目录
展示
博客项目
1.创建项目
1)创建 maven 项目,并添加webapp目录
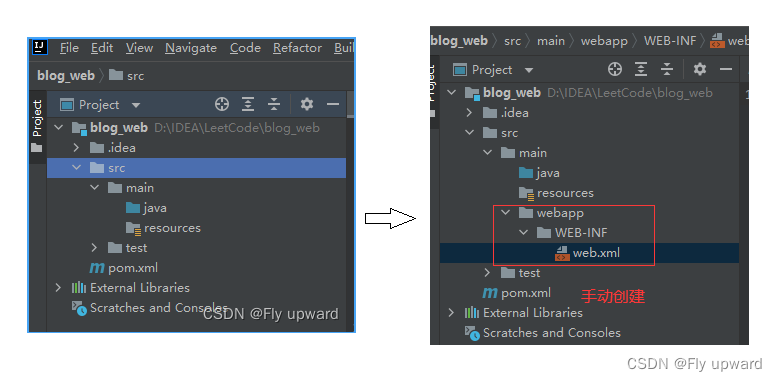
2)配置web.xml
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
</web-app>3)配置 pom.xm
<dependencies>
<!--引入servlet-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet/javax.servlet-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!--引入 jackson-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.fasterxml.jackson.core/jackson-databind -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.12.6.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--引入 mysql-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
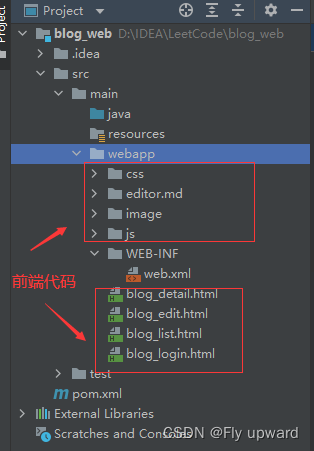
</dependencies>4)引入前端代码
将前端的代码复制到 webapp 目录下
2. 数据库设计
2.1 表设计
需要设计两张表,文章表和用户表
文章表用来存储博客文,用户表用于存储登录用户
--创建库
create database if not exists blog_web;
use blog_web;
drop table if exists blog;
--建博客表
create table blog (
blogId int primary key auto_increment,
title varchar(1024),
content mediumtext,--内容,存放大量数据
userId int,
postTime datetime --时间
);
--插入数据
insert into blog values(null, '博客一', '认真学 C', 1, now());
insert into blog values(null, '博客二', '认真学 GO', 1, now());
--用户表
drop table if exists user;
create table user (
userId int primary key auto_increment,--自增主键
username varchar(128) unique, --用户唯一
password varchar(128)
);
--用户
insert into user values(null, 'FlyUpward', '');--密码自己设
insert into user values(null, 'Fly', '');--密码自己设将表复制到 mysql 中进行建表

2.2 封装数据库操作代码
先在Java目录下创建一个model包,用于存放数据库后端类
2.2.1 创建 DBUtil
这个类用于和数据库建立连接
package model;
import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DBUtil {
private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/bolg_web?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false";
private static final String USERNAME = "root";
private static final String PASSWORD = "";//自己数据库的密码
private static volatile DataSource dataSource = null;
private static DataSource getDataSource() {
if (dataSource == null) {
synchronized (DBUtil.class) {
if (dataSource == null) {
dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUrl(URL);
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser(USERNAME);
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword(PASSWORD);
}
}
}
return dataSource;
}
private static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return getDataSource().getConnection();
}
public static void close(Connection connection, PreparedStatement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}2.2.2 创建实体类
实体类用于表示数据库的记录
1)Blog.java
每个 model.Blog 对象, 对应 blog 表里的一条记录
package model;
import java.sql.Timestamp;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class Blog {
private int blogId;
private String title;
private String content;
private int UserId;
private Timestamp postTime;
public int getBlogId() {
return blogId;
}
public void setBlogId(int blogId) {
this.blogId = blogId;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public int getUserId() {
return UserId;
}
public void setUserId(int userId) {
UserId = userId;
}
/*public Timestamp getPostTime() {
return postTime;
}*/
// 把这里的 getter 方法给改了, 不是返回一个时间戳对象, 而是返回一个 String (格式化好的时间)
public String getPostTime() {
// 使用 SimpleDateFormat 来完成时间戳到格式化日期时间的转换.
