
关注我

zhisheng
转载请务必注明原创地址为:http://www.54tianzhisheng.cn/2018/04/30/springboot_SpringApplication/
前言
在 Spring Boot 项目的启动类中常见代码如下:
1@SpringBootApplication
2public class SpringbotApplication {
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 SpringApplication.run(SpringbotApplication.class, args);
5 }
6}
其中也就两个比较引人注意的地方:
@SpringBootApplicationSpringApplication.run()
对于第一个注解 @SpringBootApplication,我已经在博客 Spring Boot 2.0系列文章(六):Spring Boot 2.0中SpringBootApplication注解详解 中详细的讲解了。接下来就是深入探究第二个了 SpringApplication.run() 。
换个姿势
上面的姿势太简单了,只一行代码就完事了。
1SpringApplication.run(SpringbotApplication.class, args);
其实是支持做一些个性化的设置,接下来我们换个姿势瞧瞧:
1@SpringBootApplication
2public class SpringbotApplication {
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(SpringbotApplication.class);
5 // 自定义应用程序的配置
6 //app.setXxx()
7 app.run(args)
8 }
9}
没错,就是通过一个构造函数,然后设置相关的属性,从而达到定制化服务。有哪些属性呢?
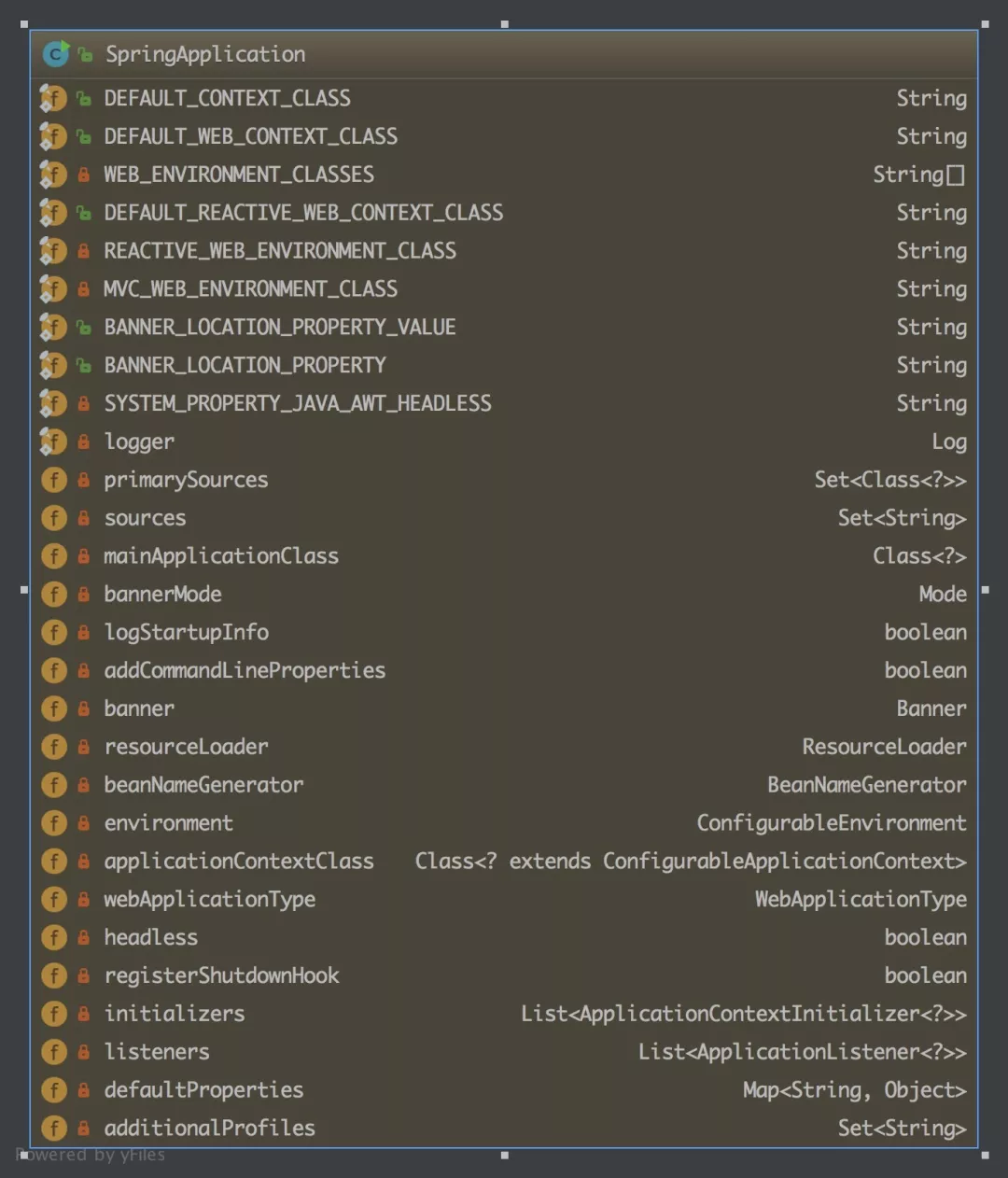
属性对应的 get/set 方法
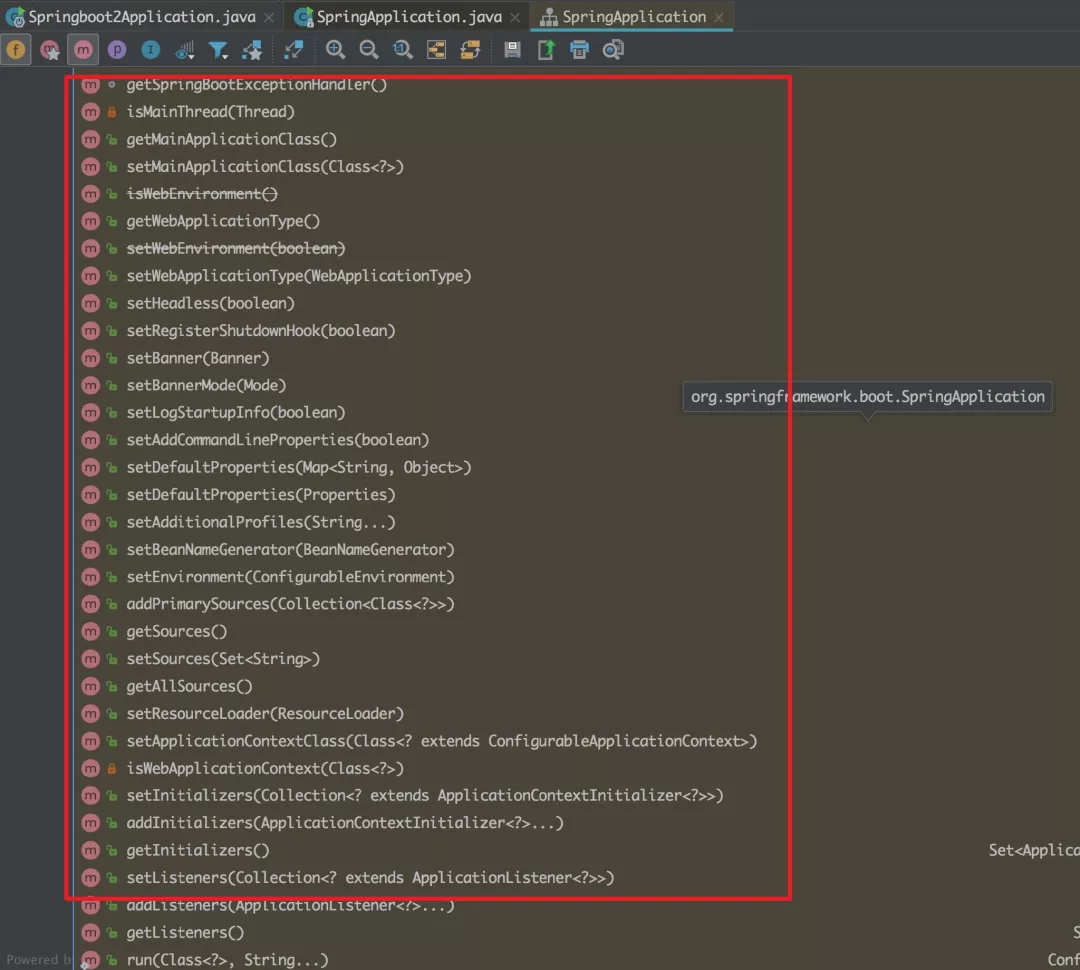
看到没,还很多呢!
