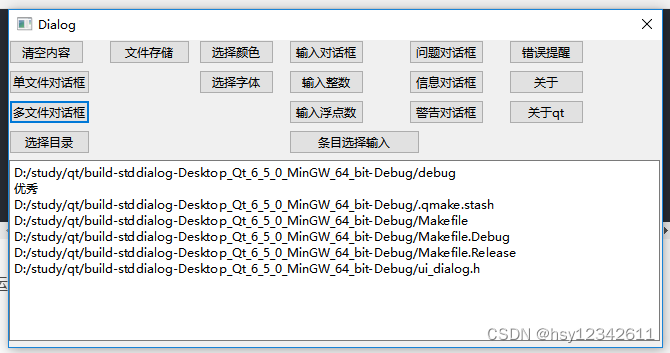
QT编程中对话框作为最常用的窗口经常被使用,本节介绍一些QT常用的标准对话框使用。
目录
1.选择单文件
文件对话框类 QFileDialog 提供了一个允许用户选择文件或文件夹的对话框。
QString fileName = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, tr("文件对话框"), "F:",tr("图片文件(* png * jpg)"));
这个函数的4个参数的作用分别是:指定父窗口、 设置对话框标题、指定默认打开的目录路径和设置文件类型过滤器。如果不指定文件过滤器,默认是选择所有类型的文件。
这里只选择 png 和 jpg 两种格式的图片文件(注意代码中 * png 和 * jpg 之间需要一个空格),那么在打开的文件对话框中只能显示目录下这两种格式的文件。
还可以设置多个不同类别的过滤器,不同类别间使用两个分号 “;;” 隔开,例如添加文本文件类型:
QString fileName = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, tr("文件对话框"), "F:",tr("图片文件(* png * jpg);;文本文件(* txt)"));
(1)样子

(2)调用方式
QString curPath = QDir::currentPath();
QString dlgTitle = "选择对话框";
QString txtLabel = "请选择一个文件";
QString filter = "文本文件(*.txt);;图片文件(*.png *.jpg *.git);;所有格式(*.*)";
QString fileName = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, dlgTitle, curPath, filter);
if (!fileName.isEmpty()) {
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(fileName);
}2.选择多文件
类似单文件选择对话框,QStringList fileNames = QFileDialog::getOpenFileNames(this, tr("文件对话框"), "F:",tr("图片文件(* png * jpg);;文本文件(* txt)"));
除了上面的两个函数,QFileDialog 类还提供了 getSaveFileName() 函数来实现保存文件对话框和文件另存为对话框,还有 getExistingDirectory() 函数来获取一个已存在的文件夹路径。
(1)样子
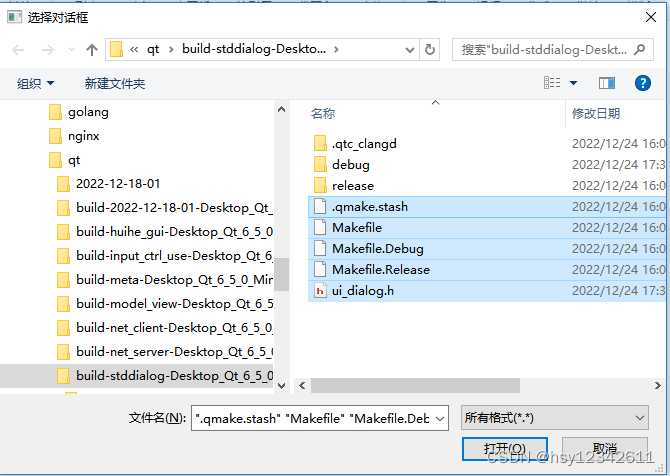
(2)调用方式
QString curPath = QDir::currentPath();
QString dlgTitle = "选择对话框";
QString txtLabel = "请选择需要的文件";
QString filter = "文本文件(*.txt);;图片文件(*.png *.jpg *.git);;所有格式(*.*)";
QStringList fileNameList = QFileDialog::getOpenFileNames(this, dlgTitle, curPath, filter);
if (fileNameList.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
//foreach(auto str, fileNameList) {
for (auto item : fileNameList) {
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(item);
}3.选择目录
(1)样子

(2)调用方式
QString curPath = QDir::currentPath();
QString dlgTitle = "选择对话框";
QString filter = "文本文件(*.txt);;图片文件(*.png *.jpg *.git);;所有格式(*.*)";
QString strDir = QFileDialog::getExistingDirectory(this, dlgTitle, curPath, QFileDialog::ShowDirsOnly);
if (strDir.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(strDir);4.文件存储
(1)样子
 (2)调用方式
(2)调用方式
QString curPath = QDir::currentPath();
QString dlgTitle = "选择对话框";
QString filter = "文本文件(*.txt);;图片文件(*.png *.jpg *.git);;所有格式(*.*)";
QString strFile = QFileDialog::getSaveFileName(this, dlgTitle, curPath, filter);
if (strFile.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(strFile);5.选择颜色
颜色对话框类 QColorDialog 提供了一个可以获取指定颜色的对话框部件。
/*** 第一种方式 ***/
//QColor color = QColorDialog::getColor(Qt::red, this, tr("颜色对话框"),QColorDialog::ShowAlphaChannel);
//qDebug() <<"color:" <<color;
/*** 第二种方式 ***/
QColorDialog dialog(Qt::red, this); // 创建对象
dialog.setOption(QColorDialog::ShowAlphaChannel); // 显示 alpha 选项
dialog.exec(); // 以模态方式运行对话框
