文章整理自西安交通大学软件学院朱利老师的课堂讲解,仅供复习参考使用,请勿转载
这一章笔记当时上的是网课,根本不知道老师在讲啥,然后记的就很迷,感觉没有层次结构,而且还全是英文名,后面几章的会好一点,都是上课跟着老师的叙述记的中文了
文章目录
- 什么是Internet
-
- 架构
- What’s the Internet: “nuts and bolts” view 基本
- What’s the Internet: a service view
- What’s a protocol?
- The network edge:
- Access networks and physical media
- FTTH:Fiber to the Home
- Ethernet Internet access
- Wireless access networks
- Physical Media
- The Network Core
- network of networks
- How do loss and delay occur?
- Protocal Layers 网络协议
- lnternet history
- 练习
电信网络:PSTN,打电话网络(public switch telephone network)
NAP:网络接入点,network access port
ISP:网络服务商,internet service provider
网络设计之初是军用发邮件的
什么是Internet
- 是一个世界范围内的计算机网络
- 是一个公用网络
架构
edges(边缘),core(内核),links(链路)
硬件
- Ends Systems
- Core: routers
- links
软件
- Protocols & App
- Networking OS
What’s the Internet: “nuts and bolts” view 基本
- millions of connected computing devices: hosts = end systems
- running network apps
- communication links
- fiber, copper, radio, satellite, LAN
- transmission rate = bandwidth
- routers:(路由) forward packets (chunks of data)
- protocols(协议)control sending, forwarding,receiving of messages(报文)
- ve.g., TCP, IP, HTTP, Skype, Ethernet
- Internet: “network of networks”
- loosely hierarchical
- public Internet versus private intranet(内部网,元区网)
- Internet standards
- RFC: Request for comments(协议)
- IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force(维护RFC的工程任务组)
What’s the Internet: a service view
- communication infrastructure enables distributed applications:
- Web, VoIP(IP网的声音服务), email, games, e-commerce, file sharing
- communication services provided to apps:
- reliable data delivery from source to destination
- 数据不丢
- 无差错
- 传输顺序不乱
- “best effort” (unreliable) data delivery
- reliable data delivery from source to destination
What’s a protocol?
protocols define format, order of msgs and actions taken on msg transmission, receipt
P r o t o c o l = { f o r m a t , o r d e r , a c t i o n s } = { s y n t a x , s e m a n t i c , r u l e s } = { 语 法 , 语 义 , 规 则 } \begin{aligned} Protocol&=\{format,order,actions\}\\ &=\{syntax,semantic,rules\}\\ &=\{语法,语义,规则\} \end{aligned} Protocol={
format,order,actions}={
syntax,semantic,rules}={
语法,语义,规则}
network protocols:
- machines rather than humans
- all communication activity in Internet governed by protocols
- Protocols are running everywhere in the Internet, different protocols are used to accomplish different communication tasks
The network edge:
- end systems (hosts):
- run application programs
- e.g. Web, email
- at “edge of network”
- client/server model(C/S)
- client host requests, receives service from always-on server
- e.g. Web browser/server; email client/server
- peer-peer model(p2p)
- minimal (or no) use of dedicated servers
- e.g. Skype, BitTorrent
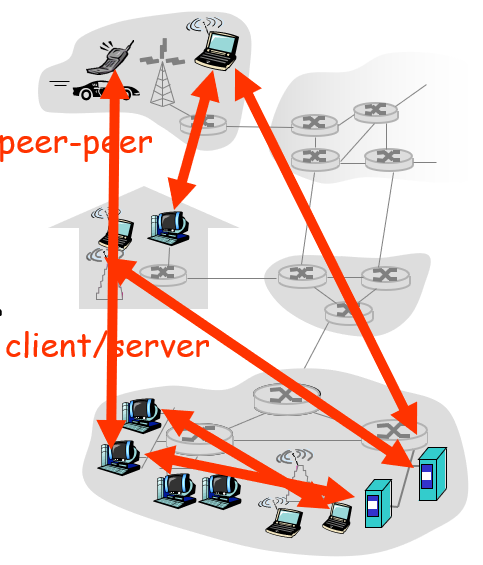
Access networks and physical media
How to connect end systems to edge router?