举个例子:你想把 Spring Boot 项目的默认 Banner 换成你自己的,就需要在这里如下:
1public static void main(String[] args) {
2// SpringApplication.run(Springboot2Application.class, args);
3 SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(Springboot2Application.class);
4 application.setBanner((environment, sourceClass, out) -> {
5 //这里打印一个logo
6 System.out.println(" _ _ _\n" +
7 " | | (_) | |\n" +
8 " ____| |__ _ ___ | |__ ___ _ __ __ _\n" +
9 "|_ /| '_ \\ | |/ __|| '_ \\ / _ \\| '_ \\ / _` |\n" +
10 " / / | | | || |\\__ \\| | | || __/| | | || (_| |\n" +
11 "/___||_| |_||_||___/|_| |_| \\___||_| |_| \\__, |\n" +
12 " __/ |\n" +
13 " |___/\n");
14 });
15 application.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.CONSOLE);
16 //你还可以干其他的定制化初始设置
17 application.run(args);
18}
现在重启项目,你就会发现,控制台的 logo 已经换成你自己的了。
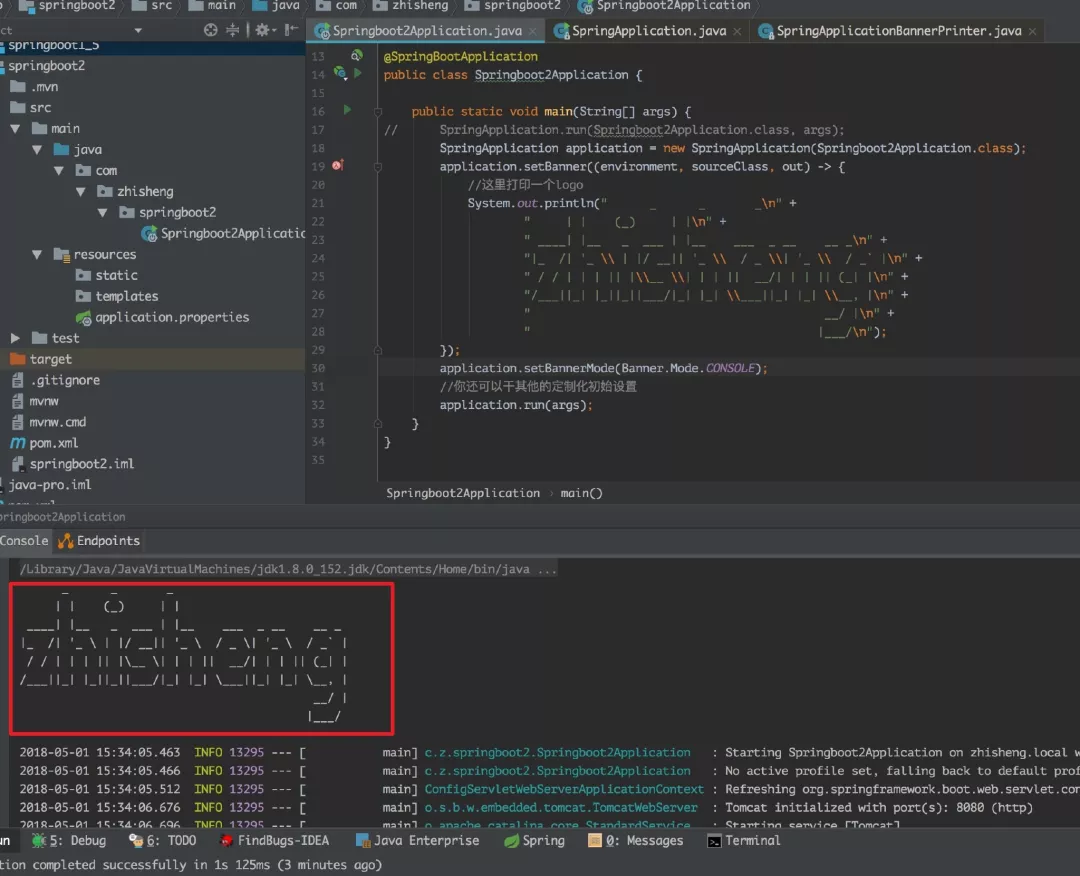
当然了,你可能会觉得这样写有点复杂,嗯嗯,确实,这样硬编码在代码里确实不太友好。你还可以在src/main/resources路径下新建一个banner.txt文件,banner.txt中填写好需要打印的字符串内容即可。
从该类中可以看到在 Spring Boot 2 中引入了个新的 WebApplicationType 和 WebEnvironment。
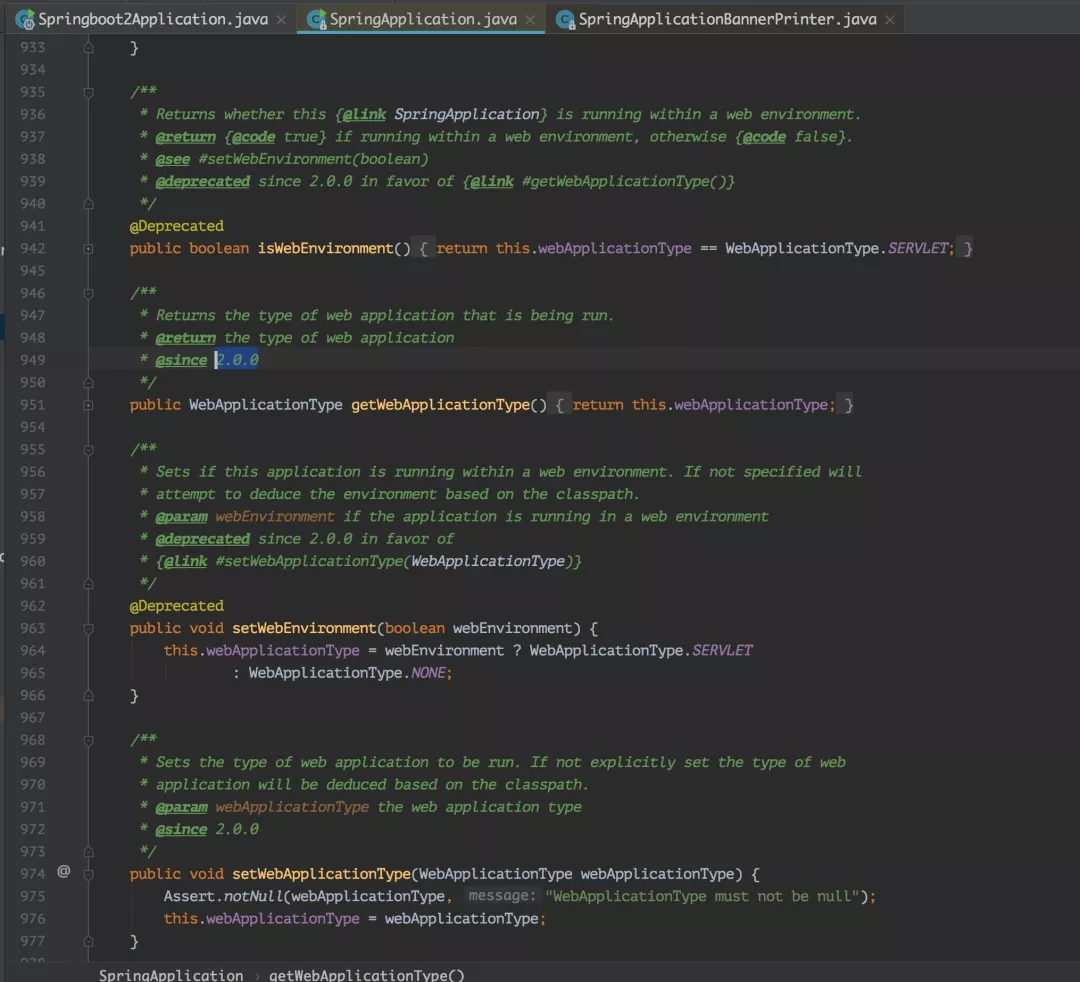
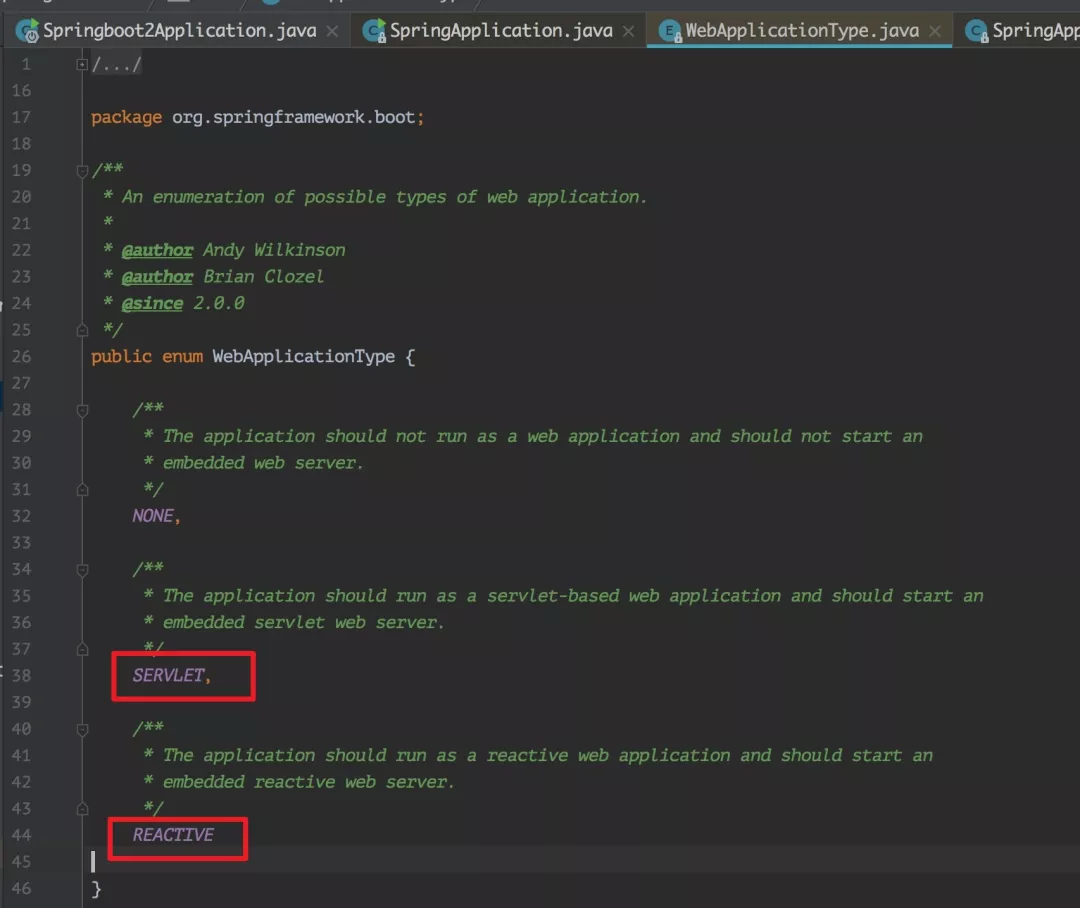
确实,这也是 Spring Boot 2 中比较大的特性,它是支持响应式编程的。我之前在文章 Spring Boot 2.0系列文章(二):Spring Boot 2.0 新特性详解 中也介绍过,以后有机会会介绍它的,这里我先卖个关子。
SpringApplication 初始化
SpringApplication.run() 的实现才是我们要深入探究的主角,该方法代码如下:
1//静态方法,可用于使用默认配置运行 SpringApplication
2public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource,
3 String... args) {
4 return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
5}
6public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources,
7 String[] args) {
8 return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
9}
在这个静态方法中,创建 SpringApplication 对象,并调用该对象的 run 方法。
1public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
2 this(null, primarySources);
3}
4//创建一个 SpringApplication 实例,应用上下文会根据指定的主要资源加载 beans ,实例在调用 run 方法之前可以定制化
5@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
6public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
7 this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
8 Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
9 this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
10 this.webApplicationType = deduceWebApplicationType();
11 setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
12 ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
13 setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
14 this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
15}
首先是进入单个参数的构造方法,然后进入两参数的构造方法(ResourceLoader 为 null),然后进行初始化。
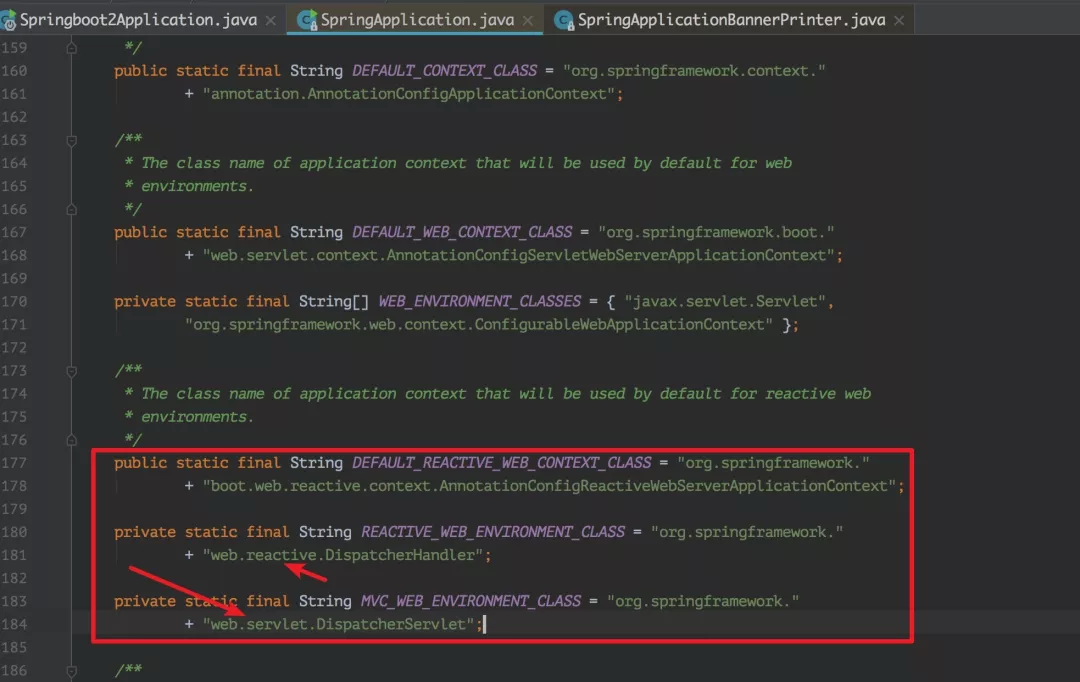
1、deduceWebApplicationType() : 推断应用的类型 ,创建的是一个 SERVLET 应用还是 REACTIVE应用或者是 NONE
1private static final String REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
2private static final String MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
3private static final String[] WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
4 "org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
5
6private WebApplicationType deduceWebApplicationType() {
7 if (ClassUtils.isPresent(REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS, null)
8 && !ClassUtils.isPresent(MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS, null)) {
9 return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE; //该程序是 REACTIVE 程序
10 }
11 for (String className : WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES) {
12 if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
13 return WebApplicationType.NONE; //该程序为 NONE
14 }
15 }
16 return WebApplicationType.SERVLET; //默认返回是 SERVLET 程序
17}
2、setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)):初始化 classpath 下的所有的可用的 ApplicationContextInitializer。
1)、getSpringFactoriesInstances()