QColor color = dialog.currentColor(); // 获取颜色对话框当前颜色
qDebug() <<"color:" <<color; // 输出颜色信息
第一种方式,使用了 QColorDialog 的静态函数 getColor() 来获取颜色,它的3个参数的作用分别是设置初始颜色、父窗口和对话框标题。第一种方式的好处是不用不用创建对象。但是如果想要更灵活地设置时,采用第二种方式,先创建对象,然后进行各项设置。两者的实现效果是等效的。
颜色对话框类 QColorDialog 提供了一个可以获取指定颜色的对话框部件。
/*** 第一种方式 ***/
//QColor color = QColorDialog::getColor(Qt::red, this, tr("颜色对话框"),QColorDialog::ShowAlphaChannel);
//qDebug() <<"color:" <<color;
/*** 第二种方式 ***/
QColorDialog dialog(Qt::red, this); // 创建对象
dialog.setOption(QColorDialog::ShowAlphaChannel); // 显示 alpha 选项
dialog.exec(); // 以模态方式运行对话框
QColor color = dialog.currentColor(); // 获取颜色对话框当前颜色
qDebug() <<"color:" <<color; // 输出颜色信息
第一种方式,使用了 QColorDialog 的静态函数 getColor() 来获取颜色,它的3个参数的作用分别是设置初始颜色、父窗口和对话框标题。第一种方式的好处是不用不用创建对象。但是如果想要更灵活地设置时,采用第二种方式,先创建对象,然后进行各项设置。两者的实现效果是等效的。
(1)样子
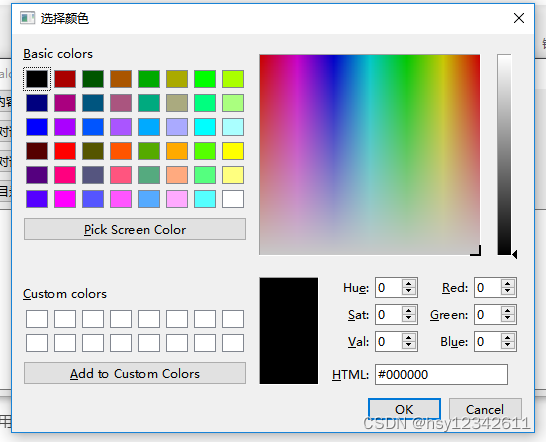
(2)调用方式
QPalette pal = ui->plainTextEdit->palette();
QColor inColor = pal.color(QPalette::Text);
QColor color = QColorDialog::getColor(inColor, this, "选择颜色");
if (!color.isValid()) {
return;
}
pal.setColor(QPalette::Text, color);
ui->plainTextEdit->setPalette(pal);6.选择字体
字体对话框 QFontDialog 类提供了一个可以选择字体的对话框部件。
// ok 用于标记是否单击了 OK 按钮。然后获得选择的字体
bool ok;
QFont font = QFontDialog::getFont(&ok, this);
// 如果单击 Cancel 按钮,那么更改字体
if (ok)
ui->pushButton_3->setFont(font);
else
qDebug() <<tr("没有选择字体!");
这里使用了 QFileDidog 类的 getFont() 静态函数来获取选择的字体。第一个参数是 bool 类型变量,用来存放按下的按钮状态,比如在打开的字体对话框中单击了 OK 按钮,那么这里的 ok 就为 true,从而告诉用户已经选择了字体。
(1)样子

(2)调用方式
bool ok = false;
QFont inFont = ui->plainTextEdit->font();
QFont font = QFontDialog::getFont(&ok, inFont, this, "选择字体");
if (!ok) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->setFont(font);7.输入字符换/整数/浮点数/条目
输人对话框 QInputDialog 类用来提供一个简单方便的对话框,从而从用户那里获取一个单一的数值或字符串。
bool ok;
// 获取字符串
QString string = QInputDialog::getText(this, tr("输入字符串对话框"),tr("请输入用户名:"),QLineEdit::Normal, tr("admin"), &ok);
if(ok)
qDebug() <<tr("string:") <<string;
// 获取整数
int value1 = QInputDialog::getInt(this, tr("输入整数对话框"),tr("请输入 -1000到1000之间的数值"), 100, -1000, 1000, 10, &ok);
if(ok)
qDebug() <<tr("value1:") <<value1;
// 获取浮点数
double value2 = QInputDialog::getDouble(this, tr("输入浮点数对话框"),tr("请输入-1000到1000之间的数值"), 0.00, -1000, 1000, 2, &ok);
if(ok) qDebug() << "value2:" << value2;
// 获取条目
QString item = QInputDialog::getItem(this, tr("输入条目对话框"),tr("请选择或输入一个条目"), items, 0, true, &ok);
if(ok) qDebug() << "item:" << item;
这里一共创建了 4 个不同类型的输入对话框。
getText() 函数可以提供一个可输入字符串的对话框,参数的作用分别是:指定父窗口、设置窗口标题、设置对话框中的标签的显示文本、设置输入的字符串的显示模式、设置输人框中的默认字符串和设置获取按下按钮信息的 bool 变量。
getInt() 函数可以提供一个输入整型数值的对话框,其中的参数100表示默认的数值是100,-1000表示可输入的最小值是-1000,1000表示可输人的最大值是1000,10表示使用箭头按钮,数值每次变化10。
getDouble() 函数可以提供一 个输人浮点型数值的对话框,其中的参数2表示小数的位数为2。
getltem() 函数提供一个可以输入一个条目的对话框,需要先给它提供一些条目,例如这里定义的QStringList类型的items。它的参数0表示默认显示列表中的第0个条目;然后是参数true,设置条目是否可以被更改,true就是可以被更改。
