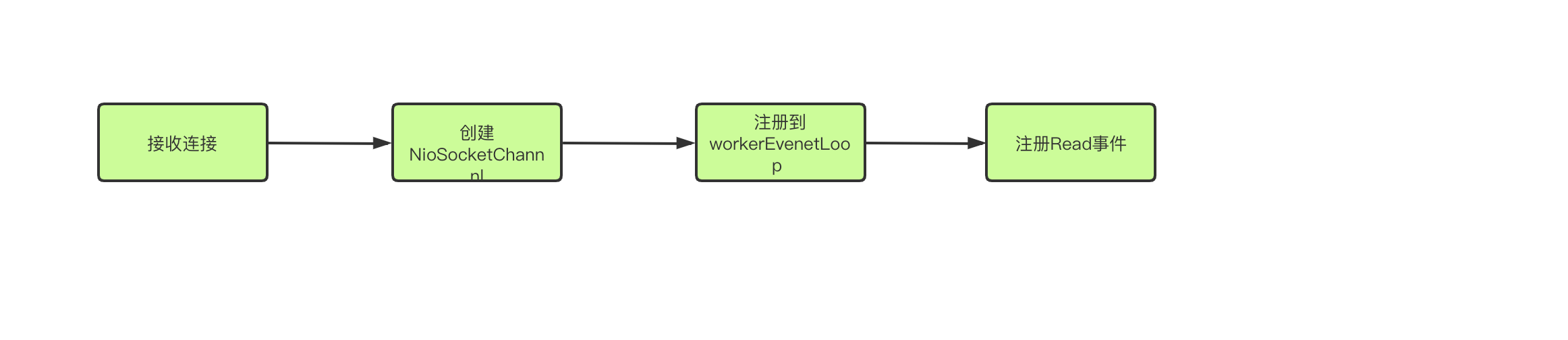
natty 请求过程源码
在之前的笔记中有记录netty的内部处理图:netty模型原理
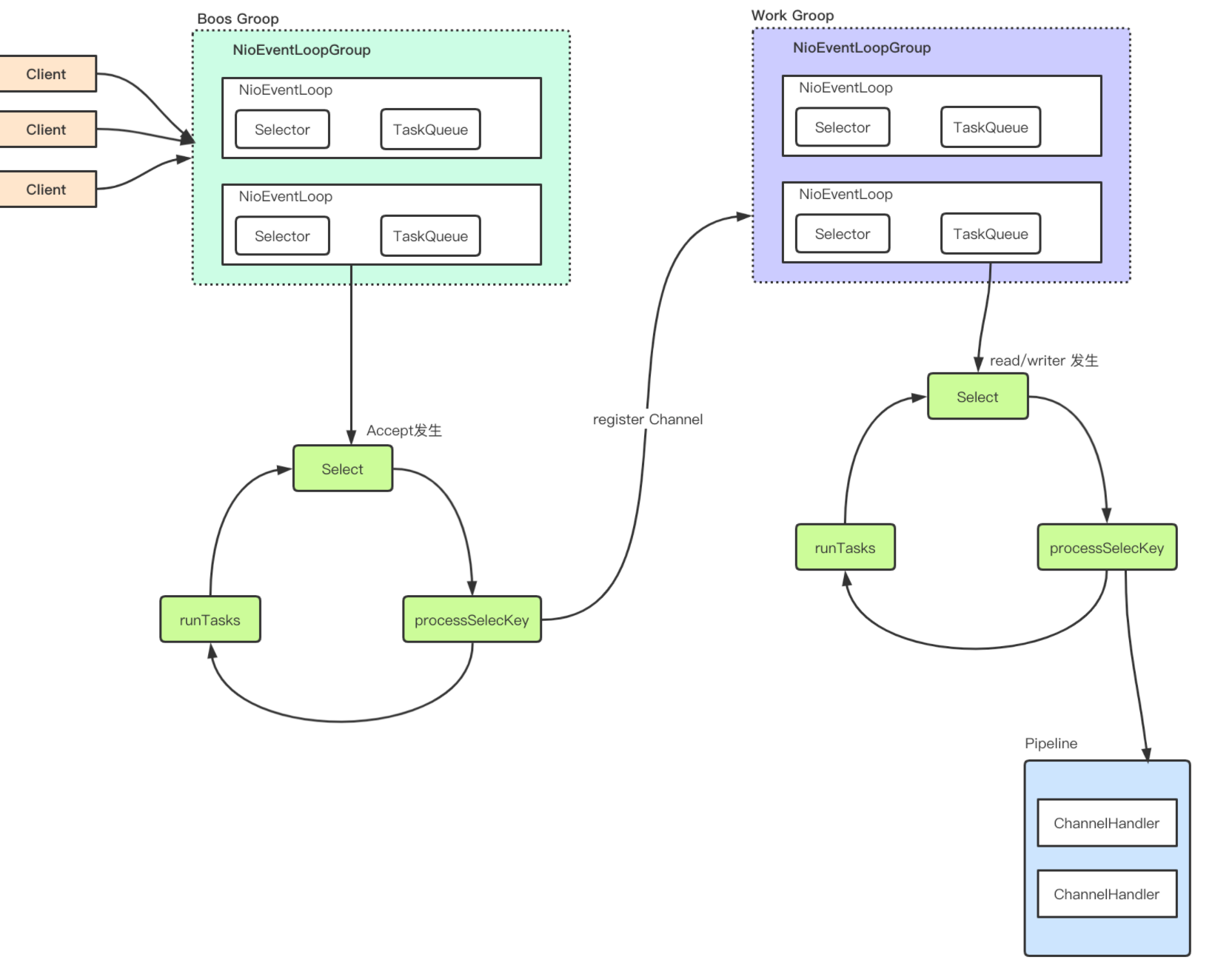
现在就在源码中找到这模型的基本实现:
先介绍一下:EventLoop是一个死循环主要是循环处理3件事情:1、等待NIO事件发生 2、处理NIO事件 3、处理任务事件
- NioEventLoop代码如下:
@Override
// 部分代码节选....
protected void run() {
int selectCnt = 0;
// 这是一个死循环处理
for (;;) {
try {
// 等待处理
try {
if (!hasTasks()) {
// 核心流程1: select 等待事件发生
strategy = select(curDeadlineNanos);
}
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
if (strategy > 0) {
// 核心流程2: 创建channel并注册到 workerEventLoop当中
processSelectedKeys();
}
} finally {
// 核心流程3: 处理任务
ranTasks = runAllTasks();
}
流程1:select(curDeadlineNanos)
调用selector 的select 方法,默认阻塞一秒钟, 如果有定时任务,则在定时任务剩余时间的基础上在加上0.5秒进行阻塞。当执行execute 方法的时候,也就是添加任务的时候,唤醒selecor, 防止selecotr 阻塞时间长
// 内部也是调用selector的select方法
private int select(long deadlineNanos) throws IOException {
if (deadlineNanos == NONE) {
return selector.select();
}
//
long timeoutMillis = deadlineToDelayNanos(deadlineNanos + 995000L) / 1000000L;
return timeoutMillis <= 0 ? selector.selectNow() : selector.select(timeoutMillis);
}
流程2:processSelectedKeys()
创建Channel并将其注册到workeventloop上
private void processSelectedKeys() {
if (selectedKeys != null) {
processSelectedKeysOptimized();
} else {
processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());
}
}
继续进入下一层代码2.1 read()方法