1private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
2 return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
3}
4//获取所有的 Spring 工厂实例
5private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
6Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
7 ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
8 // Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
9 Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)); //获取所有 Spring Factories 的名字
10 List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,
11 classLoader, args, names);
12 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances); //Spring 工厂实例排序
13 return instances;
14}
15//根据读取到的名字创建对象(Spring 工厂实例)
16private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
17 Class<?>[] parameterTypes, ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {
18 List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
19 for (String name : names) {
20 try {
21 Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
22 Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
23 Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
24 T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
25 instances.add(instance);
26 }
27 catch (Throwable ex) {
28 throw new IllegalArgumentException(
29 "Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
30 }
31 }
32 return instances;
33}
上面的 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames() ,是从 META-INF/spring.factories 的资源文件中,读取 key 为org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer 的 value。
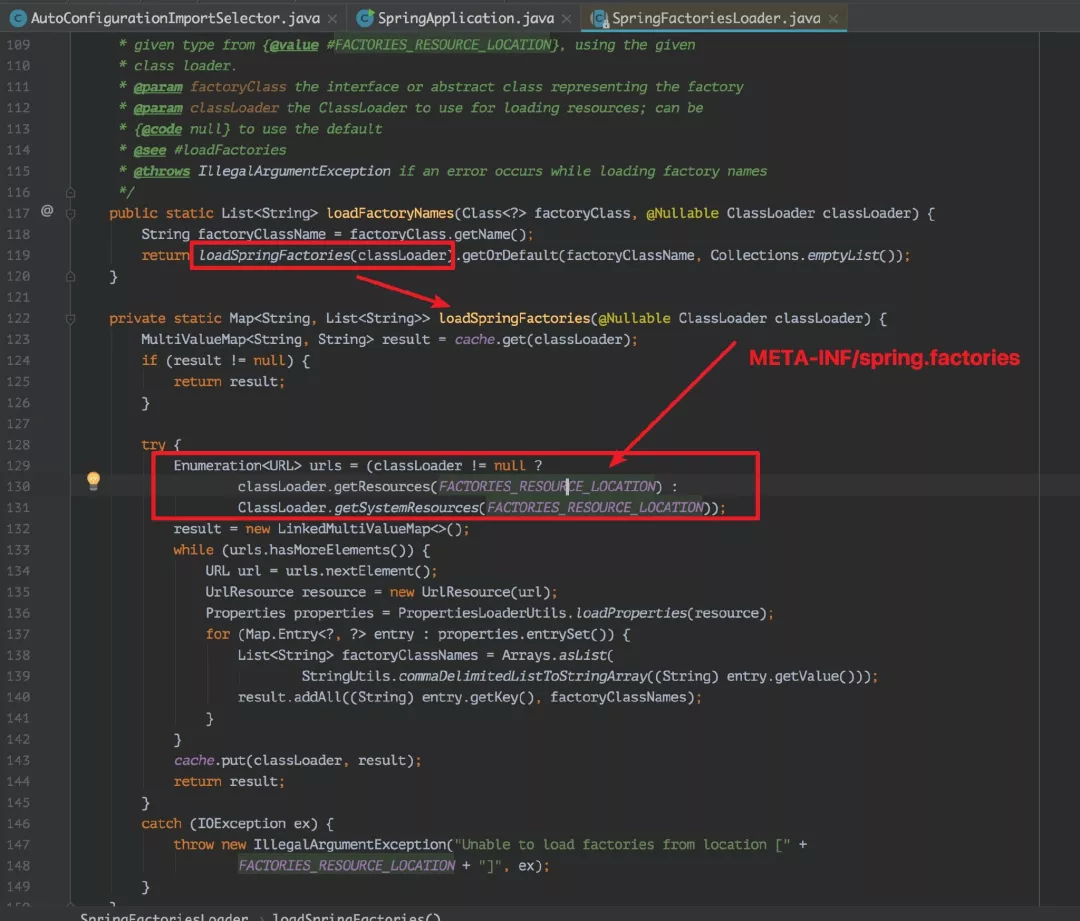
而 spring.factories 的部分内容如下:
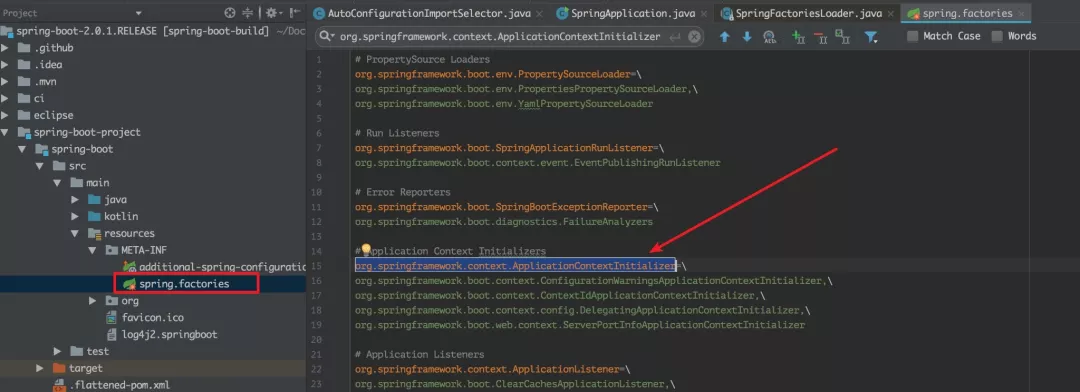
可以看到,最近的得到的,是 ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer 这四个类的名字。
2)、setInitializers():
1public void setInitializers(
2 Collection<? extends ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers) {
3 this.initializers = new ArrayList<>();
4 this.initializers.addAll(initializers);
5}
所以,这里 setInitializers() 所得到的成员变量 initializers 就被初始化为ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer 这四个类的对象组成的 list。
3、setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)):初始化 classpath 下的所有的可用的 ApplicationListener。
1)、getSpringFactoriesInstances() 和上面的类似,但是它是从 META-INF/spring.factories 的资源文件中,获取到 key 为 org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener 的 value。
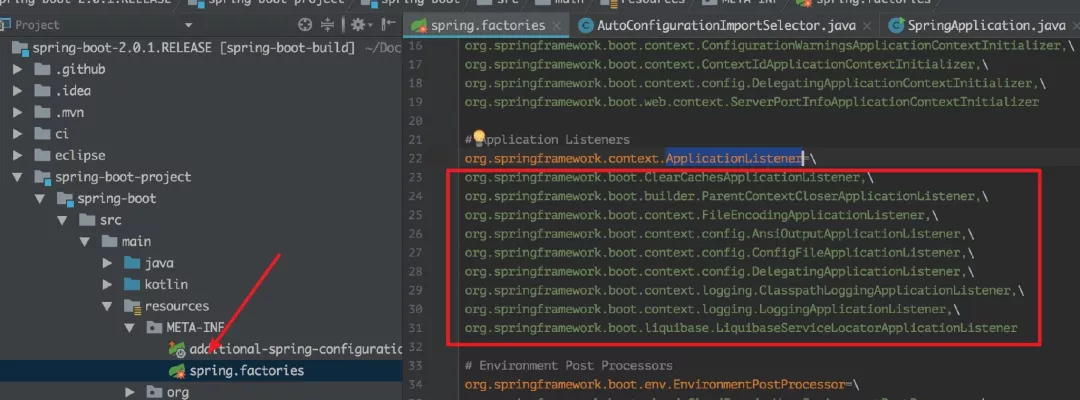
2)、setListeners():
1public void setListeners(Collection<? extends ApplicationListener<?>> listeners) {
2 this.listeners = new ArrayList<>();
3 this.listeners.addAll(listeners);
4}
所以,这里 setListeners() 所得到的成员变量 listeners 就被初始化为 ClearCachesApplicationListener,ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,FileEncodingApplicationListener,AnsiOutputApplicationListener ,ConfigFileApplicationListener,DelegatingApplicationListener,ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,LoggingApplicationListener,LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener 这九个类的对象组成的 list。
4、deduceMainApplicationClass() :根据调用栈,推断出 main 方法的类名
1private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
2 try {
3 StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
4 for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
5 if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
6 return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
7 }
8 }
9 }
10 catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
11 // Swallow and continue
12 }
13 return null;
14}
run 方法背后的秘密
上面看完了构造方法后,已经初始化了一个 SpringApplication 对象,接下来调用其 run 方法,代码如下:
1//运行 Spring 应用程序,创建并刷新一个新的 ApplicationContext
2public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
3 StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
4 stopWatch.start();