- residential access nets(驻家接入方式)
- institutional access networks (school, company)(单位接入网络)
- mobile access networks(移动接入网络)
Keep in mind(关键点):
- bandwidth (bits per second) of access network?
- shared or dedicated?
- fee
Dial-up Modem
拨号方式
Internet的通信方式为串行通信,使用的方式就是Modem(不知道啥意识)
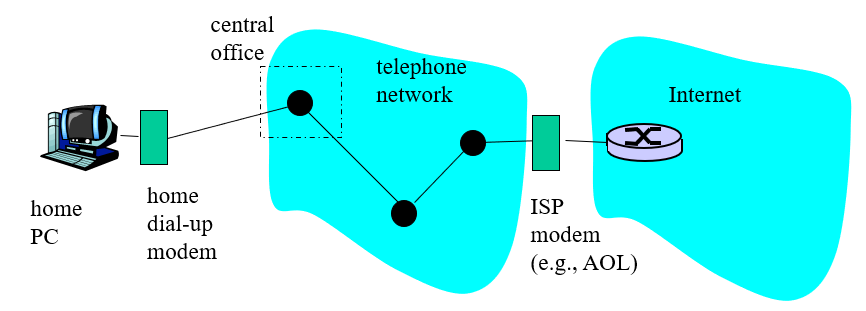
- Uses existing telephony infrastructure
- Home is connected to central office(电话网络的服务商)
- up to 56Kbps direct access to router (often less)
- Can’t surf and phone at same time: not “always on”(不能同时上网和打电话)
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL)
不对称的数字用户线
DSLAM:数字用户线接入复用器
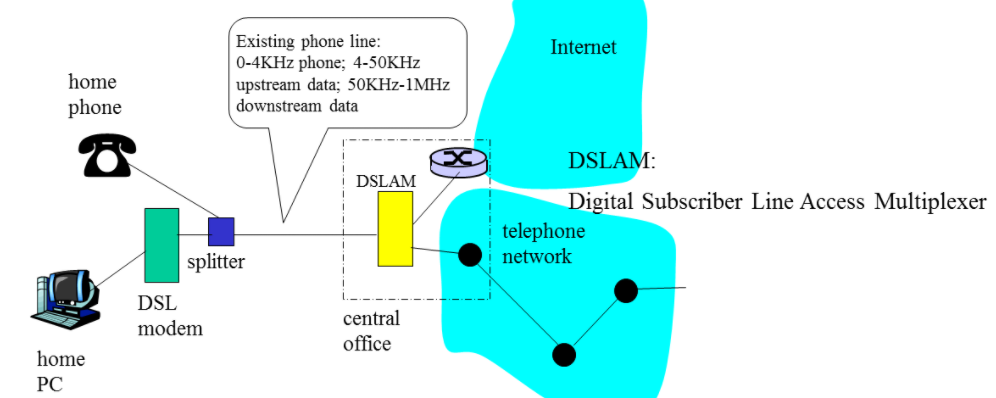
下行链路的带宽宽一点,下行链路的带宽窄一点
下行是从服务商到自己这里
上行是从自己这里到服务商
- Also uses existing telephone infrastructure
- up to 1 Mbps upstream (today typically < 256 kbps)
- up to 8 Mbps downstream (today typically < 1 Mbps)
- dedicated physical line to telephone central office
Residential access: HFC
混合光纤同轴电缆
CMTS:电缆modem终端系统

驻家使用的是同轴电缆,到服务商使用的是电缆
- HFC: hybrid fiber coax
- asymmetric: up to 30Mbps downstream, 2 Mbps upstream(不是专用的,好多家共享的)
- network of cable and fiber attaches homes to ISP router
- homes share access to router
- unlike DSL, which has dedicated access
FTTH:Fiber to the Home
optical line termial:光学线终端
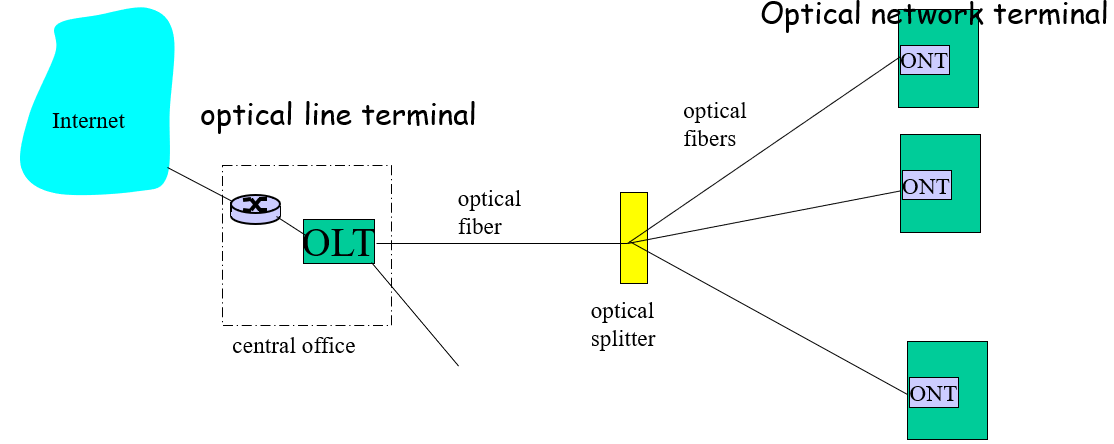
- Optical links from central office to the home
- Two competing optical technologies:
- Passive Optical network:PON, no power supply(被动光网,无需供电)
