1.springboot的创建
1. 简介
Spring Boot它本身并不提供Spring框架的核心特性以及扩展功能,只是用于快速、敏捷地开发新一代基于Spring框架的应用程序。
同时它集成了大量常用的第三方库配置(例如Jackson, JDBC, Mongo, Redis, Mail等等)
Spring Boot应用中这些第三方库几乎可以零配置的开箱即用(out-of-the-box),大部分的Spring Boot应用都 只需要非常少量的配置代码,开发者能够更加专注于业务逻辑。
优点:
1)快速的创建应用
2)使用嵌入式servlet容器,生成可直接运行的jar包,简化部署
3)大量的自动配置简化开发
4)starters自动依赖于版本控制
2. 开发示例
2.1 创建springboot工程


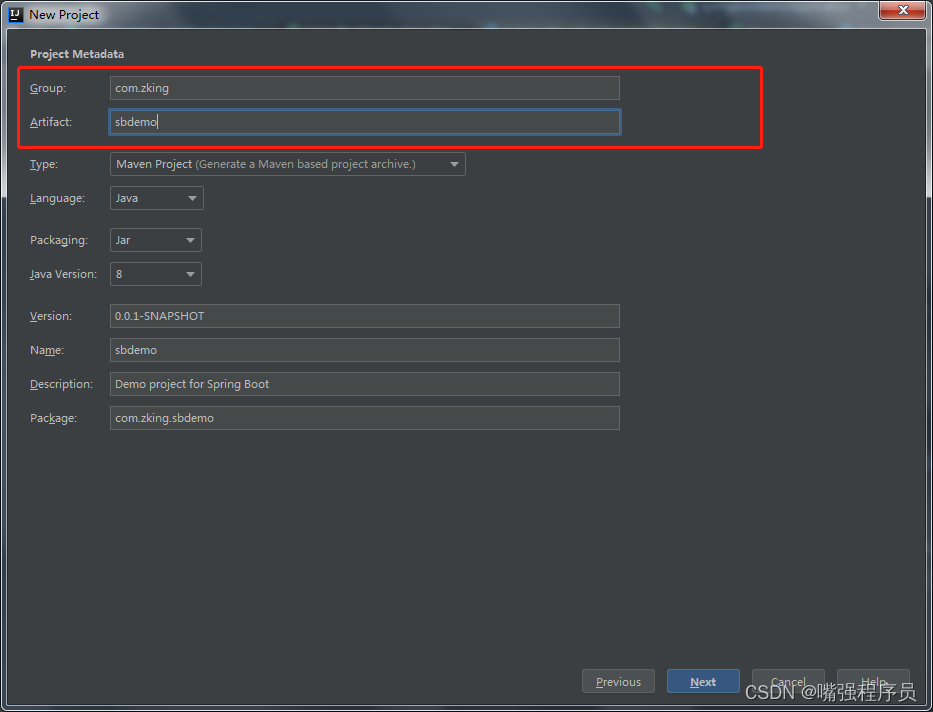


3. 启动类
springboot应用都会有一个启动类,

springboot默认扫描启动类所在包下的所有子包,也可以使用@ComponentScan注解指定扫描的包。
4. 常用注解
| @SpringBootApplication | 这是 Spring Boot 最最最核心的注解,用在 Spring Boot 主类上,标识这是一个 Spring Boot 应用,用来开启 Spring Boot 的各项能力。其实这个注解就是 @SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan 这三个注解的组合,也可以用这三个注解来代替 @SpringBootApplication 注解 |
| @Configuration | 基于JavaConfig的配置形式,相当于xml配置文件中的bean配置,任何一个标注了@Bean的方法,其返回值将作为一个bean定义注册到Spring的IoC容器,方法名将默认成该bean定义的id |
| @ComponentScan | 功能其实就是自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件(比如@Component和@Repository等)或者bean定义,最终将这些bean定义加载到IoC容器中。我们可以通过basePackages等属性来细粒度的定制@ComponentScan自动扫描的范围,如果不指定,则默认Spring框架实现会从声明@ComponentScan所在类的package进行扫描。(注:所以SpringBoot的启动类最好是放在root package下,因为默认不指定basePackages。) |
| @EnableAutoConfiguration | 借助@Import的支持,收集和注册特定场景相关的bean定义。允许 Spring Boot 自动配置注解,开启这个注解之后,Spring Boot 就能根据当前类路径>下的包或者类来配置 Spring Bean |
| @SpringBootConfiguration | 这个注解就是 @Configuration 注解的变体,只是用来修饰是 Spring Boot 配置而已,或者可利于 Spring Boot 后续的扩展 |
| @Conditional | 这是 Spring 4.0 添加的新注解,用来标识一个 Spring Bean 或者 Configuration 配置文>件,当满足指定的条件才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnBean | 组合 @Conditional 注解,当容器中有指定的 Bean 才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnMissingBean | 组合 @Conditional 注解,和 @ConditionalOnBean 注解相反,当容器中没有指定的 Bean 才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnClass | 组合 @Conditional 注解,当容器中有指定的 Class 才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnMissingClass | 组合 @Conditional 注解,和 @ConditionalOnMissingClass 注解相反,当容器中没有指定的 Class 才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnWebApplication | 组合 @Conditional 注解,当前项目类型是 WEB 项目才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication | 组合 @Conditional 注解,和 @ConditionalOnWebApplication 注解相反,当前项目类型不是 WEB 项目才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnProperty | 组合 @Conditional 注解,当指定的属性有指定的值时才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnExpression | 组合 @Conditional 注解,当 SpEL 表达式为 true 时才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnJava | 组合 @Conditional 注解,当运行的 Java JVM 在指定的版本范围时才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnResource | 组合 @Conditional 注解,当类路径下有指定的资源才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnJndi | 组合 @Conditional 注解,当指定的 JNDI 存在时才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnCloudPlatform | 组合 @Conditional 注解,当指定的云平台激活时才开启配置 |
| @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate | 组合 @Conditional 注解,当指定的 class 在容器中只有一个 Bean,或者同时有多个但为首选时才开启配置 |
| @ConfigurationProperties | 用来加载额外的配置(如 .properties 文件),可用在 @Configuration 注解类,或者 @Bean 注解方法上面 |
| @EnableConfigurationProperties | 一般要配合 @ConfigurationProperties 注解使用,用来开启对 @ConfigurationProperties 注解配置 Bean 的支持 |
| @AutoConfigureAfter | 用在自动配置类上面,表示该自动配置类需要在另外指定的自动配置类配置完之后。如 Mybatis 的自动配置类,需要在数据源自动配置类之后,@AutoConfigureAfter(DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class) public class MybatisAutoConfiguration |
| @AutoConfigureBefore | 这个和 @AutoConfigureAfter 注解使用相反,表示该自动配置类需要在另外指定的自动配置类配置之前 |
| @Import | 这是 Spring 3.0 添加的新注解,用来导入一个或者多个 @Configuration 注解修饰的类,这在 Spring Boot 里面应用很多 |
| @ImportResource | 这是 Spring 3.0 添加的新注解,用来导入一个或者多个 Spring 配置文件,这对 Spring Boot 兼容老项目非常有用,因为有些配置无法通过 Java Config 的形式来配置就只能用这个注解来导入 |
5. springboot配置文件
springboot的配置文件常用的有两种格式:yml,properties。使用哪种方式主要看个人习惯。
#端口号
server.port=8080
#上线文路径
server.servlet.context-path=/
#指定uri编码
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=utf-8
#日志配置
logging.config=classpath:logback-spring.xml6. 开发一个controller

2.freemarker的使用
1. freemarker是什么
FreeMarker 是一款 模板引擎: 即一种基于模板和要改变的数据, 并用来生成输出文本(HTML网页,电子邮件,配置文件,源代码等)的通用工具。 它不是面向最终用户的,而是一个Java类库,是一款程序员可以嵌入他们所开发产品的组件。 
1.1 优点
-
freemarker模板中不能使用java代码,有利于严格的mvc分离
-
性能比较好
-
内置了丰富的功能,使用方便
-
可以在servlet容器外使用,模板不会被编译成class,不占用PermGen空间(从jdk8开始使用元空间)
