句。
3.事务结束于:
1>执行COMMIT或ROLLBACK语句
2>执行一条DDL语句,例如CREATE TABLE语句;在这种情况下,会自动执行COMMIT语句
3>执行一条DCL语句,例如GRANT语句,在这种情况下,会自动执行COMMIT语句
4>断开与数据库的连接
5>执行了一条DML语句,该语句却失败了;在这种情况下,会为这个无效的DML语句执行ROLLBACK语句
注:
DML(Data manipulation language ):
它们是INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE,这3条命令是用来对数据库里的数据进行操作的语言。
其中,SELECT属于DQL数据查询语言(Data Query Language)。
DDL(Data definition language):
DDL比DML要多,主要的命令有CREATE、ALTER、DROP等,DDL主要是用来定义或改变表(TABLE)的结构,数据类型,表之间的链接和约束等初始化工作上,它们大多在建立表时使用。
DCL(Data Control language):
数据库控制功能。是用来设置或更改数据库用户或角色权限的语句。在默认情况下只有sysadmin,dbcreator,db_owner或db_securityadmin等人员才有权利执行DCL。
4.事务的四大特性(ACID)
1>atomicity(原子性)
表示一个事务内的所有操作是一个整体,要么全部成功,要么全失败。
2>consistency(一致性)
表示一个事务内有一个操作失败时,所有的更改过的数据都必须回滚到修改前的状态。
3>isolation(隔离性)
事务查看数据时数据所处的状态,要么是另一个并发事务修改它之前的状态,要么是另一个事务修改它之后的状态,事务不会查看中间状态的数据。
4>durability(持久性)
持久性事务完成之后,它对于系统的影响是永久性的。
5.事务隔离级别(从低到高):
-读取未提交(Read Uncommitted)
-读取已提交(Read Committed)
-可重复读(Repeatable Read)
-序列化(Serializable)
/* * 测试事务的基本概念和用法 * */ public class Demo06 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; PreparedStatement ps1 = null; try { //加载驱动类 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //建立连接(连接对象内部其实包含了Socket对象,是一个远程连接。比较耗时,这是Connection管理对象的一个要点!) // 真正开发中,为了提高效率,都会使用连接池来管理连接对象! conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true", "root", "123456"); conn.setAutoCommit(false); //默认为true,JDBC中默认自动提交事务 ps = conn.prepareStatement("insert into testjdbc (id,name,registerTime) values (?,?,?)"); ps.setObject(1,1); ps.setObject(2, "张三"); ps.setObject(3, new Date(System.currentTimeMillis())); ps.execute(); System.out.println("插入一个用户"); try { Thread.sleep(6000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } ps1 = conn.prepareStatement("insert into testjdbc (id,name,registerTime) values (?,?,?)"); ps1.setObject(1, 2); ps1.setObject(2, "李四"); ps1.setObject(3, new Date(System.currentTimeMillis())); ps1.execute(); System.out.println("插入一个用户"); conn.commit(); //手动提交事务 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); try { conn.rollback(); //回滚,若某个DML语句出错,则滚回到事务开始前 } catch (SQLException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if (ps1 != null) { try { ps1.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (ps != null) { try { ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
六、时间类型
java.util.Date
-子类:java.sql.Date 表示年月日
-子类java.sql.Time 表示时分秒
-子类java.sql.Timestamp 表示年月日时分秒
日期比较处理
-插入随机日期
-取出指定日期范围的记录
/* * 测试时间处理(java.sql.Date,Time,Timestamp) * */ public class Demo07 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { //加载驱动类 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //建立连接(连接对象内部其实包含了Socket对象,是一个远程连接。比较耗时,这是Connection管理对象的一个要点!) // 真正开发中,为了提高效率,都会使用连接池来管理连接对象! conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true", "root", "123456"); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { ps = conn.prepareStatement("insert into testjdbc (id,name,registerTime,lastLoginTime) values (?,?,?,?)"); ps.setObject(1,i+1); ps.setObject(2, "小刘"+i); int rand =10000000+ new java.util.Random().nextInt(); Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()-rand); ps.setObject(3, date); //Timestamp stamp = new Timestamp(2015, 10, 15, 8, 15, 20, 12); Timestamp stamp = new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()-rand); //如果需要插入指定日期,可以使用Calendar、DateFormat ps.setObject(4,stamp); ps.execute(); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); try { conn.rollback(); //回滚,滚回到事务开始前 } catch (SQLException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if (ps != null) { try { ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
/* * 测试时间处理(java.sql.Date,Time,Timestamp),取出时间段的数据 * */ public class Demo08 { /* * 将字符串代表的日期转为long数字(格式:yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss) * */ public static long str2Date(String dateStr) { DateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"); try { return format.parse(dateStr).getTime(); } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return 0; } } public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //加载驱动类 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); //建立连接(连接对象内部其实包含了Socket对象,是一个远程连接。比较耗时,这是Connection管理对象的一个要点!) // 真正开发中,为了提高效率,都会使用连接池来管理连接对象! conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true", "root", "123456"); /* ps = conn.prepareStatement(" select * from testjdbc where registerTime>? and registerTime<?"); Date start = new Date(str2Date("2018-5-12 10:23:45")); Date end = new Date(str2Date("2018-5-14 10:23:45")); ps.setObject(1, start); ps.setObject(2, end);*/ ps = conn.prepareStatement(" select * from testjdbc where lastLoginTime>? and lastLoginTime<?"); Timestamp start = new Timestamp(str2Date("2018-5-10 10:23:45")); Timestamp end = new Timestamp(str2Date("2018-5-10 13:23:45")); ps.setObject(1, start); ps.setObject(2, end); rs = ps.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getInt(1) + "-->" + rs.getString(2) + "-->" + rs.getDate(4) + "-->" + rs.getTimestamp(5)); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if (rs != null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (ps != null) { try { ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