- Active Optical Network:AON(主动光网,需要供电)
- Much higher Internet rates; fiber also carries television and phone services
Ethernet Internet access
以太网
局域网里面的交换设备
Wireless access networks
无线局域网接入
- shared wireless access network connects end system to router
- via base station aka “access point”
wifi:是access point
基站是base station
需要区分清楚
Physical Media
- Bit: propagates between
transmitter/rcvr pairs - physical link: what lies between transmitter & receiver
- guided media:
- signals propagate in solid media: copper, fiber, coax
- unguided media:
- signals propagate freely, e.g., radio
Twisted Pair (TP)
双绞线
- two insulated copper wires
- Category 3: traditional phone wires, 10 Mbps Ethernet
- C5, C5+, C6

Coaxial cable
同轴电缆
- two concentric copper conductors
- bidirectional
- baseband:
- single channel on cable
- legacy Ethernet
- broadband:
- multiple channels on cable
- HFC

Fiber optic cable
光缆
- glass fiber carrying light pulses, each pulse a bit
- high-speed operation:
- high-speed point-to-point transmission (e.g., 10’s-100’s Gps)
- low error rate: repeaters spaced far apart ; immune to electromagnetic noise
需要使用光纤焊接机将两根光缆焊接起来
需要使用光缆接续盒将焊点保护起来
radio
- signal carried in electromagnetic spectrum
- no physical “wire”
- bidirectional
- propagation environment effects:
- reflection
- obstruction by objects
- interference
The Network Core
- mesh of interconnected routers
- the fundamental question: how is data transferred through net?