(1)样子
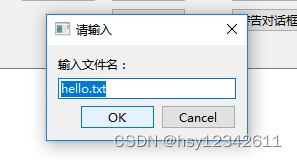



(2)调用方式
QString dlgTitle = "输入文字对话框";
bool ok = false;
QString str = QInputDialog::getText(this, "请输入", "输入文件名:", QLineEdit::Normal, "hello.txt", &ok);
if (!ok) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(str);
QString dlgTitle = "输入整数对话框";
QString strLabel = "请输入整数";
int defaultValue = ui->plainTextEdit->font().pointSize();
int minValue = 0;
int maxValue = 100;
bool ok = false;
int value = QInputDialog::getInt(this, dlgTitle, strLabel, defaultValue, minValue, maxValue, 1, &ok);
if (!ok) {
return;
}
QFont font = ui->plainTextEdit->font();
font.setPointSize(value);
ui->plainTextEdit->setFont(font);
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(QString::asprintf("输入整数: %d", value));
QString dlgTitle = "输入浮点数对话框";
QString strLabel = "请输入浮点数";
double defaultValue = 23.345;
double minValue = 0;
double maxValue = 100;
bool ok = false;
double value = QInputDialog::getDouble(this, dlgTitle, strLabel, defaultValue, minValue, maxValue, 2, &ok);
if (!ok) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(QString::asprintf("输入浮点数: %f", value));
QStringList items;
items << "不及格" << "及格" << "良好" << "优秀";
QString dlgTitle = "输入条目对话框";
QString strLabel = "请选择条目";
bool ok = false;
QString text = QInputDialog::getItem(this, dlgTitle, strLabel, items, 0, true, &ok);
if (!ok || text.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(text);QStringList items;
items << "不及格" << "及格" << "良好" << "优秀";
QString dlgTitle = "输入条目对话框";
QString strLabel = "请选择条目";
bool ok = false;
QString text = QInputDialog::getItem(this, dlgTitle, strLabel, items, 0, true, &ok);
if (!ok || text.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(text);8.消息对话框
消息对话框 QMessageBox 类提供了 一个模态的对话框用来通知用户一些信息,或者向用户提出一个问题并且获取答案。
// 问题对话框
int ret1 = QMessageBox::question(this, tr("问题对话框"),tr("你了解Qt吗?"), QMessageBox::Yes, QMessageBox::No);
if(ret1 == QMessageBox::Yes)
qDebug() << tr("问题!");
// 提示对话框
int ret2 = QMessageBox::information(this, tr("提示对话框"),tr("这是Qt书籍!"), QMessageBox::Ok);
if(ret2 == QMessageBox::Ok)
qDebug() << tr("提示!");
// 警告对话框
int ret3 = QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("警告对话框"),tr("不能提前结束!"), QMessageBox::Abort);
if(ret3 == QMessageBox::Abort)
qDebug() << tr("警告!");
// 错误对话框
int ret4 = QMessageBox::critical(this, tr("严重错误对话框"),tr("发现一个严重错误!现在要关闭所有文件!"), QMessageBox::YesAll);
if(ret4 == QMessageBox::YesAll)
qDebug() << tr("错误");
// 关于对话框
QMessageBox::about(this, tr("关于对话框"),tr("yafeilinux致力于Qt及Qt Creator的普及工作!"));
这里创建了4个不同类型的消息对话框,分别拥有不同的图标及提示音(这个是操作系统设置的),参数分别是父窗口、标题栏、显示信息和拥有的按钮。这里使用的按钮都是 QMessageBox 类提供的标准按钮,可以根据返回值来判断用户按下了哪个按钮。