// 读的事件发生后调用read方法
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}
// ||
// ||
// V
// 部分关键代码节选
@Override
public void read() {
assert eventLoop().inEventLoop();
final ChannelConfig config = config();
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
boolean closed = false;
Throwable exception = null;
try {
try {
do {
// 这行incMessagesRead 创建一个SocketChannel并把他包装成一个NioSocketChannel 放到localRead容器当中
/**
* incMessagesRead内部逻辑
* SocketChannel ch = SocketUtils.accept(javaChannel());
* buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
*/
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
} catch (Throwable t) {
exception = t;
}
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
// 这里会执行pipeline 中所有Handler的fireChannelRead方法 其中有一个
// ServerBootStrapAcceptor 的Handler这里执行了关键的步骤
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
核心流程2.1.1 : SrverBootStrapAcceptor的fireChannelRead方法
- 将该NioSocketChannel注册到childGroup 中的-一个EventLoop. 上, 并添加一个监听器。
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
// msg强转成Channel
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
// 设置各种属性
setChannelOptions(child, childOptions, logger);
setAttributes(child, childAttrs);
try {
// 将channal注册到childGroup中 并添加监听器 (就是WorkEventLoop)
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
流程3:runAllTasks()
这里就是执行处理一系列任务
四、小结
总体流程