// 这个转换过程, 需要在构造方法中指定要转换的格式, 然后调用 format 来进行转换
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return simpleDateFormat.format(postTime);
}
public void setPostTime(Timestamp postTime) {
this.postTime = postTime;
}
}2) User.java
对于用户表里的每一条记录
package model;
public class User {
private int userId = 0;
private String username = "";
private String password = "";
public int getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(int userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
2.2.3 封装数据库增删改查
解 DAODAO 全称为 "data access object",主要的功能就是对于某个数据库表进行增删改查.一般每张数据库表会对应一个 DAO 类. 这是一种给类命名的习惯做法, 并不是强制要求
package model;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class BlogDao {
//1.插入博客
public void insert(Blog blog) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
//1)和数据库建立连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
//2)构造sql语句
String sql = "insert into blog values(null,?,?,?,now())";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,blog.getTitle());
statement.setString(2,blog.getContent());
statement.setInt(3,blog.getUserId());
//30执行SQL
statement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
// 2. 能够获取到博客表中的所有博客的信息 (用于在博客列表页, 此处每篇博客不一定会获取到完整的正文)
public List<Blog> selectAll() {
List<Blog> blogs = new ArrayList<>();
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil. getConnection();
String sql = "select * from blog order by postTime desc";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();//查询
while (resultSet.next()) {
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setBlogId(resultSet.getInt("blogId"));
blog.setTitle(resultSet.getString("title"));
// 这里需要针对内容进行截断(太长了, 就去掉后面)
String content = resultSet.getString("content");
// 这个数字具体写多少, 都可以灵活应对!!
if (content.length() > 10) {
content = content.substring(0,10) + "......";
}
blog.setContent(content);
blog.setUserId(resultSet.getShort("userId"));
blog.setPostTime(resultSet.getTimestamp("postTime"));
blogs.add(blog);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
return blogs;
}
// 3. 能够根据博客 id 获取到指定的博客内容 (用于在博客详情页)
public Blog selectOne(int blogId) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from blog where blogId = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,blogId);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
// 此处我们是使用 主键 来作为查询条件的. 查询结果, 要么是 1 , 要么是 0.
if (resultSet.next()) {
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setBlogId(resultSet.getInt("blogId"));
blog.setTitle(resultSet.getString("title"));
blog.setContent(resultSet.getString("content"));
blog.setUserId(resultSet.getShort("userId"));
blog.setPostTime(resultSet.getTimestamp("postTime"));
return blog;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
return null;
}
// 4. 从博客表中, 根据博客 id 删除博客.
public void delete(int blogId) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "delete from blog where blogId = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,blogId);
statement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, null);
}
}
}2)创建 UserDao 类
package model;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
//提供了针对用户表的基本操作
public class UserDao {
public void insert(User user){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into user values(null,?,?)";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1, user.getUsername());
statement.setString(2, user.getPassword());
statement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
//主要实现
// 1. 根据用户名来查找用户信息
//这个会在登录逻辑中使用
public User selectByName(String username) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from user where username = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1, username);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
// 此处 username 使用 unique 约束, 要么能查到一个, 要么一个都查不到.
if (resultSet.next()) {
User user = new User();
user.setUserId(resultSet.getInt("userId"));
user.setUsername(resultSet.getString("username"));
user.setPassword(resultSet.getString("password"));
return user;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
return null;
}
// 2. 根据用户 id 来找用户信息.
// 博客详情页, 就可以根据用户 id 来查询作者的名字, 把作者名字显示出来.
public User selectById(int userId) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from user where userId = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1, userId);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
// 此处 username 使用 unique 约束, 要么能查到一个, 要么一个都查不到.
if (resultSet.next()) {
User user = new User();
user.setUserId(resultSet.getInt("userId"));
user.setUsername(resultSet.getString("username"));
user.setPassword(resultSet.getString("password"));
return user;
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
return null;
}
}3.实现博客列表
3.1 约定前后端交互接口
[ 请求 ]GET / blog[ 响应 ][{blogId : 1 ,title : " 第一篇博客 " ,content : " 博客摘要 " ,userId : 1 ,postTime : "2022-07-06 12:00:00"},{blogId : 2 ,title : " 第二篇博客 " ,content : " 博客摘要 " ,userId : 1 ,postTime : "2022-07-06 12:10:00"},...]
