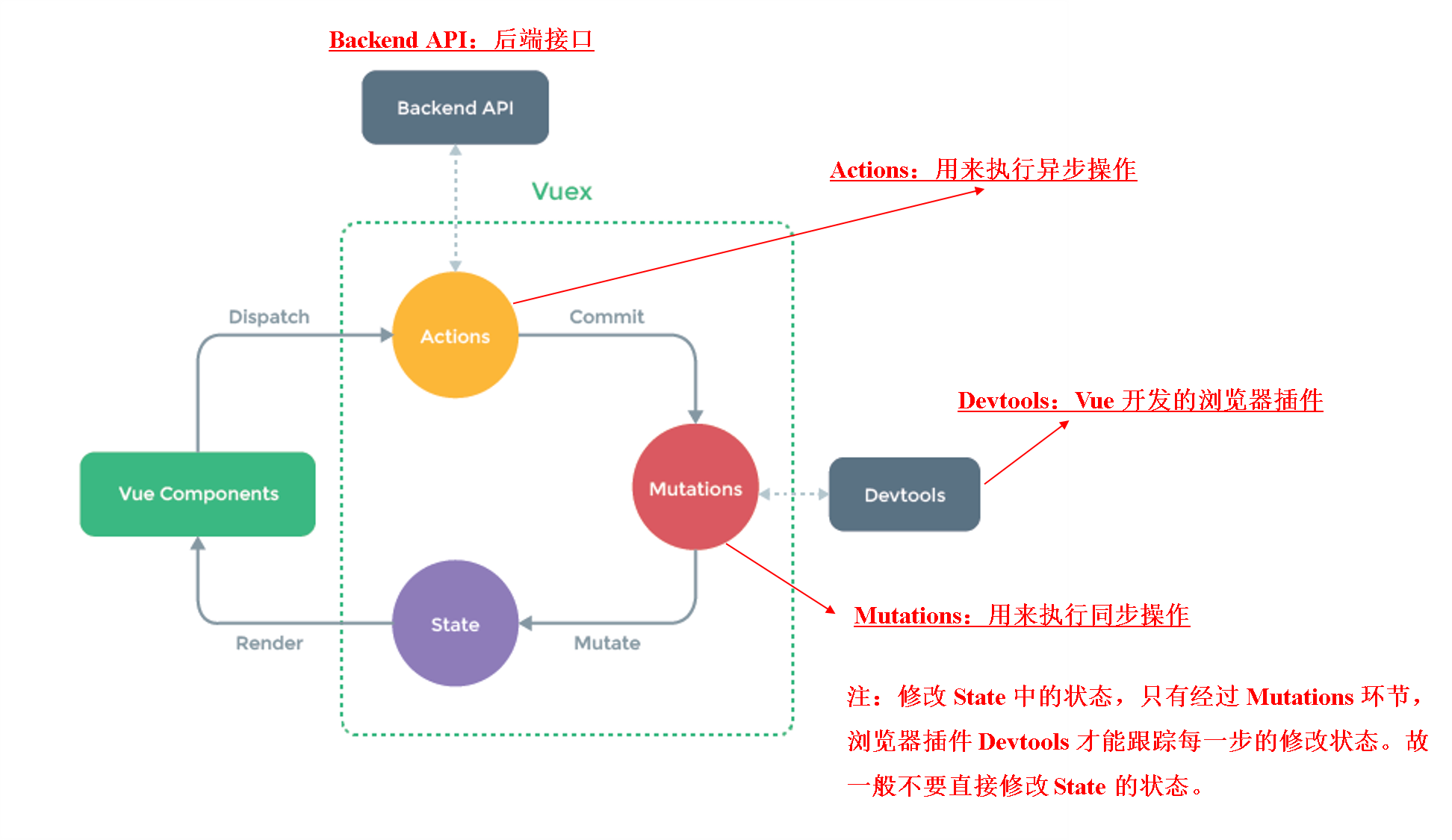
Vuex 是一个专门为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式,它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。可以理解为:将多个组件共享的变量全部存储在一个对象里面,然后将这个对象放在顶层的 Vue 实例中,让其他组件可以使用,它最大的特点是响应式。
一般情况下,我们会在 Vuex 中存放一些需要在多个界面中进行共享的信息。比如用户的登录状态、用户名称、头像、地理位置信息、商品的收藏、购物车中的物品等,这些状态信息,我们可以放在统一的地方,对它进行保存和管理。
Vuex 插件的安装
npm install --save [email protected]
注意版本问题:vue 的 2.x 版本对应 vuex 的 3.x 版本,vue 的 3.x 版本对应 vuex 的 4.x 版本
在 src 目录下新建 store 文件夹,创建 index.js文件引入、安装、创建并导出Vuex对象。
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
//1.安装插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
//2.创建对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
counter:1000
},
mutations:{
},
actions:{
},
getters:{
},
modules:{
}
})
//3.导出使用
export default store
和 vue-router 的使用方式一样,在 main.js 文件中挂载使用
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
store 对象中存放的东西是固定的,主要有:state、mutations、actions、getters、modules
下图是官方给出的vuex状态管理图例
Vuex的基本使用
安装浏览器插件:devtools 方便调试
state:存放需要共享的状态信息,使用时通过 $store.state.counter 即可拿到状态信息。

