文章目录
一、本次学习重点内容:
-
本堂课的知识要点有哪些?
1、go语言特性
2、go基础语法
二、详细知识点介绍:
1、什么是Go语言
特点:
1.高性能、高并发
2.语法简单、学习曲线平缓
3.丰富的标准库
4.完善的工具链
5.静态链接
6.快速编译
7.跨平台
8.垃圾回收
2、为什么字节跳动全面使用go语言:
1.最初使用的 Python,由于性能问题换成了Go
2.C++不太适合在线 Web业务
3.早期团队非Java 背景
4.性能比较好
5.部署简单、学习成本低
6.内部 RPC和 HTTP框架的推广
3、开发环境——安装Golang:
参考一下三个网站:
https://go.dev/
https://studygolang.com/dl
https://goproxy.cn/
4、推荐编辑器:VScode、Goland
5、基础语法
1、HolleWorld
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// 终端输出hello world
fmt.Println("Hello world!")
}
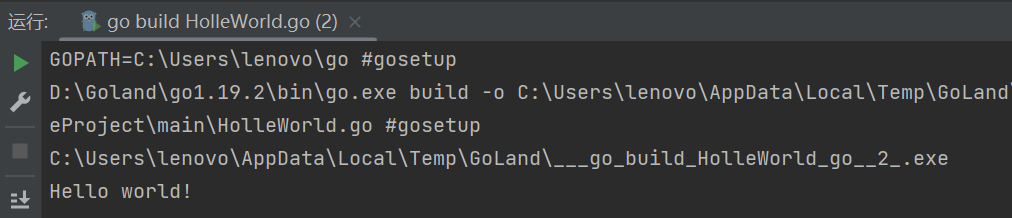
运行结果:
2、基础语法——变量声明
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
func main() {
// 变量声明方式
// 1 var 变量名 = 变量值(自动进行类型检测)
var a = 1
var b = "ok"
var c = true
var m, n = 3, 4
fmt.Println(a, b, c, m, n)
// 2 var 变量名 类型
var a1 int
var b1 string
var c1 int = 20
a1 = 100
b1 = "b1ok"
fmt.Println(a1, b1, c1)
// 3 变量名 := 变量值 (自动类型检测)
a2 := 10
b2 := "b2"
c2 := b2 + "ok"
fmt.Println(a2, b2, c2)
// 常量声明方式
const s string = "常量"
const h = 500000000
const l = 3e20 / h
fmt.Println(s, h, l, math.Sin(h), math.Sin(l))
}
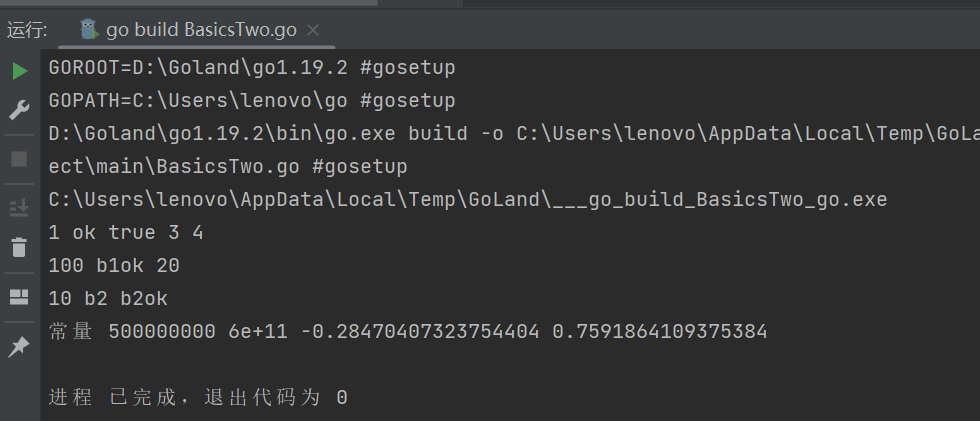
运行结果:
3、基础语法——if-else
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
if 7%4 == 0 {
fmt.Println("ok")
} else {
fmt.Println("no")
}
if i := 10; i < 0 {
fmt.Println(1)
} else if i < 5 {
fmt.Println(2)
} else {
fmt.Println(3)
}
}
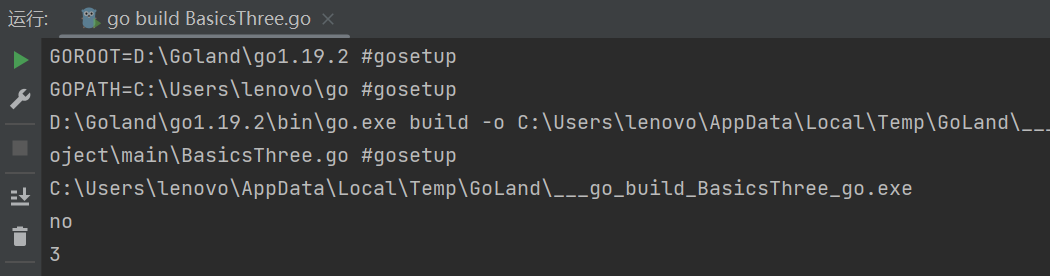
运行结果:
4、基础语法——循环
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
//死循环
for {
fmt.Println("死循环")
break
}
// 经典for循环
