EVM
待办清单
- analysis.go
- common.go
- contract.go
- contracts.go
- doc.go
- eips.go
- errors.go
- evm.go
- gas.go
- gas_table.go
- instructions.go
- interface.go
- interpreter.go
- jump_table.go
- logger.go
- memory.go
- memory_table.go
- opcodes.go
- operations_acl.go
- stack.go
- stack_table.go
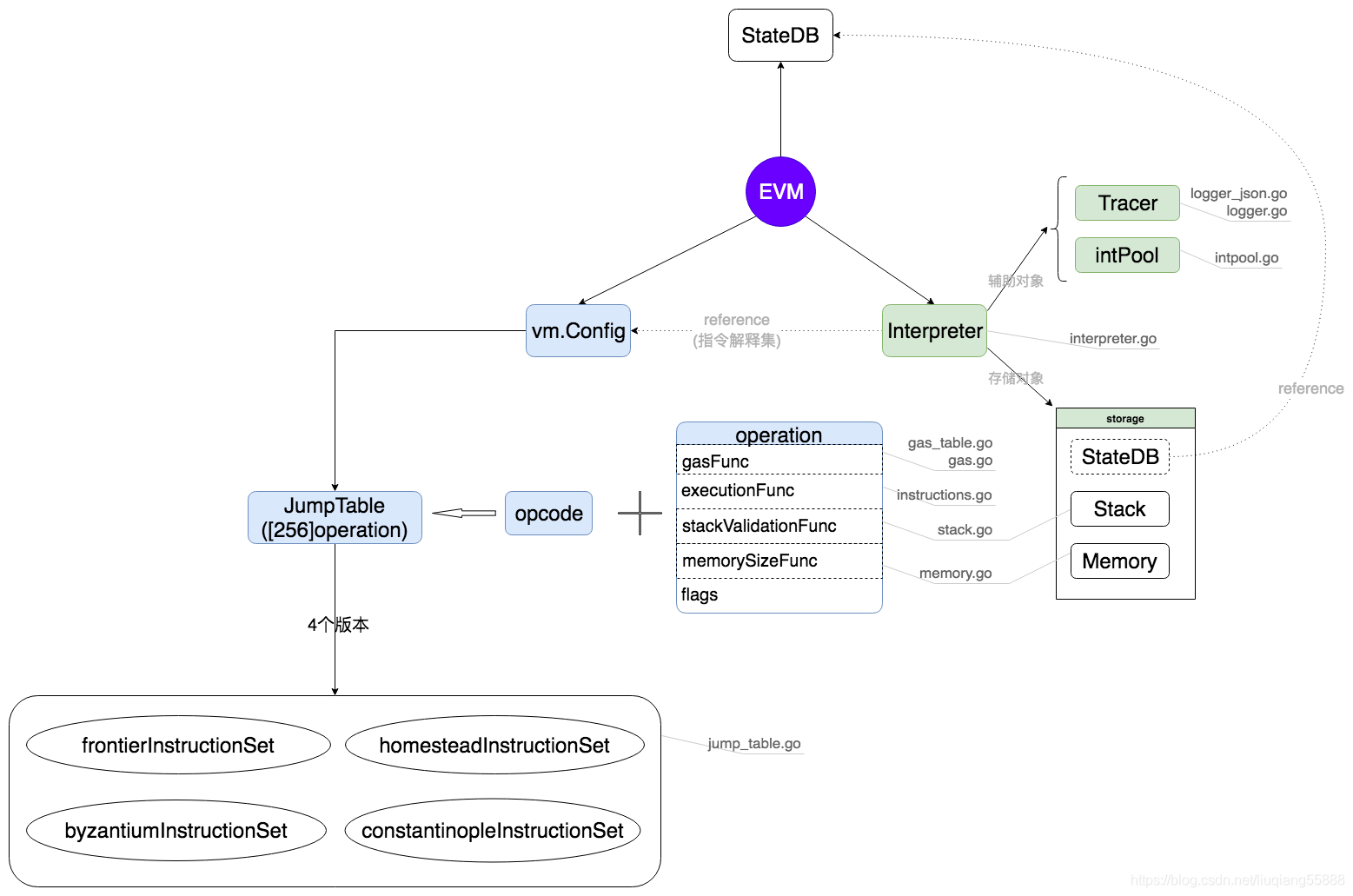
结构与流程
2020年版本的evm结构
大致流程
编写合约 > 生成abi > 解析abi得出指令集 > 指令通过opcode来映射成操作码集 > 生成一个operation[256]
以太坊虚拟机的工作流程:
由solidity语言编写的智能合约,通过编译器编译成bytecode,之后发到以太坊上,以太坊底层通过evm模块支持合约的执行和调用,调用时根据合约获取代码,即合约的字节码,生成环境后载入到 EVM 执行。
opcodes.go
OptionCode(操作码)
OpCode
文件opcodes.go中定义了所有的OpCode,该值是一个byte,合约编译出来的bytecode中,一个OpCode就是上面的一位。opcodes按功能分为9组,以第一位十六进制数来分类,例如0x1x,0x2x。
例如第一组为 算术 操作
// 0x0 range - arithmetic ops.
