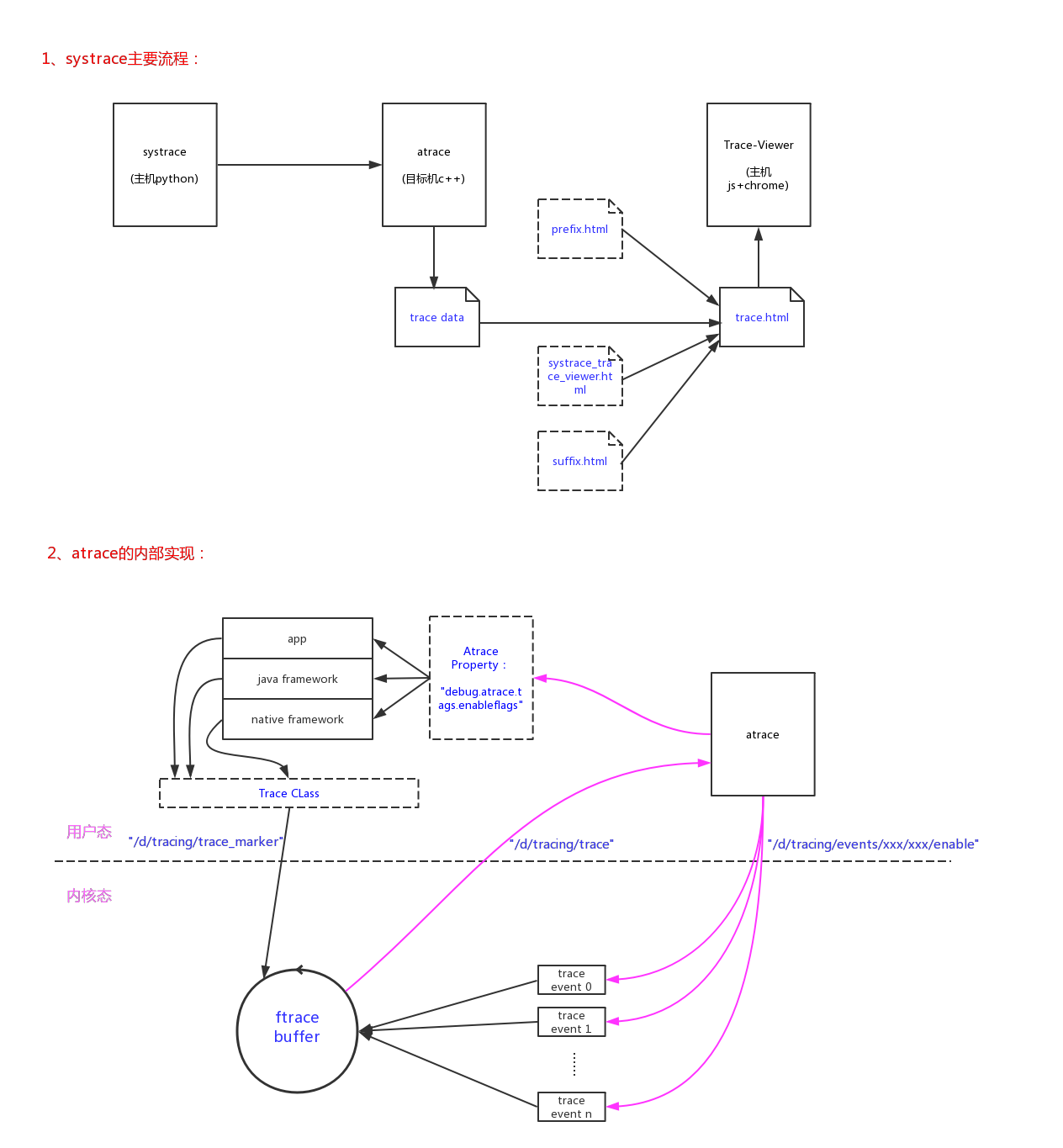
上图基本就能说清systrace的整个框架:
- 1、systrace调用atrace抓取目标机的trace数据;
- 2、systrace把trace数据和’prefix.html’、‘suffix.html’、'systrace_trace_viewer.html’合成一个’trace.html’文件;
- 3、使用chrome浏览器打开’trace.html’就可以非常方便的以图形化的形式来查看和分析trace数据。背后是Trace-Viewer的脚本在运行;
内核态和用户态的存储trace数据的实现:
- 1、内核trace信息,通过trace event记录到ftrace的buffer中;
- 2、用户态(app/java framework/native)是通过使用Trace类来记录trace信息的,也是记录到内核ftrace buffer当中的,是通过"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace_marker"接口记录的。
1、systrace的使用
在定位Android性能问题的时候,我们经常会用到systrace工具。配置到adb,连接上目标手机,在主机侧使用类似命令启动systrace:
ASOP_ROOT/external/chromium-trace/catapult/systrace/bin$ ./systrace -o trace.html -t 10 gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle
Starting tracing (10 seconds)
Tracing completed. Collecting output...
Outputting Systrace results...
Tracing complete, writing results
Wrote trace HTML file: file:///ASOP_ROOT/external/chromium-trace/catapult/systrace/bin/trace.html
systrace命令在ASOP源码包的ASOP_ROOT/external/chromium-trace/catapult/systrace/bin路径下。上述命令的参数:
- ‘-t 10’,指定了抓取trace的时长为10s;
- ‘-o trace.html’,指定了trace的输出文件;
- ‘gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle’,指定了需要抓取的事件;
在命令启动以后,我们就可以在目标机上进行滑动、启动app等一系列操作,10s内的这些操作都会被记录下来最后dump进trace.html文件。我们可以通过google的chrome浏览器来查看、分析trace.html:‘google-chrome trace.html’。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-qqCrtMms-1614825016918)(FD8E0E30D8DE443AA3E1B1CA80D33780)]
可以通过’-l’选项来查看目标机支持的systrace事件全集:
$ ./systrace -l
gfx - Graphics
input - Input
view - View System
webview - WebView
wm - Window Manager
am - Activity Manager
sm - Sync Manager
audio - Audio
video - Video
camera - Camera
hal - Hardware Modules
app - Application
res - Resource Loading
dalvik - Dalvik VM
rs - RenderScript
bionic - Bionic C Library
power - Power Management
pm - Package Manager
ss - System Server
database - Database
network - Network
adb - ADB
pdx - PDX services
sched - CPU Scheduling
irq - IRQ Events
freq - CPU Frequency
idle - CPU Idle
disk - Disk I/O
workq - Kernel Workqueues
memreclaim - Kernel Memory Reclaim
regulators - Voltage and Current Regulators
binder_driver - Binder Kernel driver
binder_lock - Binder global lock trace
pagecache - Page cache
NOTE: more categories may be available with adb root
还可以通过’–help’选项来查看systrace命令的详细选项:
$ ./systrace --help
Usage: systrace [options] [category1 [category2 ...]]
Example: systrace -b 32768 -t 15 gfx input view sched freq
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-o FILE write trace output to FILE
-j, --json write a JSON file
--link-assets (deprecated)
--asset-dir=ASSET_DIR
(deprecated)
-e DEVICE_SERIAL_NUMBER, --serial=DEVICE_SERIAL_NUMBER
adb device serial number
--timeout=TIMEOUT timeout for start and stop tracing (seconds)
--collection-timeout=COLLECTION_TIMEOUT
timeout for data collection (seconds)
-t N, --time=N trace for N seconds
--target=TARGET choose tracing target (android or linux)
-b N, --buf-size=N use a trace buffer size of N KB
-l, --list-categories
list the available categories and exit
Atrace options:
--atrace-categories=ATRACE_CATEGORIES
Select atrace categories with a comma-delimited list,
e.g. --atrace-categories=cat1,cat2,cat3
-k KFUNCS, --ktrace=KFUNCS
specify a comma-separated list of kernel functions to
trace
--no-compress Tell the device not to send the trace data in
compressed form.