about() 函数没有返回值,因为它默认只有一个按钮,与其相似的还有一个 aboutQt() 函数,用来显示现在使用的 Qt 版本等相关信息。如果想使用自己的图标和自定义按钮,那么可以创建 QMessageBox 类对象,然后使用相关函数进行操作。
(1)样子

(2)调用方式
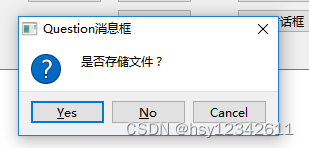
QString dlgTitle = "Question消息框";
QString strLabel = "是否存储文件?";
QMessageBox::StandardButtons result;
result = QMessageBox::question(this, dlgTitle, strLabel, QMessageBox::Yes|QMessageBox::No|QMessageBox::Cancel,
QMessageBox::NoButton);
QString str;
if (QMessageBox::Yes == result) {
str = "Yes被选中";
}
else if (QMessageBox::No== result) {
str = "No被选中";
}
else if (QMessageBox::Cancel == result) {
str = "Cancel被选中";
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(str);
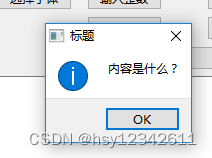
QMessageBox::information(this, "标题", "内容是什么?", QMessageBox::Ok);
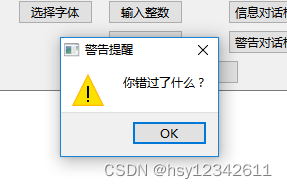
QMessageBox::warning(this, "警告提醒", "你错过了什么?", QMessageBox::Ok);
QMessageBox::critical(this, "异常提醒", "不好了,出错了", QMessageBox::Ok);
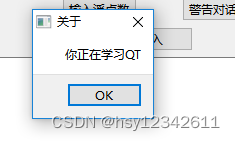
QMessageBox::about(this, "关于", "你正在学习QT");
9.进度对话框
进度对话框 QProgressDialog 对一个耗时较长的操作进度提供了反馈。
QProgressDialog dialog(tr("文件复制进度"), tr("取消"), 0, 50000, this);
dialog.setWindowTitle(tr("进度对话框")); // 设置窗口标题
dialog.setWindowModality(Qt::WindowModal); // 将对话框设置为模态
dialog.show();
// 演示复制进度
for(int i=0; i<50000; i++)
{
dialog.setValue(i); // 设置进度条的当前值
QCoreApplication::processEvents(); // 避免界面冻结
if(dialog.wasCanceled()) // 按下取消按钮则中断
break;
}
dialog.setValue(50000); // 这样才能显示100%,因为for循环中少加了一个数
qDebug() << tr("复制结束!");
这里创建了一个 QProgressDialog 类对象 dialog,构造函数的参数分别为对话框的标签内容、取消按钮的显示文本、最小值、最大值和父窗口。然后将其设置为了模态对话框并显示。
后面的 for() 循环语句模拟了文件复制过程,使用 setValue() 函数使进度条向前推进。为了避免长时间的操作而使用户界面冻结,必须不断调用 QCoreApplication 类的静态函数 processEvents (), 可以将它放在 for() 循环语句中。
然后使用 QProgressDialog 的 wasCanceled() 函数来判断用户是否单击了 “取消”按钮,如果是, 则中断复制过程。这里使用了模态对话框,其实 QProgressDialog 还可以实现非模态对话框,不过它需要定时器等的帮助。
进度对话框 QProgressDialog 对一个耗时较长的操作进度提供了反馈。
QProgressDialog dialog(tr("文件复制进度"), tr("取消"), 0, 50000, this);
dialog.setWindowTitle(tr("进度对话框")); // 设置窗口标题
dialog.setWindowModality(Qt::WindowModal); // 将对话框设置为模态
dialog.show();
// 演示复制进度
for(int i=0; i<50000; i++)
{
dialog.setValue(i); // 设置进度条的当前值
QCoreApplication::processEvents(); // 避免界面冻结
if(dialog.wasCanceled()) // 按下取消按钮则中断
break;
}
dialog.setValue(50000); // 这样才能显示100%,因为for循环中少加了一个数
qDebug() << tr("复制结束!");
这里创建了一个 QProgressDialog 类对象 dialog,构造函数的参数分别为对话框的标签内容、取消按钮的显示文本、最小值、最大值和父窗口。然后将其设置为了模态对话框并显示。
后面的 for() 循环语句模拟了文件复制过程,使用 setValue() 函数使进度条向前推进。为了避免长时间的操作而使用户界面冻结,必须不断调用 QCoreApplication 类的静态函数 processEvents (), 可以将它放在 for() 循环语句中。
然后使用 QProgressDialog 的 wasCanceled() 函数来判断用户是否单击了 “取消”按钮,如果是, 则中断复制过程。这里使用了模态对话框,其实 QProgressDialog 还可以实现非模态对话框,不过它需要定时器等的帮助。
进度对话框 QProgressDialog 对一个耗时较长的操作进度提供了反馈。
QProgressDialog dialog(tr("文件复制进度"), tr("取消"), 0, 50000, this);
dialog.setWindowTitle(tr("进度对话框")); // 设置窗口标题
