JUC并发编程与源码分析
JUC四大口诀
- 高内聚低耦合前提下,封装思想
- 判断、干活、通知
- 防止虚假唤醒,wait方法要注意使用while判断
- 注意标志位flag,可能是volatile的
为什么多线程极其重要?
- 硬件方面: 摩尔定律失效
2003年开始CPU主频已经不在翻倍,而是采用多核而不是更快的主频
主频不再提高且核数在不断添加的情况下,要想让程序更快就要用到并行或并发编程 - 软件方面:
- zhuanability(可转性)
- 高并发系统,异步+回调等生产需求
一、线程基础知识
1.1 线程的start方法
线程是通过start的方法启动执行的,主要内容在native方法start0中
Openjdk和JNI一般是一一对应的,Thread.java对应的就是Thread.c。start0其实就是JVM_StartThread。此时查看源代码可以看到在jvm.h中找到了声明,jvm.cpp中有实现。
JNI = Java Native Interface
- thread.c
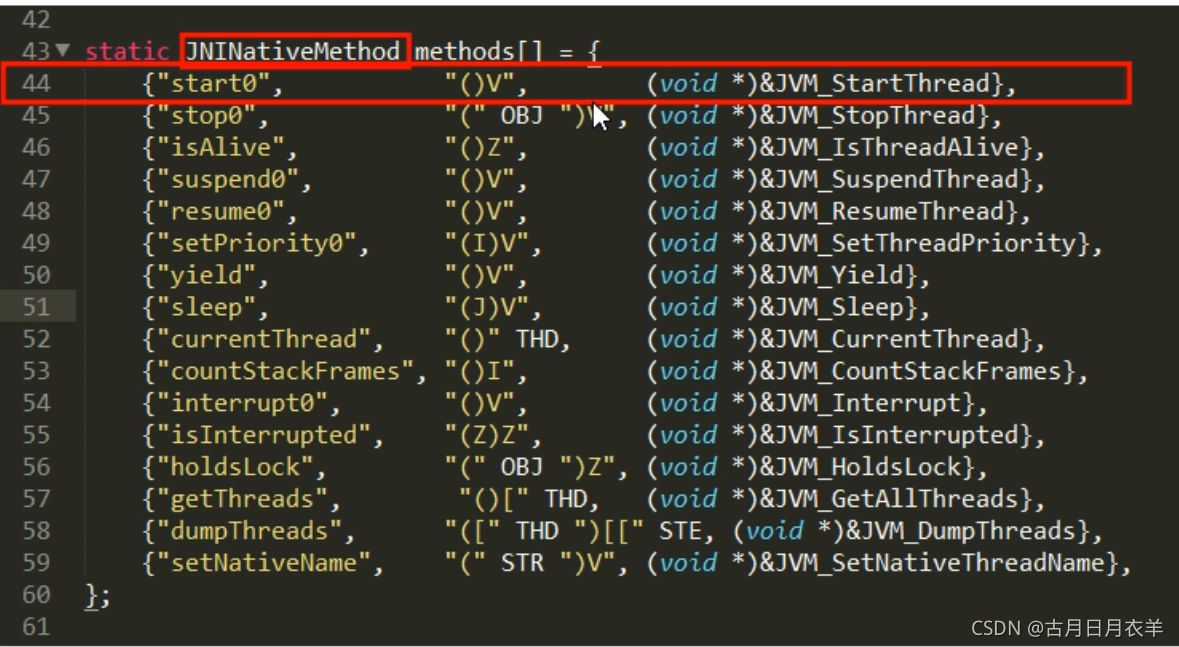
- jvm.cpp
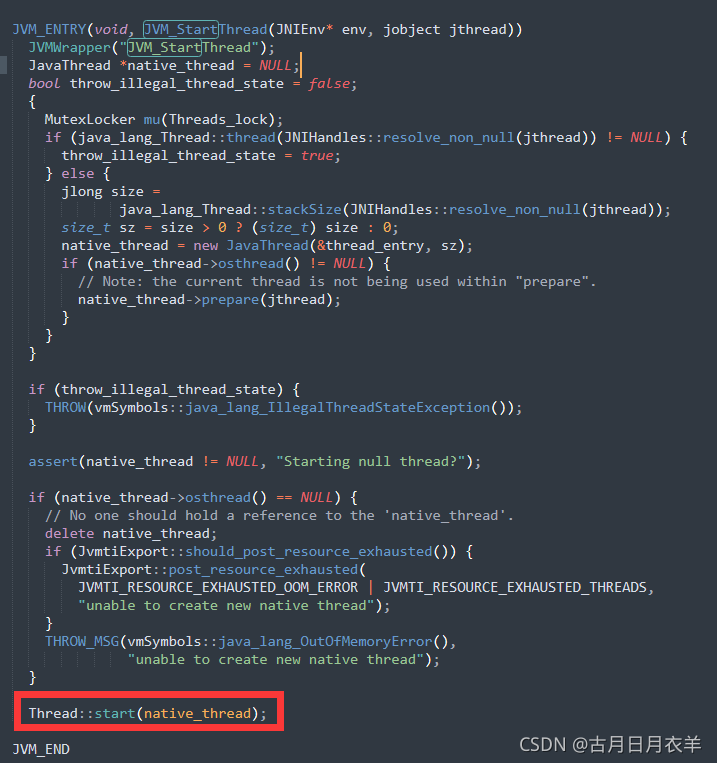
- thread.cpp
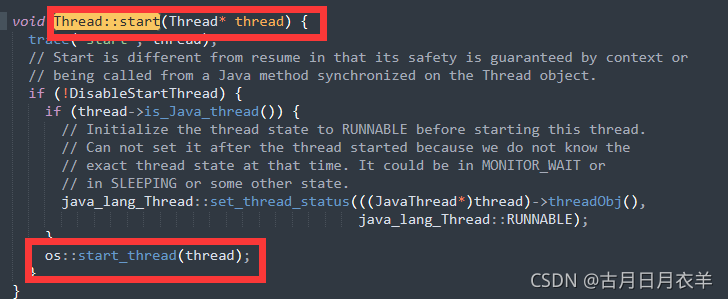
1.2 线程相关概念
1.2.1 进程
是程序的⼀次执⾏,是系统进⾏资源分配和调度的独⽴单位,每⼀个进程都有它⾃⼰的内存空间和系统资源
1.2.2 线程
- 在同⼀个进程内⼜可以执⾏多个任务,⽽这每⼀个任务我们就可以看做是⼀个线程
- ⼀个进程可以包含多个线程
何为进程和线程
- 一个进程可以包含多个线程
- 一个进程的内存空间是共享的,每个线程都可以使用这些共享内存。
- 一个线程使用进程的共享内存后,其他线程必须等他结束,才能使用这一块内存,防止多个线程同时读写某一块内存区域
- 某些内存区域,可以提供给固定数量的线程使用
- 可以使用信号量,用来保证多个线程不会相互冲突
- 操作系统的设计,因此可以归结为三点: (1) 以多进程形式,允许多个任务同时运行; (2) 以多线程形式,允许单个任务分成不同的部分运行; (3)提供协调机制,一方面防止进程之间和线程之间产生冲突,另一方面允许进程之间和线程之间共享资源。
1.2.3 管程
执行线程要求先持有管程,然后才能执行方法,最后当方法完成(无论是正常完成还是非正常完成)时释放管程。在方法执行期间,执行线程持有了管程,其它任何线程都无法再获取到同一个管程。
Monitor(监视器),也就是我们平时所说的锁
Monitor其实是一种同步机制,他的义务是保证(同一时间)只有一个线程可以访问被保护的数据和代码。
JVM中同步是基于进入和退出监视器对象(Monitor,管程对象)来实现的,每个对象实例都会有一个Monitor对象,
Object o = new Object();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (o)
{
}
},"t1").start();
Monitor对象会和Java对象一同创建并销毁,它底层是由C++语言来实现的。
1.3 用户线程和守护线程
守护线程: 是一种特殊的线程,在后台默默完成一些系统性的服务,比如垃圾回收线程
用户线程: 是系统的工作线程,它会完成这个程序需要完成的业务操作
- Java线程分为用户线程和守护线程
- 线程的daemon属性为true表示是守护线程,false表示是用户线程