const (
STOP OpCode = 0x0
ADD OpCode = 0x1
MUL OpCode = 0x2
SUB OpCode = 0x3
DIV OpCode = 0x4
SDIV OpCode = 0x5
MOD OpCode = 0x6
SMOD OpCode = 0x7
ADDMOD OpCode = 0x8
MULMOD OpCode = 0x9
EXP OpCode = 0xa
SIGNEXTEND OpCode = 0xb
)
可以使用表格来总结
| opCodeRange | 对应操作 |
|---|---|
| 0x0 | 算术操作 |
| 0x10 | 比较操作 |
| 0x20 | 加密操作 |
| 0x30 | 状态闭包 |
| 0x40 | 区块操作 |
| 0x50 | 存储和执行操作 |
| 0x60 | 压栈操作 |
| 0x80 | 克隆操作 |
| 0x90 | 交换操作 |
| 0xa0 | 日志操作 |
| 0xf0 | 闭包 |
实现了判断能否压栈、操作码的byte类型和string类型互相转换的函数或接口。
func StringToOp(str string) OpCode
func (op OpCode) String() string
func (op OpCode) IsPush() bool
AddressLength = 20
HashLength = 32
type Address [AddressLength]byte
type bitvec [ ]byte
// Hash represents the 32 byte Keccak256 hash of arbitrary data.
type Hash [HashLength]byte
contract.go
该文件中包含了饭回合约的调用者信息和value、判断gas值是否足够运行合约执行、
合约的结构
type Contract struct {
// CallerAddress is the result of the caller which initialised this
// contract. However when the "call method" is delegated this value
// needs to be initialised to that of the caller's caller.
CallerAddress common.Address
caller ContractRef
self ContractRef
jumpdests map[common.Hash]bitvec // Aggregated result of JUMPDEST analysis.
analysis bitvec // Locally cached result of JUMPDEST analysis
Code []byte
CodeHash common.Hash
CodeAddr *common.Address
Input []byte
Gas uint64
value *big.Int
}
func NewContract(caller ContractRef, object ContractRef, value *big.Int, gas uint64) *Contract
该函数构造了新的合约,且如果是被合约调用,则复用该合约的 jumpdests

func (c *Contract) validJumpdest(dest *uint256.Int) bool
func (c *Contract) isCode(udest uint64) bool
存在两段校验的函数检验代码跳转是否合法以及
- int类型的大小为 8 字节
- int8类型大小为 1 字节
- int16类型大小为 2 字节
- int32类型大小为 4 字节
- int64类型大小为 8 字节
analysis.go
func (c *Contract) AsDelegate() *Contract
AsDelegate将合约设置为委托调用并返回当前合同(用于链式调用)
stack.go
为了应对高并发情况下的栈资源问题,代码中创建了 栈池 来保存一些被创造但未使用的栈空间。
var stackPool = sync.Pool{
New: func() interface{
} {
return &Stack{
data: make([]uint256.Int, 0, 16)}
},
}
除了一些栈该有的基础操作以外,还有:
func (st *Stack) swap(n int) 将从栈顶开始数的第 n 个和栈顶元素交换
func (st *Stack) dup(n int) 复制栈顶元素,并将其压栈
func (st *Stack) Back(n int) *uint256.Int 返回栈底元素
stack_table.go
一些栈的辅助函数
Memory.go
type Memory struct {
store []byte
lastGasCost uint64
}
为以太坊虚拟机提供一个简单存储的模型
func (m *Memory) Set(offset, size uint64, value []byte)
func (m *Memory) Set32(offset uint64, val *uint256.Int)
func (m *Memory) Resize(size uint64)
func (m *Memory) GetCopy(offset, size int64) (cpy []byte) // 截取切片中的一段 (offset,offset+size)