dialog.setWindowModality(Qt::WindowModal); // 将对话框设置为模态
dialog.show();
// 演示复制进度
for(int i=0; i<50000; i++)
{
dialog.setValue(i); // 设置进度条的当前值
QCoreApplication::processEvents(); // 避免界面冻结
if(dialog.wasCanceled()) // 按下取消按钮则中断
break;
}
dialog.setValue(50000); // 这样才能显示100%,因为for循环中少加了一个数
qDebug() << tr("复制结束!");
这里创建了一个 QProgressDialog 类对象 dialog,构造函数的参数分别为对话框的标签内容、取消按钮的显示文本、最小值、最大值和父窗口。然后将其设置为了模态对话框并显示。
后面的 for() 循环语句模拟了文件复制过程,使用 setValue() 函数使进度条向前推进。为了避免长时间的操作而使用户界面冻结,必须不断调用 QCoreApplication 类的静态函数 processEvents (), 可以将它放在 for() 循环语句中。
然后使用 QProgressDialog 的 wasCanceled() 函数来判断用户是否单击了 “取消”按钮,如果是, 则中断复制过程。这里使用了模态对话框,其实 QProgressDialog 还可以实现非模态对话框,不过它需要定时器等的帮助。
进度对话框 QProgressDialog 对一个耗时较长的操作进度提供了反馈。
QProgressDialog dialog(tr("文件复制进度"), tr("取消"), 0, 50000, this);
dialog.setWindowTitle(tr("进度对话框")); // 设置窗口标题
dialog.setWindowModality(Qt::WindowModal); // 将对话框设置为模态
dialog.show();
// 演示复制进度
for(int i=0; i<50000; i++)
{
dialog.setValue(i); // 设置进度条的当前值
QCoreApplication::processEvents(); // 避免界面冻结
if(dialog.wasCanceled()) // 按下取消按钮则中断
break;
}
dialog.setValue(50000); // 这样才能显示100%,因为for循环中少加了一个数
qDebug() << tr("复制结束!");
这里创建了一个 QProgressDialog 类对象 dialog,构造函数的参数分别为对话框的标签内容、取消按钮的显示文本、最小值、最大值和父窗口。然后将其设置为了模态对话框并显示。
后面的 for() 循环语句模拟了文件复制过程,使用 setValue() 函数使进度条向前推进。为了避免长时间的操作而使用户界面冻结,必须不断调用 QCoreApplication 类的静态函数 processEvents (), 可以将它放在 for() 循环语句中。
然后使用 QProgressDialog 的 wasCanceled() 函数来判断用户是否单击了 “取消”按钮,如果是, 则中断复制过程。这里使用了模态对话框,其实 QProgressDialog 还可以实现非模态对话框,不过它需要定时器等的帮助。
10.向导对话框
向导对话框 QWizard 类提供了一个设计向导界面的框架。对于向导对话框读者应该已经很熟悉了,比如安装软件时的向导和创建项目时的向导。QWizard之所以被称为框架,是因为它具有设计一个向导的全部功能函数,可以使用它来实现想要的效果。Qt 演示程序中的 Dialogs 分类下有 Trivial Wizard、License Wizard 和 Class Wizard这3个示例程序,可以参考一下。
这里定义了 3 个返回值为 QWizardPage 类对象的指针的函数,用来生成3个向导页面:
QWizardPage * MyWidget::createPage1() // 向导页面1
{
QWizardPage *page = new QWizardPage;
page->setTitle(tr("介绍"));
return page;
}
QWizardPage * MyWidget::createPage2() // 向导页面2
{
QWizardPage *page = new QWizardPage;
page->setTitle(tr("用户选择信息"));
return page;
}
QWizardPage * MyWidget::createPage3() // 向导页面3
{
QWizardPage *page = new QWizardPage;
page->setTitle(tr("结束"));
return page;
}
// 向导对话框
void MyWidget::on_pushButton_clicked()
{
QWizard wizard(this);
wizard.setWindowTitle(tr("向导对话框"));
wizard.addPage(createPage1()); // 添加向导页面
wizard.addPage(createPage2());
wizard.addPage(createPage3());
wizard.exec();
}
这里新建了 QWizard 类对象,然后使用 addPage() 函数为其添加了 3 个页面,这里的参数是 QWizardPage 类型的指针,所以直接使用了生成向导页面函数。运行程序可以看到,向导页面出现的顺序和添加向导页面的顺序是一致的。
其他对话框:
还有3个与打印有关的标准对话框类QPageSetupDialog(页面设置对话框)、QPrintDialog(打印对话框)和 QPrintPreviewDialog(打印预览对话框)这里暂时不介绍。关于这些对话框的使用,Qt提供了一个示例程序 Standard Dialogs,它在 Dialogs 分类中。
完整代码如下:
#include "dialog.h"
#include "ui_dialog.h"
#include <QDir>
#include <QFileDialog>