- 当程序中所有用户线程执行完毕之后,不管守护线程是否结束,系统都会自动退出
- 设置守护线程,需要在start()方法之前进行
代码
package com.atguigu.itdachang;
public class DaemonDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"t 开始运行,"+(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon() ? "守护线程":"用户线程"));
while (true) {
}
}
, "t1");
//线程的daemon属性为true表示是守护线程,false表示是用户线程
t1.setDaemon(true);
t1.start();
//3秒钟后主线程再运行
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("----------main线程运行完毕");
}
}
二、CompletableFuture
2.1 Future和Callable接口
Future接口定义了操作异步任务执行的一些方法,如获取异步任务的执行结果、取消任务的执行、判断任务是否被取消、判断任务执行是否完毕等。
Callable接口中定义了需要有返回的任务需要实现的方法。
比如主线程让一个子线程去执行任务,子线程可能比较耗时,启动子线程开始执行任务后,主线程就去做其他事情了,过了一会才去获取子任务的执行结果。
2.2 FutureTask
2.2.1 Future接口相关架构
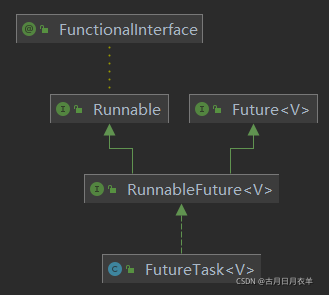
2.2.2. get()阻塞
一旦调用get()方法,不管是否计算完成都会导致阻塞
代码
public class CompletableFutureDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException
{
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(() -> {
System.out.println("-----come in FutureTask");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ""+ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextint(100);
}
);
Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask,"t1");
t1.start();
//3秒钟后才出来结果,还没有计算你提前来拿(只要一调用get方法,对于结果就是不见不散,会导致阻塞)
//System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"t"+futureTask.get());
//3秒钟后才出来结果,我只想等待1秒钟,过时不候
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"t"+futureTask.get(1L,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"t"+" run... here");
}
}
2.2.3 isDone()轮询
轮询的方式会耗费无谓的CPU资源,而且也不见得能及时地得到计算结果.