-a APP_NAME, --app=APP_NAME
enable application-level tracing for comma-separated
list of app cmdlines
--from-file=FROM_FILE
read the trace from a file (compressed) rather than
running a live trace
BattOr trace options:
--battor-categories=BATTOR_CATEGORIES
Select battor categories with a comma-delimited list,
e.g. --battor-categories=cat1,cat2,cat3
--serial-map=SERIAL_MAP
File containing pregenerated map of phone serial
numbers to BattOr serial numbers.
--battor-path=BATTOR_PATH
specify a BattOr path to use
--battor Use the BattOr tracing agent.
Ftrace options:
--ftrace-categories=FTRACE_CATEGORIES
Select ftrace categories with a comma-delimited list,
e.g. --ftrace-categories=cat1,cat2,cat3
WALT trace options:
--walt Use the WALT tracing agent. WALT is a device for
measuring latency of physical sensors on phones and
computers. See https://github.com/google/walt
2、主机systrace命令的实现(python)
systrace实质上是一个python文件,整个python相关包在ASOP_ROOT/external/chromium-trace/catapult/路径下,以此路径为根(root=ASOP_ROOT/external/chromium-trace/catapult),我们来分析它的实现过程:
./systrace/bin/systrace:
import os
import sys
# (1) 将'./systrace/'路径加入到python的搜索路径 #
_SYSTRACE_DIR = os.path.abspath(
os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), os.path.pardir))
sys.path.insert(0, _SYSTRACE_DIR)
# (2) 这样就能找到'./systrace/systrace/run_systrace.py'模块并导入 #
from systrace import run_systrace
# (3) 调用run_systrace.py模块中的main()函数 #
if __name__ == '__main__':
sys.exit(run_systrace.main())
↓
./systrace/systrace/run_systrace.py:
# (3.1) main()函数继续调用main_impl()函数 #
def main():
main_impl(sys.argv)
↓
def main_impl(arguments):
# Parse the command line options.
# (3.1.1) 将用户输入的参数解析为options和categories #
options, categories = parse_options(arguments)
# Override --atrace-categories and --ftrace-categories flags if command-line
# categories are provided.
# (3.1.2) 如果解析出了trace事件categories #
# 根据options.target指定的平台'android'/'linux',来给options中的选项赋值 #
# 平台是使用sytrace命令的'--target=TARGET'选项来指定的,如果没有指定默认值是'android' #
if categories:
if options.target == 'android':
options.atrace_categories = categories
elif options.target == 'linux':
options.ftrace_categories = categories
else:
raise RuntimeError('Categories are only valid for atrace/ftrace. Target '
'platform must be either Android or Linux.')
↓
./systrace/systrace/run_systrace.py:
# Include atrace categories by default in Systrace.
# (3.1.3) 如果平台是'android',且没有指定trace事件,给出默认的trace事件 #
if options.target == 'android' and not options.atrace_categories:
options.atrace_categories = atrace_agent.DEFAULT_CATEGORIES
# (3.1.4) 如果平台是'android',且不是从文件中读取数据,那么就是从实际的目标机中读取数据了 #
if options.target == 'android' and not options.from_file:
# 初始化adb #
initialize_devil()
# 如果没有指定目标机的serialnumber,尝试读取 #
if not options.device_serial_number:
devices = [a.GetDeviceSerial() for a in adb_wrapper.AdbWrapper.Devices()]
if len(devices) == 0:
raise RuntimeError('No ADB devices connected.')
elif len(devices) >= 2:
raise RuntimeError('Multiple devices connected, serial number required')
options.device_serial_number = devices[0]
# If list_categories is selected, just print the list of categories.
# In this case, use of the tracing controller is not necessary.
# (3.1.5) 如果当前是'systrace -l'命令,列出目标机支持的所有trace事件后直接返回 #
if options.list_categories:
if options.target == 'android':
# 调用'systrace/systrace/tracing_agents/atrace_agent.py'文件中的list_categories()函数 #
# 最后调用的是`adb shell atrace --list_categories'命令 #
atrace_agent.list_categories(options)
elif options.target == 'linux':
ftrace_agent.list_categories(options)
return
# Set up the systrace runner and start tracing.
# (3.1.6) 如果是普通的trace命令,根据'systrace/systrace/systrace_runner.py'模块中的SystraceRunner类来创建对象 #
controller = systrace_runner.SystraceRunner(
os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)), options)
# (3.1.6.1) 开始tracing #
controller.StartTracing()
# Wait for the given number of seconds or until the user presses enter.
# pylint: disable=superfluous-parens
# (need the parens so no syntax error if trying to load with Python 3)
if options.from_file is not None:
print('Reading results from file.')
elif options.trace_time:
print('Starting tracing (%d seconds)' % options.trace_time)
time.sleep(options.trace_time)
else:
raw_input('Starting tracing (stop with enter)')
# Stop tracing and collect the output.
print('Tracing completed. Collecting output...')
# (3.1.6.2) 停止tracing #
controller.StopTracing()
print('Outputting Systrace results...')
# (3.1.6.3) 输出tracing结果到文件中 #
controller.OutputSystraceResults(write_json=options.write_json)
我们可以看到trace过的重点最后落在SystraceRunner对象的创建,以及.StartTracing()/.StopTracing()/.OutputSystraceResults()几个方法上。
下面我们详细分析一下这几个步骤的实现过程。
2.1、SystraceRunner类的初始化
SystraceRunner类在systrace_runner.py文件当中,我们来查看起具体实现。
./systrace/systrace/systrace_runner.py:
AGENT_MODULES = [android_process_data_agent, atrace_agent,
atrace_from_file_agent, battor_trace_agent,
ftrace_agent, walt_agent]
class SystraceRunner(object):
def __init__(self, script_dir, options):
"""Constructor.
Args:
script_dir: Directory containing the trace viewer script
(systrace_trace_viewer.html)
options: Object containing command line options.
"""
# Parse command line arguments and create agents.
self._script_dir = script_dir
self._out_filename = options.output_file
# (1) #
agents_with_config = tracing_controller.CreateAgentsWithConfig(
options, AGENT_MODULES)
# (2) #
controller_config = tracing_controller.GetControllerConfig(options)
# Set up tracing controller.
# (3) #
self._tracing_controller = tracing_controller.TracingController(
agents_with_config, controller_config)
- 1、分析tracing_controller.CreateAgentsWithConfig()的实现;
./systrace/systrace/tracing_controller.py:
def CreateAgentsWithConfig(options, modules):
"""Create tracing agents.
This function will determine which tracing agents are valid given the
options and create those agents along with their corresponding configuration
object.
Args:
options: The command-line options.
modules: The modules for either Systrace or profile_chrome.
TODO(washingtonp): After all profile_chrome agents are in
Systrace, this parameter will no longer be valid.
Returns:
A list of AgentWithConfig options containing agents and their corresponding
configuration object.
"""
result = []
# (1.1) 遍历modules中的agent调用相应的函数。对'android'来说,基本只会调用到atrace_agent、android_process_data_agent #
for module in modules:
# (1.1.1) #
config = module.get_config(options)
# (1.1.2) #
agent = module.try_create_agent(config)
if agent and config:
# (1.1.3) 创建一个AgentWithConfig类的对象,用来存储config和agent #
result.append(AgentWithConfig(agent, config))
return [x for x in result if x and x.agent]
|→
./systrace/systrace/tracing_agents/atrace_agent.py:
# (1.1.1) 创建一个AtraceConfig类的对象,用来存储optios中的相关配置 #
def get_config(options):
return AtraceConfig(options.atrace_categories,
options.trace_buf_size, options.kfuncs,
options.app_name, options.compress_trace_data,
options.from_file, options.device_serial_number,
options.trace_time, options.target)
↓
class AtraceConfig(tracing_agents.TracingConfig):
def __init__(self, atrace_categories, trace_buf_size, kfuncs,
app_name, compress_trace_data, from_file,
device_serial_number, trace_time, target):
tracing_agents.TracingConfig.__init__(self)
self.atrace_categories = atrace_categories
self.trace_buf_size = trace_buf_size
self.kfuncs = kfuncs
self.app_name = app_name
self.compress_trace_data = compress_trace_data
self.from_file = from_file
self.device_serial_number = device_serial_number
self.trace_time = trace_time
self.target = target
# (1.1.2) 创建一个AtraceAgent类的对象 #
def try_create_agent(config):
"""Create an Atrace agent.
