ES7-ES11重点学习笔记
一、ECMASript 7 新特性
1、Array.prototype.includes
Includes 方法用来检测数组中是否包含某个元素,返回布尔类型值
2、指数操作符
在 ES7 中引入指数运算符「**」,用来实现幂运算,功能与 Math.pow 结果相同
3、测试用例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>ES7 新特性</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const mingzhu = ['西游记', '红楼梦', '三国演义', '水浒传'];
//判断
console.log(mingzhu.includes('西游记')); //true
console.log(mingzhu.includes('金瓶梅')); //false
// **
console.log(2 ** 10); // 1024
console.log(Math.pow(2, 10)); //1024
</script>
</body>
</html>
二、ECMASript 8 新特性
1、async 函数
- async 函数的返回值为 promise 对象,
- promise 对象的结果由 async 函数执行的返回值决定
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>async函数</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//async 函数
async function fn() {
// 返回一个字符串
//return '尚硅谷'; //Promise {<fulfilled>: "尚硅谷"}
// 如果返回的结果不是一个 Promise 类型的对象, 返回的结果就是成功 Promise 对象
//return; //Promise {<fulfilled>: undefined}
//抛出错误, 返回的结果是一个失败的 Promise
//throw new Error('出错啦!'); // Error: 出错啦!
//返回的结果如果是一个 Promise 对象
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功的数据');
// reject("失败的错误");
});
}
const result = fn();
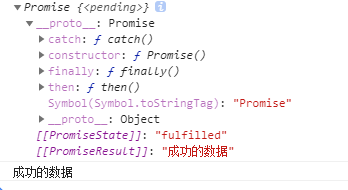
console.log(result)
//调用 then 方法
result.then(value => {
console.log(value); //成功的数据
}, reason => {
console.warn(reason);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2、await 表达式
- await 必须写在 async 函数中
- await 右侧的表达式一般为 promise 对象
- await 返回的是 promise 成功的值
- await 的 promise 失败了, 就会抛出异常, 需要通过 try…catch 捕获处理
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>await</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//创建 promise 对象
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("用户数据");
//reject("失败啦!");
})
// await 要放在 async 函数中.
async function main() {
try {
let result = await p;
console.log(result); // 用户数据
} catch (e) {
console.log(e); //失败啦!
}
}
//调用函数
main();
</script>
</body>
</html>
3、async 和 await 两种语法结合可以让异步代码像同步代码一样
1、async 和 await 结合读取文件
测试用例resources文件夹里的内容
js文件内容
//1. 引入 fs 模块
const fs = require("fs");
//读取『为学』
function readWeiXue() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile("./resources/为学.md", (err, data) => {
//如果失败
if (err) reject(err);
//如果成功
resolve(data);
})
})
}
function readChaYangShi() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile("./resources/插秧诗.md", (err, data) => {
//如果失败
if (err) reject(err);
//如果成功
resolve(data);
})
})
}
function readGuanShu() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile("./resources/观书有感.md", (err, data) => {
//如果失败
if (err) reject(err);
//如果成功
resolve(data);
})
})
}
//声明一个 async 函数
async function main() {
//获取为学内容
let weixue = await readWeiXue();
//获取插秧诗内容
let chayang = await readChaYangShi();
// 获取观书有感
let guanshu = await readGuanShu();
console.log(weixue.toString());
console.log(chayang.toString());
console.log(guanshu.toString());
}
main();
运行结果

2、async 和 await 结合封装AJAX请求
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>发送 AJAX 请求</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 发送 AJAX 请求, 返回的结果是 Promise 对象
function sendAJAX(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//1. 创建对象
const x = new XMLHttpRequest();
//2. 初始化
x.open('GET', url);
//3. 发送
x.send();
//4. 事件绑定
x.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (x.readyState === 4) {
if (x.status >= 200 && x.status < 300) {
//成功啦
resolve(x.response);
} else {
//如果失败
reject(x.status);
}
}
}
})
}
//promise then 方法测试
// sendAJAX("https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke").then(value=>{
// console.log(value);
// }, reason=>{})
// async 与 await 测试 axios
async function main() {
//发送 AJAX 请求
let result = await sendAJAX("https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke");
//再次测试
let tianqi = await sendAJAX(
'https://www.tianqiapi.com/api/?version=v1&city=%E5%8C%97%E4%BA%AC&appid=23941491&appsecret=TXoD5e8P'
)
console.log(tianqi);
}
main();
</script>
</body>
</html>
4、Object.values 和 Object.entries
- Object.values()方法返回一个给定对象的所有可枚举属性值的数组
- Object.entries()方法返回一个给定对象自身可遍历属性 [key,value] 的数组