如果想要异步获取结果,通常都会以轮询的方式去获取结果,尽量不要阻塞
小总结
- 不见不散
- 过时不候
- 轮询
2.2.4如何完成一些复杂的任务?
- 应对Future的完成时间,完成了可以告诉我,也就是我们的回调通知
- 将两个异步计算合成一个异步计算,这两个异步计算互相独立,同时第二个又依赖第一个的结果。
- 当Future集合中某个任务最快结束时,返回结果。
- 等待Future集合中的所有任务都完成
2.3 对Future的改进
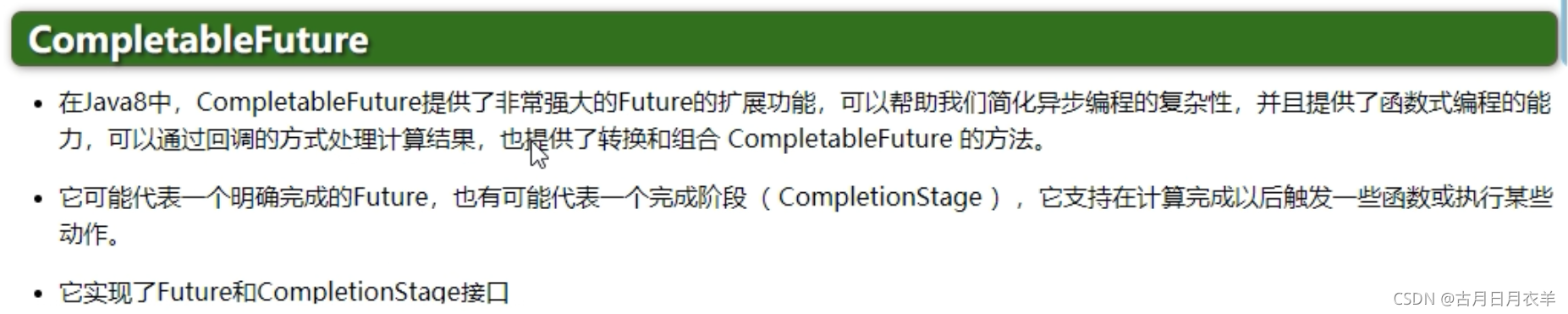
2.3.1 CompletableFuture和CompletionStage源码介绍
2.3.1.1 类架构说明
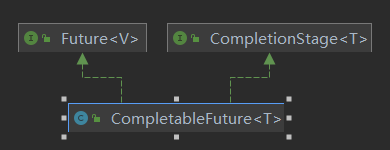
2.3.1.2 接口CompletionStage是什么?

代表异步计算过程中的某一个阶段,一个阶段完成以后可能会触发另外一个阶段,有些类似Linux系统的管道分隔符传参数。
2.3.1.3 类CompletableFuture是什么?