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
fmt.Println("经典for循环:", i)
}
// 替代while循环的for循环
j := 0
for j <= 5 {
fmt.Println("替代while循环的for循环", j)
j++
}
// 加强for循环
arr := [3]int{
11, 22, 33}
for i, a := range arr {
fmt.Println("加强for循环:", i, a)
}
}
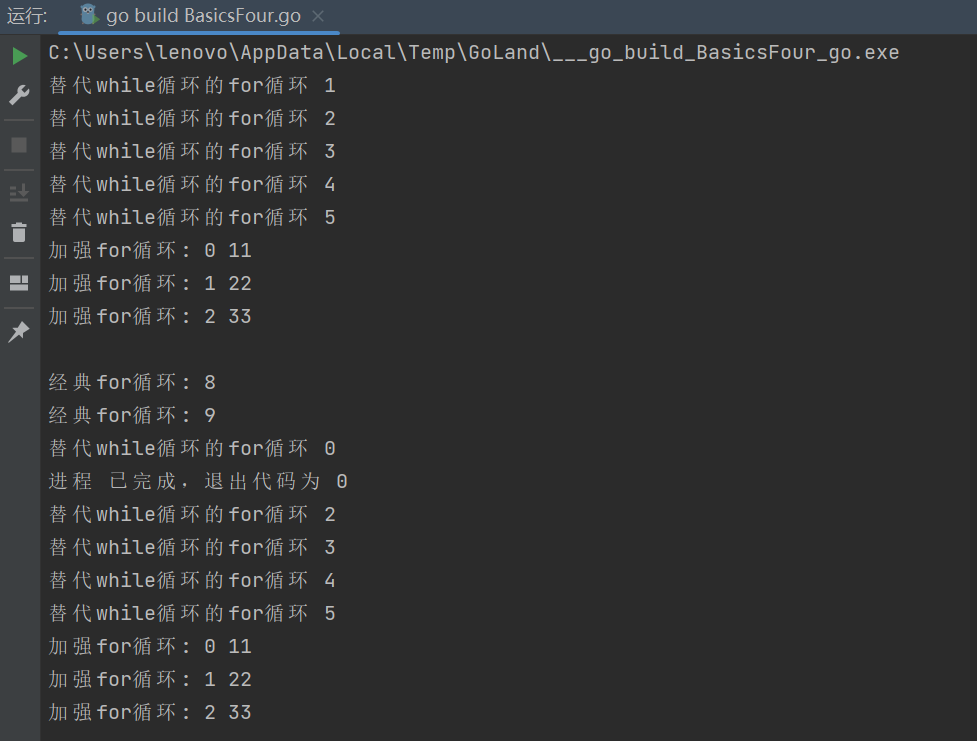
运行结果:
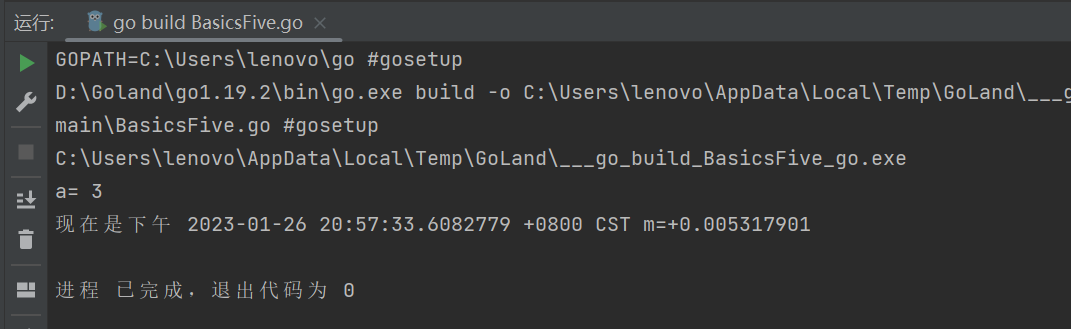
5、基础语法——switch
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
//经典switch
a := 3
switch a {
case 1:
fmt.Println("a=", 1)
case 2:
fmt.Println("a=", 2)
case 3, 4:
fmt.Println("a=", 3 ,"or" ,4)
default:
fmt.Println("其他")
}
//允许使用判断语句的switch
t := time.Now()
switch {
case t.Hour() < 12:
fmt.Println("现在是上午", t)
default:
fmt.Println("现在是下午", t)
}
}
运行结果:
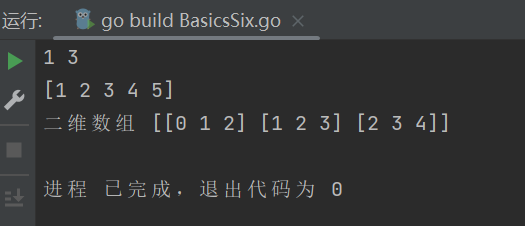
6、基础语法——数组
//go:build ignore
// +build ignore
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
//方式一
var a [3]int
a[2] = 1
fmt.Println(a[2], len(a))
//方式二
b := [5]int{
1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
fmt.Println(b)
//二维数组
var c [3][3]int
for i := 0; i < 3; i++ {
for j := 0; j < 3; j++ {
c[i][j] = i + j
}
}
fmt.Println("二维数组", c)
}
运行结果:
7、基础语法——切片
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
//声明 使用make()函数
s := make([]string, 3)
s[0] = "a"
s[1] = "b"
s[2] = "c"
fmt.Println("get:", s[2])
fmt.Println("len", len(s))
//切片增加
s = append(s, "d")
s = append(s, "e", "f")
fmt.Println(s)
// 切片复制
c := make([]string, len(s))
copy(c, s)
println(c) //打印地址
fmt.Println(c)
//常见切片操作
fmt.Println(s[2:5])
fmt.Println(s[:5])