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>ES8 对象方法扩展</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//声明对象
const school = {
name: "尚硅谷",
cities: ['北京', '上海', '深圳'],
xueke: ['前端', 'Java', '大数据', '运维']
};
//获取对象所有的键
console.log(Object.keys(school)); //Array(3)0: "name"1: "cities"2: "xueke"length: 3__proto__: Array(0)
//获取对象所有的值
console.log(Object.values(school));
/*
Array(3)
0: "尚硅谷"
1: (3) ["北京", "上海", "深圳"]
2: (4) ["前端", "Java", "大数据", "运维"]
length: 3
__proto__: Array(0)
*/
//entries
console.log(Object.entries(school));
/*
Array(3)
0: (2) ["name", "尚硅谷"]
1: (2) ["cities", Array(3)]
2: (2) ["xueke", Array(4)]
length: 3
__proto__: Array(0)
*/
//创建 Map
const m = new Map(Object.entries(school));
console.log(m.get('cities'));
/*
Array(3)
0: "北京"
1: "上海"
2: "深圳"
length: 3
__proto__: Array(0)
*/
//对象属性的描述对象
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(school));
/*
{name: {…}, cities: {…}, xueke: {…}}
cities: {value: Array(3), writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
name: {value: "尚硅谷", writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
xueke: {value: Array(4), writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
__proto__: Object
*/
// const obj = Object.create(null, {
// name: {
// //设置值
// value: '尚硅谷',
// //属性特性
// writable: true,
// configurable: true,
// enumerable: true
// }
// });
</script>
</body>
</html>
三、ECMASript 9 新特性
1、Rest/Spread 属性
Rest 参数与 spread 扩展运算符在 ES6 中已经引入,不过 ES6 中只针对于数组,
在 ES9 中为对象提供了像数组一样的 rest 参数和扩展运算符
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>对象展开</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
Rest 参数与 spread 扩展运算符在 ES6 中已经引入,不过 ES6 中只针对于数组,
在 ES9 中为对象提供了像数组一样的 rest 参数和扩展运算符
-->
<script>
//rest 参数
function connect({
host,
port,
...user
}) {
console.log(host); //127.0.0.1
console.log(port); //3306
console.log(user);
/*
Object
password: "root"
type: "master"
username: "root"
__proto__: Object
*/
}
connect({
host: '127.0.0.1',
port: 3306,
username: 'root',
password: 'root',
type: 'master'
});
//对象合并
const skillOne = {
q: '天音波'
}
const skillTwo = {
w: '金钟罩'
}
const skillThree = {
e: '天雷破'
}
const skillFour = {
r: '猛龙摆尾'
}
const mangseng = {
...skillOne,
...skillTwo,
...skillThree,
...skillFour
};
console.log(mangseng)
/*
Object
e: "天雷破"
q: "天音波"
r: "猛龙摆尾"
w: "金钟罩"
__proto__: Object
*/
</script>
</body>
</html>
2、正则表达式命名捕获组
ES9 允许命名捕获组使用符号『?<name>』,这样获取捕获结果可读性更强
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>正则扩展-命名捕获分组</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// //声明一个字符串
// let str = '<a href="http://www.atguigu.com">尚硅谷</a>';
// //提取 url 与 『标签文本』
// const reg = /<a href="(.*)">(.*)<\/a>/;
// //执行
// const result = reg.exec(str);
// console.log(result);
// /*
// 0: "<a href=\"http://www.atguigu.com\">尚硅谷</a>"
// 1: "http://www.atguigu.com"
// 2: "尚硅谷"
// groups: undefined
// index: 0
// input: "<a href=\"http://www.atguigu.com\">尚硅谷</a>"
// length: 3
// __proto__: Array(0)
// */
// console.log(result[1]); ///http://www.atguigu.com
// console.log(result[2]); //尚硅谷
let str = '<a href="http://www.atguigu.com">尚硅谷</a>';
//分组命名
const reg = /<a href="(?<url>.*)">(?<text>.*)<\/a>/;
const result = reg.exec(str);
console.log(result)
/*
(3) ["<a href="http://www.atguigu.com">尚硅谷</a>", "http://www.atguigu.com", "尚硅谷", index: 0, input: "<a href="http://www.atguigu.com">尚硅谷</a>", groups: {…}]
0: "<a href=\"http://www.atguigu.com\">尚硅谷</a>"
1: "http://www.atguigu.com"
2: "尚硅谷"
groups:
text: "尚硅谷"
url: "http://www.atguigu.com"
index: 0
input: "<a href=\"http://www.atguigu.com\">尚硅谷</a>"
length: 3
__proto__: Array(0)
*/
console.log(result.groups.url); //http://www.atguigu.com
console.log(result.groups.text); //尚硅谷
</script>
</body>
</html>
3、正则表达式反向断言
ES9 支持反向断言,通过对匹配结果前面的内容进行判断,对匹配进行筛选。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>正则扩展-反向断言</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//声明字符串
let str = 'JS5211314你知道么555啦啦啦';
//正向断言
const reg = /\d+(?=啦)/;
const result = reg.exec(str);
//反向断言
const reg = /(?<=么)\d+/;
const result = reg.exec(str);
console.log(result);
</script>
</body>
</html>
4、正则表达式 dotAll 模式