七、CLOB(Character Large Object)
-用于存储大量文本数据
-大字段有些特殊,不同数据库处理的方式不一样,大字段的操作常常以流的方式来处理。而非一般字段,一次即可读出数据
Mysql中相关类型:
-TINYTEXT最大长度为255(2^[8]-1)字符的TEXT列。
-TEXT最大长度为65,535(2^[16]-1)字符的TEXT列。
-MEDIUMTEXT最大长度为16,777,215(2^[24]-1)字符的TEXT列。
-LONGTEXT最大长度为1,294,967,295或4GB(2^[32]-1)字符的TEXT列。
/* * 测试CLOB 文本大对象的使用 * 包含:将字符串、文件内容插入数据库中的CLOB字段,将CLOB字段值取出来的操作 * */ public class Demo09 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; Reader r = null; try { //加载驱动类 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); //建立连接(连接对象内部其实包含了Socket对象,是一个远程连接。比较耗时,这是Connection管理对象的一个要点!) // 真正开发中,为了提高效率,都会使用连接池来管理连接对象! conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true", "root", "123456"); ps = conn.prepareStatement("insert into testjdbc (id,name,myInfo) values (?,?,?)"); ps.setInt(1, 12); ps.setString(2,"小何"); //将文本文件输入到数据库中 ps.setClob(3, new FileReader("/home/deepin/Desktop/test/test.txt")); // 讲程序中的字符串输入到数据库的CLOB字段中 ps.setClob(3,new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new ByteArrayInputStream("AAAA".getBytes())))); ps.executeUpdate(); ps = conn.prepareStatement("select * from testjdbc where id=?"); ps.setObject(1, 11); rs = ps.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { Clob c = rs.getClob("myInfo"); r = c.getCharacterStream(); int temp = 0; while ((temp = r.read()) != -1) { System.out.print((char) temp); } } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if (r != null) { r.close(); } if (rs != null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (ps != null) { try { ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
八、BLOB(Binary Large Object)
-用于存储大量二进制数据
-大字段有些特殊,不同数据库处理的方式不一样,大字段的操作常常以流的方式来处理。而非一般字段,一次即可读出数据
Mysql中相关类型:
-TINYBLOB最大长度为255(2^[8]-1)字节的BLOB列。
-BLOB最大长度为65,535(2^[16]-1)字节的BLOB列。
-MEDIUMBLOB最大长度为16,777,215(2^[24]-1)字节的BLOB列。
-LONGBLOB最大长度为1,294,967,295或4GB(2^[32]-1)字节的BLOB列。
/* * 测试BLOB 二进制大对象的使用 * */ public class Demo10 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; InputStream is =null; OutputStream os = null; try { //加载驱动类 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); //建立连接(连接对象内部其实包含了Socket对象,是一个远程连接。比较耗时,这是Connection管理对象的一个要点!) // 真正开发中,为了提高效率,都会使用连接池来管理连接对象! conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true", "root", "123456"); ps = conn.prepareStatement("insert into testjdbc (id,name,headImg) values (?,?,?)"); //将图片插入到数据中 ps.setObject(1, 13); ps.setObject(2, "小张"); ps.setBlob(3, new FileInputStream("/home/deepin/Desktop/test/icon.jpg")); ps.execute(); //将数据库中图片信息读出并保存起来 ps = conn.prepareStatement("select * from testjdbc where id=?"); ps.setObject(1, 13); rs = ps.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { Blob c = rs.getBlob("headImg"); is = c.getBinaryStream(); os = new FileOutputStream("/home/deepin/Desktop/test/icon1.jpg"); int temp = 0; while ((temp = is.read()) != -1) { os.write(temp); //System.out.print((char) temp); } } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if (os != null) { os.close(); } if (is != null) { is.close(); } if (rs != null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (ps != null) { try { ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
JDBC总结:
public class JDBCUtil { static Properties pros = null; //可以帮助获取和处理资源文件中的信息 static { //加载JDBCUtil类时调用 pros = new Properties(); try { pros.load(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db")); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //获取oracle连接 public static Connection getOracleConn() { //加载驱动类 try { Class.forName(pros.getProperty("oracleDriver")); return DriverManager.getConnection(pros.getProperty("oracleURL"), pros.getProperty("oracleUser"), pros.getProperty("oraclePwd")); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } //获取数据库连接 public static Connection getMysqlConn() { //加载驱动类 try { Class.forName(pros.getProperty("mysqlDriver")); return DriverManager.getConnection(pros.getProperty("mysqlURL"), pros.getProperty("mysqlUser"), pros.getProperty("mysqlPwd")); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } public static void close( Connection conn) { if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void close(Statement ps, Connection conn) { if (ps != null) { try { ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement ps, Connection conn) { if (rs != null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (ps != null) { try { ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
/* * 测试使用JDBCUtil工具类来简化JDBC开发 * */ public class Demo11 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; conn = JDBCUtil.getMysqlConn(); try { ps = conn.prepareStatement("insert into testjdbc (id,name)values (?,?)"); ps.setInt(1, 16); ps.setString(2, "小四"); ps.execute(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } JDBCUtil.close(rs, ps, conn); } }
资源文件
mysqlDriver:com.mysql.jdbc.Driver mysqlURL:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true mysqlUser=root mysqlPwd=123456 oracleDriver:oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver oracleURL:jdbc:oracle:thin:@host:port/library oracleUser=scott oraclePwd=tiger