对 state 的状态信息进行修改:先拿到 store 对象,然后通过commit 提交 mutations 中的方法。

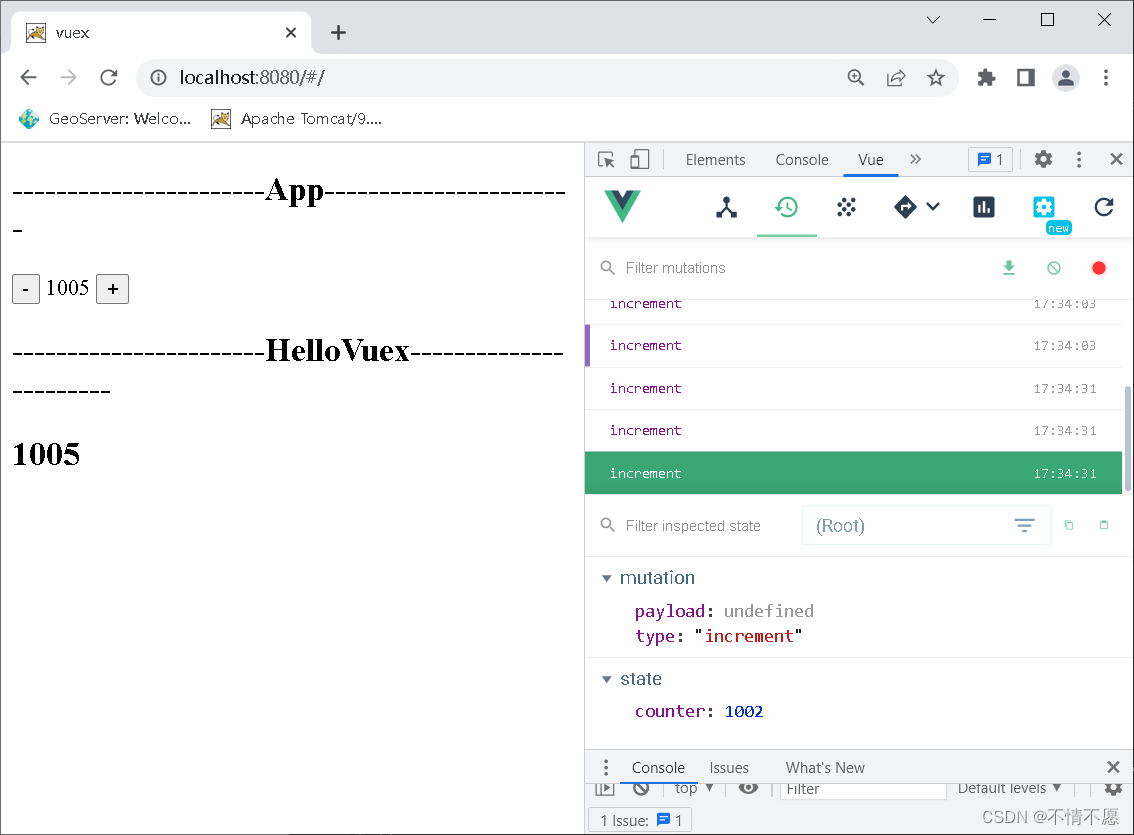
使用 devtools调试界面,可以跟踪查看每一次事件操作。
 Vuex 核心概念
Vuex 核心概念
State:
单一状态树即单一数据源,在一个项目中只使用一个store对象,来存储所有共享的状态信息。
Getters:
类似于计算属性,在数据展示前进行一些变化处理,具有缓存功能,能够提高运行效率。eg:
getters:{
powerCounter(state){
return state.counter * state.counter
},
more20stu(state){
return state.students.filter(s => s.age > 20)
},
more20stuLength(state,getters){
return getters.more20stu.length
},
moreAgeStu(state){
return function(age){
return state.students.filter(s => s.age > age)
}
}
}
使用时,通过:$store.getters.powerCounter 获取:
<h2>{
{$store.getters.powerCounter}}</h2>
<h2>{
{$store.getters.more20stu}}</h2>
<h2>{
{$store.getters.more20stuLength}}</h2>
<h2>{
{$store.getters.moreAgeStu(18)}}</h2>
需要手动传参数时,可以在 getters 中返回一个 function:eg
moreAgeStu(state){
return function(age){
return state.students.filter(s => s.age > age)
}
}
调用时传入参数即可:
<h2>{
{$store.getters.moreAgeStu(18)}}</h2>
Mutations:
store/index.js
mutations:{//定义一些方法
increment(state){
state.counter++