正则表达式中点.匹配除回车外的任何单字符,标记『s』改变这种行为,允许行终止符出现
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>正则扩展-dotAll模式</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//dot . 元字符 除换行符以外的任意单个字符
let str = `
<ul>
<li>
<a>肖生克的救赎</a>
<p>上映日期: 1994-09-10</p>
</li>
<li>
<a>阿甘正传</a>
<p>上映日期: 1994-07-06</p>
</li>
</ul>`;
//声明正则
// const reg = /<li>\s+<a>(.*?)<\/a>\s+<p>(.*?)<\/p>/;
const reg = /<li>.*?<a>(.*?)<\/a>.*?<p>(.*?)<\/p>/gs;
//执行匹配
// const result = reg.exec(str);
let result;
let data = [];
while (result = reg.exec(str)) {
data.push({
title: result[1],
time: result[2]
});
}
//输出结果
console.log(data);
</script>
</body>
</html>
四、ECMASript 10 新特性
1、Object.fromEntries
将二维数组转换为对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Object.fromEntries</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//二维数组
/* const result = Object.fromEntries([
['name','尚硅谷'],
['xueke', 'Java,大数据,前端,云计算']
]);
console.log(result) */
/*
Object
name: "尚硅谷"
xueke: "Java,大数据,前端,云计算"
__proto__: Object
*/
//Map
const m = new Map();
m.set('name', 'ATGUIGU');
const result = Object.fromEntries(m);
console.log(result)
/*
{name: "ATGUIGU"}
name: "ATGUIGU"
__proto__: Object
*/
//Object.entries ES8
const arr = Object.entries({
name: "尚硅谷"
})
console.log(arr);
/*
[Array(2)]
0: (2) ["name", "尚硅谷"]
length: 1
__proto__: Array(0)
*/
</script>
</body>
</html>
2、trimStart 和 trimEnd
trimStart 去除左侧空格
trimEnd 去除右侧空格
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>trimStart 与 trimEnd</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// trim
let str = ' iloveyou ';
console.log(str);
console.log(str.trimStart());
console.log(str.trimEnd());
</script>
</body>
</html>

3、Array.prototype.flat 与 flatMap
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>flat 与 flatMap</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//flat 平
//将多维数组转化为低维数组
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6]];
console.log(arr.flat()) //[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
const arr2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6, [7, 8, 9]]];
//参数为深度 是一个数字
console.log(arr2.flat(2)); //[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
//flatMap
const arr3 = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const result = arr3.flatMap(item => [item * 10]);
console.log(result); //[10, 20, 30, 40]
</script>
</body>
</html>
4、Symbol.prototype.description
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Symbol.prototype.description</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//创建 Symbol
let s = Symbol('尚硅谷');
console.log(s.description); //尚硅谷
</script>
</body>
</html>
五、ECMASript 11 新特性
1、私有属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>私有属性</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
class Person {
//公有属性
nameaa;
//私有属性
#age;
#weight;
//构造方法初始化
constructor(name, age, weight) {
this.name = name;
this.#age = age;
this.#weight = weight;
}
intro() {
console.log(this.name); //晓红
console.log(this.#age); //18
console.log(this.#weight); //45kg
}
}
//实例化
const girl = new Person('晓红', 18, '45kg');
// console.log(girl.name); //晓红
// console.log(girl.#age); //Uncaught SyntaxError: Private field '#age' must be declared in an enclosing class
// console.log(girl.#weight);
girl.intro();
</script>
</body>
</html>
2、Promise.allSettled
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Promise.allSettled</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//声明两个promise对象
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('商品数据 - 1');
}, 1000)
});
const p2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
//resolve('商品数据 - 2');
reject('出错啦!');
}, 1000)
});
//调用 allsettled 方法,始终返回成功的状态
//const res = Promise.allSettled([p1, p2]);
/*
Promise {<pending>}
__proto__: Promise
[[PromiseState]]: "fulfilled"
[[PromiseResult]]: Array(2)
0: {status: "fulfilled", value: "商品数据 - 1"}
1: {status: "rejected", reason: "出错啦!"}
length: 2
__proto__: Array(0)
*/
//只有全部成功才能返回成功
const res = Promise.all([p1, p2]);
/*
Promise {<pending>}
__proto__: Promise
[[PromiseState]]: "rejected"
[[PromiseResult]]: "出错啦!"
