前言
今天来教大家做一个文件搜索工具,专门来找你电脑里的【学习资料】,嘿嘿

开发环境
- 解释器: Python 3.8.8 | Anaconda, Inc.
- 编辑器: pycharm 专业版
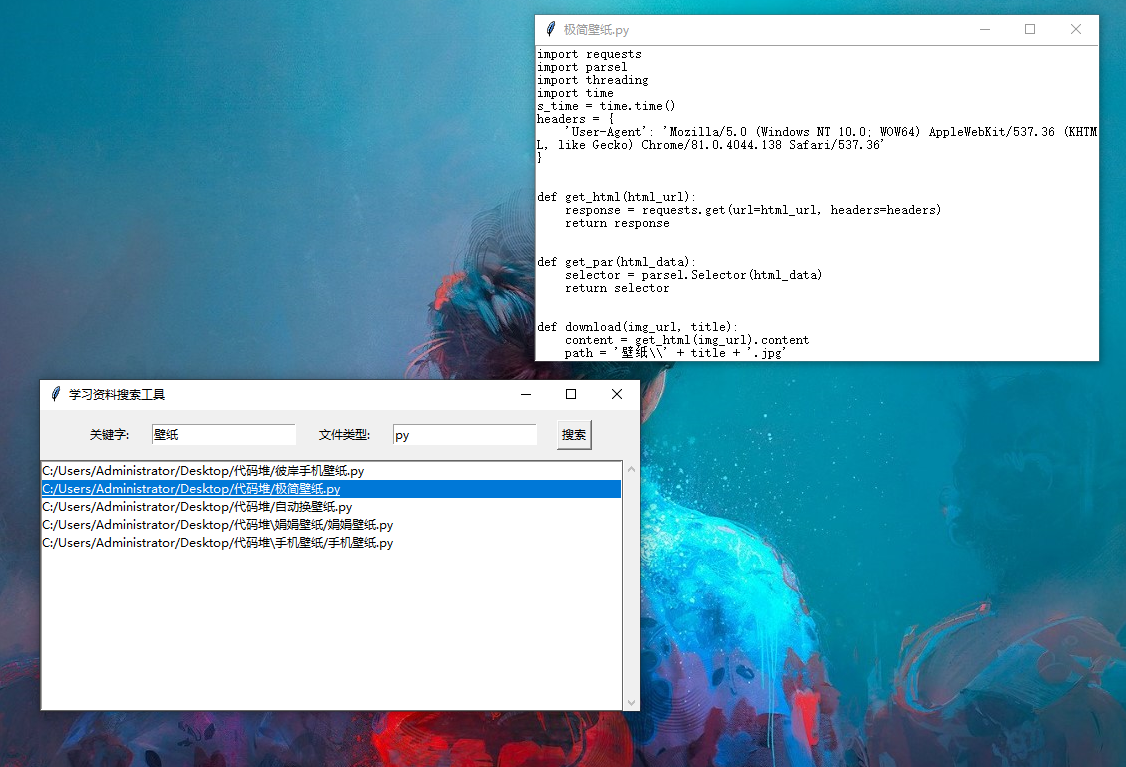
先演示效果
开始代码,先导入模块
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
import os
创建窗口
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry('600x300')
root.title('学习资料搜索工具')
root.mainloop()
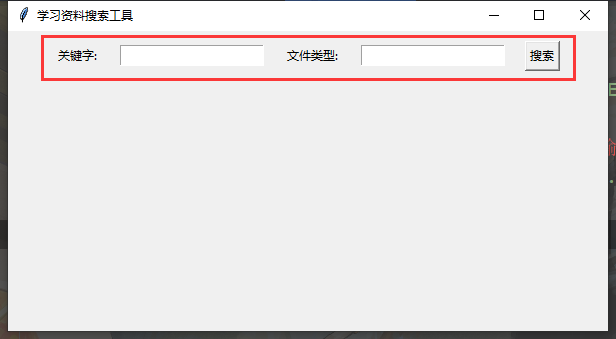
搜索栏
search_frame = tk.Frame(root)
search_frame.pack()
tk.Label(search_frame, text='关键字:').pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10, pady=10)
key_entry = tk.Entry(search_frame) # 创建一个输入框
key_entry.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10, pady=10) # 将输入框显示到界面
tk.Label(search_frame, text='文件类型:').pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10, pady=10)
type_entry = tk.Entry(search_frame)
type_entry.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10, pady=10)
button = tk.Button(search_frame, text='搜索')
button.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10, pady=10)
显示框
list_box = tk.Listbox(root)
list_box.pack(side=tk.LEFT, fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
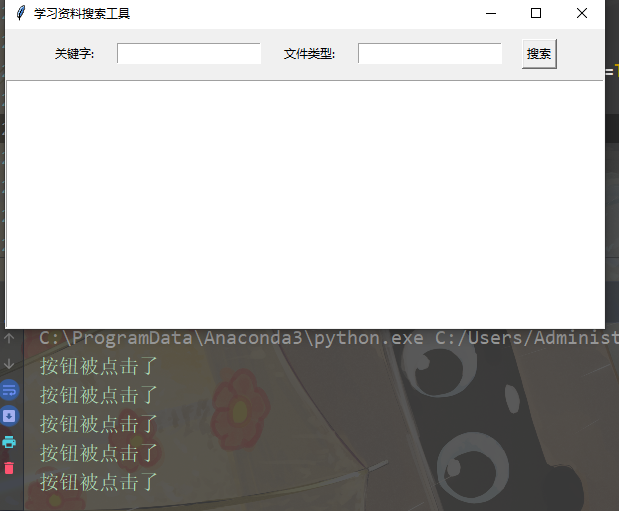
点击搜索按钮
def search():
print('按钮被点击了')
button.config(command=search)
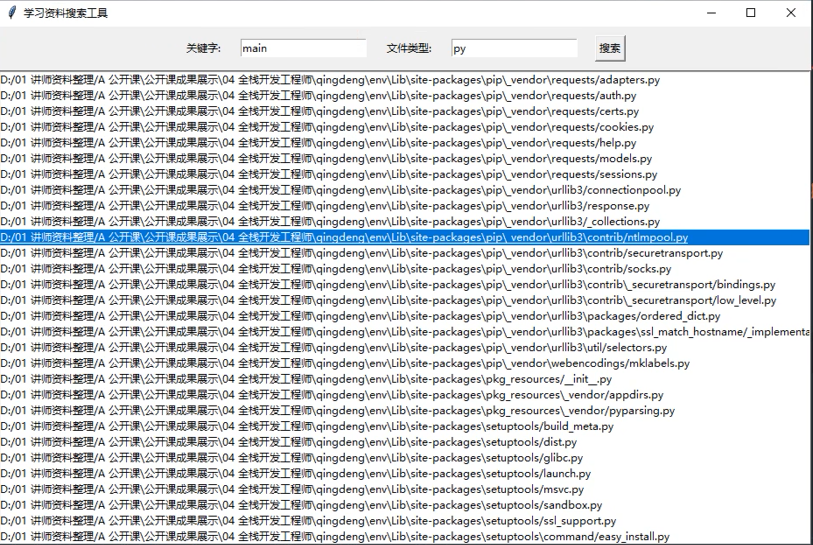