},
decrement(state){
state.counter--
},
incrementCount(state, payload){
//1.普通提交方式
//state.counter += count
//2.特殊提交方式
state.counter += payload.count
},
addStudent(state, obj){
state.students.push(obj)
}
}
组件调用 :传递的参数(payload)可以是一个对象
<template>
<div>
<button @click="addCount(5)">+5</button>
<button @click="addCount(10)">+10</button>
<button @click="addStudent({id:105, name:'name6', age:29})">添加学生</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:"HelloVuex",
methods:{
addCount(count){
//1.普通的提交风格
// this.$store.commit('incrementCount',count)
//2.特殊的提交风格
this.$store.commit({
type:'incrementCount',
count:count
})
},
addStudent(stu){
this.$store.commit('addStudent',stu)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
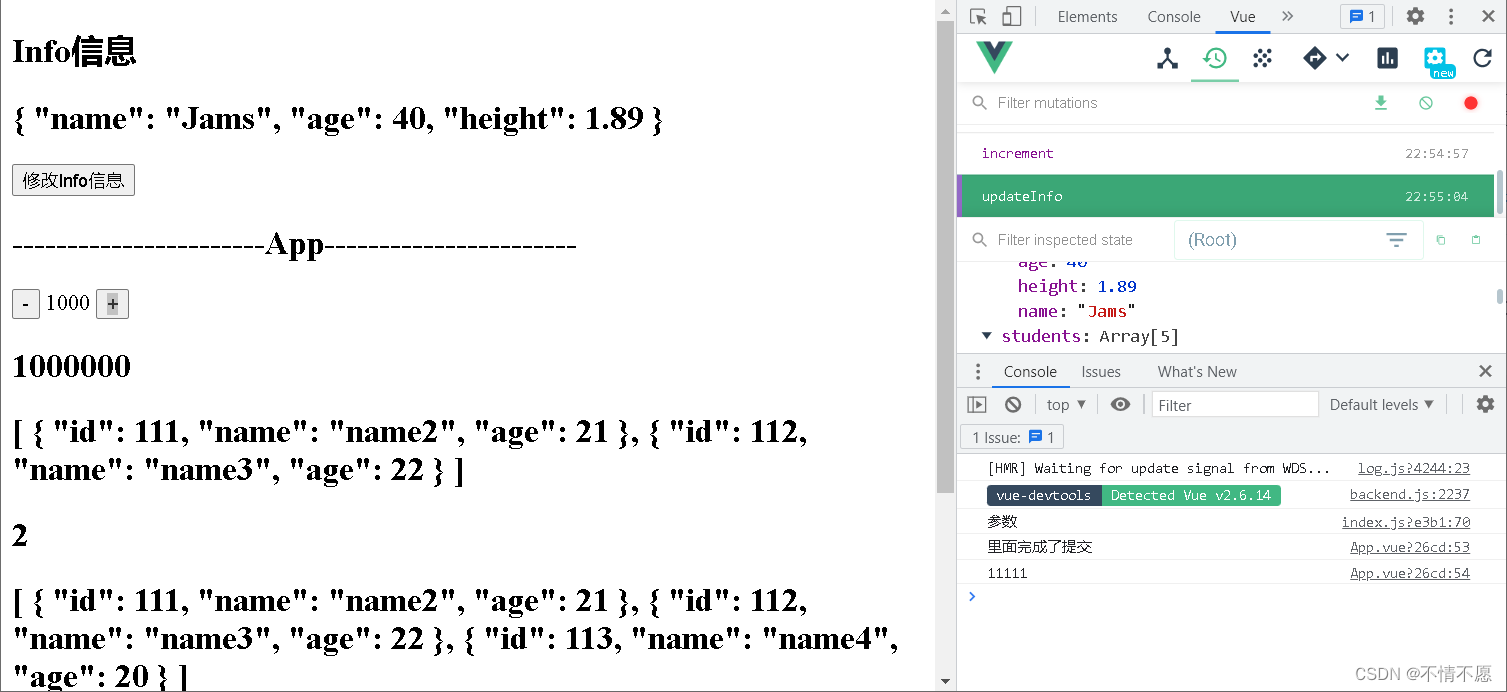
mutations在处理异步操作时,能够引起页面的响应式变化,但是 devtools 无法进行监听。
比如:在 mutations 中执行以下代码
updateInfo(state){
setTimeout(() => {
state.info.name = 'James'
}, 1000);
}
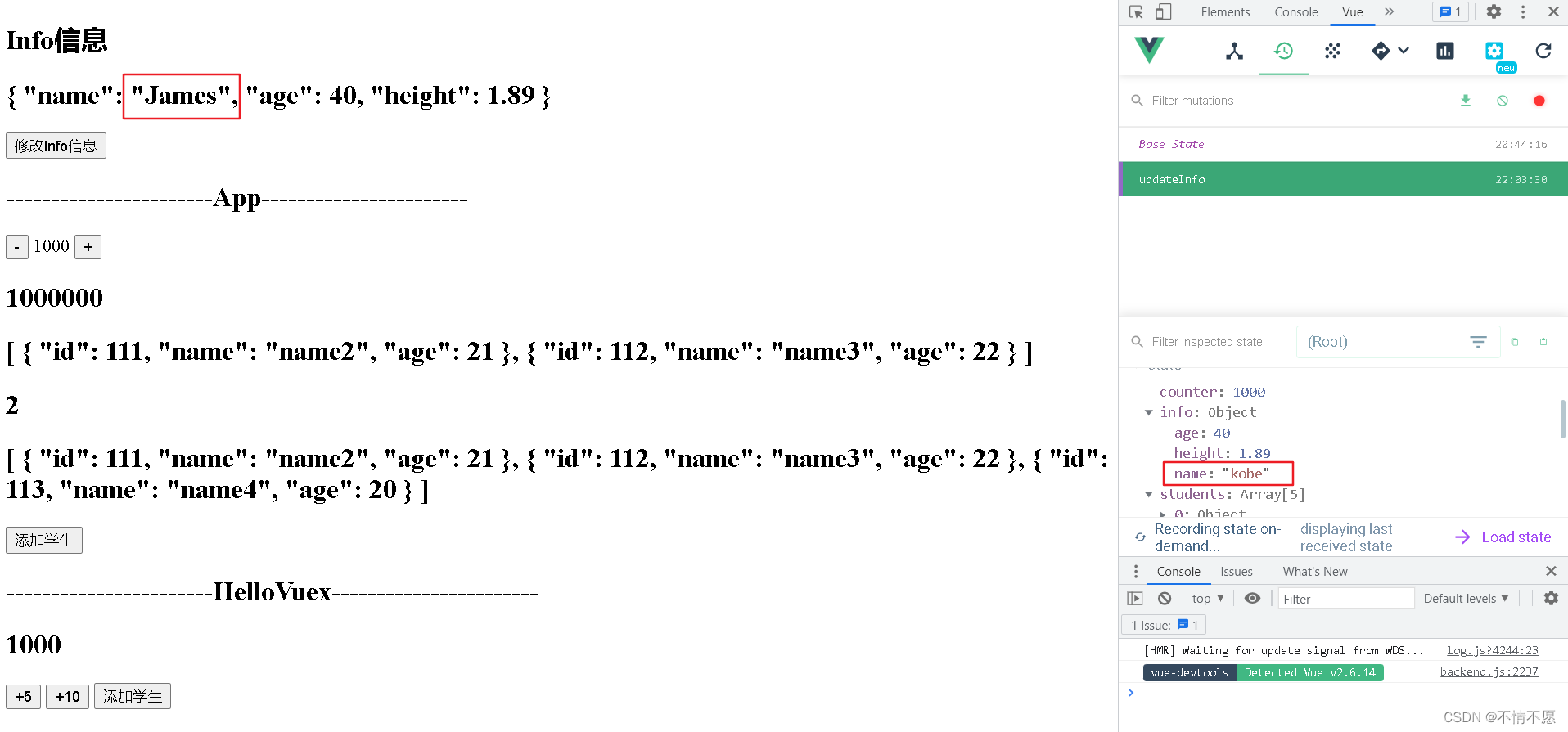
Actions:
如果确实需要进行一些异步操作,比如网络请求,建议在 Actions 中进行处理,这样 devtools 就能够进行跟踪,由 Actions 处理异步操作,具体的函数部分仍交由 Mutations 进行处理。
