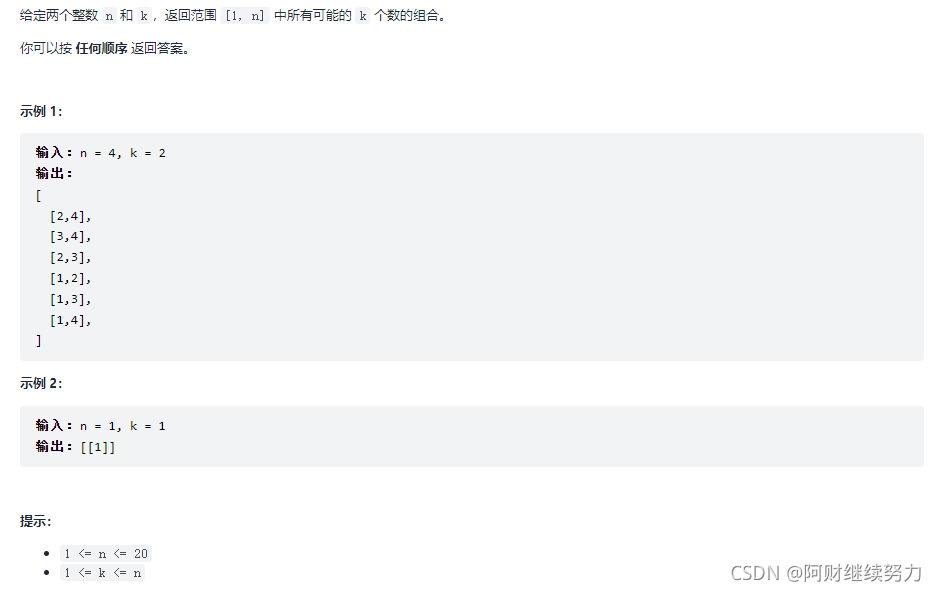
1. 题目
2. 思路
(1) 递归
- 递归的两大核心:
- 终止条件。这道题的终止条件有两个:当k=1时,返回1个包含n个数的集合;当n=k时,返回n个包含1个数的集合。
- f(n)与f(n-1)的关系。这道题从n个数中找出k个数的组合,其结果分成两部分:一部分是从n-1个数中找出k个数的组合,另一部分是先从n-1个数中找出k-1个数的组合,然后每个组合都加入n,最后合并两个部分,即可得到结果。
- 一般是从后往前推导,先找终止条件,然后找f(n)与f(n-1)的关系,在f(n-1)的结果上进行加工得到f(n)的结果。
(2) DFS+剪枝策略
- 参考二叉树的深度优先搜索,利用移除最后一个元素实现回溯。
(3) 字典序法
3. 代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.combine(4, 2));
}
}
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> res;
List<Integer> temp;
if (k == 1) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
temp = new ArrayList<>();
temp.add(i);
res.add(temp);
}
return res;
}
if (n == k) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
temp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
temp.add(i);
}
res.add(temp);
return res;
}
res = combine(n - 1, k);
List<List<Integer>> sub = combine(n - 1, k - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < sub.size(); i++) {
sub.get(i).add(n);
res.add(sub.get(i));
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution1 {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
dfs(1, n, k);
return res;
}
private void dfs(int cur, int n, int k) {
if (temp.size() + (n - cur + 1) < k) {
return;
}
if (temp.size() == k) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
temp.add(cur);
dfs(cur + 1, n, k);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
dfs(cur + 1, n, k);
}
}
class Solution2 {
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
temp.add(i);
}
temp.add(n + 1);
int j = 0;
while (j < k) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp.subList(0, k)));
j = 0;
while (j < k && temp.get(j) + 1 == temp.get(j + 1)) {
temp.set(j, j + 1);
j++;
}
temp.set(j, temp.get(j) + 1);
}
return res;
}
}
