参考:https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/linuxonibm/com.ibm.linux.z.l0wlcb00/l0wlcb00_miimonitor.html
https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/linuxonibm/com.ibm.linux.z.l0wlcb00/l0wlcb00_miimonitor.html
https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/linuxonibm/com.ibm.linux.z.l0wlcb00/l0wlcb00_miimonitorvsarpmonitor.html
Linux bonding驱动支持两种 link monitor:MII (Media Independent Interface) monitor and the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) monitor。
这两中link monitor不能同时存在,你一次只能选择选择一种。而且也不是所有的bonding modes支持这两种link monitor,支持MII的占大多数。
MII monitor vs. ARP monitor
The MII monitor is driver-dependent. It monitors the links from the device to the nearest connected switch. If the failure occurs beyond the nearest connected switch, it cannot be detected by MII monitor. However, the ARP monitor is based on the communication to the target hosts designated by their IP addresses. Even if the link is beyond the nearest connected switch, the APR monitor can detect it.
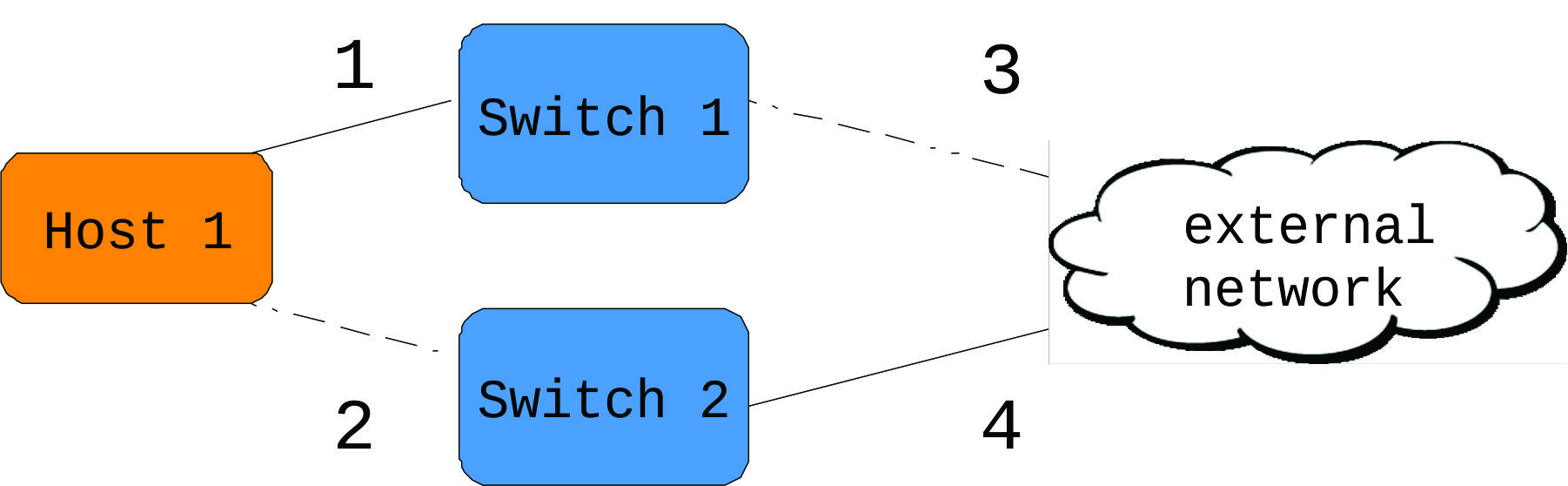
Figure 1 shows a network typology in which Host 1 is connected to two independent switches. Both of the switches are connected to an external network. If link 2 is broken, both MII and ARP monitors will be able to detect it, since the link is within the nearest connected switch. If link 3 is broken, only ARP monitor can detect it.
The MII monitor is appropriate for bonding when the network communication is within a LAN. The ARP IP target-based monitor is suitable for bonding that is expected to communicate to an outside network.
MII monitor
MII monitor周期检查MII (Media Independent Interface)提供的信息。如果MII反映了某个网络设备故障,那么bonding driver会把这个故障设备标记为关闭。与MII monitor有关的选项:
miimon
指定MII monitor多久检查一次MII (Media Independent Interface)提供的信息。默认值是0,也就是禁用MII monitor的检查功能。对于Linux on Z,这个值通常为1000
Linux on IBM Z (or Linux on z for short, and previously Linux on z Systems) is the collective term for the Linux operating system compiled to run on IBM mainframes, especially IBM Z and IBM LinuxONE servers. Similar terms which imply the same meaning are Linux on zEnterprise, Linux on zSeries, Linux/390, Linux/390x, etc. The terms zLinux or z/Linux are also sometimes used, but these terms are discouraged by IBM as they create the implication of an IBM-offered or IBM-distributed version of Linux, which is incorrect.

A pair of IBM mainframes. On the left is the IBM Z z13. On the right is the IBM LinuxONE Rockhopper.
use_carrier
指定miimon是否应使用MII或ETHTOOL ioctls与netif_carrier_ok()来确定链接状态。 默认值是1,这使得可以使用netif_carrier_ok()。 这由Linux on Z上的qeth设备驱动程序支持。
updelay
指定在检测到链路恢复后启用从设备之前要等待的时间(以毫秒为单位)。 updelay的数值应该是miimon数值的倍数。
downdelay
指定检测到链路故障后禁用从设备的时间(以毫秒为单位)。 downdelay的数值应该是miimon数值的倍数。
Figure 1. Example: Using the MII monitor miimon=1000 use_carrier=1 updelay=5000 downdelay=2000
ARP monitor
The ARP monitor checks the links by periodically sending ARP packets to the designated targets. If there is no reply from a certain device, it considers the device to be down. The ARP monitor generates regular traffic by issuing ARP probes. The ARP monitor is not supported by all of the bonding modes. Requested options are:
- arp_interval
- Specifies the ARP link monitoring frequency in milliseconds. The default value is 0, which disables the ARP monitor. A reasonable value could be 1000.
- arp_ip_target
- These are the IP addresses of targets of the ARP request sent to determine the health of the link to the targets. Multiple IP addresses must be separated by a comma. At least one IP address must be given for ARP monitoring to function. The maximum number of targets that can be specified is 16.
-
Figure 1. Example: Using the ARP monitor arp_interval=1000 arp_ip_target=192.0.2.29,192.0.2.30