3.2 实现服务器代码
1)先获取数据库列表并转换成json 格式,看是否交互成功
@WebServlet("/blog")
public class BlogServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {//从数据库中查询到博客列表,转成json 格式
//获取博客列表
BlogDao blogDao = new BlogDao();
List<Blog> blogs = blogDao.selectAll();
//转换
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(blogs);
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
}
}2) 通过postman 验证可知,交互成功
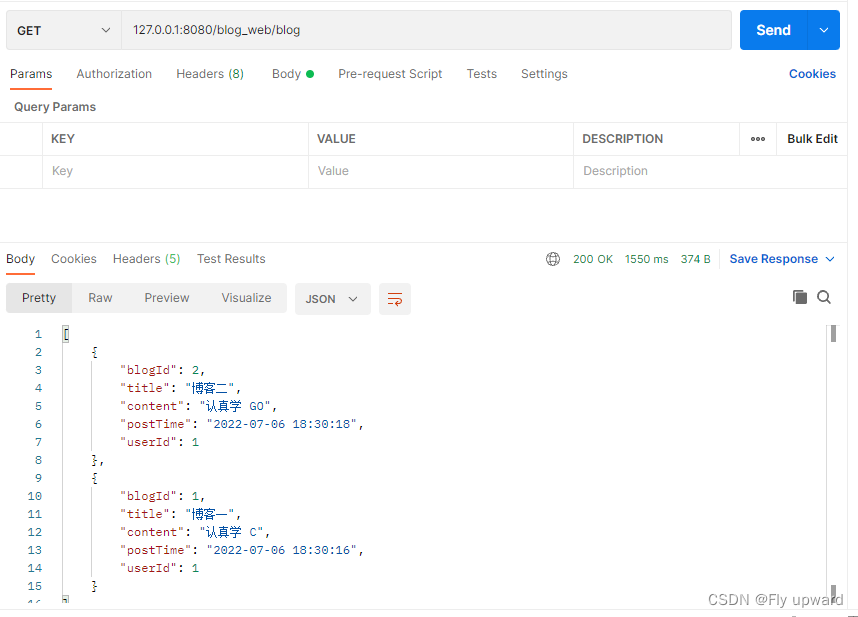
3.3 实现客户端代码
<script src="http://libs.baidu.com/jquery/2.0.0/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script>
// 在页面加载的时候, 通过 ajax 给服务器发送数据, 获取到博客列表信息, 并且显示在界面上.
function getBlogList() {
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
url: 'blog',
success: function(body) {
// 获取到的 body 就是一个 js 对象数组, 每个元素就是一个 js 对象, 根据这个对象构造 div
// 1. 先把 .right 里原有的内容给清空
let rightDiv = document.querySelector('.right');
rightDiv.innerHTML = '';
// 2. 遍历 body, 构造出一个个的 blogDiv
for (let blog of body) {
let blogDiv = document.createElement('div');
blogDiv.className = 'blog';
// 构造标题
let titleDiv = document.createElement('div');
titleDiv.className = 'title';
titleDiv.innerHTML = blog.title;
blogDiv.appendChild(titleDiv);
// 构造发布时间
let dateDiv = document.createElement('div');
dateDiv.className = 'date';
dateDiv.innerHTML = blog.postTime;
blogDiv.appendChild(dateDiv);
// 构造博客的摘要
let descDiv = document.createElement('div');
descDiv.className = 'desc';
descDiv.innerHTML = blog.content;
blogDiv.appendChild(descDiv);
// 构造 查看全文
let a = document.createElement('a');
a.innerHTML = '查看全文 >>';
// 此处希望点击之后能够跳转到 博客详情页 !!