func (m *Memory) GetPtr(offset, size int64) // 返回切片中的一段的指针
func (m *Memory) Len() int
func (m *Memory) Data() []byte
Memory_table.go
衡量一些操作所消耗的内存大小同时判断是否会发生栈溢出,如keccak256、callDataCopy、MStore等
EVM.go
EVM机器位宽为256位,即32个字节,256位机器字宽不同于我们经常见到主流的64位的机器字宽
设计256位宽的原因:
- 时间,智能合约是否能执行得更快
- 空间,这样是否整体字节码的大小会有所减少gas成本
区块上下文
这里的Random same as difficulty(具体是什么还不知道)
前三个为函数类型,依次作用为 查询转账者账户是否有充足ether支持转账操作、转账操作、获取第n个区块的hash
其余为一些基础的区块信息,如币基交易地址、Gaslimit、区块高、时间戳、难度值和基础费用
区块一旦创建,区块信息不可以被修改
type BlockContext struct {
// CanTransfer returns whether the account contains
// sufficient ether to transfer the value
CanTransfer CanTransferFunc
// Transfer transfers ether from one account to the other
Transfer TransferFunc
// GetHash returns the hash corresponding to n
GetHash GetHashFunc
// Block information
Coinbase common.Address // Provides information for COINBASE
GasLimit uint64 // Provides information for GASLIMIT
BlockNumber *big.Int // Provides information for NUMBER
Time *big.Int // Provides information for TIME
Difficulty *big.Int // Provides information for DIFFICULTY
BaseFee *big.Int // Provides information for BASEFEE
Random *common.Hash // Provides information for PREVRANDAO
}
交易上下文
Origin是什么,就是第一个交易
type TxContext struct {
// Message information
Origin common.Address // Provides information for ORIGIN
GasPrice *big.Int // Provides information for GASPRICE
}
EVM结构
evm是以太坊虚拟机基础对象,提供工具处理对应上下文中的交易。运行过程中一旦发生错误,状态会回滚并且不退还gas费用,运行中产生的任务错误都会被归结为代码错误。
type EVM struct
// Context provides auxiliary blockchain related information
Context BlockContext
TxContext
// StateDB gives access to the underlying state
StateDB StateDB
// Depth is the current call stack
depth int
// chainconfig是决定区块链设置的核心配置。
//chainconfig以块为单位存储在数据库中。这意味着
//任何一个网络,通过它的起源块来识别,都可以有它自己的
//一组配置选项。
// 包含了chainId,该链什么时候发生硬分叉,该链难度总和到多少的时候发生更新等信息
chainConfig *params.ChainConfig
// chain rules contains the chain rules for the current epoch
// rules包装了config信息,属于语法糖,是一次性接口,不应
chainRules params.Rules
// virtual machine configuration options used to initialise the
// evm.
// 解释器的配置信息
Config Config
// global (to this context) ethereum virtual machine
// used throughout the execution of the tx.
interpreter *EVMInterpreter
// abort is used to abort the EVM calling operations
// NOTE: must be set atomically
// 能够终止evm调用操作
abort int32
// callGasTemp holds the gas available for the current call. This is needed because the
// available gas is calculated in gasCall* according to the 63/64 rule and later
// applied in opCall*.
