在流水线里面一定要做异常处理,如果不做异常处理就会导致流水线直接报错,有些报错可以容忍,那么就可以去捕获异常,避免它报错。

try是去测试语句有没有报错,如果报错了就会将其错误打印出来,如果没有报错就会执行finally。
/*
如果println(a,b)失败(肯定失败,因为有语法错误)
catch捕获错误,并打印错误。
finally 总是执行。
*/
try {
println(a,b)
}
catch(Exception e) {
println(e)
}
finally {
println("done")
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
任何编程语言都需要异常处理来处理运行时错误,从而可以保持应用程序的正常流程。
异常通常会破坏应用程序的正常流程,这就是为什么我们需要在我们的应用程序中使用异常处理的原因。
例外大致分为以下类别 -
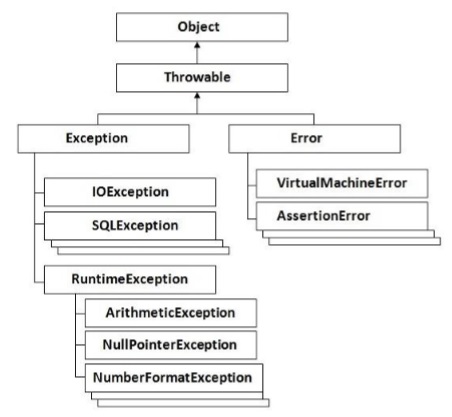
- 检测异常 -扩展Throwable类(除了RuntimeException和Error)的类称为检查异常egIOException,SQLException等。检查的异常在编译时检查。
一个典型的情况是FileNotFoundException。假设您的应用程序中有以下代码,它从E盘中的文件读取。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("E://file.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
}
}如果文件(file.txt)不在E盘中,那么将引发以下异常。
抓取:java.io.FileNotFoundException:E:\ file.txt(系统找不到指定的文件)。
java.io.FileNotFoundException:E:\ file.txt(系统找不到指定的文件)。
- 未经检查的异常 -扩展RuntimeException的类称为未检查异常,例如,ArithmeticException,NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException等。未检查的异常在编译期不检查,而是在运行时检查。
一个典型的情况是ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException,当您尝试访问大于数组长度的数组的索引时,会发生这种情况。以下是这种错误的典型例子。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
def arr = new int[3];
arr[5] = 5;
}
}当上面的代码执行时,将引发以下异常。
抓取:java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:5
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:5
- 错误 -错误无法恢复。 OutOfMemoryError,VirtualMachineError,AssertionError等。
这些是程序永远不能恢复的错误,将导致程序崩溃。
下图显示了如何组织Groovy中的异常层次结构。它都基于Java中定义的层次结构。
捕捉异常
方法使用try和catch关键字的组合捕获异常。 try / catch块放置在可能生成异常的代码周围。
try {
//Protected code
} catch(ExceptionName e1) {
//Catch block
}所有可能引发异常的代码都放在受保护的代码块中。
在catch块中,您可以编写自定义代码来处理异常,以便应用程序可以从异常中恢复。
让我们看一个类似的代码示例,我们在上面看到一个索引值大于数组大小的数组。但这次让我们将我们的代码包装在try / catch块中。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
try {
def arr = new int[3];
arr[5] = 5;
} catch(Exception ex) {
println("Catching the exception");
}
println("Let's move on after the exception");
}
}当我们运行上面的程序,我们将得到以下结果
Catching the exception
Let's move on after the exception从上面的代码,我们在try块中包装错误的代码。在catch块中,我们只是捕获我们的异常并输出一个异常已经发生的消息。
多个捕获块
可以有多个catch块来处理多种类型的异常。对于每个catch块,根据引发的异常的类型,您将编写代码来相应地处理它。
让我们修改上面的代码来具体捕捉ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。以下是代码段。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
try {
def arr = new int[3];
arr[5] = 5;
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
println("Catching the Array out of Bounds exception");
}catch(Exception ex) {
println("Catching the exception");
}
println("Let's move on after the exception");
}
}当我们运行上面的程序,我们将得到以下结果
Catching the Aray out of Bounds exception
Let's move on after the exception从上面的代码,你可以看到ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException catch块首先被捕获,因为它意味着异常的标准。
finally块
finally块跟在try块或catch块之后。代码的finally块总是执行,而不管异常的发生。
使用finally块可以运行任何你想要执行的清除类型语句,无论在受保护代码中发生什么。该块的语法如下。
try {
//Protected code
} catch(ExceptionType1 e1) {
//Catch block
} catch(ExceptionType2 e2) {
//Catch block
} catch(ExceptionType3 e3) {
//Catch block
} finally {
//The finally block always executes.