Args:
config: Command line config.
"""
# 根据config的配置,判断当前Atrace agent是否需要创建 #
if config.target != 'android':
return None
if config.from_file is not None:
return None
if not config.atrace_categories:
return None
# Check device SDK version.
device_sdk_version = util.get_device_sdk_version()
if device_sdk_version < version_codes.JELLY_BEAN_MR2:
print ('Device SDK versions < 18 (Jellybean MR2) not supported.\n'
'Your device SDK version is %d.' % device_sdk_version)
return None
return AtraceAgent(device_sdk_version)
↓
class AtraceAgent(tracing_agents.TracingAgent):
def __init__(self, device_sdk_version):
super(AtraceAgent, self).__init__()
self._device_sdk_version = device_sdk_version
self._adb = None
self._trace_data = None
self._tracer_args = None
self._collection_thread = None
self._device_utils = None
self._device_serial_number = None
self._config = None
self._categories = None
|→
./systrace/systrace/tracing_agents/android_process_data_agent.py:
def try_create_agent(config):
if config.target != 'android':
return None
if config.from_file is not None:
return None
return AndroidProcessDataAgent()
↓
class AndroidProcessDataAgent(tracing_agents.TracingAgent):
def __init__(self):
super(AndroidProcessDataAgent, self).__init__()
self._trace_data = ""
self._device = None
- 2、分析tracing_controller.GetControllerConfig()的实现;
./systrace/systrace/tracing_controller.py:
# (2.1) 创建一个TracingControllerConfig类的对象,用来存储optios中的相关配置 #
def GetControllerConfig(options):
return TracingControllerConfig(options.output_file, options.trace_time,
options.write_json,
options.link_assets, options.asset_dir,
options.timeout, options.collection_timeout,
options.device_serial_number, options.target)
↓
class TracingControllerConfig(tracing_agents.TracingConfig):
def __init__(self, output_file, trace_time, write_json,
link_assets, asset_dir, timeout, collection_timeout,
device_serial_number, target):
tracing_agents.TracingConfig.__init__(self)
self.output_file = output_file
self.trace_time = trace_time
self.write_json = write_json
self.link_assets = link_assets
self.asset_dir = asset_dir
self.timeout = timeout
self.collection_timeout = collection_timeout
self.device_serial_number = device_serial_number
self.target = target
- 3、分析tracing_controller.TracingController()的实现;
./systrace/systrace/tracing_controller.py:
# (3.1) 创建一个TracingController类的对象,稍后的start/stop/output操作都使用该对象的方法 #
class TracingController(object):
def __init__(self, agents_with_config, controller_config):
"""Create tracing controller.
Create a tracing controller object. Note that the tracing
controller is also a tracing agent.
Args:
agents_with_config: List of tracing agents for this controller with the
corresponding tracing configuration objects.
controller_config: Configuration options for the tracing controller.
"""
self._child_agents = None
# (3.1.1) 存储agent对象和config #
self._child_agents_with_config = agents_with_config
# (3.1.2) 新建一个TracingControllerAgent类的对象 #
self._controller_agent = TracingControllerAgent()
# (3.1.3) 存储controller层级的config #
self._controller_config = controller_config
self._trace_in_progress = False
self.all_results = None
2.2、SystraceRunner.StartTracing()
入口是SystraceRunner类的.StartTracing()方法,./systrace/systrace/systrace_runner.py:
class SystraceRunner(object):
def StartTracing(self):
# (1) #
self._tracing_controller.StartTracing()
↓
继续调用到TracingController类的.StartTracing()方法,./systrace/systrace/tracing_controller.py:
class TracingController(object):
def StartTracing(self):
"""Start tracing for all tracing agents.
This function starts tracing for both the controller tracing agent
and the child tracing agents.
Returns:
Boolean indicating whether or not the start tracing succeeded.
Start tracing is considered successful if at least the
controller tracing agent was started.
"""
# (1.1) 设置对象中的tracing启动标志 #
assert not self._trace_in_progress, 'Trace already in progress.'
self._trace_in_progress = True
# Start the controller tracing agents. Controller tracing agent
# must be started successfully to proceed.
# (1.2) 启动成员对象_controller_agent的.StartAgentTracing()方法 #
# 记录一些log #
if not self._controller_agent.StartAgentTracing(
self._controller_config,
timeout=self._controller_config.timeout):
print 'Unable to start controller tracing agent.'
return False
# Start the child tracing agents.
succ_agents = []
# (1.3) 逐个启动agent list中agent的.StartAgentTracing()方法 #
# 对'Android'来说,就一个agent:AtraceAgent #
for agent_and_config in self._child_agents_with_config:
agent = agent_and_config.agent
config = agent_and_config.config
# 启动agent #
if agent.StartAgentTracing(config,
timeout=self._controller_config.timeout):
# 把启动成功的agent加入succ_agents list #
succ_agents.append(agent)
else:
print 'Agent %s not started.' % str(agent)
# Print warning if all agents not started.
na = len(self._child_agents_with_config)
ns = len(succ_agents)
if ns < na:
print 'Warning: Only %d of %d tracing agents started.' % (ns, na)
self._child_agents = succ_agents
return True
|→
继续调用到AtraceAgent类的.StartTracing()方法,./systrace/systrace/tracing_agents/atrace_agent.py:
class AtraceAgent(tracing_agents.TracingAgent):
@py_utils.Timeout(tracing_agents.START_STOP_TIMEOUT)
def StartAgentTracing(self, config, timeout=None):
assert config.atrace_categories, 'Atrace categories are missing!'
self._config = config
# systrace命令下达的需要trace的事件 #
self._categories = config.atrace_categories
if isinstance(self._categories, list):
self._categories = ','.join(self._categories)
# 使用'atrace --list_categories'获取的目标机支持的可trace事件 #
avail_cats = get_available_categories(config, self._device_sdk_version)
# (1.3.1) 判断命令中是否有目标机不支持的trace事件 #
unavailable = [x for x in self._categories.split(',') if
x not in avail_cats]
self._categories = [x for x in self._categories.split(',') if
x in avail_cats]
if unavailable:
print 'These categories are unavailable: ' + ' '.join(unavailable)
self._device_utils = device_utils.DeviceUtils(config.device_serial_number)
self._device_serial_number = config.device_serial_number
# (1.3.2) 构造参数:'atrace ... categories' #
# '...'包括以下选项: #
# '-z': compress_trace_data #
# '-t trace_time' #
# '-b trace_buf_size' #
# '-a app_name' #
# '-k kfuncs' #
self._tracer_args = _construct_atrace_args(config,
self._categories)
# (1.3.3) 执行命令:'atrace ... categories --async_start' #
self._device_utils.RunShellCommand(
self._tracer_args + ['--async_start'], check_return=True)
return True
|→
继续调用到AndroidProcessDataAgent类的.StartTracing()方法,./systrace/systrace/tracing_agents/android_process_data_agent.py:
class AndroidProcessDataAgent(tracing_agents.TracingAgent):
@py_utils.Timeout(tracing_agents.START_STOP_TIMEOUT)
def StartAgentTracing(self, config, timeout=None):
self._device = device_utils.DeviceUtils(config.device_serial_number)
self._trace_data += self._get_process_snapshot()
return True
↓
def _get_process_snapshot(self):
use_legacy = False
try:
dump = self._device.RunShellCommand( \
PS_COMMAND_PROC, check_return=True, as_root=True, shell=True)
except AdbShellCommandFailedError:
use_legacy = True
# Check length of 2 as we execute two commands, which in case of failure
# on old devices output 1 line each.
if use_legacy or len(dump) == 2:
logging.debug('Couldn\'t parse ps dump, trying legacy method ...')
dump = self._device.RunShellCommand( \
PS_COMMAND_PROC_LEGACY, check_return=True, as_root=True, shell=True)
if len(dump) == 2:
logging.error('Unable to extract process data!')
return ""
return '\n'.join(dump) + '\n'
# 实际上就是在StartTracing()和StopTracing()时,各调用一次如下的ps命令 #
PS_COMMAND_PROC = "ps -A -o USER,PID,PPID,VSIZE,RSS,WCHAN,ADDR=PC,S,NAME,COMM" \
"&& ps -AT -o USER,PID,TID,CMD"
2.3、SystraceRunner.StopTracing()
入口是SystraceRunner类的.StopTracing()方法,./systrace/systrace/systrace_runner.py:
class SystraceRunner(object):
def StopTracing(self):
# (1) #
self._tracing_controller.StopTracing()
↓
继续调用到TracingController类的.StopTracing()方法,./systrace/systrace/tracing_controller.py:
class TracingController(object):
def StopTracing(self):
"""Issue clock sync marker and stop tracing for all tracing agents.