- circuit switching(电路交换):
- dedicated circuit per call: telephone net
- packet-switching(包交换):
- data sent thru net in discrete “chunks”
- 存储+转发
Circuit Switching
End-end resources reserved for “call”
拨号后相应的资源(带宽)就留好了,需要有一个呼叫建立(拨号)的过程
- link bandwidth, switch capacity
- dedicated resources: no sharing
- circuit-like (guaranteed) performance
- call setup required
network resources (e.g., bandwidth) divided into “pieces”
- pieces allocated to calls
- resource piece idle if not used by owning call (no sharing)
通信方式(电话网络使用的方式,不是internet使用的)
- FDM:frequency division multiplex(频率复用)
- HDTV,ADSL,WLAN
- TDM:time division multiplex(时分复用)
- telephone
- CDMA:code division multiplex access
- WDM(光缆通信)
FDM和TMD对比
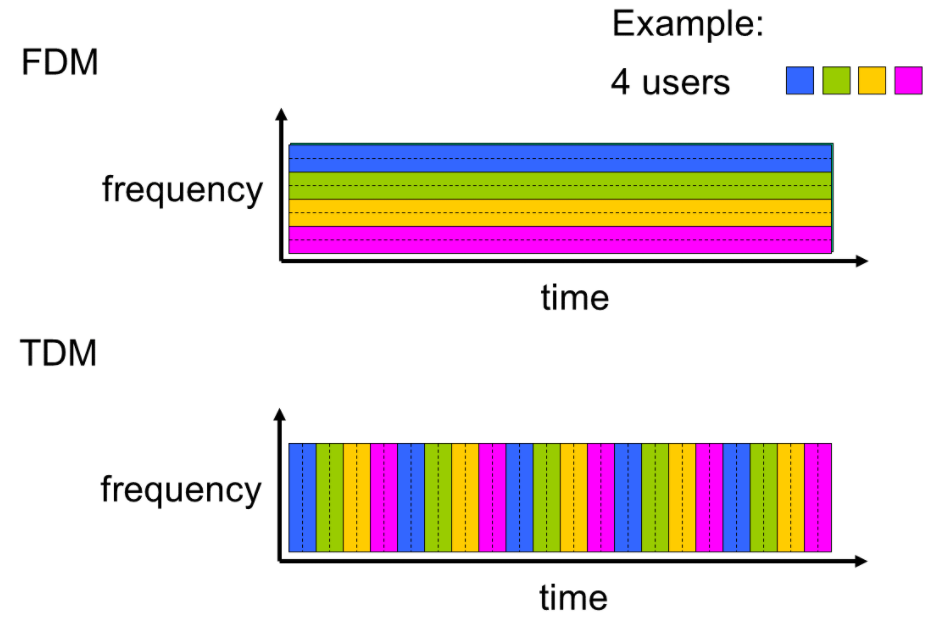
例子

Packet Switching
each end-end data stream divided into packets
- user A, B packets share network resources
- each packet uses full link bandwidth
- resources used as needed
resource contention
- aggregate resource demand can exceed amount available
- congestion: packets queue, wait for link use
- store and forward: packets move one hop at a time
- Node receives complete packet before forwarding
Statistical Multiplexing(统计复用)
A->D的最大带宽为1.6Mb/s
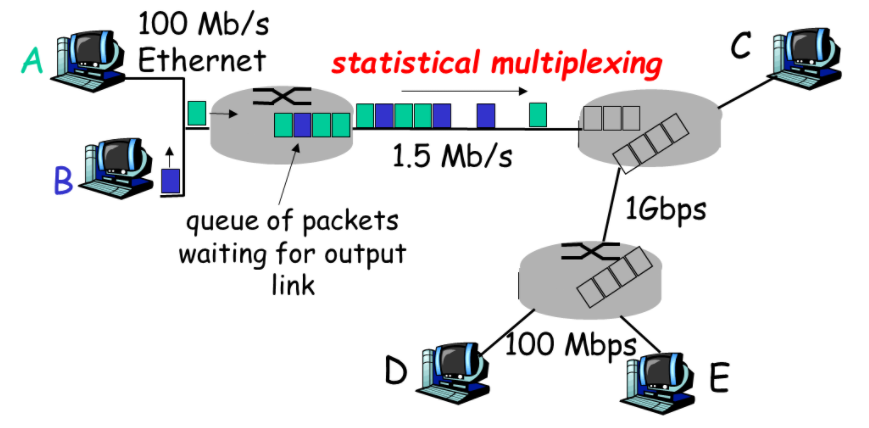
store-and-forward
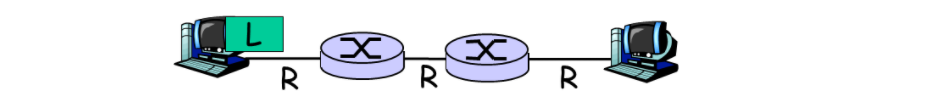
- takes L/R seconds to transmit (push out) packet of L bits on to link at R bps
