在 Java NIO 中,ByteBuffer 是用于存储和传输数据的一种数据结构。它提供了高效的数据存储和读取能力,使得 Java NIO 能够高效地处理大量的数据输入输出。
ByteBuffer 的作用包括以下几个方面:
-
存储数据:ByteBuffer 可以存储任意长度的数据,可以根据需要动态地分配内存空间。通过 wrap() 方法可以将 ByteBuffer 包装成一个 Java ByteBuffer 对象,使得它可以被序列化和反序列化。
-
读取数据:ByteBuffer 提供了 read() 方法来读取数据,可以读取任意长度的数据,并且可以异步读取。read() 方法返回实际读取的数据长度,如果读取失败,则返回 -1。
-
写入数据:ByteBuffer 提供了 put() 方法来写入数据,可以异步写入数据。put() 方法将数据写入到 ByteBuffer 中,并将其标记为已填充。在写入数据后,可以使用 flush() 方法将数据写入到目的地。
-
连接数据:ByteBuffer 提供了连接数据的功能。通过连接数据,可以将多个数据包组合成一个数据包进行传输。连接数据可以提高数据传输的效率,减少数据传输的延迟。
总之,ByteBuffer 是 Java NIO 中的核心数据结构,它提供了高效的数据存储和读取能力,使得 Java NIO 能够高效地处理大量的数据输入输出。
创建ByteBuffer
@Test
public void createByteBuffer(){
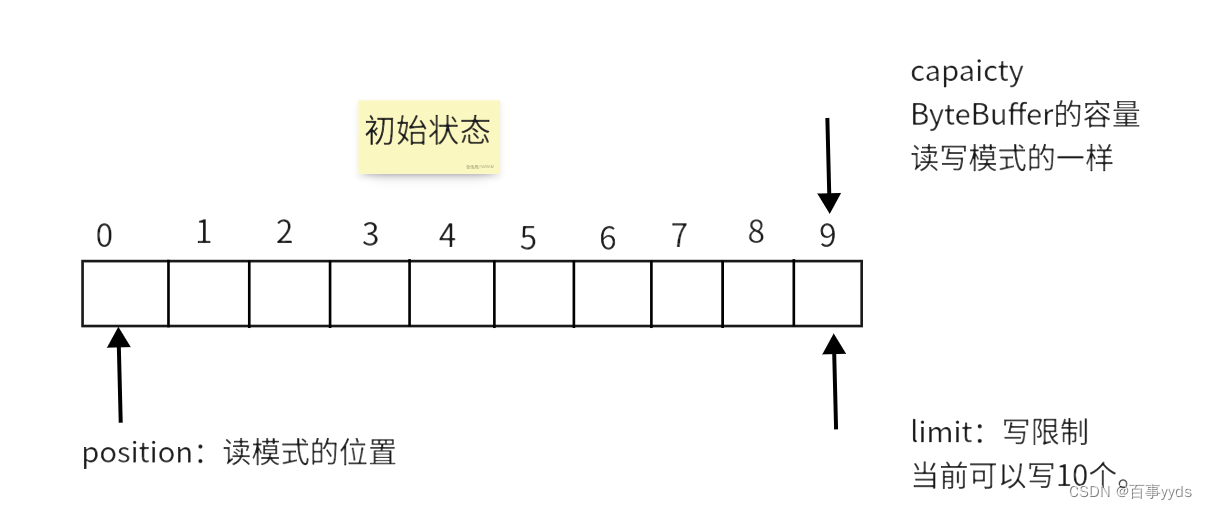