This function stops both the controller tracing agent
and the child tracing agents. It issues a clock sync marker prior
to stopping tracing.
Returns:
Boolean indicating whether or not the stop tracing succeeded
for all agents.
"""
# (1.1) 清除对象中的tracing启动标志 #
assert self._trace_in_progress, 'No trace in progress.'
self._trace_in_progress = False
# Issue the clock sync marker and stop the child tracing agents.
self._IssueClockSyncMarker()
succ_agents = []
# (1.2) 逐个调用agent list中agent的.StopAgentTracing()方法 #
# 对'Android'来说,就一个agent:AtraceAgent #
for agent in self._child_agents:
if agent.StopAgentTracing(timeout=self._controller_config.timeout):
succ_agents.append(agent)
else:
print 'Agent %s not stopped.' % str(agent)
# Stop the controller tracing agent. Controller tracing agent
# must be stopped successfully to proceed.
# (1.3) 调用成员对象_controller_agent的.StartAgentTracing()方法 #
# 记录一些log #
if not self._controller_agent.StopAgentTracing(
timeout=self._controller_config.timeout):
print 'Unable to stop controller tracing agent.'
return False
# Print warning if all agents not stopped.
na = len(self._child_agents)
ns = len(succ_agents)
if ns < na:
print 'Warning: Only %d of %d tracing agents stopped.' % (ns, na)
self._child_agents = succ_agents
# Collect the results from all the stopped tracing agents.
all_results = []
# (1.4) 汇总agent list中agent和成员对象_controller_agent所有的result #
for agent in self._child_agents + [self._controller_agent]:
try:
result = agent.GetResults(
timeout=self._controller_config.collection_timeout)
if not result:
print 'Warning: Timeout when getting results from %s.' % str(agent)
continue
if result.source_name in [r.source_name for r in all_results]:
print ('Warning: Duplicate tracing agents named %s.' %
result.source_name)
all_results.append(result)
# Check for exceptions. If any exceptions are seen, reraise and abort.
# Note that a timeout exception will be swalloed by the timeout
# mechanism and will not get to that point (it will return False instead
# of the trace result, which will be dealt with above)
except:
print 'Warning: Exception getting results from %s:' % str(agent)
print sys.exc_info()[0]
raise
self.all_results = all_results
return all_results
|→
继续调用到AtraceAgent类的.StopAgentTracing()方法,./systrace/systrace/tracing_agents/atrace_agent.py:
class AtraceAgent(tracing_agents.TracingAgent):
@py_utils.Timeout(tracing_agents.START_STOP_TIMEOUT)
def StopAgentTracing(self, timeout=None):
"""Stops tracing and starts collecting results.
To synchronously retrieve the results after calling this function,
call GetResults().
"""
# (1.2.1) 启动stop tracing的线程 #
self._collection_thread = threading.Thread(
target=self._collect_and_preprocess)
self._collection_thread.start()
return True
↓
def _collect_and_preprocess(self):
"""Collects and preprocesses trace data.
Stores results in self._trace_data.
"""
# (1.2.1.1) dump trace数据,并stop tracing #
trace_data = self._collect_trace_data()
# (1.2.1.2) 对获取的trace数据进行预处理 #
self._trace_data = self._preprocess_trace_data(trace_data)
↓
def _collect_trace_data(self):
"""Reads the output from atrace and stops the trace."""
# (1.2.1.1.1) dump出trace数据 #
# 执行命令:'atrace ... categories --async_dump' #
dump_cmd = self._tracer_args + ['--async_dump']
result = self._device_utils.RunShellCommand(
dump_cmd, raw_output=True, large_output=True, check_return=True)
# (1.2.1.1.2) 找到trace数据中'TRACE\:'开头的位置 #
data_start = re.search(TRACE_START_REGEXP, result)
if data_start:
data_start = data_start.end(0)
else:
raise IOError('Unable to get atrace data. Did you forget adb root?')
# (1.2.1.1.3) 清除trace数据中类似无效数据:r'^capturing trace\.\.\. done|^capturing trace\.\.\.' #
output = re.sub(ADB_IGNORE_REGEXP, '', result[data_start:])
# (1.2.1.1.4) stop tracing #
# 执行命令:'atrace ... categories --async_stop' #
self._stop_trace()
return output
def _preprocess_trace_data(self, trace_data):
"""Performs various processing on atrace data.
Args:
trace_data: The raw trace data.
Returns:
The processed trace data.
"""
# (1.2.1.2.1) 对trace数据进行一些strp和解压 #
if trace_data:
trace_data = strip_and_decompress_trace(trace_data)
if not trace_data:
print >> sys.stderr, ('No data was captured. Output file was not '
'written.')
sys.exit(1)
# (1.2.1.2.2) 修复MISSING_TGIDS #
if _FIX_MISSING_TGIDS:
# Gather proc data from device and patch tgids
procfs_dump = self._device_utils.RunShellCommand(
'echo -n /proc/[0-9]*/task/[0-9]*',
shell=True, check_return=True)[0].split(' ')
pid2_tgid = extract_tgids(procfs_dump)
trace_data = fix_missing_tgids(trace_data, pid2_tgid)
# (1.2.1.2.3) 修复CIRCULAR_TRACES #
if _FIX_CIRCULAR_TRACES:
trace_data = fix_circular_traces(trace_data)
return trace_data
|→
继续调用到AndroidProcessDataAgent类的.StopAgentTracing()方法,./systrace/systrace/tracing_agents/android_process_data_agent.py:
class AndroidProcessDataAgent(tracing_agents.TracingAgent):
@py_utils.Timeout(tracing_agents.START_STOP_TIMEOUT)
def StopAgentTracing(self, timeout=None):
self._trace_data += self._get_process_snapshot()
return True
↓
def _get_process_snapshot(self):
use_legacy = False
try:
dump = self._device.RunShellCommand( \
PS_COMMAND_PROC, check_return=True, as_root=True, shell=True)
except AdbShellCommandFailedError:
use_legacy = True
# Check length of 2 as we execute two commands, which in case of failure
# on old devices output 1 line each.
if use_legacy or len(dump) == 2:
logging.debug('Couldn\'t parse ps dump, trying legacy method ...')
dump = self._device.RunShellCommand( \
PS_COMMAND_PROC_LEGACY, check_return=True, as_root=True, shell=True)
if len(dump) == 2:
logging.error('Unable to extract process data!')
return ""
return '\n'.join(dump) + '\n'
# 实际上就是在StartTracing()和StopTracing()时,各调用一次如下的ps命令 #
PS_COMMAND_PROC = "ps -A -o USER,PID,PPID,VSIZE,RSS,WCHAN,ADDR=PC,S,NAME,COMM" \
"&& ps -AT -o USER,PID,TID,CMD"
2.4、SystraceRunner.OutputSystraceResults()
入口是SystraceRunner类的.OutputSystraceResults()方法,./systrace/systrace/systrace_runner.py:
class SystraceRunner(object):
def OutputSystraceResults(self, write_json=False):
"""Output the results of systrace to a file.
If output is necessary, then write the results of systrace to either (a)
a standalone HTML file, or (b) a json file which can be read by the
trace viewer.