- store and forward:
- entire packet must arrive at router before it can be transmitted on next link
- delay = 3L/R (assuming zero propagation delay)
Example:
- L = 7.5 Mbits
- R = 1.5 Mbps
- transmission delay = 15 sec
3*7.5/1.5=15s
Packet switching versus circuit switching
ATM:异步传输模式(async transmit mode)
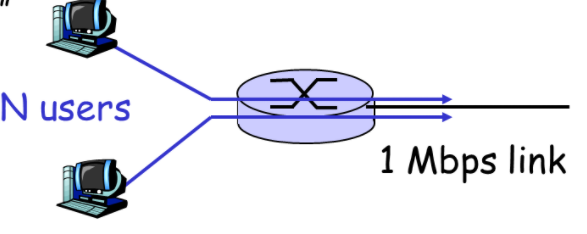
- 1 Mb/s link
- each user:
- 100 kb/s when “active”
- active 10% of time
- circuit-switching:
- 10 users
- packet switching:
- with 35 users, probability for 10 active at same time is less than 0.0004
分组交换网络的好处
- great for bursty data(适合突发数据)
- resource sharing/utilization better(更好地资源共享)
- simpler, no call setup(比较简单,没有拨号的过程)
- More users carried(能承载的用户量更大)
分组交换网络的缺点
- 不适合实时性较高的东西
- excessive congestion: packet delay and loss
- protocols needed for reliable data transfer, congestion control
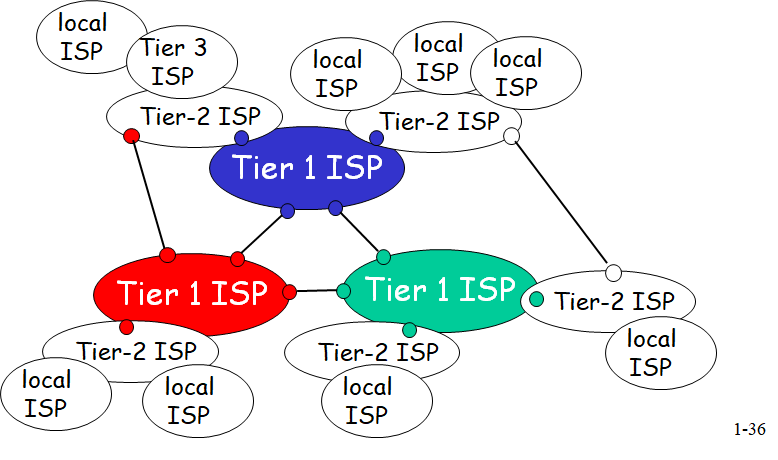
network of networks
网络是大致分层的
- at center: “tier-1” ISPs (e.g., Verizon, Sprint, AT&T, Cable and Wireless), national/international coverage
- treat each other as equals
- Tier-2 ISPs: smaller (often regional) ISPs
- Connect to one or more tier-1 ISPs, possibly other tier-2 ISPs
- Tier-3 ISPs and local ISPs
- last hop (“access”) network (closest to end systems)
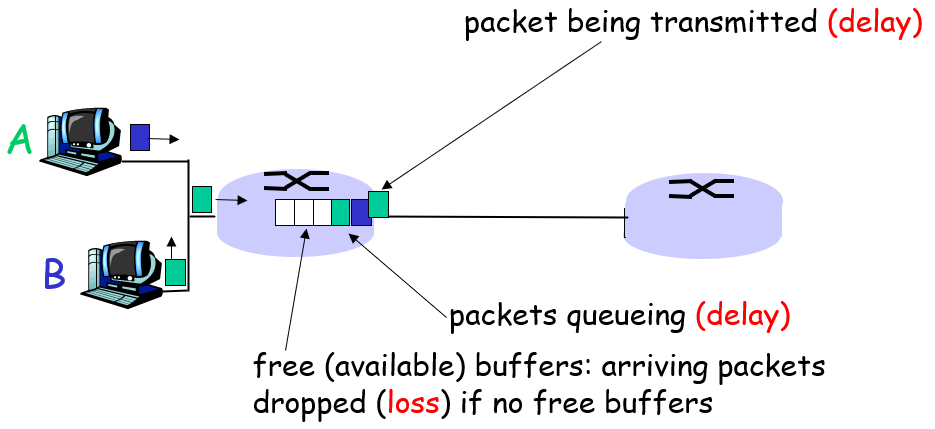
How do loss and delay occur?