fmt.Println(s[2:])
}
运行结果:

8、基础语法——map
//go:build ignore
// +build ignore
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
m := make(map[string]int)
m["one"] = 1
m["two"] = 2
fmt.Println(m) //map[one:1 two:2]
fmt.Println(len(m)) //2
fmt.Println(m["one"]) //1
fmt.Println(m["two"]) //2
r, ok := m["one"]
fmt.Println(r, ok) // 1 ture
delete(m, "one")
fmt.Println(m) //map[two:2]
m1 := map[string]int{
"one": 1, "two": 2}
fmt.Println(m1) //map[one:1 two:2]
for k, v := range m1 {
fmt.Println(k, v)
//two 2
//one 1
}
}
9、基础语法——函数
//go:build ignore
// +build ignore
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
res := add(1, 2)
fmt.Println(res) //3
m := map[string]int{
"one": 11, "two": 22}
v, ok := exists(m, "two")
fmt.Println(v, ok) //22 true
}
//常见定义方式
func add(a int, b int) int {
return a + b
}
func add1(a, b int) int {
return a + b
}
func exists(m map[string]int, k string) (v int, ok bool) {
v, ok = m[k]
return v, ok
}
10、基础语法——指针
//go:build ignore
// +build ignore
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
n := 5
add1(n)
fmt.Println(n)// 5
add2(&n)
fmt.Println(n)// 7
}
func add1(a int) {
a += 2
}
func add2(a *int) {
*a += 2
}
三、实践练习例子:
开启一个http端口
package main
/*
开启一个http服务
*/
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("ok")
http.Handle("/", http.FileServer(http.Dir(".")))
http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8080", nil)
}
运行结果:

四、课后个人总结:
本章基础语法部分感觉和还算比较容易,总结go中有c++的结构体和指针。go中for循环和switch十分灵活,数组切片和python一样也十分灵活。