// 这个跳转过程需要告知服务器要访问的是哪个博客的详情页.
a.href = 'blog_detail.html?blogId=' + blog.blogId;
blogDiv.appendChild(a);
// 把 blogDiv 挂到 dom 树上!
rightDiv.appendChild(blogDiv);
}
},
error: function() {
alert("获取博客列表失败!");
}
});
}
getBlogList();
</script>
验证
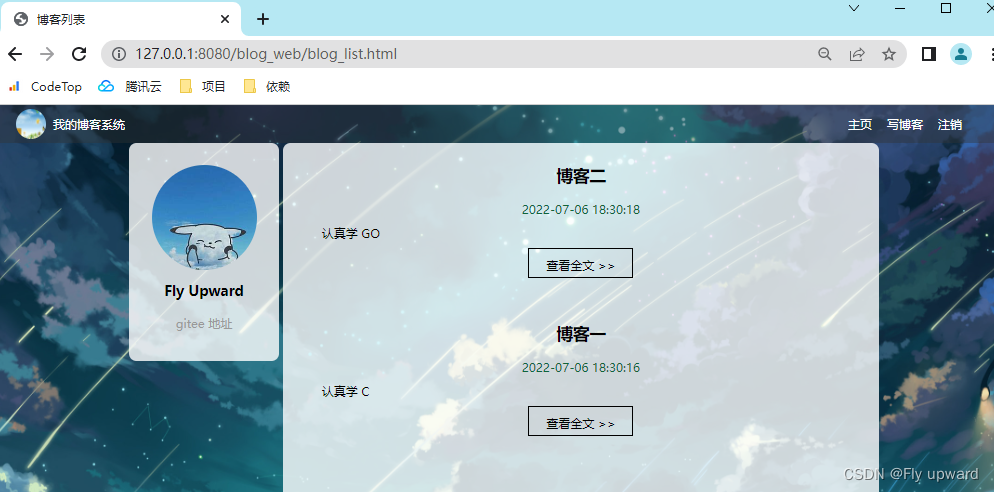
4. 实现博客详情
4.1 约定前后端交互接口
[ 请求 ]GET / blog ? blogId = 1[ 响应 ]{blogId : 1 ,title : " 第一篇博客 " ,content : " 博客正文 " ,userId : 1 ,postTime : "2022-07-06 12:00:00"},
4.2 实现服务器代码
根据 blogId 参数是否存在, 判定当前是获取博客列表还是获取博客详情
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf8");
BlogDao blogDao = new BlogDao();
// 先尝试获取到 req 中的 blogId 参数. 如果该参数存在, 说明是要请求博客详情
// 如果该参数不存在, 说明是要请求博客的列表.
String param = req.getParameter("blogId");
if (param == null) {
//不存在参数,获取列表
List<Blog> blogs = blogDao.selectAll();
//把blog 对象转成json 格式
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(blogs);
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
} else {
// 存在参数, 获取博客详情
int blogId = Integer.parseInt(param);
Blog blog = blogDao.selectOne(blogId);
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(blog);
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
}
}
4.3 实现客户端代码
1) 引入 editor.md
<!-- 引入 editor.md 的依赖 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="editor.md/css/editormd.min.css" />
<script src="js/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="editor.md/lib/marked.min.js"></script>
<script src="editor.md/lib/prettify.min.js"></script>
<script src="editor.md/editormd.js"></script><!-- 右侧内容详情 -->
<div class="right">
<!-- 使用这个 div 来包裹整个博客的内容详情 -->
<div class="blog-content">
<!-- 博客标题 -->
<h3></h3>
<!-- 博客的时间 -->
<div class="date"></div>
<!-- 正文 -->
<div id="content" style="opacity: 80%"></div>
</div>
</div> <script>
function getBlogDetail() {
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
// location.search 拿到了形如 '?blogId=1' 这样的一段内容
url: 'blog' + location.search,
success: function(body) {
// 根据 body 中的内容来构造页面
// 1. 构造博客标题
let h3 = document.querySelector(".blog-content>h3");
h3.innerHTML = body.title;
//2.构造博客发布时间
let dateDiv = document.querySelector('.date');
dateDiv.innerHTML = body.postTime;
// 3. 构造博客正文
// 如果直接把 content 设为 innerHTML, 此时展示在界面上的内容, 是原始的 markdown 字符串
// 此处需要的是渲染后的, 带有格式的效果
// let content = document.querySelector('#content');
// content.innerHTML = body.content;
// 第一个参数对应 id=content 的 html 标签. 渲染后得到的 html 片段就会被放到这个 标签下.