#include <QColorDialog>
#include <QFontDialog>
#include <QInputDialog>
#include <QMessageBox>
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Dialog)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
delete ui;
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonClear_clicked()
{
ui->plainTextEdit->clear();
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonFile_clicked()
{
QString curPath = QDir::currentPath();
QString dlgTitle = "选择对话框";
QString txtLabel = "请选择一个文件";
QString filter = "文本文件(*.txt);;图片文件(*.png *.jpg *.git);;所有格式(*.*)";
QString fileName = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, dlgTitle, curPath, filter);
if (!fileName.isEmpty()) {
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(fileName);
}
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonMulFile_clicked()
{
QString curPath = QDir::currentPath();
QString dlgTitle = "选择对话框";
QString txtLabel = "请选择需要的文件";
QString filter = "文本文件(*.txt);;图片文件(*.png *.jpg *.git);;所有格式(*.*)";
QStringList fileNameList = QFileDialog::getOpenFileNames(this, dlgTitle, curPath, filter);
if (fileNameList.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
//foreach(auto str, fileNameList) {
for (auto item : fileNameList) {
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(item);
}
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonSelDir_clicked()
{
QString curPath = QDir::currentPath();
QString dlgTitle = "选择对话框";
QString filter = "文本文件(*.txt);;图片文件(*.png *.jpg *.git);;所有格式(*.*)";
QString strDir = QFileDialog::getExistingDirectory(this, dlgTitle, curPath, QFileDialog::ShowDirsOnly);
if (strDir.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(strDir);
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonFileSave_clicked()
{
QString curPath = QDir::currentPath();
QString dlgTitle = "选择对话框";
QString filter = "文本文件(*.txt);;图片文件(*.png *.jpg *.git);;所有格式(*.*)";
QString strFile = QFileDialog::getSaveFileName(this, dlgTitle, curPath, filter);
if (strFile.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(strFile);
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonSelColor_clicked()
{
QPalette pal = ui->plainTextEdit->palette();
QColor inColor = pal.color(QPalette::Text);
QColor color = QColorDialog::getColor(inColor, this, "选择颜色");
if (!color.isValid()) {
return;
}
pal.setColor(QPalette::Text, color);
ui->plainTextEdit->setPalette(pal);
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonSelFont_clicked()
{
bool ok = false;
QFont inFont = ui->plainTextEdit->font();
QFont font = QFontDialog::getFont(&ok, inFont, this, "选择字体");
if (!ok) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->setFont(font);
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonInput_clicked()
{
QString dlgTitle = "输入文字对话框";