callGasTemp uint64
}
创建evm,只能用一次
func NewEVM(blockCtx BlockContext, txCtx TxContext, statedb StateDB, chainConfig *params.ChainConfig, config Config) *EVM
reset EVM的交易上下文和状态数据库
func (evm *EVM) Reset(txCtx TxContext, statedb StateDB)
能够通过原子的修改abort使得取消任何evm操作
func (evm *EVM) Cancel()
func (evm *EVM) Cancelled() bool
合约预编译的作用
预编译合约是 EVM 中用于提供更复杂库函数(通常用于加密、散列等复杂操作)的一种折衷方法,这些函数不适合编写操作码。 它们适用于简单但经常调用的合约,或逻辑上固定但计算量很大的合约。 预编译合约是在使用节点客户端代码实现的,因为它们不需要 EVM,所以运行速度很快。 与使用直接在 EVM 中运行的函数相比,它对开发人员来说成本也更低。
evm调用深度 <= 1024
evm调用contract的步骤
- 判断调用深度是否大于1024
- 判断是否有充足的余额支持调用
- 进行快照和预编译
- 检查该地址是否在状态数据库中存在
- 若不存在,调用一个不存在的帐户,不要做任何事情,只需ping跟踪程序,检查是否是debug模式,若不是则会创建账户
- 判断是否预编译,若是调用节点客户端代码实现;反之,创建合约对象并加载被调用地址和地址的hash以及代码信息,后用解释器来运行
- 若运行过程中有任何错误,则状态将会回滚到操作前快照处,并消耗gas
以太坊中的调用call、callcode和delegatecall
| 调用方式 | 修改的storage | 调用者的msg.sender | 被调用者的msg.sender | 执行的上下文 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| call | 被调用者的storage | 交易发起者的地址 | 调用者的地址 | 被调用者 |
| callcode | 调用者的storage | 调用者的地址 | 调用者的地址 | 调用者 |
| delegatecall | 调用者的storage | 交易发起者的地址 | 调用者的地址 | 调用者 |
还有staticCall调用过程中不允许进行任何修改操作,可以用view来修饰,因此在函数实现中会给解释器的运行函数中的read-only参数传入true值。
创建合约
nonce值指定交易数,每发起一笔交易确认后nonce值+1
interpreter.go
解释器中会有一个配置结构体,能够选择debug模式,包含追踪操作码的evm日志,一些eip提议的配置,evm跳表
type Config struct {
Debug bool // Enables debugging
Tracer EVMLogger // Opcode logger
NoBaseFee bool // Forces the EIP-1559 baseFee to 0 (needed for 0 price calls)
EnablePreimageRecording bool // Enables recording of SHA3/keccak preimages
JumpTable *JumpTable // EVM instruction table, automatically populated if unset
ExtraEips []int // Additional EIPS that are to be enabled
}
范围上下文
解释器结构,包含evm指针,配置信息,hasher??,是否只读,返回数据信息
type EVMInterpreter struct {
evm *EVM
cfg Config
hasher crypto.KeccakState // Keccak256 hasher instance shared across opcodes
hasherBuf common.Hash // Keccak256 hasher result array shared aross opcodes
readOnly bool // Whether to throw on stateful modifications
returnData []byte // Last CALL's return data for subsequent reuse
}
func NewEVMInterpreter(evm *EVM, cfg Config) *EVMInterpreter
传入evm和配置信息构建新的解释器,根据配置信息设置该链的规则,如遵循eip158、eip150提议。
func (in *EVMInterpreter) Run(contract *Contract, input []byte, readOnly bool) (ret []byte, err error)
会控制解释器堆栈调用的深度的加减,同时会用传入的合约、和栈池中调用一个栈来创建一个全新的上下文,并为它新建一个memory模型。
run函数中主要部分是处理一个死循环,只会在停止、返回、自毁和出错的时候停止。
通过循环一直执行合约中的操作,并且每次执行之前都要验证堆栈是否在限制范围之中,还要计算由于动态使用空间导致的动态gas费用,检查完这些之后才会由operation来执行操作。
jump_table.go
operation结构体
type operation struct {
execute executionFunc
constantGas uint64
dynamicGas gasFunc
minStack int // 堆栈中需要已有多少项
maxStack int // 堆栈中最多能有多少项(否则执行这个操作的时候会溢出)
memorySize memorySizeFunc // 返回该操作需要的内存大小
}
其中 executionFunc 有四处实现
func makeLog(size int) executionFunc
func makePush(size uint64, pushByteSize int) executionFunc
func makeDup(size int64) executionFunc
func makeSwap(size int64) executionFunc
memorySizeFunc 的实现在memory_table.go文件中
// memory_table.go
func memoryMLoad(stack *Stack) (uint64, bool) {