2.3.2 CompletableFuture核心的四个静态方法,来创建一个异步操作。
runAsync无返回值
public static CompletableFuture runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static CompletableFuture runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor)
supplyAsync有返回值
public static CompletableFuture runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Supplier supplier,Executor executor)
代码
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 20, 1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(50), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t-------come in");
});
System.out.println(future1.get());
CompletableFuture<Void> future2 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t----come int");
}, threadPoolExecutor);
System.out.println(future2.get());
CompletableFuture<Integer> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t-------come in");
return 100;
});
System.out.println(future3.get());
CompletableFuture<Integer> future4 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t----come int");
return 200;
}, threadPoolExecutor);
System.out.println(future4.get());
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
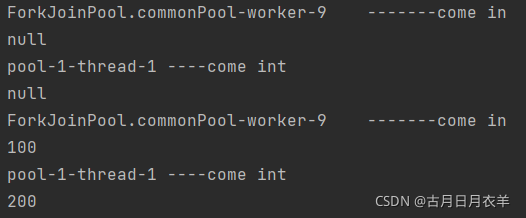
上述Executor executor参数说明
- 没有指定Executor的方法,直接使用默认的ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。
- 如果指定线程池,则使用我们自定义的或者特别指定的线程池执行异步代码
Code之通用演示,减少阻塞和轮询
- 从Java8开始引入了CompletableFuture,它是Future的功能增强版,
可以传入回调对象,当异步任务完成或者发生异常时,自动调用回调对象的回调方法
代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException
{
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 20, 1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(50), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 1;
}).thenApply(f -> {
return f + 2;
}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
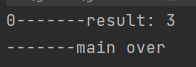
System.out.println("0-------result: " + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
});
//主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:暂停3秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("-------main over");
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
CompletableFuture的优点
- 异步任务结束时,会自动回调某个对象的方法;
- 异步任务出错时,会自动回调某个对象的方法;
- 主线程设置好回调后,不再关心异步任务的执行,异步任务之间可以顺序执行
2.3.3 get和join的对比
get()和join()是一样的,区别就是join不抛出异常。
测试代码
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 1;
}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("-----result: " + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}).join());
//}).get());
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); }
2.4 案例(电商网站的比价需求)
需求说明
- 功能 -> 性能
- 对内微服务多系统调用
- 对外网站比价
经常出现在等待某条 SQL 执行完成后,再继续执行下一条 SQL ,而这两条 SQL 本身是并无关系的,可以同时进行执行的。
我们希望能够两条 SQL 同时进行处理,而不是等待其中的某一条 SQL 完成后,再继续下一条。同理,
对于分布式微服务的调用,按照实际业务,如果是无关联step by step的业务,可以尝试是否可以多箭齐发,同时调用。
我们去比同一个商品在各个平台上的价格,要求获得一个清单列表,
1 step by step,查完京东查淘宝,查完淘宝查天猫…
2 all 一口气同时查询。。。。。
代码
/**
* 案例说明:电商比价需求
* 1 同一款产品,同时搜索出同款产品在各大电商的售价;
* 2 同一款产品,同时搜索出本产品在某一个电商平台下,各个入驻门店的售价是多少
*
* 出来结果希望是同款产品的在不同地方的价格清单列表,返回一个List<String>
* 《mysql》 in jd price is 88.05
* 《mysql》 in pdd price is 86.11
* 《mysql》 in taobao price is 90.43
*
* 3 要求深刻理解
* 3.1 函数式编程
* 3.2 链式编程
* 3.3 Stream流式计算
*/
public class CompletableFutureNetMallDemo {
static List<NetMall> list = Arrays.asList(
new NetMall("jd"),
new NetMall("pdd"),
new NetMall("taobao"),
new NetMall("dangdangwang"),
new NetMall("tmall")
);
//同步 ,step by step
/**
* List<NetMall> ----> List<String>
* @param list
* @param productName
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getPriceByStep(List<NetMall> list,String productName) {
return list
.stream().