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);//分配堆内存 10字节 受到GC的影响 读写速度较慢
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(10);//分配直接内存 读写速度快 但是要分配内存的事件慢
}
写数据
buffer.put(new byte[]{97,98,99});
buffer.put((byte) 'd');
//channel.read(buffer); 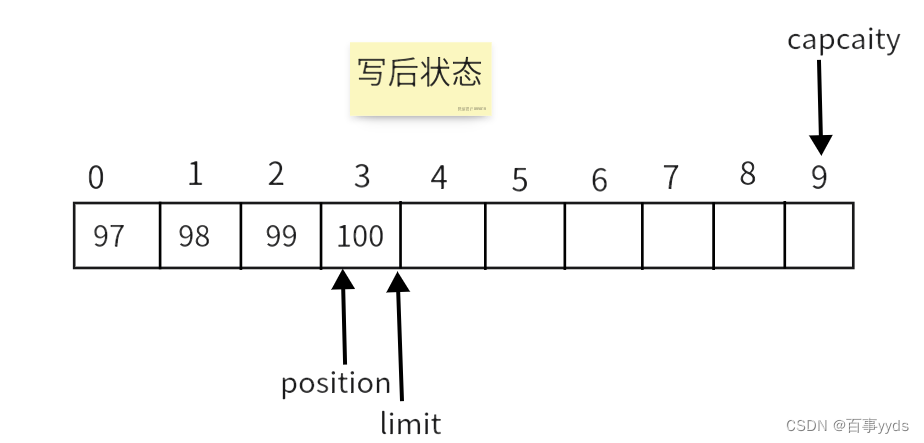
读数据
buffer.flip();//切换读模式
channel.write()//读数据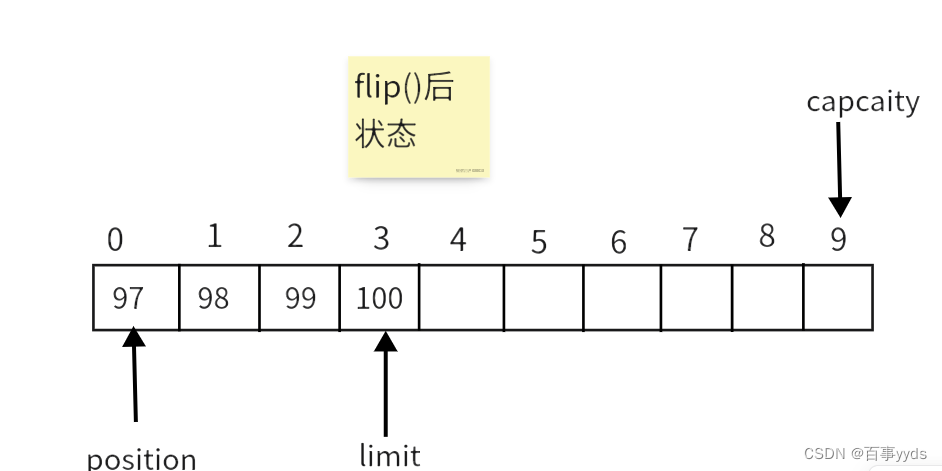
byte b = buffer.get();
System.out.println((char)b);
b = buffer.get();
System.out.println((char)b);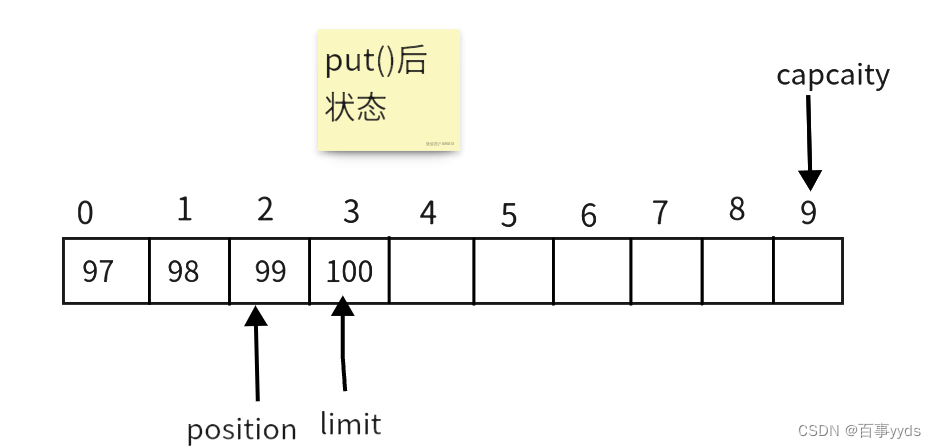
buffer.compact();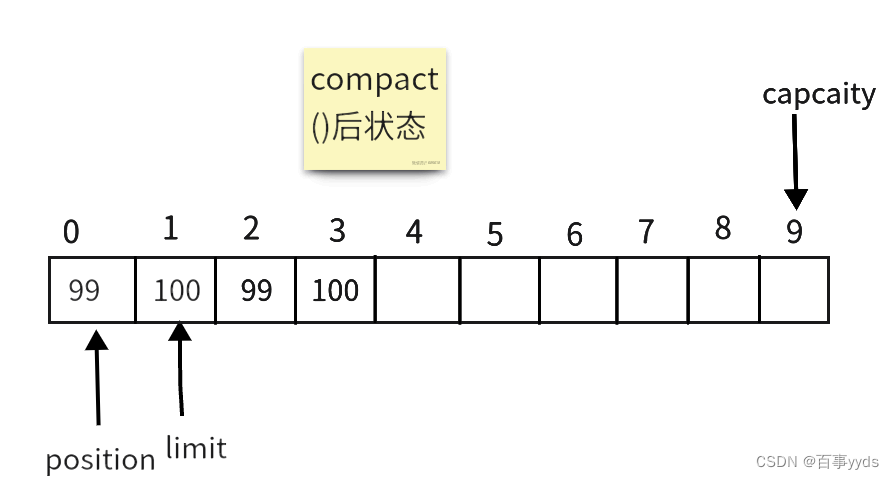
buffer.clear();
System.out.println(buffer.limit());//10 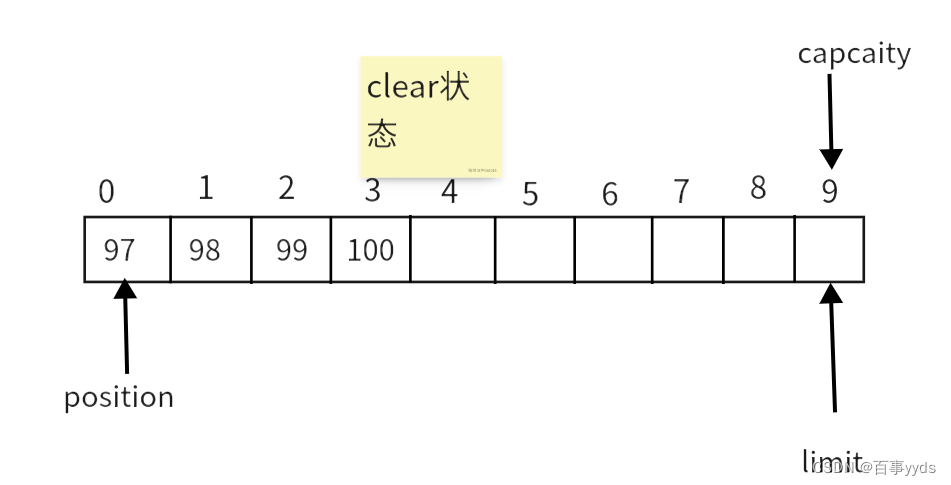
buffer.rewind()// 重新读
ByteBuffer 与字符串的转换
/*