Args:
write_json: Whether to output to a json file (if false, use HTML file)
"""
print 'Tracing complete, writing results'
if write_json:
# (1) 输出成jason格式 #
result = output_generator.GenerateJSONOutput(
self._tracing_controller.all_results,
self._out_filename)
else:
# (2) 输出成html格式 #
# all_results是上一步stoptracing时得到的trace结果 #
# _out_filename是使用'-o'选项指定的文件名 #
result = output_generator.GenerateHTMLOutput(
self._tracing_controller.all_results,
self._out_filename)
print '\nWrote trace %s file: file://%s\n' % (('JSON' if write_json
else 'HTML'), result)
↓
继续调用到output_generator模块中的GenerateHTMLOutput()函数,./systrace/systrace/output_generator.py:
def GenerateHTMLOutput(trace_results, output_file_name):
"""Write the results of systrace to an HTML file.
Args:
trace_results: A list of TraceResults.
output_file_name: The name of the HTML file that the trace viewer
results should be written to.
"""
def _ReadAsset(src_dir, filename):
return open(os.path.join(src_dir, filename)).read()
# TODO(rnephew): The tracing output formatter is able to handle a single
# systrace trace just as well as it handles multiple traces. The obvious thing
# to do here would be to use it all for all systrace output: however, we want
# to continue using the legacy way of formatting systrace output when a single
# systrace and the tracing controller trace are present in order to match the
# Java verison of systrace. Java systrace is expected to be deleted at a later
# date. We should consolidate this logic when that happens.
# (2.1) 如果result list中成员个数大于3,使用新方法NewGenerateHTMLOutput #
if len(trace_results) > 3:
NewGenerateHTMLOutput(trace_results, output_file_name)
return os.path.abspath(output_file_name)
systrace_dir = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
# (2.2) 尝试更新./systrace/systrace/systrace_trace_viewer.html文件 #
try:
from systrace import update_systrace_trace_viewer
except ImportError:
pass
else:
update_systrace_trace_viewer.update()
trace_viewer_html = _ReadAsset(systrace_dir, 'systrace_trace_viewer.html')
# Open the file in binary mode to prevent python from changing the
# line endings, then write the prefix.
# (2.3) 读出'prefix.html','suffix.html','systrace_trace_viewer.html'文件的内容备用 #
systrace_dir = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
html_prefix = _ReadAsset(systrace_dir, 'prefix.html')
html_suffix = _ReadAsset(systrace_dir, 'suffix.html')
trace_viewer_html = _ReadAsset(systrace_dir,
'systrace_trace_viewer.html')
# Open the file in binary mode to prevent python from changing the
# line endings, then write the prefix.
# (2.4) 打开一个名为'xxx.html'的输出文件,准备写入 #
html_file = open(output_file_name, 'wb')
# (2.4.1) 首先写入'prefix.html'的内容 #
# 并且把其中的'{
{SYSTRACE_TRACE_VIEWER_HTML}}'字符用'systrace_trace_viewer.html'的文件内容替换 #
html_file.write(html_prefix.replace('{
{SYSTRACE_TRACE_VIEWER_HTML}}',
trace_viewer_html))
# Write the trace data itself. There is a separate section of the form
# <script class="trace-data" type="application/text"> ... </script>
# for each tracing agent (including the controller tracing agent).
# (2.4.2) 逐个按格式写入trace_results中的trace数据 #
html_file.write('<!-- BEGIN TRACE -->\n')
for result in trace_results:
html_file.write(' <script class="trace-data" type="application/text">\n')
html_file.write(_ConvertToHtmlString(result.raw_data))
html_file.write(' </script>\n')
html_file.write('<!-- END TRACE -->\n')
# Write the suffix and finish.
# (2.4.3) 最后写入'suffix.html'的内容 #
html_file.write(html_suffix)
html_file.close()
final_path = os.path.abspath(output_file_name)
return final_path
2.4、执行的命令
我们在devil/devil/android/device_utils.py的RunShellCommand.run()和devil/devil/utils/cmd_helper.py的Popen()处加上调试打印,看到’./systrace -o trace.html -t 10 gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle‘命令的具体执行过程如下:
ASOP_ROOT/external/chromium-trace/catapult/systrace/bin/systrace -o trace.html -t 10 gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', 'devices']
run: ( c=/data/local/tmp/cache_token;echo $EXTERNAL_STORAGE;cat $c 2>/dev/null||echo;echo "636d6fb8-d59c-11e8-ae24-b8ca3a959992">$c &&getprop )>/data/local/tmp/temp_file-4aec8d95e60eb
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', '-s', '872QADT5KWKRG', 'shell', '( ( c=/data/local/tmp/cache_token;echo $EXTERNAL_STORAGE;cat $c 2>/dev/null||echo;echo "636d6fb8-d59c-11e8-ae24-b8ca3a959992">$c &&getprop )>/data/local/tmp/temp_file-4aec8d95e60eb );echo %$?']
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', '-s', '872QADT5KWKRG', 'pull', '/data/local/tmp/temp_file-4aec8d95e60eb', '/tmp/tmple_FOq/tmp_ReadFileWithPull']
run: su 0 ls /root && ! ls /root
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', '-s', '872QADT5KWKRG', Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', 'shell''-s', , '8'( su 0 ls72QADT5KWKRG', /root && ! ls /root 'shell', );echo'rm -f /data/local/tmp/ %$?']temp_file-4aec8d95e60eb']
run: ps -A -o USER,PID,PPID,VSIZE,RSS,WCHAN,ADDR=PC,S,NAME,COMM&& ps -AT -o USER,PID,TID,CMD
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', '-s', '872QADT5KWKRG', 'shell', '( ps -A -o USER,PID,PPID,VSIZE,RSS,WCHAN,ADDR=PC,S,NAME,COMM&& ps -AT -o USER,PID,TID,CMD );echo %$?']
run: atrace --list_categories
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', '-s', '872QADT5KWKRG', 'shell', '( atrace --list_categories );echo %$?']
run: atrace -z -t 10 -b 4096 gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle --async_start
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', '-s', '872QADT5KWKRG', 'shell', '( atrace -z -t 10 -b 4096 gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle --async_start );echo %$?']
Starting tracing (10 seconds)
Tracing completed. Collecting output...
run: ps -A -o USER,PID,PPID,VSIZE,RSS,WCHAN,ADDR=PC,S,NAME,COMM&& ps -AT -o USER,PID,TID,CMD
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', '-s', '872QADT5KWKRG', 'shell', '( ps -A -o USER,PID,PPID,VSIZE,RSS,WCHAN,ADDR=PC,S,NAME,COMM&& ps -AT -o USER,PID,TID,CMD );echo %$?']
run: ( atrace -z -t 10 -b 4096 gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle --async_dump )>/data/local/tmp/temp_file-57edea8625b51
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', '-s', '872QADT5KWKRG', 'shell', '( ( atrace -z -t 10 -b 4096 gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle --async_dump )>/data/local/tmp/temp_file-57edea8625b51 );echo %$?']
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', '-s', '872QADT5KWKRG', 'pull', '/data/local/tmp/temp_file-57edea8625b51', '/tmp/tmp_preLk/tmp_ReadFileWithPull']
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', '-s', '872QADT5KWKRG', 'shell', 'rm -f /data/local/tmp/temp_file-57edea8625b51']
run: atrace -z -t 10 -b 4096 gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle --async_stop
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', '-s', '872QADT5KWKRG', 'shell', '( atrace -z -t 10 -b 4096 gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle --async_stop );echo %$?']
run: echo -n /proc/[0-9]*/task/[0-9]*
Popen: [u'/usr/bin/adb', '-s', '872QADT5KWKRG', 'shell', '( echo -n /proc/[0-9]*/task/[0-9]* );echo %$?']
Outputting Systrace results...