packets queue in router buffers
- 链路的数据包到达率超过了输出链路容量
- packets queue, wait for turn
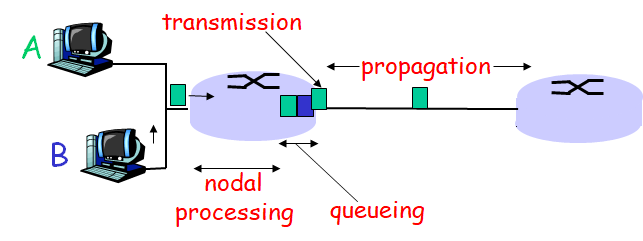
Delay in packet-switched networks
- nodal processing: (节点处理)
- check bit errors
- determine output link,确定输出口
- queueing(排队)
- time waiting at output link for transmission (等待传输)
- depends on congestion level of router 取决于路由器的拥塞级别
- 是一个非线性关系
- Transmission delay(传送延迟)
- R=link bandwidth (bps)
- L=packet length (bits)
- time to send bits into link = L/R
- Propagation delay(传播延迟)
- d = length of physical link
- s = propagation speed in medium (3x108 m/s)
- propagation delay = d/s
Nodal delay
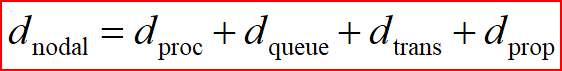
- d p r o c d_{proc} dproc = processing delay
- typically a few microsecs or less
- d q u e u e d_{queue } dqueue= queuing delay(最不能够忽略不计)
- depends on congestion
- d t r a n s d_{trans } dtrans= transmission delay
- = L/R, significant for low-speed links
- d p r o p d_{prop } dprop= propagation delay
- a few microsecs to hundreds of msecs
Queueing delay (revisited)
队列延迟
- R=link bandwidth (bps)
- L=packet length (bits)
- a=average packet arrival rate
traffic intensity = La/R
- La/R ~ 0: average queueing delay small
- La/R -> 1: delays become large
- La/R > 1: more “work” arriving than can be serviced, average delay infinite!(可能丢包)

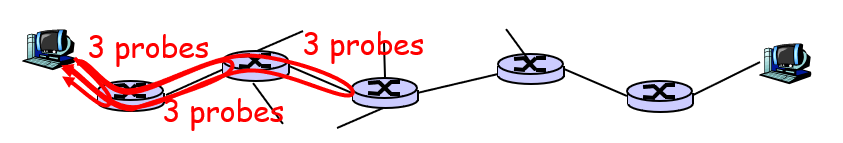
查看网络链接的命令
- ping hostname or IP address
- Tracert 202.117.1.13
For all i:
- sends three packets that will reach router i on path towards destination
- router i will return packets to sender
- sender records time interval between transmission and reply.
