一、概述
CountDownLatch允许一个或多个线程等待其他线程完成操作。
1.1 案例
假设由50个线程,有一个原子类AtomicInteger,50个线程都对该类进行自增1000次
代码
public class AtomicDemo {
static AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
atomicInteger.incrementAndGet();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
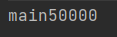
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + atomicInteger.get());
}
}
如果执行上面的代码会出现结果不对的情况,原因就是main线程打印结果时,50个线程自增的操作还未执行完。
解决方案
使用CountDownLatch进行计数,知道50个线程都完成自增操作之后,再进行打印结果操作
public class AtomicDemo {
static AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(50);
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
atomicInteger.incrementAndGet();
}
} catch (Exception exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
} finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
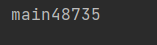
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + atomicInteger.get());
}
}
此时我们就不会出现结果不正确的情况了。