Tracing complete, writing results
Wrote trace HTML file: file:///home/pengweilin/sdb2/m1872/code/repo/external/chromium-trace/catapult/systrace/bin/pwl1.html
精简起来是调用目标机上的atrace命令实现的:
adb shell atrace -z -t 10 -b 4096 gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle --async_start
adb shell atrace -z -t 10 -b 4096 gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle --async_dump > /data/local/tmp/temp_file-57edea8625b51
adb pull /data/local/tmp/temp_file-57edea8625b51 /tmp/tmp_preLk/tmp_ReadFileWithPull
adb shell rm -f /data/local/tmp/temp_file-57edea8625b51
adb shell atrace -z -t 10 -b 4096 gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle --async_stop
3、目标机atrace命令的实现(c++)
从上一节可以看到主机的systrace命令实际最后都是调用目标机上的atrace命令实现的。从atrace的命令格式上看,分为两部分:
- [options]:就是’-‘和’–'打头的选项;
- [categories…]:指定需要trace哪些事件。就是类似’gfx view wm am dalvik input sched freq idle’这些;
$ atrace --help
usage: atrace [options] [categories...]
options include:
-a appname enable app-level tracing for a comma separated list of cmdlines
-b N use a trace buffer size of N KB
-c trace into a circular buffer
-f filename use the categories written in a file as space-separated
values in a line
-k fname,... trace the listed kernel functions
-n ignore signals
-s N sleep for N seconds before tracing [default 0]
-t N trace for N seconds [default 5]
-z compress the trace dump
--async_start start circular trace and return immediately
--async_dump dump the current contents of circular trace buffer
--async_stop stop tracing and dump the current contents of circular
trace buffer
--stream stream trace to stdout as it enters the trace buffer
Note: this can take significant CPU time, and is best
used for measuring things that are not affected by
CPU performance, like pagecache usage.
--list_categories
list the available tracing categories
-o filename write the trace to the specified file instead
of stdout.
atrace的源码在ASOP_ROOT/frameworks/native/cmds/atrace/atrace.cpp,我们来具体分析一下它的实现:
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
bool async = false;
bool traceStart = true;
bool traceStop = true;
bool traceDump = true;
bool traceStream = false;
/* (1) atrace跟"--help"选项,印出帮助信息 */
if (argc == 2 && 0 == strcmp(argv[1], "--help")) {
showHelp(argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
/* (2) ftrace目录是否存在 */
if (!findTraceFiles()) {
fprintf(stderr, "No trace folder found\n");
exit(-1);
}
/* (3) 逐条解析atrace的命令参数 */
for (;;) {
int ret;
int option_index = 0;
static struct option long_options[] = {
{"async_start", no_argument, 0, 0 },
{"async_stop", no_argument, 0, 0 },
{"async_dump", no_argument, 0, 0 },
{"list_categories", no_argument, 0, 0 },
{"stream", no_argument, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 }
};
/* (3.1) 尝试使用option来解析atrace的命令参数 */
ret = getopt_long(argc, argv, "a:b:cf:k:ns:t:zo:",
long_options, &option_index);
/* (3.2) 如果使用option解析失败,尝试使用category来进行解析 */
if (ret < 0) {
for (int i = optind; i < argc; i++) {
if (!setCategoryEnable(argv[i], true)) {
fprintf(stderr, "error enabling tracing category \"%s\"\n", argv[i]);
exit(1);
}
}
break;
}
/* (3.3) 根据解析出来的option,设置flag */
switch(ret) {
case 'a':
g_debugAppCmdLine = optarg;
break;
case 'b':
g_traceBufferSizeKB = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'c':
g_traceOverwrite = true;
break;
case 'f':
g_categoriesFile = optarg;
break;
case 'k':
g_kernelTraceFuncs = optarg;
break;
case 'n':
g_nohup = true;
break;
case 's':
g_initialSleepSecs = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 't':
g_traceDurationSeconds = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'z':
g_compress = true;
break;
case 'o':
g_outputFile = optarg;
break;
case 0:
if (!strcmp(long_options[option_index].name, "async_start")) {
async = true;
traceStop = false;
traceDump = false;
g_traceOverwrite = true;
} else if (!strcmp(long_options[option_index].name, "async_stop")) {
async = true;
traceStart = false;
} else if (!strcmp(long_options[option_index].name, "async_dump")) {
async = true;
traceStart = false;
traceStop = false;
} else if (!strcmp(long_options[option_index].name, "stream")) {
traceStream = true;
traceDump = false;
} else if (!strcmp(long_options[option_index].name, "list_categories")) {
listSupportedCategories();
exit(0);
}
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
showHelp(argv[0]);
exit(-1);
break;
}
}
registerSigHandler();
if (g_initialSleepSecs > 0) {
sleep(g_initialSleepSecs);
}
bool ok = true;
/* (4) "-- async_start" option命令的实际执行动作 */
if (traceStart) {
/* (4.1) */
ok &= setUpTrace();
/* (4.2) */
ok &= startTrace();
}
if (ok && traceStart) {
if (!traceStream) {
printf("capturing trace...");
fflush(stdout);
}
// We clear the trace after starting it because tracing gets enabled for
// each CPU individually in the kernel. Having the beginning of the trace
// contain entries from only one CPU can cause "begin" entries without a
// matching "end" entry to show up if a task gets migrated from one CPU to
// another.
/* (4.3) 清除trace内容 */
ok = clearTrace();
/* (4.4) 通过trace_marker文件接口,写入同步信息 */
writeClockSyncMarker();
/* (4.5) async==false的支持 */
if (ok && !async && !traceStream) {
// Sleep to allow the trace to be captured.
struct timespec timeLeft;
timeLeft.tv_sec = g_traceDurationSeconds;
timeLeft.tv_nsec = 0;
do {
if (g_traceAborted) {
break;
}
} while (nanosleep(&timeLeft, &timeLeft) == -1 && errno == EINTR);
}
/* (4.6) traceStream的支持 */
if (traceStream) {
streamTrace();
}
}
// Stop the trace and restore the default settings.
/* (5) "-- async_stop" option命令的实际执行动作 */
if (traceStop)
stopTrace();
/* (6) "-- async_dump" option命令的实际执行动作 */
if (ok && traceDump) {
if (!g_traceAborted) {
printf(" done\n");
fflush(stdout);
int outFd = STDOUT_FILENO;
if (g_outputFile) {
outFd = open(g_outputFile, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);
}
if (outFd == -1) {
printf("Failed to open '%s', err=%d", g_outputFile, errno);
} else {
dprintf(outFd, "TRACE:\n");
dumpTrace(outFd);
if (g_outputFile) {
close(outFd);
}
}
} else {
printf("\ntrace aborted.\n");
fflush(stdout);
}
clearTrace();
} else if (!ok) {
fprintf(stderr, "unable to start tracing\n");
}
// Reset the trace buffer size to 1.
if (traceStop)
cleanUpTrace();
return g_traceAborted ? 1 : 0;
}
3.1、categories
categories指的是可被trace的事件的类别,它的全集如下:
/* Tracing categories */
static const TracingCategory k_categories[] = {
{ "gfx", "Graphics", ATRACE_TAG_GRAPHICS, {
{ OPT, "events/mdss/enable" },
} },
{ "input", "Input", ATRACE_TAG_INPUT, { } },
{ "view", "View System", ATRACE_TAG_VIEW, { } },
{ "webview", "WebView", ATRACE_TAG_WEBVIEW, { } },
{ "wm", "Window Manager", ATRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, { } },
{ "am", "Activity Manager", ATRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, { } },
{ "sm", "Sync Manager", ATRACE_TAG_SYNC_MANAGER, { } },
{ "audio", "Audio", ATRACE_TAG_AUDIO, { } },
{ "video", "Video", ATRACE_TAG_VIDEO, { } },
{ "camera", "Camera", ATRACE_TAG_CAMERA, { } },
{ "hal", "Hardware Modules", ATRACE_TAG_HAL, { } },
{ "app", "Application", ATRACE_TAG_APP, { } },
{ "res", "Resource Loading", ATRACE_TAG_RESOURCES, { } },
{ "dalvik", "Dalvik VM", ATRACE_TAG_DALVIK, { } },
{ "rs", "RenderScript", ATRACE_TAG_RS, { } },
{ "bionic", "Bionic C Library", ATRACE_TAG_BIONIC, { } },
{ "power", "Power Management", ATRACE_TAG_POWER, { } },
{ "pm", "Package Manager", ATRACE_TAG_PACKAGE_MANAGER, { } },
{ "ss", "System Server", ATRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER, { } },
{ "database", "Database", ATRACE_TAG_DATABASE, { } },
{ "network", "Network", ATRACE_TAG_NETWORK, { } },
{ "adb", "ADB", ATRACE_TAG_ADB, { } },
{ k_coreServiceCategory, "Core services", 0, { } },
{ k_pdxServiceCategory, "PDX services", 0, { } },
{ "sched", "CPU Scheduling", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/sched/sched_switch/enable" },
{ REQ, "events/sched/sched_wakeup/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/sched/sched_waking/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/sched/sched_blocked_reason/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/sched/sched_cpu_hotplug/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/cgroup/enable" },
} },
{ "irq", "IRQ Events", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/irq/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/ipi/enable" },
} },
{ "i2c", "I2C Events", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/i2c/enable" },
{ REQ, "events/i2c/i2c_read/enable" },
{ REQ, "events/i2c/i2c_write/enable" },
{ REQ, "events/i2c/i2c_result/enable" },
{ REQ, "events/i2c/i2c_reply/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/i2c/smbus_read/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/i2c/smbus_write/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/i2c/smbus_result/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/i2c/smbus_reply/enable" },
} },
{ "freq", "CPU Frequency", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/power/cpu_frequency/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/power/clock_set_rate/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/power/cpu_frequency_limits/enable" },
} },
{ "membus", "Memory Bus Utilization", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/memory_bus/enable" },
} },
{ "idle", "CPU Idle", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/power/cpu_idle/enable" },
} },
{ "disk", "Disk I/O", 0, {
{ OPT, "events/f2fs/f2fs_sync_file_enter/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/f2fs/f2fs_sync_file_exit/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/f2fs/f2fs_write_begin/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/f2fs/f2fs_write_end/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/ext4/ext4_da_write_begin/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/ext4/ext4_da_write_end/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/ext4/ext4_sync_file_enter/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/ext4/ext4_sync_file_exit/enable" },
{ REQ, "events/block/block_rq_issue/enable" },
{ REQ, "events/block/block_rq_complete/enable" },
} },
{ "mmc", "eMMC commands", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/mmc/enable" },
} },
{ "load", "CPU Load", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/cpufreq_interactive/enable" },
} },
{ "sync", "Synchronization", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/sync/enable" },
} },
{ "workq", "Kernel Workqueues", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/workqueue/enable" },
} },
{ "memreclaim", "Kernel Memory Reclaim", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/vmscan/mm_vmscan_direct_reclaim_begin/enable" },
{ REQ, "events/vmscan/mm_vmscan_direct_reclaim_end/enable" },
{ REQ, "events/vmscan/mm_vmscan_kswapd_wake/enable" },
{ REQ, "events/vmscan/mm_vmscan_kswapd_sleep/enable" },
{ REQ, "events/lowmemorykiller/enable" },
} },
{ "regulators", "Voltage and Current Regulators", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/regulator/enable" },
} },
{ "binder_driver", "Binder Kernel driver", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/binder/binder_transaction/enable" },
{ REQ, "events/binder/binder_transaction_received/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/binder/binder_set_priority/enable" },
} },
{ "binder_lock", "Binder global lock trace", 0, {
{ OPT, "events/binder/binder_lock/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/binder/binder_locked/enable" },
{ OPT, "events/binder/binder_unlock/enable" },
} },
{ "pagecache", "Page cache", 0, {
{ REQ, "events/filemap/enable" },
} },
};
这些categories可以简单分为3类:
- 1、使用内核ftrace的trace event实现的内核事件。例如"sched",.sysfiles字段指定了trace event的路径;
- 2、使用Trace类实现的用户态事件(app/java framework/native)。例如"input",.tags字段指定了trace tag;
- 3、service类型的事件。如k_coreServiceCategory和k_pdxServiceCategory;
具体目标机可能只支持categories全集中的一部分,所以atrace会对命令参数中指定的categories本机是否支持进行判断:
main() -> setCategoryEnable():
static bool setCategoryEnable(const char* name, bool enable)
{
/* (1) 逐个判断命令参数中的categories,本机是否支持 */
for (size_t i = 0; i < arraysize(k_categories); i++) {
const TracingCategory& c = k_categories[i];
if (strcmp(name, c.name) == 0) {
/* (2) 判断categories是否支持 */
if (isCategorySupported(c)) {
g_categoryEnables[i] = enable;
return true;
} else {
/* (3) 如果本机不支持categories,原因是否是没有root权限? */
if (isCategorySupportedForRoot(c)) {
fprintf(stderr, "error: category \"%s\" requires root "
"privileges.\n", name);
/* (4) 本机不支持categories,报错 */
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "error: category \"%s\" is not supported "
"on this device.\n", name);
}
return false;
}
}
}
fprintf(stderr, "error: unknown tracing category \"%s\"\n", name);
return false;
}
↓
static bool isCategorySupported(const TracingCategory& category)
{
/* (2.1) 如果category是k_coreServiceCategory,判断name是否为"core_services",判断"ro.atrace.core.services"的property是否存在 */
if (strcmp(category.name, k_coreServiceCategory) == 0) {
return !android::base::GetProperty(k_coreServicesProp, "").empty();
}
/* (2.2) 如果category是k_pdxServiceCategory,判断name是否为"pdx" */
if (strcmp(category.name, k_pdxServiceCategory) == 0) {
return true;
}
bool ok = category.tags != 0;
/* (2.2) 如果category是使用了内核的trace event,判断trace4event相应的文件是否存在是否可写 */
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SYS_FILES; i++) {
const char* path = category.sysfiles[i].path;
bool req = category.sysfiles[i].required == REQ;
if (path != NULL) {
if (req) {
if (!fileIsWritable(path)) {
return false;
} else {
ok = true;
}
} else {
ok = true;
}
}
}
return ok;
}
我们也可以使用atrace命令的"–list_categories"选项,列出当前目标机支持的所有categories:
main() -> listSupportedCategories():
static void listSupportedCategories()
{
/* (1) 逐个遍历k_categories数组中的所有category */
for (size_t i = 0; i < arraysize(k_categories); i++) {
const TracingCategory& c = k_categories[i];
/* (2) 判断当前目标机系统是否支持 */
if (isCategorySupported(c)) {
printf(" %10s - %s\n", c.name, c.longname);
}
}
}
3.2、’–async_start’
当atrace命令使用了’–async_start’选项以后,会启动指定的所有categories:
static bool setUpTrace()
{
bool ok = true;
// Set up the tracing options.
/* (4.1.1) 如果categories是使用文件指定的,解析文件中的categories并使能 */
ok &= setCategoriesEnableFromFile(g_categoriesFile);
/* (4.1.2) 根据'-c'选项,配置trace event的overwrite:"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/options/overwrite" */
ok &= setTraceOverwriteEnable(g_traceOverwrite);
/* (4.1.3) 根据'-b'选项,配置trace event的buffer size:"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/buffer_size_kb" */
ok &= setTraceBufferSizeKB(g_traceBufferSizeKB);
// TODO: Re-enable after stabilization
//ok &= setCmdlineSize();
/* (4.1.4) 根据选项,配置:"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace_clock" */
ok &= setClock();
/* (4.1.5) 使能:"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/options/print-tgid" */
ok &= setPrintTgidEnableIfPresent(true);
/* (4.1.6) 根据'-k'选项指定的需要trace的kernel 函数,
配置当前tracer为function_graph:"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/current_tracer"
在filter中配置需要trace的函数名:"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/set_ftrace_filter"
*/
ok &= setKernelTraceFuncs(g_kernelTraceFuncs);
// Set up the tags property.
uint64_t tags = 0;
/* (4.1.7) 把categories中需要trace的tag进行'或'操作,并配置到"debug.atrace.tags.enableflags"的property中 */
for (size_t i = 0; i < arraysize(k_categories); i++) {
if (g_categoryEnables[i]) {
const TracingCategory &c = k_categories[i];
tags |= c.tags;
}
}
ok &= setTagsProperty(tags);
bool coreServicesTagEnabled = false;
for (size_t i = 0; i < arraysize(k_categories); i++) {
if (strcmp(k_categories[i].name, k_coreServiceCategory) == 0) {
coreServicesTagEnabled = g_categoryEnables[i];
}
// Set whether to poke PDX services in this session.
if (strcmp(k_categories[i].name, k_pdxServiceCategory) == 0) {
g_tracePdx = g_categoryEnables[i];
}
}
/* (4.1.8) 根据'-a'选项指定的需要trace的app name,最多指定16个,
配置到"debug.atrace.app_%d"的property当中
*/
std::string packageList(g_debugAppCmdLine);
if (coreServicesTagEnabled) {
if (!packageList.empty()) {
packageList += ",";
}
packageList += android::base::GetProperty(k_coreServicesProp, "");
}
ok &= setAppCmdlineProperty(&packageList[0]);
/* (4.1.9) 让defaultServiceManager()中的所有service重新读取property,使修改的配置生效 */
ok &= pokeBinderServices();
/* (4.1.10) 让::android::hardware::defaultServiceManager()中的所有service重新读取property,使修改的配置生效 */
pokeHalServices();
/* (4.1.11) 如果categories指定了"pdx",让pdx service重新读取property,使修改的配置生效 */
if (g_tracePdx) {
ok &= ServiceUtility::PokeServices();
}
// Disable all the sysfs enables. This is done as a separate loop from
// the enables to allow the same enable to exist in multiple categories.
/* (4.1.12) disable掉所有的trace event */
ok &= disableKernelTraceEvents();
// Enable all the sysfs enables that are in an enabled category.
/* (4.1.13) 根据categories数组中的配置,使能相应的trace event */
for (size_t i = 0; i < arraysize(k_categories); i++) {
if (g_categoryEnables[i]) {
const TracingCategory &c = k_categories[i];
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_SYS_FILES; j++) {
const char* path = c.sysfiles[j].path;
bool required = c.sysfiles[j].required == REQ;
if (path != NULL) {
if (fileIsWritable(path)) {
ok &= setKernelOptionEnable(path, true);
} else if (required) {
fprintf(stderr, "error writing file %s\n", path);
ok = false;
}
}
}
}
}
return ok;
}
static bool startTrace()
{
return setTracingEnabled(true);
}
↓
// Enable or disable kernel tracing.
static bool setTracingEnabled(bool enable)
{
/* (4.2.1) 打开总开关:"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/tracing_on" */
return setKernelOptionEnable(k_tracingOnPath, enable);
}
3.3、’–async_dump’
当atrace命令使用了’–async_dump’选项以后,会dump出trace内容:
main()
{
/* (6) "-- async_dump" option命令的实际执行动作 */
if (ok && traceDump) {
if (!g_traceAborted) {
printf(" done\n");
fflush(stdout);
/* (6.1) 默认的dump信息输出句柄 */
int outFd = STDOUT_FILENO;
/* (6.2) 使用'-o'选项指定的dump信息输出句柄 */
if (g_outputFile) {
outFd = open(g_outputFile, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);
}
if (outFd == -1) {
printf("Failed to open '%s', err=%d", g_outputFile, errno);
} else {
dprintf(outFd, "TRACE:\n");
/* (6.3) 读出"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace"的内容dump到输出句柄 */
dumpTrace(outFd);
if (g_outputFile) {
close(outFd);
}
}
} else {
printf("\ntrace aborted.\n");
fflush(stdout);
}
clearTrace();
} else if (!ok) {
fprintf(stderr, "unable to start tracing\n");
}
}
↓
3.4、’–async_stop’
当atrace命令使用了’–async_stop’选项以后,会停止所有categories的trace信息抓取:
static void stopTrace()
{
setTracingEnabled(false);
}
↓
static bool setTracingEnabled(bool enable)
{
/* (5.1) 关闭总开关:"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/tracing_on" */
return setKernelOptionEnable(k_tracingOnPath, enable);
}
4、目标机Trace类的使用(java/c++)
atrace只是一个控制命令,实际的trace数据路径是这样分工的:
- 1、内核trace信息,通过trace event记录到ftrace的buffer中;
- 2、用户态(app/java framework/native)是通过使用Trace类来记录trace信息的,实际上是通过"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace_marker"接口记录到内核ftracebuffer当中的。
我们查看atrace dump出来的原始信息,可以看到对应的"tracing_mark_write"字段:
ndroid.systemui-1856 ( 1856) [001] ...1 89888.553074: tracing_mark_write: S|1856|animator:alpha|62928891
ndroid.systemui-1856 ( 1856) [001] ...1 89888.553096: tracing_mark_write: F|1856|animator:alpha|62928891
ndroid.systemui-1856 ( 1856) [001] ...1 89888.553110: tracing_mark_write: S|1856|animator:scaleX|37096049
ndroid.systemui-1856 ( 1856) [001] ...1 89888.553131: tracing_mark_write: F|1856|animator:scaleX|37096049
这样内核态和用户态的trace数据最后都写入到了ftrace buffer当中,也实现了时间同步,最后通过"/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace"接口读出。
在用户态的各个层次是这样使用Trace类的:
4.1、app
import android.os.Trace;
Trace.beginSection(String sectionName)
Trace.EndSection()
详细例子可以参考:systrace
public class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyViewHolder> {
...
@Override
public MyViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
Trace.beginSection("MyAdapter.onCreateViewHolder");
MyViewHolder myViewHolder;
try {
myViewHolder = MyViewHolder.newInstance(parent);
} finally {
// In 'try...catch' statements, always call <code><a href="/reference/android/os/Trace.html#endSection()">endSection()</a></code>
// in a 'finally' block to ensure it is invoked even when an exception
// is thrown.
Trace.endSection();
}
return myViewHolder;
}</p>
<p>@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(MyViewHolder holder, int position) {
Trace.beginSection("MyAdapter.onBindViewHolder");
try {
try {
Trace.beginSection("MyAdapter.queryDatabase");
RowItem rowItem = queryDatabase(position);
mDataset.add(rowItem);
} finally {
Trace.endSection();
}
holder.bind(mDataset.get(position));
} finally {
Trace.endSection();
}
}
...
}
然后通过python systrace.py --app=sectionName 指定apk,或者通过ddms选择指定apk,抓取systrace分析。
4.2、Java framework
import android.os.Trace;
Trace.traceBegin(long traceTag, String methodName)
Trace.traceEnd(long traceTag)
4.3、Native framework
#include <cutils/trace.h>
ATRACE_CALL()
5、主机Trace-Viewer的实现(js)
从systrace python文件的解析我们可以看到,最后把trace数据和’prefix.html’、‘suffix.html’、'systrace_trace_viewer.html’合成一个’trace.html’文件,使用chrome浏览器打开’trace.html’就可以非常方便的以图形化的形式来查看和分析trace数据。
这里面的关键就是Trace-Viewer,核心是其中的js脚本。该项目的github主页。
本人js功底太差,看了一堆资料还是不得要领。如有感兴趣的同学可以继续深入研究,Trace-Viewer功能非常强大,用来做trace数据的分析和实现再合适不过了,如果可以利用起来自己修改非常强大。
一些参考文档:
catapult on github
Trace-Viewer
Trace Event Format
extending-and-customizing-trace-viewer
Trace Viewer getting-started
Trace Viewer doc
<template>标签
和 Polymer 一起加入 Web 组件革命
The Trace Event Profiling Tool (about:tracing)
Recording Tracing Runs
Understanding about:tracing results
FrameViewer How-To
这里面最有名的一个问题是在trace.html中加上一条自定义的trace曲线,主要步骤如下:
- 1、在内核中实现自己的trace event;
- 2、在atrace.cpp代码的k_categories[]数组中加上对应的category;
- 3、在Trace-Viewer中加上对这类category的解析,Trace-Viewer对数据的解析都是通过parser来实现的,可以仿照linux_perf中的实现增加一条parser,重新生成’systrace_trace_viewer.html’、'trace.html’文件即可。