actions:{
//context:上下文 === store
aUpdateInfo(context,payload){
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('updateInfo',payload)
console.log(payload);
}, 5000);
}
}
组件中使用时,调用:this.$store.dispatch(‘aUpdateInfo’)
updateInfo(){
// this.$store.commit('updateInfo')
this.$store.dispatch('aUpdateInfo','参数')
}
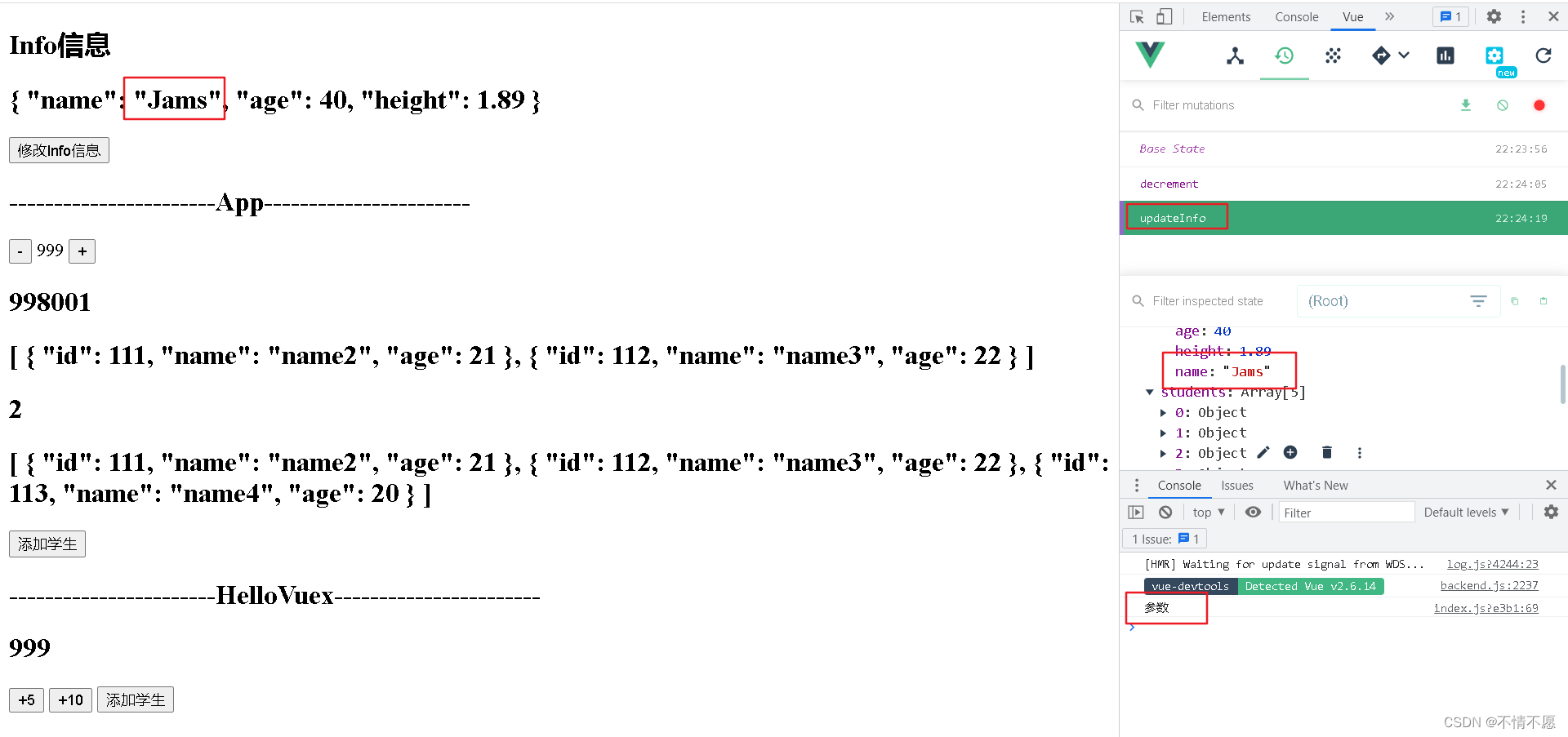 结合Promise使用:
结合Promise使用:
actions:{
//context:上下文 === store
aUpdateInfo(context, payload){
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('updateInfo');
console.log(payload);
resolve('11111')
}, 1000);
})
}
}
updateInfo(){
// this.$store.commit('updateInfo')
this.$store
.dispatch('aUpdateInfo','参数')
.then(res =>{
console.log('里面完成了提交');
console.log(res);
})
}
Modules:
分模块管理数据
const moduleA = {
state:{
name: 'moduleA'
},
mutations:{
updateName(state,payload){
state.name = payload
}
},
getters:{
fullname(state){
return state.name + '1111'
},
fullname2(state, getters){
return getters.fullname + '2222'
},
fullname3(state, getters, rootState){
