SWM32S单片机有1个SDIO接口,支持多媒体卡(MMC)、SD 存储卡、SDIO 卡等设备,可以使用软件方法或者 DMA 方法(SDIO 模块内部 DMA,与芯片 DMA 模块无关)进行数据传输。其特点如下:

1.SDIO配置
SDIO的引脚不像UART和SPI等数字外设一样可以灵活配置,它是固定的几个引脚,如下图
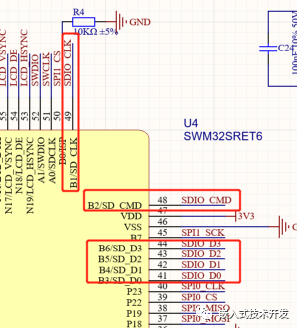
使用起来也比较简单,相关的库函数已经封装好了,直接调用就行。
首先需要配置一下相关引脚的复用功能为SDIO:
PORT_Init(PORTB, PIN1, PORTB_PIN1_SD_CLK, 0);
PORT_Init(PORTB, PIN2, PORTB_PIN2_SD_CMD, 1);
PORT_Init(PORTB, PIN3, PORTB_PIN3_SD_D0, 1);
PORT_Init(PORTB, PIN4, PORTB_PIN4_SD_D1, 1);
PORT_Init(PORTB, PIN5, PORTB_PIN5_SD_D2, 1);
PORT_Init(PORTB, PIN6, PORTB_PIN6_SD_D3, 1);然后直接调用初始化的函数就行:
result = SDIO_Init(10000000);其中形参为SDIO的时钟频率。
SD卡读写的相关函数也已经封装好了,包括DMA和非DMA方式,直接调用即可:
uint32_t SDIO_BlockWrite(uint32_t block_addr, uint32_t buff[]);
uint32_t SDIO_BlockRead(uint32_t block_addr, uint32_t buff[]);
uint32_t SDIO_MultiBlockWrite(uint32_t block_addr, uint16_t block_cnt, uint32_t buff[]);
uint32_t SDIO_MultiBlockRead(uint32_t block_addr, uint16_t block_cnt, uint32_t buff[]);
uint32_t SDIO_DMABlockWrite(uint32_t block_addr, uint16_t block_cnt, uint32_t buff[]);
uint32_t SDIO_DMABlockRead(uint32_t block_addr, uint16_t block_cnt, uint32_t buff[]);2.FatFs移植
底层读写函数有了以后,移植FatFs也就比较简单了,首先将FatFs的相关文件添加到工程中:
我们需要实现的接口函数在diskio.c文件中,包括至少以下3个函数:
初始化函数,直接将端口配置、SDIO初始化添加到该函数中:
DSTATUS disk_initialize (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
//result = RAM_disk_initialize();
// translate the reslut code here
stat = STA_NOINIT;
return stat;
case DEV_MMC :
//result = MMC_disk_initialize();
// translate the reslut code here
PORT_Init(PORTB, PIN1, PORTB_PIN1_SD_CLK, 0);
PORT_Init(PORTB, PIN2, PORTB_PIN2_SD_CMD, 1);
PORT_Init(PORTB, PIN3, PORTB_PIN3_SD_D0, 1);
PORT_Init(PORTB, PIN4, PORTB_PIN4_SD_D1, 1);
PORT_Init(PORTB, PIN5, PORTB_PIN5_SD_D2, 1);
PORT_Init(PORTB, PIN6, PORTB_PIN6_SD_D3, 1);
result = SDIO_Init(10000000);
if(result == SD_RES_OK)
{
stat = RES_OK;
sd_initialized = 1;
}
else
{
stat = STA_NOINIT;
sd_initialized = 0;
}
return stat;
case DEV_USB :
//result = USB_disk_initialize();
// translate the reslut code here
stat = STA_NOINIT;
return stat;
}
return STA_NOINIT;
}读函数:
DRESULT disk_read (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */
LBA_t sector, /* Start sector in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to read */
)
{
DRESULT res;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// translate the arguments here
//result = RAM_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
res = RES_PARERR;
return res;
case DEV_MMC :
if(count == 1)
{
result = SDIO_BlockRead(sector, (uint32_t *)buff);
}
else
{
//result = SDIO_MultiBlockRead(sector, count, (uint32_t *)buff);
result = SDIO_DMABlockRead(sector, count, (uint32_t *)buff);//使用DMA或非DMA模式均可
}
if(result == SD_RES_OK)
res = RES_OK;
else
res = RES_ERROR;
return res;
case DEV_USB :
// translate the arguments here
//result = USB_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
res = RES_PARERR;
return res;
}
return RES_PARERR;
}写函数:
DRESULT disk_write (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
const BYTE *buff, /* Data to be written */
LBA_t sector, /* Start sector in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to write */
)
{
DRESULT res;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// translate the arguments here
//result = RAM_disk_write(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
res = RES_PARERR;
return res;
case DEV_MMC :
if(count == 1)
{
result = SDIO_BlockWrite(sector, (uint32_t *)buff);
}
else
{
//result = SDIO_MultiBlockWrite(sector, count, (uint32_t *)buff);
result = SDIO_DMABlockWrite(sector, count, (uint32_t *)buff);//使用DMA或非DMA模式均可
}
if(result == SD_RES_OK)
res = RES_OK;
else
res = RES_ERROR;
return res;
case DEV_USB :
// translate the arguments here
//result = USB_disk_write(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
res = RES_PARERR;
return res;
}
return RES_PARERR;
}还有一个函数是用户获取SD卡容量等信息的,如下:
DRESULT disk_ioctl (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE cmd, /* Control code */
void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{
DRESULT res;
//int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// Process of the command for the RAM drive
res = RES_PARERR;
return res;
case DEV_MMC :
switch ( cmd )
{ //fatfs内核使用cmd调用
case GET_SECTOR_COUNT: //sector count
*(DWORD*)buff = SD_cardInfo.CardCapacity / 512;
return RES_OK;
case GET_SECTOR_SIZE: //sector size, 传入block size(SD),单位bytes
*(DWORD*)buff = 512;
return RES_OK;
case GET_BLOCK_SIZE: //block size, 由上文可得,对于SD2.0卡最大8192,最小 1
*(DWORD*)buff = 1; //单位为 sector(FatFs)
return RES_OK;
case CTRL_SYNC: //同步命令,貌似FatFs内核用来判断写操作是否完成
return RES_OK;
}
res = RES_OK;
return res;
case DEV_USB :
// Process of the command the USB drive
res = RES_PARERR;
return res;
}
return RES_PARERR;
} 接口部分实现后,就可以调用相关的函数实现文件的读写了,测试程序如下:res = f_mount(&fatfs, "sd:", 1);
if(res != FR_OK)
{
printf("sdcard init fail!\r\n");
}
res = f_open(&filw, "sd:test.txt", FA_CREATE_ALWAYS | FA_WRITE);
if(res != FR_OK)
{
printf("create file fail!\r\n");
}
res = f_write(&filw, str, strlen(str), &len);
if(res != FR_OK)
{
printf("write file fail!\r\n");
}
f_close(&filw);文件系统的配置可以在"ffconf.h"文件中根据实际需求进行修改。