*/
console.log(res);
</script>
</body>
</html>
3、String.prototype.matchAll
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>String.prototype.matchAll</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let str = `<ul>
<li>
<a>肖生克的救赎</a>
<p>上映日期: 1994-09-10</p>
</li>
<li>
<a>阿甘正传</a>
<p>上映日期: 1994-07-06</p>
</li>
</ul>`;
//声明正则
const reg = /<li>.*?<a>(.*?)<\/a>.*?<p>(.*?)<\/p>/sg
//调用方法
const result = str.matchAll(reg);
// for(let v of result){
// console.log(v);
// }
const arr = [...result];
console.log(arr);
</script>
</body>
</html>
4、可选链操作符
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>可选链操作符</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// ?.
function main(config) {
// const dbHost = config && config.db && config.db.host;
const dbHost = config?.db?.host;
console.log(dbHost);
}
main({
db: {
host: '192.168.1.100',
username: 'root'
},
cache: {
host: '192.168.1.200',
username: 'admin'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
5、动态 import 导入
hello.js
export function hello(){
alert('Hello');
}
app.js
// import * as m1 from "./hello.js";
//获取元素
const btn = document.getElementById('btn');
btn.onclick = function(){
import('./hello.js').then(module => {
module.hello();
});
}
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>动态 import </title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">点击</button>
<script src="./js/app.js" type="module"></script>
</body>
</html>
6、Bigint
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>BigInt</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//大整形
let n = 521n;
console.log(n, typeof(n)); //521n "bigint"
//函数
let n1 = 123;
console.log(BigInt(n1)); //123n
//console.log(BigInt(1.2)); //Uncaught RangeError: The number 1.2 cannot be converted to a BigInt because it is not an integer
//大数值运算
let max = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
console.log(max); //9007199254740991
console.log(max + 1); //9007199254740992
console.log(max + 2); //9007199254740992
console.log(BigInt(max)) //9007199254740991n
console.log(BigInt(max) + BigInt(1)) //9007199254740992n
console.log(BigInt(max) + BigInt(2)) //9007199254740993n
</script>
</body>
</html>
7、globalThis 对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>globalThis</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
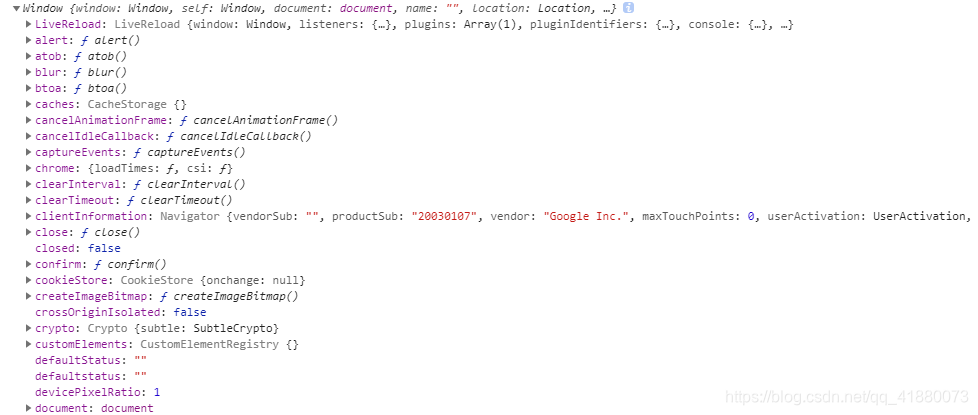
console.log(globalThis); //window
</script>
</body>
</html>
js文件内容
console.log(globalThis);