Throughput
互联网上丢包是一种常态
- 路由器发送端队列满了
- TTL寿命到0会被主动丢掉(垃圾包)
- 接收端的缓存满了
throughput: rate (bits/time unit) at which bits transferred between sender/receiver
instantaneous 瞬时速率: rate at given point in time
average 平均速率: rate over longer period of time
单位:bps

Rs(rate server):服务器发送速率
Rc(rate client):接收端接收速率
当服务器的带宽可以看为无穷时,传输速率是Rs和Rc的最小值
如果不能看为无穷时,实际传输速率是三者中的最小值,称为瓶颈
瓶颈链路(bottleneck link):link on end-end path that constrains end-end throughput
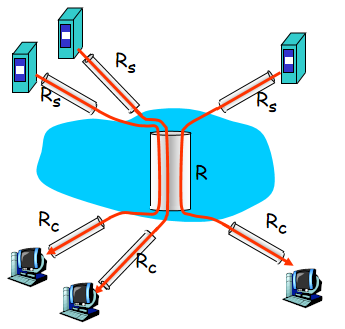
- 有十组会话(一个Rs和Rc链路)
- 每个会话端对端吞吐率是min(Rc,Rs,R/10)
- in practice: R or Rs is often bottleneck
Protocal Layers 网络协议
Hierarchical Organizing 分层架构
好处
- 对某一个模块更新的时候不用考虑其他层
- 系统结构清晰
缺点
- 分层越多,通信效率越低
Internet protocol stack-TCP/IP
TCP/IP五层模型、Internet的五层模型
- 应用层:支持网络应用
- FTP,SMTP,HTTP,apps
- 传输层:给应用层提供通信支撑
- TCP(可靠的通信,transport control protocol):不出差错,顺序不会乱
- UDP(不可靠的通信,user datagram protocol):有没有差错,顺序乱不乱不知道
- 网络层:数据报从源到目的地的路由
- IP,routing protocol(路由协议)…
- 链路层:相邻网元之间的数据传输
- PPP,(point to point protocol)
- Ethernet ,ADSL,FTTH,WI-FI…
- 物理层:bits “on the wire”
物理层是第一层,是基础
沙漏模型(sandglass Model):细腰,中间最细(传输层)
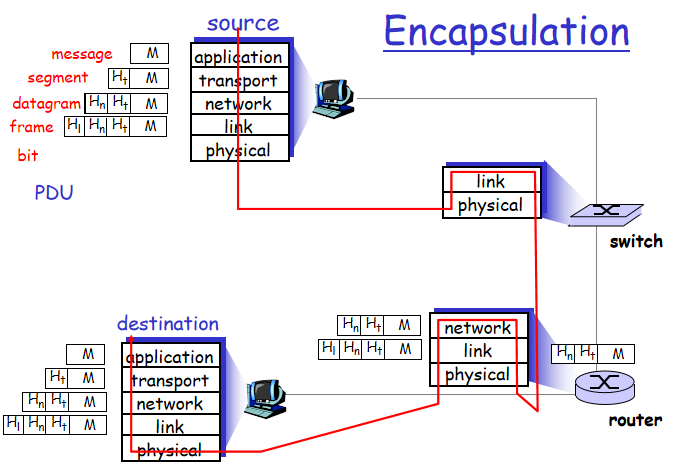
每向下走一层后,都会把上一层的整个放到下面一层的数据域中,然后后添加一个头,形成新的封装格式