5 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
6 Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
7 configureHeadlessProperty();
8 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
9 listeners.starting();
10 try {
11 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
12 args);
13 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
14 applicationArguments);
15 configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
16 Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
17 context = createApplicationContext();
18 exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
19 SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
20 new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
21 prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
22 printedBanner);
23 refreshContext(context);
24 afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
25 stopWatch.stop();
26 if (this.logStartupInfo) {
27 new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
28 .logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
29 }
30 listeners.started(context);
31 callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
32 }
33 catch (Throwable ex) {
34 handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
35 throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
36 }
37 try {
38 listeners.running(context);
39 }
40 catch (Throwable ex) {
41 handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
42 throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
43 }
44 return context;
45 }
可变个数参数 args 即是我们整个应用程序的入口 main 方法的参数。StopWatch 是来自 org.springframework.util 的工具类,可以用来方便的记录程序的运行时间。
再来看看 1.5.12 与 2.0.1 版本的 run 方法 有什么不一样的地方?
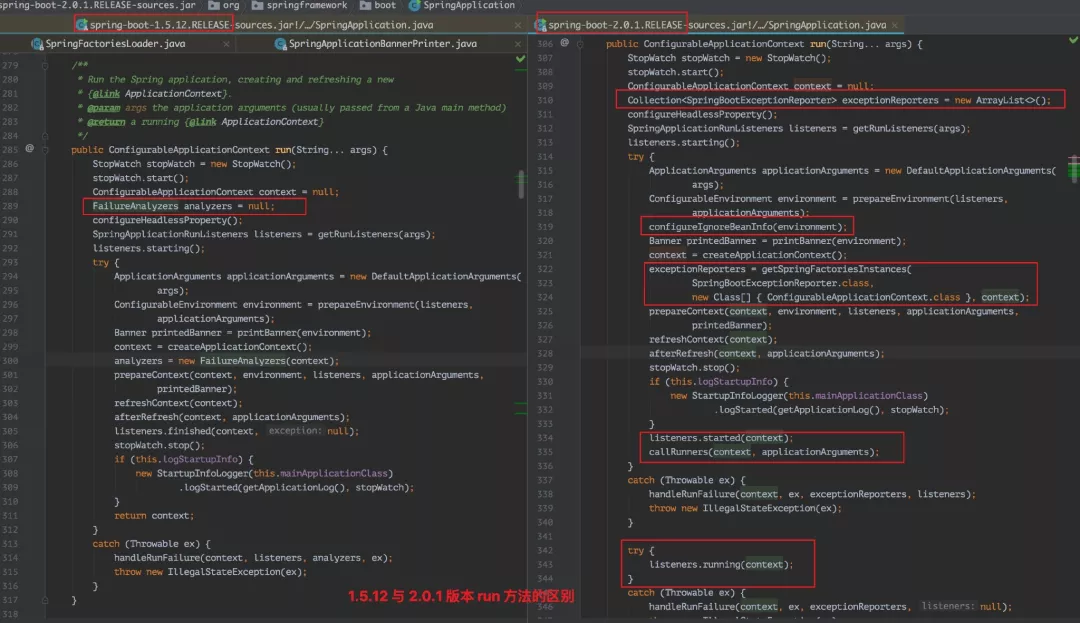
接下来好好分析上面新版本(2.0.1)的 run 方法的代码并配合比较旧版本(1.5.12)。
1、configureHeadlessProperty():设置 headless 模式
1private static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS = "java.awt.headless";
2private boolean headless = true;
3
4private void configureHeadlessProperty() {
5 System.setProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS, System.getProperty(
6 SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS, Boolean.toString(this.headless)));
7}
实际上是就是设置系统属性 java.awt.headless,该属性会被设置为 true。
2、getRunListeners():加载 SpringApplicationRunListener 对象
1 //TODO: xxx
2SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);//初始化监听器
3listeners.starting();
4try {
5 prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
6 refreshContext(context);
7 afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
8 listeners.started(context);
9 callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
10}
11try {
12 listeners.running(context);
13}
14
15private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
16 Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
17 return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, getSpringFactoriesInstances(
18 SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
19}
上面的 getRunListeners() 中也利用 SpringFactoriesLoader 加载 META-INF/spring.factories 中 key 为 SpringApplicationRunListener 的值,然后再将获取到的值作为参数传递到 SpringApplicationRunListeners 的构造方法中去创建对象。
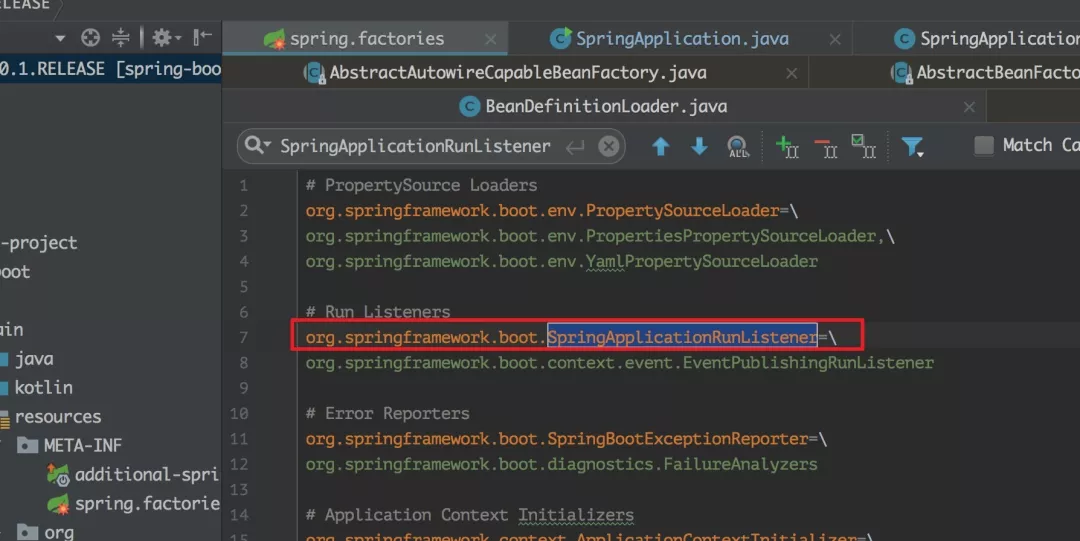
3、new DefaultApplicationArguments(args) :获取启动时传入参数 args(main 方法传进来的参数) 并初始化为 ApplicationArguments 对象。
1public DefaultApplicationArguments(String[] args) {
2 Assert.notNull(args, "Args must not be null");
3 this.source = new Source(args);
4 this.args = args;
5}
4、prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments):根据 listeners 和 applicationArguments 配置SpringBoot 应用的环境。
1private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
2 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
3 // Create and configure the environment
