#include <iostream>
#include <boost/thread.hpp>
using namespace std;
boost::mutex mutex;
void func1(int id)
{
mutex.lock();
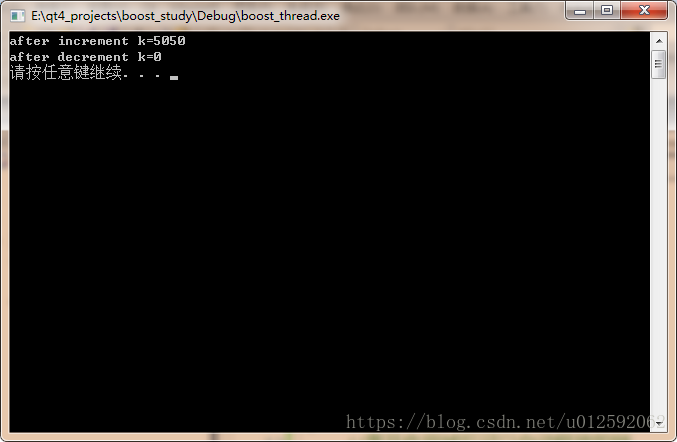
cout<<"thread #"<<id<<endl;
for (int i=1; i<6; ++i)
{
cout<<i<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
mutex.unlock();
}
int main()
{
boost::thread t1(func1, 11);
boost::thread t2(func1, 22);
boost::thread t3(func1, 33);
boost::thread t4(func1, 44);
boost::thread t5(func1, 55);
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
t4.join();
t5.join();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/thread.hpp>
using namespace std;
boost::mutex mutex;
int k=0;
void decrement()
{
//离开作用域后可以自动释放的锁
boost::unique_lock<boost::mutex> lock(mutex);
for (int i=0; i<=100; ++i)
{
k-=i;
}
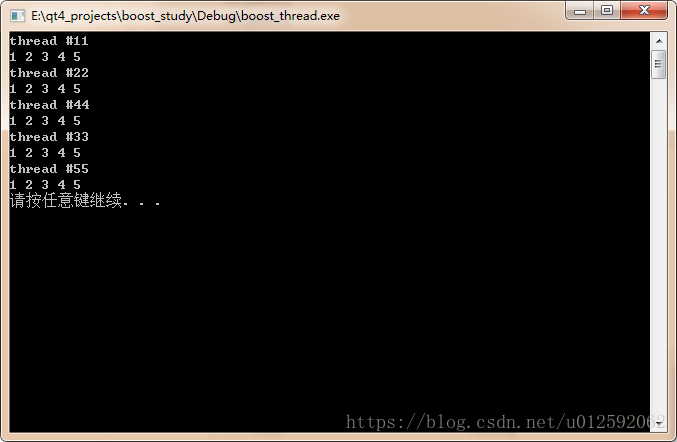
cout<<"after decrement k="<<k<<endl;
}
void increment()
{
boost::unique_lock<boost::mutex> lock(mutex);
for (int i=0; i<=100; ++i)
{
k+=i;
}
cout<<"after increment k="<<k<<endl;
}
int main()
{
boost::thread t1(increment);
boost::thread t2(decrement);
t1.join();
t2.join();
system("pause");
return 0;
}