return calcMemSize64WithUint(stack.Back(0), 32)
}
func memoryMStore8(stack *Stack) (uint64, bool) {
return calcMemSize64WithUint(stack.Back(0), 1)
}
func memoryMStore(stack *Stack) (uint64, bool) {
return calcMemSize64WithUint(stack.Back(0), 32)
}
// common.go
func calcMemSize64WithUint(off *uint256.Int, length64 uint64) (uint64, bool)
我们可以看到这几个比较熟悉的操作,MLoad、MStore、MStore8 从栈中拿出 偏移量offset地址 + length
查看是否溢出 uint64
Solidity的内存布局将前4个32字节的插槽保留
- 0x00 - 0x3f (64bytes): 暂存空间(Scratch space)
- 0x40 - 0x5f (32bytes): 空闲内存指针
- 0x60 - 0x7f (32bytes): 0 插槽值
他们的作用分别是
- 用来给hash方法和内联汇编使用
- 记录当前已经分配的内存大小,空闲内存的起始值为0x80
- 用作动态内存的初始值,不会被使用
jumpTable包含指向操作的指针
type JumpTable [256]*operation
func validate(jt JumpTable) JumpTable
检查jumpTable中的操作是否为空
我们知道 opsCode是代码的解释器,这里的operation就是opsCode的解释器,interpreter中有一个jumptable,它包含了指向操作的指针,jumptable中的操作就是对应opscode的操作,但是在不同的config配置下,操作集合也会遵循不同的规则。
例如我们可以看看部分代码
// jump_table.go
func newFrontierInstructionSet() JumpTable {
tbl := JumpTable{
STOP: {
execute: opStop,
constantGas: 0,
minStack: minStack(0, 0),
maxStack: maxStack(0, 0),
},
ADD: {
execute: opAdd,
constantGas: GasFastestStep,
minStack: minStack(2, 1),
maxStack: maxStack(2, 1),
},
......
RETURN: {
execute: opReturn,
dynamicGas: gasReturn,
minStack: minStack(2, 0),
maxStack: maxStack(2, 0),
memorySize: memoryReturn,
},
SELFDESTRUCT: {
execute: opSelfdestruct,
dynamicGas: gasSelfdestruct,
minStack: minStack(1, 0),
maxStack: maxStack(1, 0),
},
}
// Fill all unassigned slots with opUndefined.
// 将所有没有指定的插槽填充为 未定义操作
for i, entry := range tbl {
if entry == nil {
tbl[i] = &operation{
execute: opUndefined, maxStack: maxStack(0, 0)}
}
}
return validate(tbl)
}
// opscode.go
// 0x0 range - arithmetic ops.
const (
STOP OpCode = 0x0
ADD OpCode = 0x1
......
EXP OpCode = 0xa
SIGNEXTEND OpCode = 0xb
)
instructions.go
指令集合,封装了操作指定过程中的堆栈操作。
gas.go
const (
GasQuickStep uint64 = 2
GasFastestStep uint64 = 3
GasFastStep uint64 = 5
GasMidStep uint64 = 8
GasSlowStep uint64 = 10
GasExtStep uint64 = 20
)
根据是否遵循EIP150,返回实际的调用产生的费用
gas_table.go
func memoryGasCost(mem *Memory, newMemSize uint64) (uint64, error)
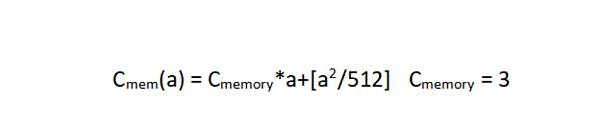
一些操作的gas值计算,如自毁、Call、Callcode、delegateCall、staticCall、内存存储等。
logger.go
EVM的日志接口,由不同的tracer或者logger实现。用于从EVM交易执行中收集执行时的信息,能够追踪交易级、调用级、opcode操作码级的信息。
contracts.go
存放预编译好的合约
common.go
存放常用工具方法
func calcMemSize64(off, l *uint256.Int) (uint64, bool)
func getData(data []byte, start uint64, size uint64) []byte
func toWordSize(size uint64) uint64
func allZero(b []byte) bool
计算内存空间是否溢出、根据给的参数返回数据切片、 返回内存扩展所需的字的大小、判断是否全0
eips.go
实现了许多eip协议的配置函数,可以通过函数的方式使能跳转表,使其能够遵循某个eip规则。
interface.go
包含stateDB、CallContext两种接口,
在evm上,evm字节码是可执行的代码,合约abi是与EVM字节码交互的接口。
ppt中首先介绍web3js , contract abi – json format , evm
contract function 用来支持外部调用,使得应用-合约能够交互,使得合约-合约之间可以联系。
evm bytecode 对应EVM中的一系列的opcode指令
前4个byte是函数名的keccak256的前4个byte 后32byte是十六进制参数 左边用0补齐
所以这个bytecode是4 + 32 = 36 byte