editormd.markdownToHTML('content', {
markdown: body.content
});
}
});
}
getBlogDetail();
</script>验证

5. 实现登陆
5.1 约定前后端交互接口
[ 请求 ]POST /loginContent-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencodedusername=test&password=“ ”[ 响应 ]HTTP/1.1 302Location: blog_list.html
5.2 实现服务器代码
@WebServlet("/login")
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf8");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf8");
// 1. 获取到请求中的参数
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
System.out.println("username=" + username + ", password=" + password);
if (username == null || "".equals(username) || password == null || "".equals(password)) {
// 请求的内容缺失, 肯定是登录失败!!
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前的用户名或密码为空,请重新输入!");
return;
}
// 2. 和数据库中的内容进行比较
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
User user = userDao.selectByName(username);
if (user == null || !user.getPassword().equals(password)) {
// 用户没有查到或者密码不匹配, 也是登录失败!
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("用户名或密码错误,请重新输入!");
return;
}
// 3. 如果比较通过, 就创建会话.
HttpSession session = req.getSession(true);
// 把刚才的用户信息, 存储到会话中.
session.setAttribute("user", user);
// 4. 返回一个重定向报文, 跳转到博客列表页.
resp.sendRedirect("blog_list.html");
}
// 这个方法用来让前端检测当前的登录状态.
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf8");
HttpSession session = req.getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
// 检测下会话是否存在, 不存在说明未登录!
User user = new User();
resp.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user));
return;
}
User user = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
if (user == null) {
// 虽然有会话, 但是会话里没有 user 对象, 也视为未登录.
user = new User();
resp.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user));
return;
}
// 已经登录的状态!!
// 注意, 此处不要把密码给返回到前端
user.setPassword("");
resp.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user));
}
}5.3 实现客户端代码
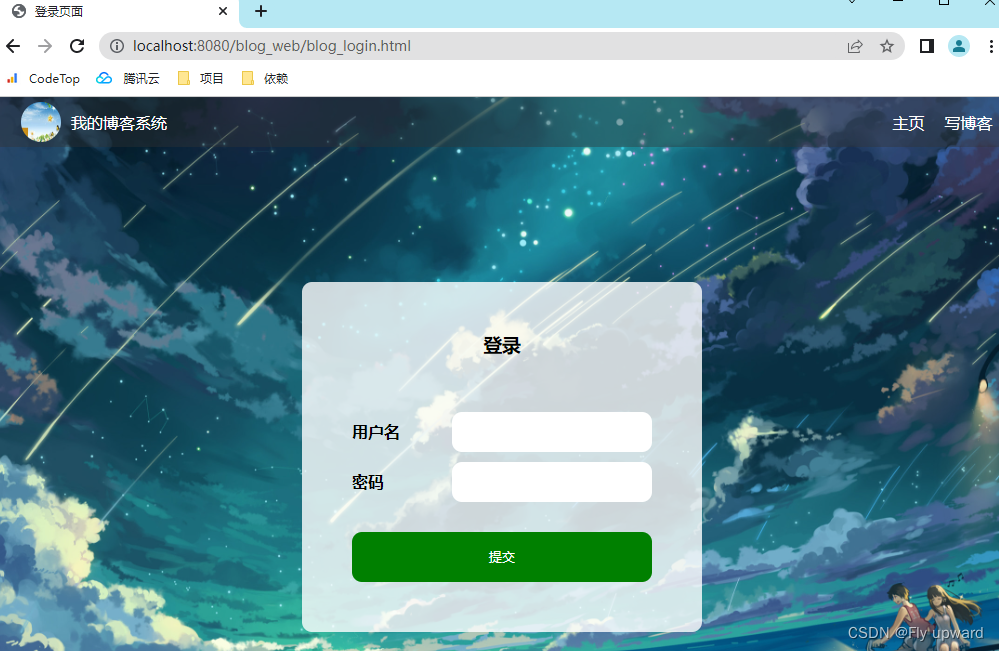
修改blog_login.html
给输入框套上一层 form 标签 . action 为 login, method 为 POST给 input 加上 name 属性。提交按钮改成 <input type="submit" id="submit" value="提交">
<div class="login-dialog">
<h3>登录</h3>
<div class="row">
<span>用户名</span>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username">
</div>
<div class="row">
<span>密码</span>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password">