-
宏定义,方便功能的封装
2. springboot整合freemarker
2.1 pom.xml
注:不需要版本 时应为springboot已经给我们定义好了版本
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId>
</dependency>2.2 项目配置文件
application.properties
# ------------------------freemarker B --------------------------
# 是否允许HttpServletRequest属性覆盖(隐藏)控制器生成的同名模型属性。
spring.freemarker.allow-request-override=false
# 是否允许HttpSession属性覆盖(隐藏)控制器生成的同名模型属性。
spring.freemarker.allow-session-override=false
# 是否启用模板缓存。
spring.freemarker.cache=false
# 模板编码。
spring.freemarker.charset=UTF-8
# 是否检查模板位置是否存在。
spring.freemarker.check-template-location=true
# Content-Type value.
spring.freemarker.content-type=text/html
# 是否启用freemarker
spring.freemarker.enabled=true
# 设定所有request的属性在merge到模板的时候,是否要都添加到model中.
spring.freemarker.expose-request-attributes=false
# 是否在merge模板的时候,将HttpSession属性都添加到model中
spring.freemarker.expose-session-attributes=false
# 设定是否以springMacroRequestContext的形式暴露RequestContext给Spring’s macro library使用
spring.freemarker.expose-spring-macro-helpers=true
# 是否优先从文件系统加载template,以支持热加载,默认为true
spring.freemarker.prefer-file-system-access=true
# 设定模板的后缀.
spring.freemarker.suffix=.ftl
# 设定模板的加载路径,多个以逗号分隔,默认:
spring.freemarker.template-loader-path=classpath:/templates/
# 设定FreeMarker keys.
spring.freemarker.settings.template_update_delay=0
spring.freemarker.settings.default_encoding=UTF-8
spring.freemarker.settings.classic_compatible=true
# 在ftl中使用request
spring.freemarker.request-context-attribute=request
# ------------------------freemarker E --------------------------2.3 Controller
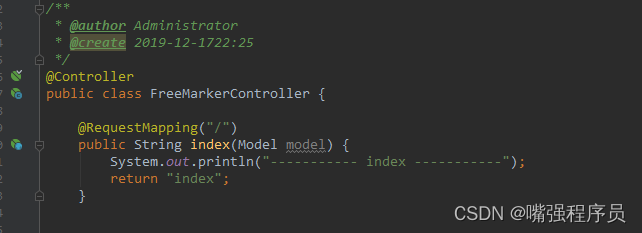
2.4 index.ftl
<!--
assign: 使用该指令你可以创建一个新的变量, 或者替换一个已经存在的变量。
-->
<#assign ctx=request.contextPath />
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>SpringBoot + Freemarker</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello boy,</h1><br data-tomark-pass>
<p>当前时间:${.now?string("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.sss")}</p>
<p>
<a href="${ctx}/commonGrammar">常用语法</a>
</p>
</body>
</html>2.5 常用功能演示
1) 在controller 生成测试数据 
@RequestMapping("/commonGrammar")
public String index(Model model) {
Map map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
map.put("key" + i, "value" + i);
}
model.addAttribute("list", Arrays.asList("string1", "string2", "string3", "string4", "string5", "string6"));
model.addAttribute("map", map);
model.addAttribute("name", " htTps://wWw.zHyD.mE ");
model.addAttribute("htmlText", "<span style=\"color: red;font-size: 16px;\">html内容</span>");
model.addAttribute("num", 123.012);
model.addAttribute("null", null);
model.addAttribute("dateObj", new Date());
model.addAttribute("bol", true);
return "commonGrammar";
}-
演示页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Freemarker 语法大全</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
<style>
html {
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 400;
}
.exp {
font-size: 12px;
color: lightgray;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>当前时间:${.now?string("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.sss")}</p>
<dl>
<dt>list长度:<span >${list?size}</span></dt>
<dt>列表</dt>
<#list list as item>
<dd>${item }, 索引:${item_index },hasNext:${item_has_next}</dd>