4 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
5 configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
6 listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
7 bindToSpringApplication(environment);
8 if (this.webApplicationType == WebApplicationType.NONE) {
9 environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
10 .convertToStandardEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment);
11 }
12 ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
13 return environment;
14}
15//如果 environment 不为空,直接 get 到,否则创建
16private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
17 if (this.environment != null) {
18 return this.environment;
19 }
20 if (this.webApplicationType == WebApplicationType.SERVLET) {
21 return new StandardServletEnvironment();
22 }
23 return new StandardEnvironment();
24}
25//配置环境
26protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,String[] args) {
27 configurePropertySources(environment, args);//配置要使用的PropertySources
28 configureProfiles(environment, args);//配置要使用的Profiles
29}
30//将环境绑定到 SpringApplication
31protected void bindToSpringApplication(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
32 try {
33 Binder.get(environment).bind("spring.main", Bindable.ofInstance(this));
34 }
35 catch (Exception ex) {
36 throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot bind to SpringApplication", ex);
37 }
38}
5、configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment):根据环境信息配置要忽略的 bean 信息
1public static final String IGNORE_BEANINFO_PROPERTY_NAME = "spring.beaninfo.ignore";
2
3private void configureIgnoreBeanInfo(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
4 if (System.getProperty(
5 CachedIntrospectionResults.IGNORE_BEANINFO_PROPERTY_NAME) == null) {
6 Boolean ignore = environment.getProperty("spring.beaninfo.ignore",
7 Boolean.class, Boolean.TRUE);
8 System.setProperty(CachedIntrospectionResults.IGNORE_BEANINFO_PROPERTY_NAME,
9 ignore.toString());
10 }
11}
6、printBanner(environment):打印标志,上面我已经说过了。
1private Banner printBanner(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
2 if (this.bannerMode == Banner.Mode.OFF) { //如果设置为 off,不打印 Banner
3 return null;
4 }
5 ResourceLoader resourceLoader = this.resourceLoader != null ? this.resourceLoader
6 : new DefaultResourceLoader(getClassLoader());
7 SpringApplicationBannerPrinter bannerPrinter = new SpringApplicationBannerPrinter(
8 resourceLoader, this.banner);
9 if (this.bannerMode == Mode.LOG) {
10 return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, logger);
11 }
12 return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, System.out);
13}
7、createApplicationContext():根据应用类型来确定该 Spring Boot 项目应该创建什么类型的 ApplicationContext ,默认情况下,如果没有明确设置的应用程序上下文或应用程序上下文类,该方法会在返回合适的默认值。
1public static final String DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext";
2public static final String DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext";
3public static final String DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext";
4
5protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
6 Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
7 if (contextClass == null) {
8 try {
9 switch (this.webApplicationType) { //根据应用程序的类型来初始化容器
10 case SERVLET: //servlet 应用程序
11 contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
12 break;
13 case REACTIVE: //reactive 应用程序
14 contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
15 break;
16 default: //默认
17 contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
18 }
19 } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
20 throw new IllegalStateException(
21 "Unable create a default ApplicationContext,please specify an ApplicationContextClass",ex);
22 }
23 }