//传入第三个参数:rootState为上一个store对象中的state
return getters.fullname2 +rootState.counter
}
},
actions:{
aUpdateName(context){//context 中 的commit只指向该模块中的mutations
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('updateName','xiaowang')
console.log(context)
},
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
counter:1000,
students:[
{id:110, name: 'name1', age: 12},
{id:111, name: 'name2', age: 21},
{id:112, name: 'name3', age: 22},
{id:113, name: 'name4', age: 20},
{id:114, name: 'name5', age: 18}
],
info:{
name: 'kobe',
age: 40,
height: 1.89
}
},
mutations:{//定义一些方法
increment(state){
state.counter++
},
decrement(state){
state.counter--
},
incrementCount(state, payload){
//1.普通提交方式
//state.counter += count
//2.特殊提交方式
state.counter += payload.count
},
addStudent(state, obj){
state.students.push(obj)
},
updateInfo(state){
state.info.name = 'Jams'//响应式:事先定义过的为响应式
// state.info['address'] = 'chengdu'//响应式
// Vue.set(state.info,'address1','Asgin')//响应式
// delete state.info.age//响应式
// Vue.delete(state.info,'height')//响应式
}
},
getters:{
powerCounter(state){
return state.counter * state.counter
},
more20stu(state){
return state.students.filter(s => s.age > 20)
},
more20stuLength(state,getters){
return getters.more20stu.length
},
moreAgeStu(state){
return function(age){
return state.students.filter(s => s.age > age)
}
}
},
actions:{
//context:上下文 === store
aUpdateInfo(context, payload){
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('updateInfo');
console.log(payload);
resolve('11111')
}, 1000);
})
}
},
modules:{
a: moduleA
}
})
组件中使用 :$store.state.a
<h2>Modules中的内容</h2>
<h2>{
{$store.state.a.name}}</h2>
<button @click="updateName">修改模块ModuleA中的名字</button>
<h2>{
{$store.getters.fullname3}}</h2>
<button @click="aupdateName">actions修改name</button>
执行模块中的方法 :直接 $store.commit 提交,故 mutations 之间定义的方法名不能重复。
updateName(){
this.$store.commit('updateName','lisa')
},
aupdateName(){
this.$store.dispatch('aUpdateName')
}
打印出的 context 信息如下:
 包含根状态下的一些 state (rootState) 和 mutations (rootMutations)。
包含根状态下的一些 state (rootState) 和 mutations (rootMutations)。