</#list>
<dt>数字遍历</dt>
<#list 1..3 as item>
<dd>数字${item}</dd>
</#list>
<dt>map</dt>
<#list map?keys as key>
<dd>${map[key]}, 索引:${key_index },hasNext:${key_has_next}</dd>
</#list>
</dl>
<dl>
<dt>字符串</dt>
<dd>普通字符串:<span >${name}</span></dd>
<dd>非html编码:<span >${htmlText}</span></dd>
<dd>html编码:<span >${htmlText?html}</span></dd>
<dd>首字母大写:<span >${name?cap_first}</span></dd>
<dd>首字母小写:<span >${name?uncap_first}</span></dd>
<dd>全小写:<span >${name?lower_case}</span></dd>
<dd>全大写:<span >${name?upper_case}</span></dd>
<dd>去除首位空格:<span >${name?trim}</span></dd>
<dd>空字符串:<span >${null?if_exists}</span></dd>
<dd>是否包含某个字符串:<span >${name?contains("wWw")?string}</span></dd>
<dd>默认值:<span >${null?default("空值默认")}</span></dd>
<dd>“${name}”字符串长度:<span >${name?length}</span></dd>
<dd>定义字符串:<span >str=码一码<#assign str="码一码"/></span></dd>
<dd>字符串拼接(1):<span >${"字符串拼接 + " + str}</span></dd>
<dd>字符串拼接(2):<span >${"字符串拼接 + ${str}"}</span></dd>
<dd>字符串截取单个字符(1):<span >${str[1]}</span></dd>
<dd>字符串截取(2):<span >${str?substring(1)}</span></dd>
<dd>字符串截取(3):<span >${str?substring(1,2)}</span></dd>
<dd>indexOf:<span >${str?index_of("一")}</span></dd>
<dd>split分割字符串:<span >
<#list "a|b|c"?split("|") as item>
${item}
</#list>
</span></dd>
<dd>if...elseif...else:<span >
<#if null == ''>
匹配if显示
<#elseif null == '1'>
匹配elseif显示
<#else>
匹配else显示
</#if></span>
</dd>
</dl>
<dl>
<dt>switch</dt>
<dd>
<#switch str>
<#case "你好">
匹配“你好”
<#break >
<#case "码一码">
匹配“码一码”
<#break >
<#default>
默认匹配
</#switch>
</dd>
</dl>
<dl>
<dt>数字</dt>
<dd>普通数字:<span >${num}</span></dd>
<dd>数字类型:<span >${num?string.number}</span></dd>
<dd>货币类型:<span >${num?string.currency}</span></dd>
<dd>百分比类型:<span >${num?string.percent}</span></dd>
<dd>格式化数字:<span >${num?string("#.###")}</span></dd>
<dd>取数字的整数部分:<span >${num?int}</span></dd>
</dl>
<dl>
<dt>运算符</dt>
<dd>不等于:!= <span >例如:${(1 != 2)?string('1 != 2', '1 == 2')}</span></dd>
<dd>等于:== <span >例如:${(1 == 1)?string('1 == 1', '1 != 1')}</span></dd>
<dd>大于(1):> <span
>例如:${(2 > 1)?string('2 > 1', '2 < 1')}。<strong>注:使用> 时必须加括号,否则可能会被当成普通的标签闭合符号而引起报错</strong></span>
</dd>
<dd>大于(2):gt <span >例如:${(2 gt 1)?string('2 gt 1', '2 lte 1')}</span></dd>
<dd>大于等于:gte <span >例如:${(2 gte 2)?string('2 gte 2', '2 lt 2')}</span></dd>
<dd>小于(1):< <span
>例如:${(1 < 2)?string('1 < 2', '1 > 2')}。<strong>注:使用< 时必须加括号,否则可能会被当成普通的标签闭合符号而引起报错</strong></span>
</dd>
<dd>小于(2):lt <span >例如:${(1 lt 2)?string('1 lt 2', '1 gte 2')}</span></dd>
<dd>小于等于:lte <span >例如:${(2 lte 2)?string('2 lte 2', '2 gt 2')}</span></dd>
</dl>
<dl>
<dt>boolean</dt>
<dd>普通boolean输出:<span >${bol}</span></dd>
<dd>boolean判断输出:<span >${bol?string('true的时候显示','false的时候显示')}</span></dd>
</dl>
<dl>
<dt>日期</dt>
<dd>${dateObj?date}</dd>
<dd>${dateObj?time}</dd>
<dd>${dateObj?string("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS")}</dd>
</dl>
<dl>
<dt>macro宏模板</dt>
<dd>
<#macro listMacro title items>
<p>${title?cap_first}:
<ul>
<#list items as item>
<li>${item?cap_first}</li>
</#list>
</ul>
<#nested >
</#macro>
</dd>
<dd>
<@listMacro items=["item1", "item2", "item3"] title="Items">
nested标签表示可以插入自定义的内容
</@listMacro>
</dd>
</dl>
</body>
</html>