1. 获取关键字、文件类型
key = key_entry.get()
file_type = type_entry.get()
print(key, file_type)
2. 实现搜索功能
dir_path = filedialog.askdirectory()
print(dir_path) # 遍历文件,实现搜索功能
file_list = os.walk(dir_path)
for root_path, dirs, files in file_list:
# 目录路径,目录下的子目录,目录下的文件
# print(root_path, dirs, files)
for file in files:
# 过滤文件类型,搜索关键字
if type_entry: # py 如果输入了类型,就进行过滤,如果没有输入,就不过滤类型
if file.endswith(file_type):
# 搜索关键字
content = open(root_path + '/' + file, mode='r', encoding='utf-8-sig').read()
if key in content:
print(root_path + '/' + file)
# 把结果显示到界面上
list_box.insert(tk.END, root_path + '/' + file)
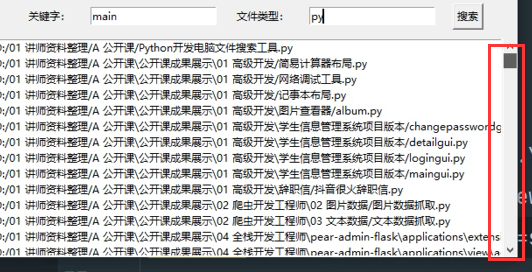
创建滚动窗口并布局到页面上
sb = tk.Scrollbar(root)
sb.pack(side=tk.RIGHT, fill=tk.Y)
sb.config(command=list_box.yview)
list_box.config(yscrollcommand=sb.set)
触发绑定事件
list_box.bind('<Double-Button-1>', list_click)
1. 获取到选中的内容
def list_click(event):
print('列表框组件的内容被点击了')
index = list_box.curselection()[0]
path = list_box.get(index)
print(path)
2. 读取选中路径的内容
content = open(path, mode='r', encoding='utf-8').read()
print(content)
3. 将内容显示到新的窗口
top = tk.Toplevel(root)
filename = path.split('/')[-1]
top.title(filename)
text = tk.Text(top)
text.pack(side=tk.LEFT, fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
text.insert(tk.END, content)