报文,段,数据报,帧统称为PDU(protocol data unit协议数据单元)
每一层的PDU叫什么一定要记住
例如第四层的PDU叫做段
- 发送端
- 将协议进行封装,封装完了称为报文(message)
- 到了传输层后,会再次封装,形成 头 + 数据域的格式 ,称为段(segment)
- 到了网络层之后,会再次风祖航,形成 头 + 数据域的格式,称为数据报(datagram),也叫做包(package)
- 到了链路层,再加一个头,称为帧(frame)
- 物理层的PDU是位(bit)
- 交换机
- 只有两层,链路层和物理层
- 到link层进行转发,称为层2转发
- 路由器
- 有三层,物理层,链路层,网络层
- 入口是物理层,进入后爬三层
- 路由器是层3设备,必须在第三层才能进行转发
- 每经过一个路由器,都必须爬三楼,下三楼
- 目的地
- 每一层都会检查是否有差错
- 如果没有问题就去掉头向上传,最后恢复为message
Internet不适合实时通信,对比电话线
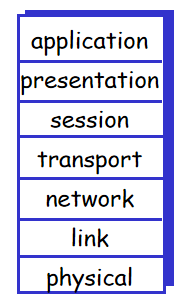
ISO/OSI reference model
OSI七层模型
能说出来七层模型都是什么就行了,自顶向下顺序不能说错
ISO:internet standard organization国际标准化组织
OSI:open system interconnection 开放系统互联
- 应用层 application
- 与五层模型的应用层不一样
- 表示层 presentation
- 解释数据的含义
- 加密,压缩(在五层模型中一般是在应用层用户自己进行的)
- 会话层 session
- 发送端和接收端进行数据同步的(设置检查点,出现问题后从检查点重新传输)
分层越多,效率越低所以现在很少有采用这种结构的
lnternet history
1967:起源于美国的一个项目,ARPAnet ,主要用来传电子邮件
1983:development of TCP/IP
TCP/IP 中间的
/不能省略,省略后仅代表两个协议,写在一起代表所有网络协议
练习
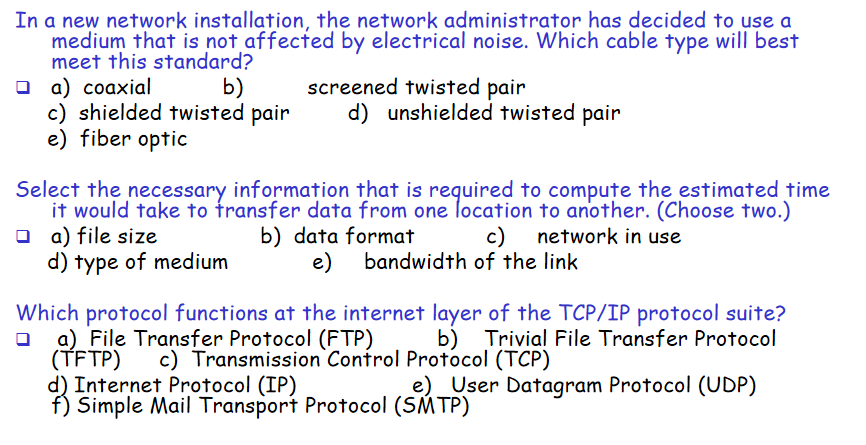
e,ae,d
a:同轴电缆
b:带滤网的双绞线
c:带屏蔽的双绞线
d:无屏蔽的双绞线
e:光缆
FTP和TFTP都在应用层
FTP:可靠的传输协议,传输层使用的是TCP
TFTP:不可靠的传输协议,速度比较快,传输层使用的是UDP
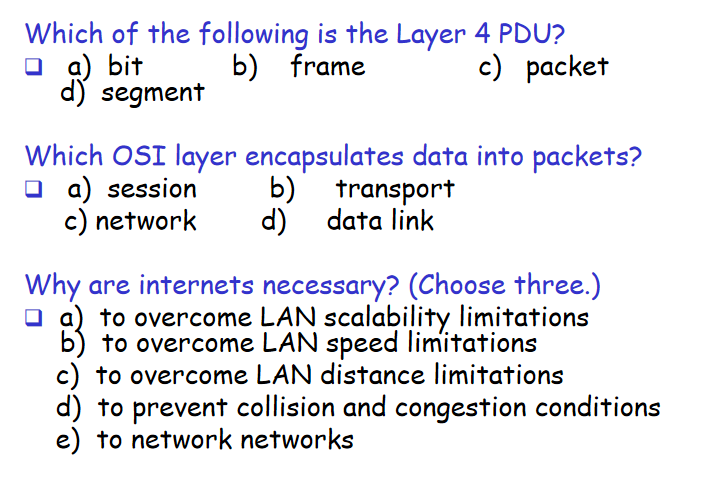
d,c,ace
- 为了克服局域网的扩展问题
- 为了解决局域网的距离限制问题
- 为了把网络连接起来