bool ok = false;
QString str = QInputDialog::getText(this, "请输入", "输入文件名:", QLineEdit::Normal, "hello.txt", &ok);
if (!ok) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(str);
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonInputIntItemSel_clicked()
{
QStringList items;
items << "不及格" << "及格" << "良好" << "优秀";
QString dlgTitle = "输入条目对话框";
QString strLabel = "请选择条目";
bool ok = false;
QString text = QInputDialog::getItem(this, dlgTitle, strLabel, items, 0, true, &ok);
if (!ok || text.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(text);
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonInputIntFloat_clicked()
{
QString dlgTitle = "输入浮点数对话框";
QString strLabel = "请输入浮点数";
double defaultValue = 23.345;
double minValue = 0;
double maxValue = 100;
bool ok = false;
double value = QInputDialog::getDouble(this, dlgTitle, strLabel, defaultValue, minValue, maxValue, 2, &ok);
if (!ok) {
return;
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(QString::asprintf("输入浮点数: %f", value));
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonInputInt_clicked()
{
QString dlgTitle = "输入整数对话框";
QString strLabel = "请输入整数";
int defaultValue = ui->plainTextEdit->font().pointSize();
int minValue = 0;
int maxValue = 100;
bool ok = false;
int value = QInputDialog::getInt(this, dlgTitle, strLabel, defaultValue, minValue, maxValue, 1, &ok);
if (!ok) {
return;
}
QFont font = ui->plainTextEdit->font();
font.setPointSize(value);
ui->plainTextEdit->setFont(font);
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(QString::asprintf("输入整数: %d", value));
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonQuestion_clicked()
{
QString dlgTitle = "Question消息框";
QString strLabel = "是否存储文件?";
QMessageBox::StandardButtons result;
result = QMessageBox::question(this, dlgTitle, strLabel, QMessageBox::Yes|QMessageBox::No|QMessageBox::Cancel,
QMessageBox::NoButton);
QString str;
if (QMessageBox::Yes == result) {
str = "Yes被选中";
}
else if (QMessageBox::No== result) {
str = "No被选中";
}
else if (QMessageBox::Cancel == result) {
str = "Cancel被选中";
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(str);
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonInformation_clicked()
{
QMessageBox::information(this, "标题", "内容是什么?", QMessageBox::Ok);
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonWarnning_clicked()
{
QMessageBox::warning(this, "警告提醒", "你错过了什么?", QMessageBox::Ok);
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonError_clicked()
{
QMessageBox::critical(this, "异常提醒", "不好了,出错了", QMessageBox::Ok);
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonAboutQt_clicked()
{
QMessageBox::aboutQt(this, "标题");
}
void Dialog::on_pushButtonAbout_clicked()
{
QMessageBox::about(this, "关于", "你正在学习QT");
}
运行效果: