Java中的链表实现介绍
学习数据结构的的链表和树时,会遇到节点(node)和链表(linked list)这两个术语,节点是处理数据结构的链表和树的基础。节点是一种数据元素,包括两个部分:一个是实际需要用到的数据;另一个存储下一个节点位置。
链表是一系列节点串联形成的数据结构,链表存储有序的元素集合,链表中的元素在内存中并不是连续放置的。每个元素由一个存储元素本身的部分和一个指向下一个元素的链接部分组成。因此链表增删非首尾元素时不需要移动元素,只需要更改链接部分的值即可。
本文仅以单链表为例介绍。
单链表每个节点的结构如下:

单链表只有一个指向其他节点的变量,也就是在这种类型的数据结构中,任何两个数据元素之间只有一个链接,参见下图:
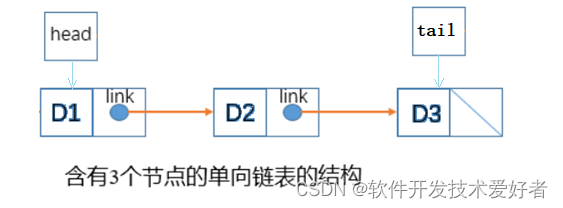
链表的操作包括了创建、删除、插入、输出等。
创建就是空间的分配,将头、尾指针及链表结点个数等初始化。删除和插入根据被操作元素的位置可以细分为头删除(插入),尾删除(插入),中间删除(插入)。
插入操作
头插入实际上是增加一个新节点,然后把新增加的结点指针指向原来头指针指向的元素,再把头指针指向新增的节点。

尾插入也是增加一个新节点,该节点指针置为null,然后把原尾结点指针指向新增加的节点,最后把尾指针指向新增加的节点即可。
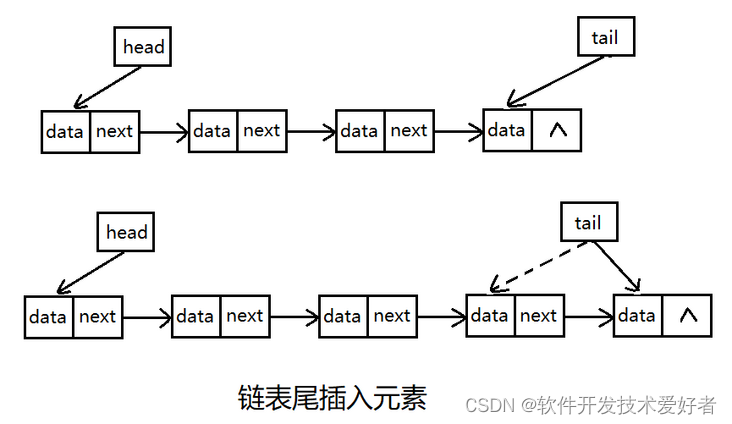
中间插入稍复杂,首先增加一个节点,然后新增节点的指针指向插入位置的后一个节点,把插入位置的前一个节点指针指向新插入节点即可。

删除操作
删除头元素时,先将头指针指向下一个节点,然后把原头结点的指针置空即可。
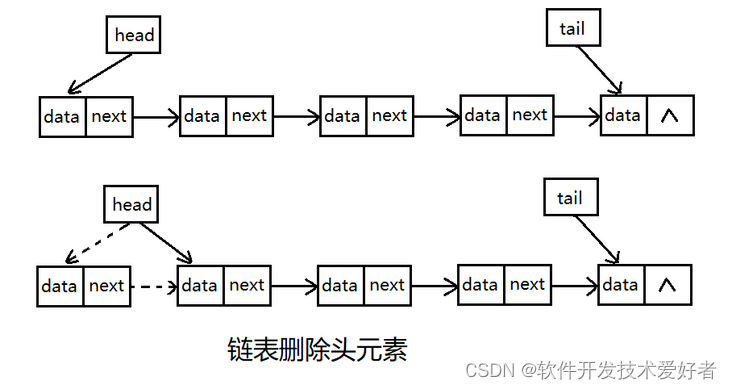
删除尾元素时,首先找到链表倒数第2个元素,然后把尾指针指向这个元素,接着把原倒数第2个元素的指针置空。

删除中间元素相对复杂一些,首先将要删除的节点的前一个节点指针指向要删除的节点的下一个节点,然后把要删除节点的指针置空。
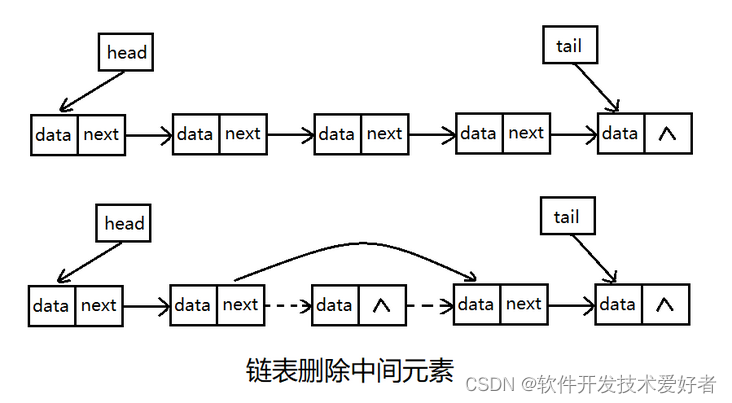
上面提到是单链表最基本的操作,除此之外还有其它操作不多说了。下面给出代码示例。
下面介绍两种实现方式。
一、使用Java.util 包的LinkedList类实现
JAVA提供的LinkedList类简要介绍
JAVA提供的LinkedList类,它也可以被当作堆栈、队列或双端队列进行操作。
LinkedList 实现 List 接口,能进行列表的相关操作。
LinkedList 实现了 Queue 接口,可作为队列使用。
LinkedList 实现 Deque 接口,即能将LinkedList当作双端队列使用。
LinkedList官方文档LinkedList (Java Platform SE 8 )
LinkedList 类位于 java.util 包中,使用前需要引入它,语法格式如下:
import java.util.LinkedList;
常用的方法(Method)及说明
| public boolean add(E e) |
链表末尾添加元素,返回是否成功,成功为 true,失败为 false。 |
| public void add(int index, E element) |
向指定位置插入元素。 |
| public boolean addAll(Collection c) |
将一个集合的所有元素添加到链表后面,返回是否成功,成功为 true,失败为 false。 |
| public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) |
将一个集合的所有元素添加到链表的指定位置后面,返回是否成功,成功为 true,失败为 false。 |
| public void addFirst(E e) |
元素添加到头部。 |
| public void addLast(E e) |
元素添加到尾部。 |
| public boolean offer(E e) |
向链表末尾添加元素,返回是否成功,成功为 true,失败为 false。 |
| public boolean offerFirst(E e) |
头部插入元素,返回是否成功,成功为 true,失败为 false。 |
| public boolean offerLast(E e) |
尾部插入元素,返回是否成功,成功为 true,失败为 false。 |
| public void clear() |
清空链表。 |
| public E removeFirst() |
删除并返回第一个元素。 |
| public E removeLast() |
删除并返回最后一个元素。 |
| public boolean remove(Object o) |
删除某一元素,返回是否成功,成功为 true,失败为 false。 |
| public E remove(int index) |
删除指定位置的元素。 |
| public E poll() |
删除并返回第一个元素。 |
| public E remove() |
删除并返回第一个元素。 |
| public boolean contains(Object o) |
判断是否含有某一元素。 |
| public E get(int index) |
返回指定位置的元素。 |
| public E getFirst() |
返回第一个元素。 |
| public E getLast() |
返回最后一个元素。 |
| public int indexOf(Object o) |
查找指定元素从前往后第一次出现的索引。 |
| public int lastIndexOf(Object o) |
查找指定元素最后一次出现的索引。 |
| public E peek() |
返回第一个元素。 |
| public E element() |
返回第一个元素。 |
| public E peekFirst() |
返回头部元素。 |
| public E peekLast() |
返回尾部元素。 |
| public E set(int index, E element) |
设置指定位置的元素。 |
| public Object clone() |
克隆该列表。 |
| public Iterator descendingIterator() |
返回倒序迭代器。 |
| public int size() |
返回链表元素个数。 |
| public ListIterator listIterator(int index) |
返回从指定位置开始到末尾的迭代器。 |
| public Object[] toArray() |
返回一个由链表元素组成的数组。 |
| public T[] toArray(T[] a) |
返回一个由链表元素转换类型而成的数组。 |
JAVA提供的LinkedList类使用示例(来源https://www.cnblogs.com/jbclown/p/16024181.html ),源码如下:
import java.util.LinkedList; // 引入 LinkedList 类
public class LinkedListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//引入LinkedList类
LinkedList<String> lList = new LinkedList<String>();
//添加元素
lList.add("hello");
lList.add("world");
lList.add("java");
lList.add("LinkedList");
//链表元素个数
System.out.println(lList.size());
//getFirst()方法获取头部元素
System.out.println(lList.getFirst()); //hello
//addFirst() 在头部添加元素
lList.addFirst("the"); //[the, hello, world, java, LinkedList]
System.out.println(lList);
//addLast() 在尾部添加元素
lList.addLast("ArrayList"); //[the, hello, world, java, LinkedList, ArrayList]
System.out.println(lList);
// removeFirst() 移除头部元素
lList.removeFirst(); // [hello, world, java, LinkedList, ArrayList]
// set(int index, E element) 指定元素替换指定位置的元素
lList.set(1,"the"); //[hello, the, java, LinkedList, ArrayList]
System.out.println(lList);
// add( int index,E element) 指定位置插入元素
lList.add(2,"world"); //[hello, the, world, java, LinkedList, ArrayList]
System.out.println(lList);
// for-each 迭代元素
System.out.println("for-each 迭代元素:");
for (String s : lList){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
输出:
4
hello
[the, hello, world, java, LinkedList]
[the, hello, world, java, LinkedList, ArrayList]
[hello, the, java, LinkedList, ArrayList]
[hello, the, world, java, LinkedList, ArrayList]
for-each 迭代元素:
hello
the
world
java
LinkedList
ArrayList
二、自定义实现类实现
Java本身就提供了非常多的数据结构,包括我们所学习的链表,如前面的介绍。我们也可以自定义实现类似功能,这可以让我们更好的理解学习链表,请看下面的介绍。
Java语言没有指针,怎样实现链表?Java语言中的对象引用实际上是一个指针(这里的指针均为概念上的意义,而非语言提供的数据类型,即Java不允许像C/C++语言那样 int *p = &a; p += 2;),可通过类来实现链表中的结点。
Java单向链表的代码实现(来源 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_60650904/article/details/125589573 )。
由链表类MyList、测试类main和异常类IndexOutOfException组成
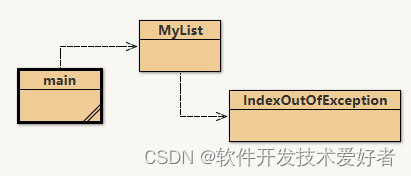
链表类MyList源码:
public class MyList {
public static class ListNode{
int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val){
this.val=val;
}
};
public ListNode head;
public void createList(){
ListNode ListNode1=new ListNode(45);
ListNode ListNode2=new ListNode(35);
ListNode ListNode3=new ListNode(55);
ListNode ListNode4=new ListNode(34);
ListNode1.next=ListNode2;
ListNode2.next=ListNode3;
ListNode3.next=ListNode4;
ListNode4.next=null;
this.head=ListNode1;
}
public void display(){
/**
* 这样会把head弄成空
*/
/*while(head!=null){
System.out.print(head.val+" ");
head=head.next;
}*/
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur=cur.next;
}
}
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
node.next=head;
head=node;
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
} else {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}
//检查index是否合法
private void checkindex(int index){
if(index<0||index>size()){
throw new IndexOutOfException("位置不合法,请重新输入:");
}
}
//找到index-1位置的节点
private ListNode FindIndexNode(int index){
ListNode cur=head;
while (index-1!=0){
cur=cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
checkindex(index);
if(index==0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
else if(index==size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
else {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur=FindIndexNode(index);
node.next=cur.next;
cur.next=node;
}
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur=this.head;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
return true;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur.next!=null) {
if (cur.next.val == key) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
return;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
ListNode cur=head.next;
ListNode pre=head;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
pre.next=cur.next;
cur=cur.next;
}else{
pre=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val==key){
head=head.next;
}
}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
int count=0;
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
cur=cur.next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
public void clear(){
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode curNext=null;
while(cur!=null){
curNext=cur.next;
cur.next=null;
cur=curNext;
}
head=null;
}
}
异常类IndexOutOfException源码:
public class IndexOutOfException extends RuntimeException{
public IndexOutOfException(){
}
public IndexOutOfException(String mes){
super(mes);
}
}
测试类main源码:
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyList list=new MyList();
list.createList();
list.display();
System.out.println(list.contains(45));
System.out.println(list.size());
list.addFirst(99);
list.display();
System.out.println();//换行
list.addLast(999);
list.display();
System.out.println();
list.addIndex(1,50);
list.display();
System.out.println();
list.removeAllKey(45);
list.display();
list.clear();
list.display();
}
}
运行结果:
45 35 55 34 true
4
99 45 35 55 34
99 45 35 55 34 999
99 50 45 35 55 34 999
99 50 35 55 34 999