目录
一、高阶函数
1.什么是高阶函数?
把函数作为参数传入,这样的函数称为高阶函数,
######################################################################
二、常用高阶函数
2.1 常用高阶函数 - map
用Python-map代码实现:f(x)=x*x
•
内置函数map,map()函数接收两个参数,一个是
函数
,一个是
Iterable(可多个)
,
•
map将传入的函数依次作用到序列的每个元素,并把结果作为新的Iterator返回。
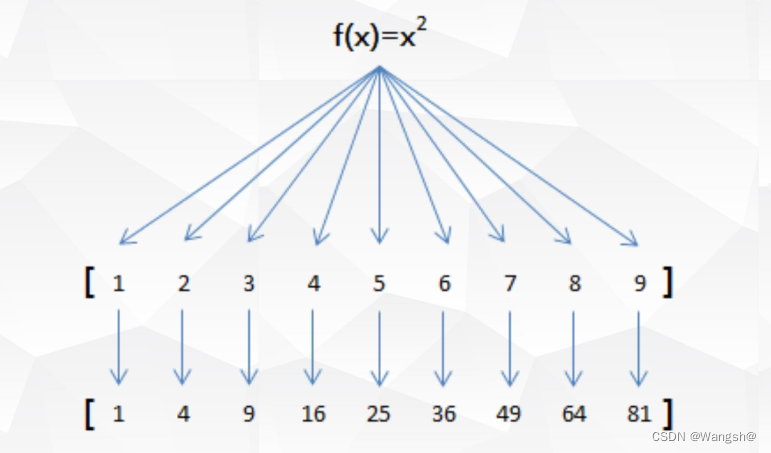
示例:使用map函数实现f(x)=x*x
注:给map传入一个函数作为参数,就要在后面传一个可迭代对象。
lst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
def func(item):
return item * item
result = map(func, lst)
# map会将func函数后面的可迭代对象lst中的元素一个个映射给func函数进行梳理
# func 得到的返回值会保存到map可迭代对象里面。
print(list(result))
# 只有一个表达式,可以使用lambda来写
result1 = map(lambda x: x**2, lst)
print(list(result1))注:传入多个参数,就要传入两个可迭代对象
lst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
lst2 = [3, 6, 7]
print(list(map(lambda x, y: x+y, lst, lst2)))
E:\python\python3.9.1\python.exe E:/tlbb/2022-07-13-高阶函数/01.高阶函数.py
[4, 8, 10]
Process finished with exit code 0map函数练习
# 有列表[1,2,3,4,5],将所有元素转换成str:['1','2','3','4','5']
lst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print(list(map(str, lst)))
# 有列表字符串'span',将各字符转换成对应的ascii码的列表[115, 112, 97, 109]
str1 = "span"
print(list(map(lambda x: ord(x), str1)))
# 有列表[-1,-2,0,1,2],将各元素转换成绝对值[1, 2, 0, 1, 2]
lst2 = [-1, -2, 0, 1, 2]
print(list(map(lambda x: abs(x), lst2)))
# 保留两位小数输出
a = [0.346574, 2.34534, 6.34523, 8.234534]
print(list(map(lambda x: float('%.2f' % x), a)))
# 转换为百分比输出
print(list(map(lambda x: f"{x*100:.2f}%", a)))######################################################################
2.2 常用高阶函数-filter
用Python-filter代码实现:在一个list中,删掉偶数,只保留奇数
•
Python内建的filter()函数用于过滤序列。和map()类似,
filter()也接收一个函数和一个序列
•
filter()把传入的函数依次作用于每个元素,然后
根据返回值是True还是False决定保留还是丢弃
该元素。
•
注意到filter()函数返回的是一个Iterator,也就是一个惰性序列。
# 取出10以内的奇数
# 当%2等于0的时候为假,对%2=1的时候为真
result = filter(lambda x: x % 2, range(10))
print(list(result))
E:\python\python3.9.1\python.exe E:/tlbb/2022-07-13-高阶函数/01.高阶函数.py
[1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
Process finished with exit code 0filter()函数练习
# 1-200以内开平方是整数的数
import math
print(list(filter(lambda x: math.sqrt(x).is_integer(), range(200))))
# 100-999内是水仙花的数
print(list(filter(lambda x: ((x//100)**3 + (x % 100//10)**3 + (x % 10)**3 == x), range(100, 999))))
# 删除空字符串
lst = ['A', '', 'B', None, 'C', ' ', 'a', 1, 0]
print(list(filter(lambda x: x and str(x).split(), lst)))
E:\python\python3.9.1\python.exe E:/tlbb/2022-07-13-高阶函数/01.高阶函数.py
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, 121, 144, 169, 196]
[153, 370, 371, 407]
['A', 'B', 'C', 'a', 1]
Process finished with exit code 0######################################################################
2.3 常用高阶函数-sorted
用Python-sorted代码实现:按绝对值大小排序
sorted()函数也是一个高阶函数,它还可以接收一个key函数来实现自定义的排序
key指定的函数将作用于list的每一个元素上,并根据key函数返回的结果进行排序。
列表里面包元组进行排序
先按照第一个值进行排序,第一个值一样再按照第二个进行排序,依次类推
# 列表里包元组的形式排序
# 先按照第一个值进行排序,第一个值一样再按照第二个进行排序,依次类推
lst = [(True, True, False),
(2, 1, 3),
(2, 2, 4),
(False, True, 2),
(False, False, 3)]
print(sorted(lst))
E:\python\python3.9.1\python.exe E:/tlbb/2022-07-13-高阶函数/01.高阶函数.py
[(False, False, 3), (False, True, 2), (True, True, False), (2, 1, 3), (2, 2, 4)]
Process finished with exit code 0
sorted练习
# 1、列表中的值忽略大小写排序
lst1 = ['bob', 'about', 'Zoo', 'Credit']
print(sorted(lst1, key=lambda x: x.lower()))
# 2、di={"a":3, "b":2, "c":4, "d":1} value值来排序
d1 = {"a": 3, "b": 2, "c": 4, "d": 1}
print(sorted(d1.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]))
E:\python\python3.9.1\python.exe E:/tlbb/2022-07-13-高阶函数/01.高阶函数.py
['about', 'bob', 'Credit', 'Zoo']
[('d', 1), ('b', 2), ('a', 3), ('c', 4)]
Process finished with exit code 0使用python实现命令:
cat access.log|grep alibaba|sort|uniq -c|surt -rn|head -10
# 用python实现 cat access.log|grep alibaba|sort|uniq -c|surt -rn|head -10
count = {}
with open("access.log", "r", encoding="utf8") as fp:
for line in fp:
if "alibaba" in line:
count[line] = count.get(line, 0) + 1
result = sorted(count.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True[:10])
print(result)######################################################################
2.4 常用高阶函数-reduce
reduce函数 需要从functools库导入
用Python-reduce代码实现:将列表[1,3,5,7,9],变成整数13579
•
reduce把一个函数作用在一个序列[x1, x2, x3, ...]上
•
这个函数必须接收两个参数
•
reduce把结果继续和序列的下一个元素做累积计算
•
reduce(f, [x1, x2, x3, x4]) => f(f(f(x1, x2), x3), x4)
将前一次得到的结果作为参数,继续传入
示例:
# reduce函数 需要从functools库导入
# reduce -- 累计
from functools import reduce
a = [1, 2, 3, 4]
def func1(x,y):
return x * 10 + y
print(reduce(func1, a))