24 //最后通过Spring的工具类 BeanUtils 初始化容器类 bean
25 return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
26}
来看看在 1.5.12 中是怎么样的?
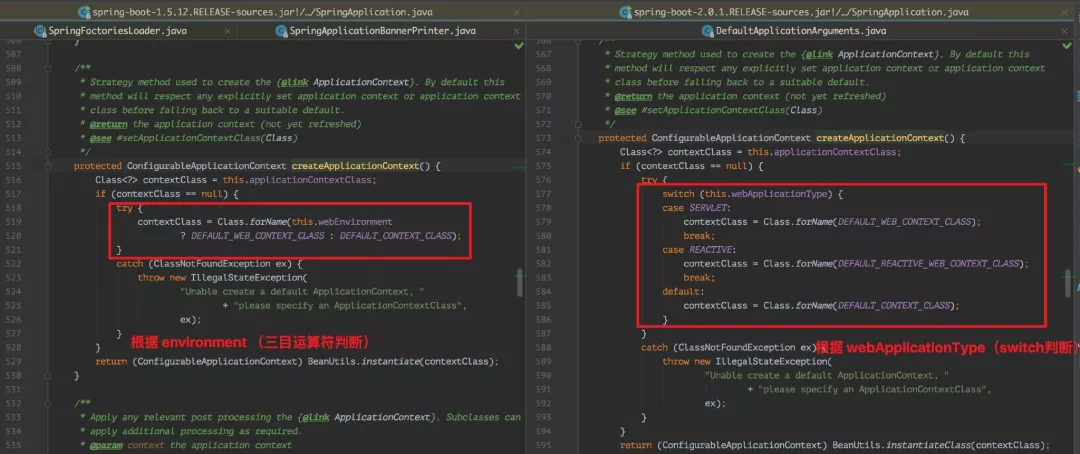
8、exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances( SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context)
1private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
2 Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
3 ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
4 // Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
5 Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(
6 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
7 List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,
8 classLoader, args, names);//根据类型 key 为 SpringBootExceptionReporter 去加载
9 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);//对实例排序
10 return instances;
11}
这里也是通过 SpringFactoriesLoader 加载 META-INF/spring.factories 中 key 为 SpringBootExceptionReporter 的全类名的 value 值。
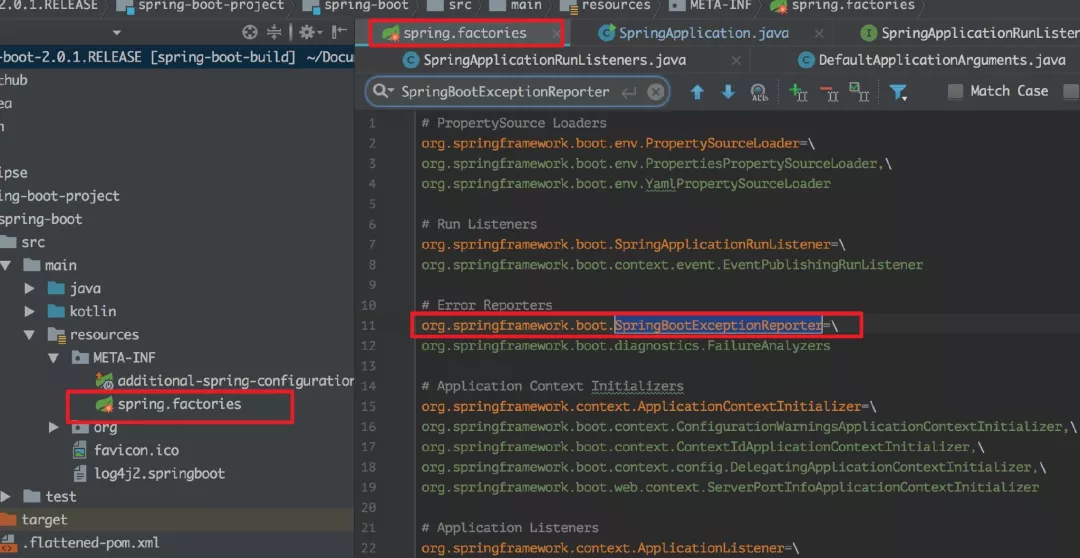
9、prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner):完成整个容器的创建与启动以及 bean 的注入功能。
1//装配 Context
2private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
3 ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
4 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
5 //将之前准备好的 environment 设置给创建好的 ApplicationContext 使用
6 context.setEnvironment(environment);
7 //1、
8 postProcessApplicationContext(context);
9 //2、
10 applyInitializers(context);
11 listeners.contextPrepared(context);
12 if (this.logStartupInfo) {//启动日志
13 logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
14 logStartupProfileInfo(context);
15 }
16 // Add boot specific singleton beans
17 context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments",
18 applicationArguments);
19 if (printedBanner != null) {
20 context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
21 }
22 // Load the sources
23 Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
24 Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
25 //3、
26 load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
27 listeners.contextLoaded(context);
28}
1)、postProcessApplicationContext(context)
1public static final String CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR = "org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationBeanNameGenerator";
2
3protected void postProcessApplicationContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
4 if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
5 context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton(
6 AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR,
7 this.beanNameGenerator);
8 }
9 if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
10 if (context instanceof GenericApplicationContext) {
11 ((GenericApplicationContext) context)
12 .setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
13 }
14 if (context instanceof DefaultResourceLoader) {
15 ((DefaultResourceLoader) context)
16 .setClassLoader(this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader());
17 }
18 }
19}
该方法对 context 进行了预设置,设置了 ResourceLoader 和 ClassLoader,并向 bean 工厂中添加了一个beanNameGenerator 。
2)、applyInitializers(context)
1protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
2 for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) {
3 Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(
4 initializer.getClass(), ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
5 Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");
6 initializer.initialize(context);
7 }
8}
在刷新之前将任何 ApplicationContextInitializer 应用于上下文
3)、load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]))
主要是加载各种 beans 到 ApplicationContext 对象中。