</div>
<div class="row">
<!-- <button>提交</button> -->
<input type="submit" id="submit" value="提交">
</div>
</div>修改blog_login.css
将 .row button{ } 和 .row button:active{ } 修改成下面的样式
.row #submit {
width: 300px;
height: 50px;
border-radius: 10px;
color: white;
background-color: rgb(0, 128, 0);
border: none;
outline: none;
margin-top: 50px;
}
.row #submit:active {
background-color: #666;
}5.4 实现强制要求登陆和写博客
当用户访问 博客列表页 和 博客详情页 时, 如果用户当前尚未登陆, 就自动跳转到登陆页面。
1)修改 BlogServlet
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
// 当前用户未登录, 不能提交博客!
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前用户未登录,不能提交博客");
return;
}
User user = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
if (user == null) {
// 当前用户未登录, 不能提交博客!
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前用户未登录,不能提交博客");
return;
}
// 一定要先指定好请求按照哪种编码来解析
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf8");
// 先从请求中, 取出参数(博客的标题和正文)
String title = req.getParameter("title");
String content = req.getParameter("content");
if (title == null || "".equals(title) || content == null || "".equals(content)) {
// 直接告诉客户端, 请求参数不对
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("提交博客失败!缺少必要参数!");
return;
}
// 构造 Blog 对象, 把当前的信息填进去, 并插入数据库中
// 此处要给 Blog 设置的属性, 主要是 title, content, userId (作者信息)
// postTime 和 blogId 都不需要手动指定, 都是插入数据库的时候自动生成的.
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setTitle(title); //标题
blog.setContent(content); //摘要
// 作者 id 就是当前提交这个博客的用户的身份信息
blog.setUserId(user.getUserId());
BlogDao blogDao = new BlogDao();
blogDao.insert(blog);
// 重定向到, 博客列表页!
resp.sendRedirect("blog_list.html");
}
2)修改 blog_list.html
<!-- 在这里引入上述的 js 文件, 就可以执行到里面的代码, 也就进行了登录状态的监测了 -->
<script src="js/common.js"></script>
<script>
// 针对博客列表页, 调用的时候传入参数
getUserInfo('blog_list.html');
</script>common.js
// 这个文件里放一些页面公共的代码
// 加上一个逻辑, 通过 GET /login 这个接口来获取下当前的登录状态~
function getUserInfo(pageName) {
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
url: 'login',
success: function(body) {
// 判定此处的 body 是不是一个有效的 user 对象(userId 是否非 0)
if (body.userId && body.userId > 0) {
// 登录成功!
// 不做处理!
console.log("当前用户登录成功! 用户名: " + body.username);
// 根据当前用户登录的情况, 把当前用户名设置到界面上
if (pageName == 'blog_list.html') {
changeUserName(body.username);
}
} else {
// 登录失败!