map(netMall -> String.format(productName + " in %s price is %.2f", netMall.getMallName(), netMall.calcPrice(productName)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
//异步 ,多箭齐发
/**
* List<NetMall> ---->List<CompletableFuture<String>> ---> List<String>
* @param list
* @param productName
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getPriceByASync(List<NetMall> list,String productName) {
return list
.stream()
.map(netMall -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> String.format(productName + " is %s price is %.2f", netMall.getMallName(), netMall.calcPrice(productName))))
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> list1 = getPriceByStep(list, "mysql");
for (String element : list1) {
System.out.println(element);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime - startTime) +" 毫秒");
System.out.println();
long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> list2 = getPriceByASync(list, "mysql");
for (String element : list2) {
System.out.println(element);
}
long endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime2 - startTime2) +" 毫秒");
}
}
class NetMall {
@Getter
private String mallName;
public NetMall(String mallName)
{
this.mallName = mallName;
}
public double calcPrice(String productName) {
//检索需要1秒钟
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); }
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble() * 2 + productName.charAt(0);
}
}
测试

2.5 CompletableFuture常用方法
2.5.1 获得结果和触发计算
2.5.1.1 获取结果
public T get()
- 不见不散
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
- 过时不候
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
- 没有计算完成的情况下,给我一个替代结果
- 立即获取结果不阻塞
- 计算完,返回计算完成后的结果
- 没算完,返回设定的valueIfAbsent值
public T join()
2.5.1.2 主动触发计算
public boolean complete(T value)
- 是否打断get方法立即返回括号值
代码
public static void m1() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 20, 1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(50), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//暂停几秒钟线程
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); }
return 1;
},threadPoolExecutor);
//System.out.println(future.get());
//System.out.println(future.get(2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); }
//System.out.println(future.getNow(9999));
//被打断输出true -44 没被打断输出false 1
System.out.println(future.complete(-44)+"\t"+future.get());
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
2.5.2 对计算结果进行处理
thenApply
- 计算结果存在依赖关系,这两个线程串行化
- 由于存在依赖关系(当前步错,不走下一步),当前步骤有异常的话就叫停。
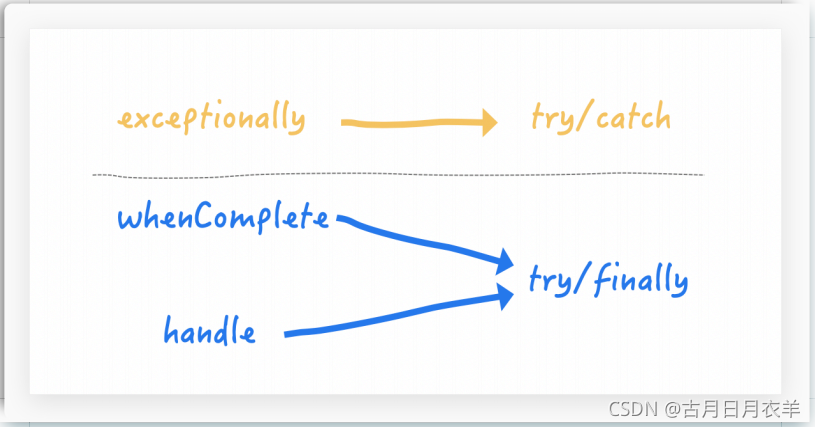
handle
- 有异常也可以往下一步走,根据带的异常参数可以进一步处理
测试代码
public static void m2() {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 20, 1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(50), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 1;
}).handle((f,e) -> {
System.out.println("-----1");
return f + 2;
}).handle((f,e) -> {
System.out.println("-----2");
return f + 3;
}).handle((f,e) -> {
System.out.println("-----3");
return f + 4;
}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("----result: " + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}).join());
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
总结

2.5.3 对计算结果进行消费
- 接收任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果
thenAccept(Consumer action)
任务 A 执行完执行 B,B 需要 A 的结果,但是任务 B 无返回值
任务之间的顺序执行
thenRun(Runnable runnable)
- 任务 A 执行完执行 B,并且 B 不需要 A 的结果
thenAccept(Consumer action)
- 任务 A 执行完执行 B,B 需要 A 的结果,但是任务 B 无返回值
thenApply(Function fn)
- 任务 A 执行完执行 B,B 需要 A 的结果,同时任务 B 有返回值
测试代码
/**
* 对计算结果进行消费
*/
public static void m3() {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 1;
}).thenApply(f -> {
return f+2;
}).thenApply(f -> {
return f+3;
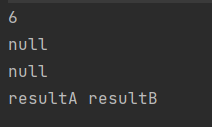
}).thenAccept(r -> System.out.println(r));
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "resultA").thenRun(() -> {
}).join());
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "resultA").thenAccept(resultA -> {
}).join());
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "resultA").thenApply(resultA -> resultA + " resultB").join());
}
2.5.4 对计算速度进行选用
- 谁快用谁
applyToEither
代码
/**
* 对计算速度进行选用
*/
public static void m4() {
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 1;
}).applyToEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 2;
}), r -> {
return r;
}).join());
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); }
}
2.5.5 对计算结果进行合并
- 两个CompletionStage任务都完成后,最终能把两个任务的结果一起交给thenCombine
- 先完成的先等着,等待其它分支任务
thenCombine
代码
/**
* thenCombine
*/
public static void m5() {
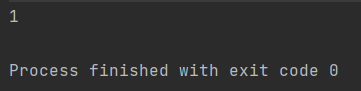
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 10;
}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 20;
}), (r1, r2) -> {
return r1 + r2;
}).join());
}