1protected void load(ApplicationContext context, Object[] sources) {
2 BeanDefinitionLoader loader = createBeanDefinitionLoader( //2
3 getBeanDefinitionRegistry(context), sources);// 1
4 if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
5 loader.setBeanNameGenerator(this.beanNameGenerator);
6 }
7 if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
8 loader.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
9 }
10 if (this.environment != null) {
11 loader.setEnvironment(this.environment);
12 }
13 loader.load();//3
14}
(1)、getBeanDefinitionRegistry(context)
获取 bean 定义注册表
1private BeanDefinitionRegistry getBeanDefinitionRegistry(ApplicationContext context) {
2 if (context instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
3 return (BeanDefinitionRegistry) context;
4 }
5 if (context instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
6 return (BeanDefinitionRegistry) ((AbstractApplicationContext) context)
7 .getBeanFactory();
8 }
9 throw new IllegalStateException("Could not locate BeanDefinitionRegistry");
10}
(2)、createBeanDefinitionLoader()
通过 BeanDefinitionLoader 的构造方法把参数(注册表、资源)传进去,然后创建 BeanDefinitionLoader。
(3)、load()
把资源全部加载。
10、refreshContext(context)
1private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
2 refresh(context);//1
3 if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
4 try {
5 context.registerShutdownHook();
6 }
7 catch (AccessControlException ex) {
8 // Not allowed in some environments.
9 }
10 }
11}
12//刷新底层的 ApplicationContext
13protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
14 Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
15 ((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
16}
refreshContext(context) 方法又调用了 refresh(context)。在调用了 refresh(context) 方法之后,调用了 registerShutdownHook 方法。继续看它的 refresh 方法:
1public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
2 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
3 // Prepare this context for refreshing.
4 prepareRefresh();
5 // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
6 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
7 // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
8 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
9 try {
10 // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
11 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
12 // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
13 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
14 // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
15 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
16 // Initialize message source for this context.
17 initMessageSource();
18 // Initialize event multicaster for this context.
19 initApplicationEventMulticaster();
20 // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
21 onRefresh();
22 // Check for listener beans and register them.
23 registerListeners();
24 // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
25 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); //1
26 // Last step: publish corresponding event.
27 finishRefresh();
28 } catch (BeansException ex) {
29 。。。
30 // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
31 destroyBeans();
32 // Reset 'active' flag.
33 cancelRefresh(ex);
34 // Propagate exception to caller.
35 throw ex;
36 } finally {
37 // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
38 // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
39 resetCommonCaches();
40 }
41 }
42}
到这里,我们就看见重点了,仔细看上的注释,正在做各种初始化工作,而今天我们关注的重点就是方法 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)。该方法进行了非懒加载 beans 的初始化工作。现在我们进入该方法内部,一探究竟。
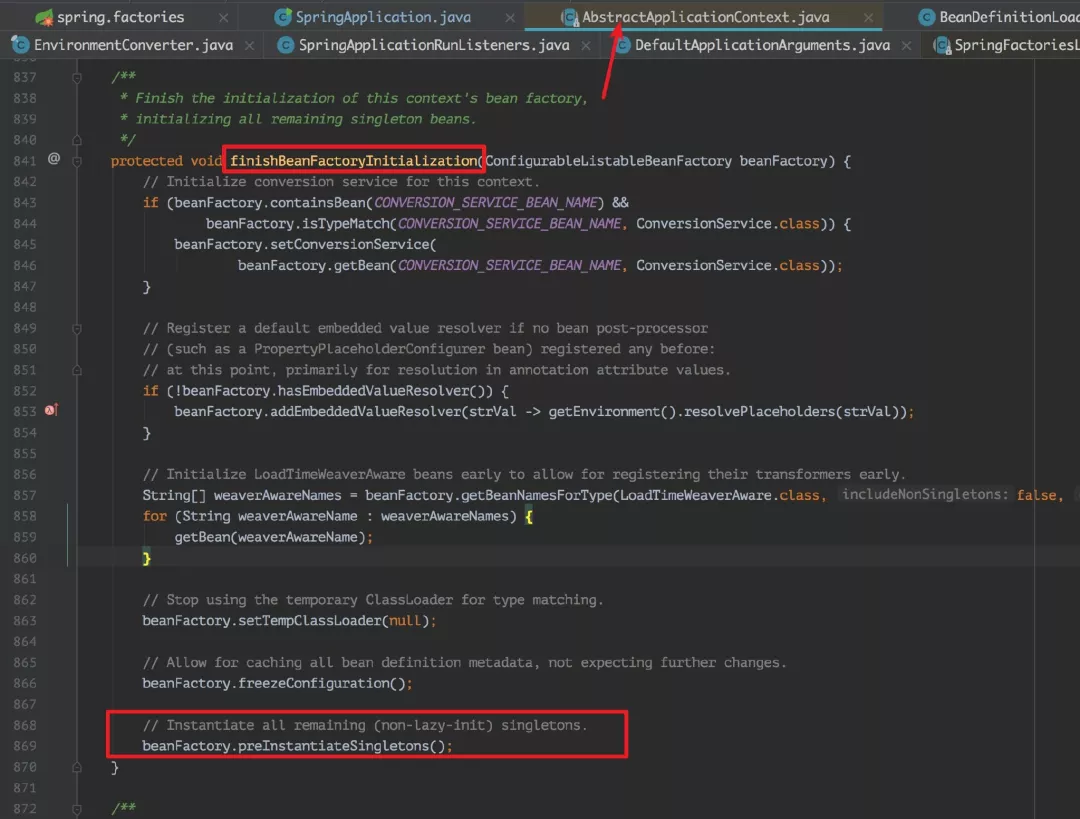
看上图方法中的最后一步,调用了 beanFactory 的 preInstantiateSingletons() 方法。此处的 beanFactory 是哪个类的实例对象呢?