// 让前端页面, 跳转到 login.html
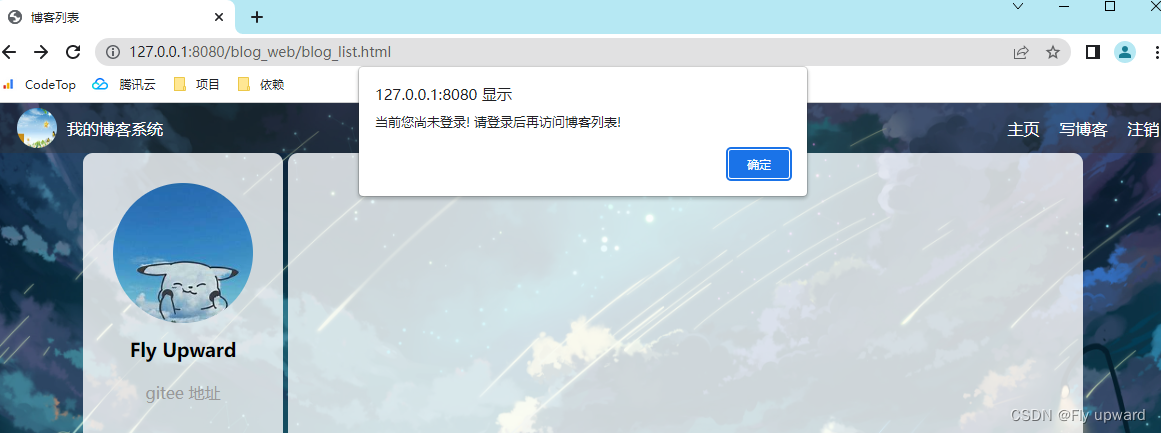
alert("当前您尚未登录! 请登录后再访问博客列表!");
location.assign('blog_login.html');
}
},
error: function() {
alert("当前您尚未登录! 请登录后再访问博客列表!");
location.assign('blog_login.html');
}
});
}
function changeUserName(username) {
let h3 = document.querySelector('.card>h3');
h3.innerHTML = username;
}3)修改 blog_detail.html
在文件中增加以下代码
// 加上一个逻辑, 通过 GET /login 这个接口来获取下当前的登录状态
function getUserInfo(pageName) {
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
url: 'login',
success: function(body) {
// 判定此处的 body 是不是一个有效的 user 对象(userId 是否非 0)
if (body.userId && body.userId > 0) {
// 登录成功!
// 不做处理!
console.log("登录成功!用户名:“+ body.username");
// 在 getUserInfo 的回调函数中, 来调用获取作者信息
getAuthorInfo(body);
} else {
// 登录失败!
// 让前端页面, 跳转到 login.html
alert("当前您未登录,请登录后再访问博客列表!");
location.assign('blog_login.html');
}
},
error: function() {
alert("当前您未登录,请登录后再访问博客列表!");
location.assign('blog_login.html');
}
});
}
// 判定用户的登录状态
getUserInfo("blog_detail.html");
4)修改 blog_edit.html
<!-- 包裹整个博客编辑页内容的顶级容器 -->
<div class="blog-edit-container">
<form action="blog" method="post" style="height:100% ">
<div class="title">
<input type="text" placeholder="在此处输入标题" name="title" id="title">
<!-- <button>发布文章</button> -->
<input type="submit" value="发布文章" id="submit">
</div>
<!-- 放置 md 编辑器 -->
<div id="editor">
<!-- 为了进行 form 的提交, 此处搞一个 textarea 多行编辑框, 借助这个编辑框来实现表单的提交 -->
<!-- 可以设置 editor.md, 让编辑器把 markdown 内容也同步的保存到这个隐藏的 textarea 中, 从而可以进行 form 提交 -->
<textarea name="content" style="display: none"></textarea>
</div>
</form>
</div>5)修改blog_edit.css
将.blog-edit-container .title button{ }
.blog-edit-container .title button:active{ }
修改成下面的样式
.blog-edit-container .title #submit {
width: 100px;
height: 40px;
border-radius: 10px;
color: white;
background-color: orange;
border: none;
outline: none;
font-size: 18px;
}
.blog-edit-container .title #submit:active {
background-color: #666;
}
验证
6. 实现显示用户信息

6.1 约定前后端交互接口
[ 请求 ]GET /authorInfo[ 响应 ]{userId: 1,username: Fly Upward}
在博客详情页, 获取当前文章作者的用户信息
[ 请求 ]GET /user?blogId=1[ 响应 ]{userId: 1,username: Fly Upward}
6.2 实现服务器代码
建一个AuthorServlet
@WebServlet("/authorInfo")
public class AuthorServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
// 通过这个方法, 来获取到指定的博客的作者信息.