字符串与数组的转换
*/
@Test
public void test(){
//String ------->ByteBuffer
//使用String.getBytes()方法
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(10);
buffer1.put("hello".getBytes());
//使用charset 自动变成读模式也就是position = 0
ByteBuffer buffer2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
//使用ByteBuffer.warp()方法 自动变成读模式
ByteBuffer buffer3 = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes());
//ByteBuffer ---->String
String str2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer2).toString();
System.out.println(str2);
}Scattering Reader
对于已知的数据长度用此方法可以避免字符串的截取
之前的文件内容
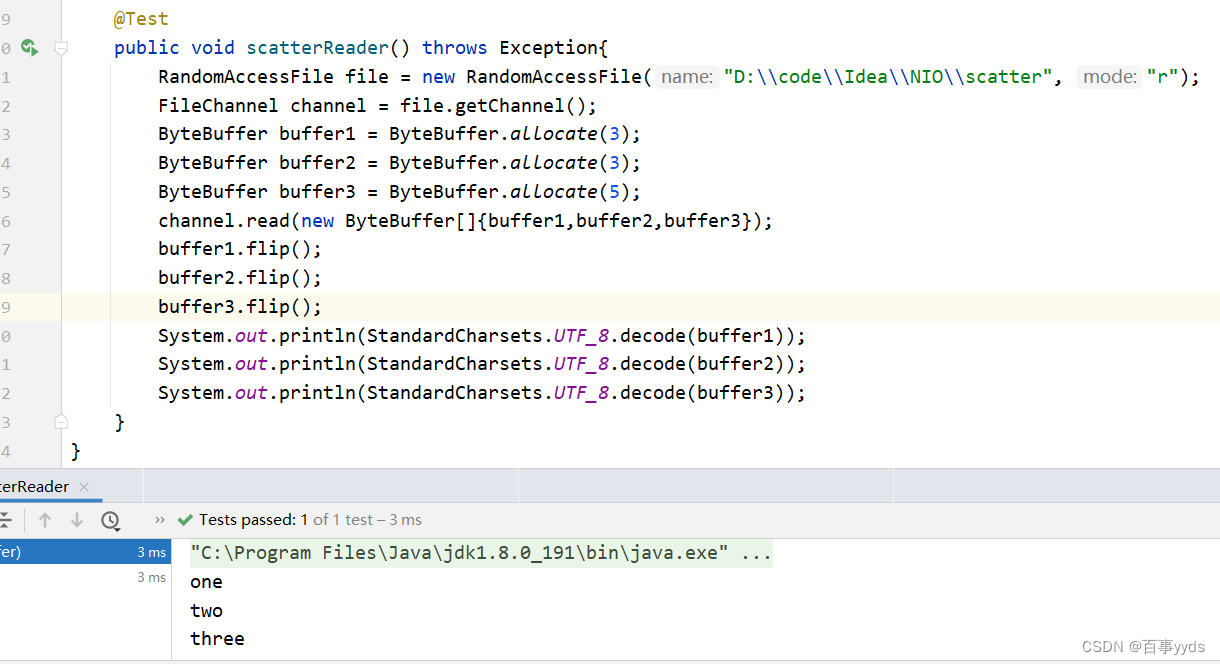
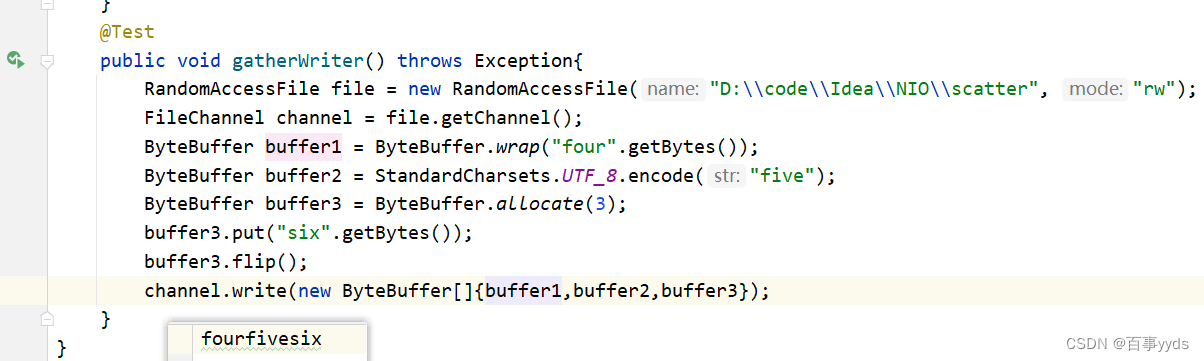
Gathering Writer
减少数据的拷贝与读取的次数
应用 (黏包,半包)
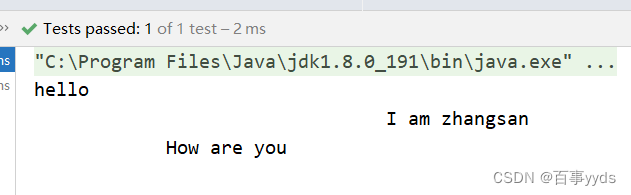
在网络传输过程中。我们可能收到下面的情况。
比如:发送的是hello\n
I am zhangsan\n
How are you\n
三个包
但是我们收到的是hello\nI am zhangsan\nHow
are you\n
两个包
@Test
public void test11() {
ByteBuffer source = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
source.put("hello\nI am zhangsan\nHow ".getBytes());
split(source);
source.put("are you\n".getBytes());
split(source);
}
public void split(ByteBuffer source){
source.flip();
for (int i = 0; i < source.limit(); i++) {
int len = i + 1 - source.position();
if ((char)source.get(i) == '\n'){
byte[] data = new byte[32];
source.get(data,source.position(),len);
for (int j = 0;j<data.length;j++){
System.out.print((char)data[j]);
}
}
}
source.compact();
}