}让我们修改我们上面的代码并添加finally代码块。以下是代码段。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
try {
def arr = new int[3];
arr[5] = 5;
} catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
println("Catching the Array out of Bounds exception");
}catch(Exception ex) {
println("Catching the exception");
} finally {
println("The final block");
}
println("Let's move on after the exception");
}
} 当我们运行上面的程序,我们将得到以下结果
Catching the Array out of Bounds exception
The final block
Let's move on after the exception以下是Groovy中提供的异常方法
public String getMessage()
返回有关已发生异常的详细消息。此消息在Throwable构造函数中初始化。
public Throwable getCause()
返回由Throwable对象表示的异常原因。
public String toString()
返回与getMessage()的结果连接的类的名称。
public void printStackTrace()
将toString()的结果与堆栈跟踪一起打印到System.err,错误输出流。
public StackTraceElement [] getStackTrace()
返回包含堆栈跟踪上的每个元素的数组。索引0处的元素表示调用堆栈的顶部,数组中的最后一个元素表示调用堆栈底部的方法。
public Throwable fillInStackTrace()
使用当前堆栈跟踪填充此Throwable对象的堆栈跟踪,添加到堆栈跟踪中的任何以前的信息。
例子
下面是使用上面给出的一些方法的代码示例 -
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
try {
def arr = new int[3];
arr[5] = 5;
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
println(ex.toString());
println(ex.getMessage());
println(ex.getStackTrace());
} catch(Exception ex) {
println("Catching the exception");
}finally {
println("The final block");
}
println("Let's move on after the exception");
}
}当我们运行上面的程序,我们将得到以下结果
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 5
5
[org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.dgmimpl.arrays.IntegerArrayPutAtMetaMethod$MyPojoMetaMet
hodSite.call(IntegerArrayPutAtMetaMethod.java:75),
org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.callsite.CallSiteArray.defaultCall(CallSiteArray.java:48) ,
org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.callsite.AbstractCallSite.call(AbstractCallSite.java:113) ,
org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.callsite.AbstractCallSite.call(AbstractCallSite.java:133) ,
Example.main(Sample:8), sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method),
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:57),
sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) ,
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:606),
org.codehaus.groovy.reflection.CachedMethod.invoke(CachedMethod.java:93),
groovy.lang.MetaMethod.doMethodInvoke(MetaMethod.java:325),
groovy.lang.MetaClassImpl.invokeStaticMethod(MetaClassImpl.java:1443),
org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.InvokerHelper.invokeMethod(InvokerHelper.java:893),
groovy.lang.GroovyShell.runScriptOrMainOrTestOrRunnable(GroovyShell.java:287),
groovy.lang.GroovyShell.run(GroovyShell.java:524),
groovy.lang.GroovyShell.run(GroovyShell.java:513),
groovy.ui.GroovyMain.processOnce(GroovyMain.java:652),
groovy.ui.GroovyMain.run(GroovyMain.java:384),
groovy.ui.GroovyMain.process(GroovyMain.java:370),
groovy.ui.GroovyMain.processArgs(GroovyMain.java:129),
groovy.ui.GroovyMain.main(GroovyMain.java:109),
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method),
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:57),
sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) ,
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:606),
org.codehaus.groovy.tools.GroovyStarter.rootLoader(GroovyStarter.java:109),
org.codehaus.groovy.tools.GroovyStarter.main(GroovyStarter.java:131),
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method),
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:57),
sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) ,
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:606),
com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMain.main(AppMain.java:144)]
The final block
Let's move on after the exception