String param = req.getParameter("blogId");
if (param == null || "".equals(param)) {
// 参数缺少了.
resp.getWriter().write("{ \"ok\": false, \"reason\": \"参数缺失!\" }");
return;
}
// 根据当前 blogId 在数据库中进行查找, 找到对应的 Blog 对象, 再进一步的根据 blog 对象, 找到作者信息.
BlogDao blogDao = new BlogDao();
Blog blog = blogDao.selectOne(Integer.parseInt(param));
if (blog == null) {
resp.getWriter().write("{ \"ok\": false, \"reason\": \"要查询的博客不存在!\" }");
return;
}
// 根据 blog 对象, 查询到用户对象
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
User author = userDao.selectById(blog.getUserId());
if (author == null) {
resp.getWriter().write("{ \"ok\": false, \"reason\": \"要查询的用户不存在!\" }");
return;
}
// 把 author 返回到浏览器这边
// 注意要把密码去掉
author.setPassword("");
resp.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(author));
}
}为了避免麻烦和混淆,服务器代码在上面的blog_list.html 和 blog_detail.html 已经实现好了。
7. 实现注销登陆
7.1 约定前后端交互接口
[ 请求 ]GET /logout[ 响应 ]HTTP/1.1 302Location: login.html
7.2 实现服务器代码
创建 LogoutServlet
@WebServlet("/logout")
public class LogoutServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 先找到当前用户的会话,
HttpSession session = req.getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
// 用户没有登录!! 谈不上注销!
resp.getWriter().write("当前用户尚未登录! 无法注销!");
return;
}
// 然后把这个用户的会话中的信息给删掉就行了!!
session.removeAttribute("user");
resp.sendRedirect("blog_login.html");
}
}8. 实现删除博客
8.1 约定前后端交互接口
[ 请求 ]GET / user ? blogId = 1[ 响应 ]{userId : 1 ,username : test ,isYourBlog : 1 , // 1 表示当前博客就是登陆者的博客 . 0 表示当前博客不是登陆者的博客}
DELETE /blog?blogId=1[ 响应 ]HTTP/1.1 200
8.2 实现服务器代码
@WebServlet("/blogDelete")
public class BlogDeleteServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 1. 检查当前用户是否登录
HttpSession session = req.getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前尚未登录, 不能删除!");
return;
}
User user = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
if (user == null) {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前尚未登录, 不能删除!");
return;
}
// 2. 获取到参数中的 blogId
String blogId = req.getParameter("blogId");
if (blogId == null || "".equals(blogId)) {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前 blogId 参数不对!");
return;
}
// 3. 获取要删除的博客信息.
BlogDao blogDao = new BlogDao();
Blog blog = blogDao.selectOne(Integer.parseInt(blogId));
if (blog == null) {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前要删除的博客不存在!");
return;
}
// 4. 再次校验, 当前的用户是否就是博客的作者
if (user.getUserId() != blog.getUserId()) {
// 这一点在前端这里其实也处理过~~ 但是此处还是再校验一次, 不是坏事!!!
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前登录的用户不是作者, 没有权限删除!");
return;
}
// 5. 确认无误, 开始删除
blogDao.delete(Integer.parseInt(blogId));
// 6. 重定向到博客列表页
resp.sendRedirect("blog_list.html");
}
}8.3 实现客户端代码
修改blog_detail.html
// 从服务器获取一下当前博客的作者信息, 并显示到界面上.
// 参数 user 就是刚才从服务器拿到的当前登录用户的信息
function getAuthorInfo(user) {
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
url: 'authorInfo' + location.search,
success: function(body) {
// 此处的 body, 就是服务器返回的 User 对象, 是文章的作者信息
if (body.username) {
// 如果响应中的 username 存在, 就把这个值设置到页面上.
changeUserName(body.username);
if (body.username == user.username) {
// 作者和登录的用户是一个人, 则显示 "删除按钮"
let navDiv = document.querySelector('.nav');
let a = document.createElement('a');
a.innerHTML = '删除';
// 期望点击删除, 构造一个形如 blogDelete?blogId=6 这样的请求
a.href = 'blogDelete' + location.search;
navDiv.appendChild(a);
}
} else {
console.log('获取作者信息失败!' + body.reason);
}
}
});