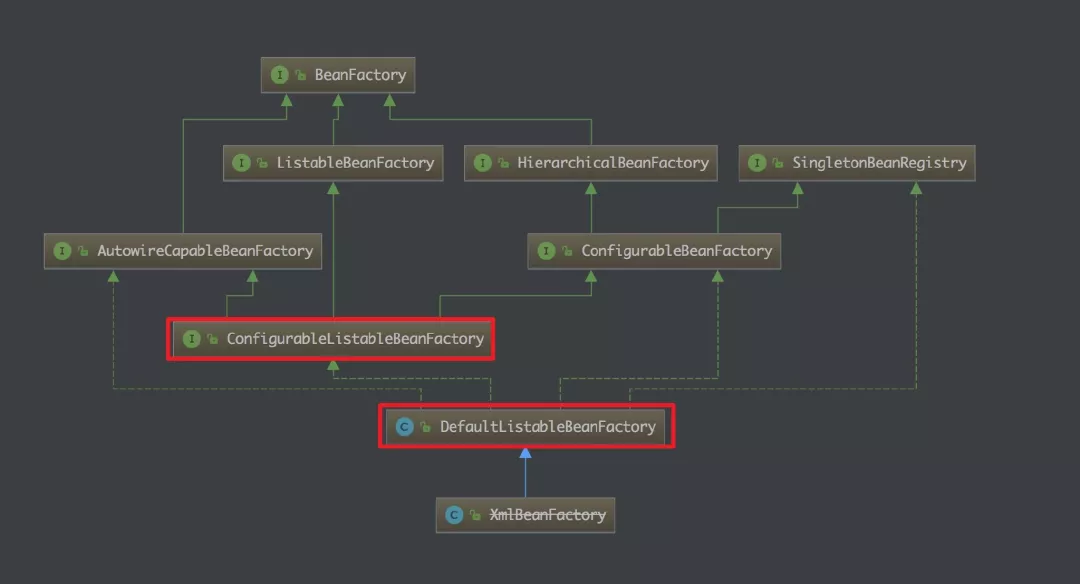
可以看到 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory 接口的实现类只有 DefaultListableBeanFactory,我们看下实现类中的 preInstantiateSingletons 方法是怎么做的。
1public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
2 // Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
3 // While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
4 List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
5
6 // Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
7 for (String beanName : beanNames) {
8 RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
9 if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
10 if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
11 Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
12 if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
13 final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
14 boolean isEagerInit;
15 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean){
16 isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)
17 ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit, getAccessControlContext());
18 } else {
19 isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
20 ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
21 }
22 if (isEagerInit) {
23 getBean(beanName);
24 }
25 }
26 } else {
27 getBean(beanName);
28 }
29 }
30 }
31
32 // Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
33 for (String beanName : beanNames) {
34 Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
35 if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
36 final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
37 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
38 AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
39 smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
40 return null;
41 }, getAccessControlContext());
42 } else {
43 smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
44 }
45 }
46 }
47}
从上面的代码中可以看到很多调用了 getBean(beanName) 方法,跟踪此方法进去后,最终发现 getBean 调用了AbstractBeanFactory 类的 doGetBean(xxx) 方法,doGetBean(xxx) 方法中有这么一段代码:
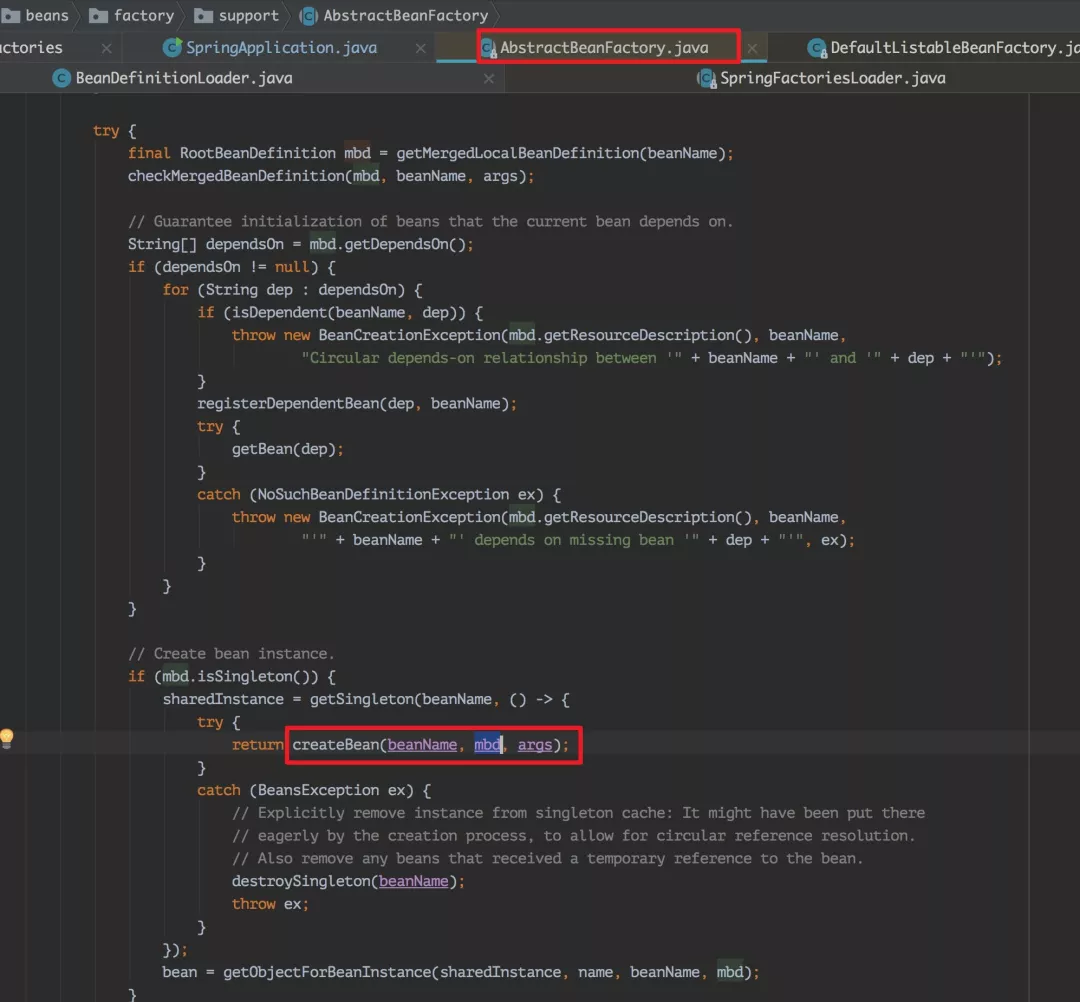
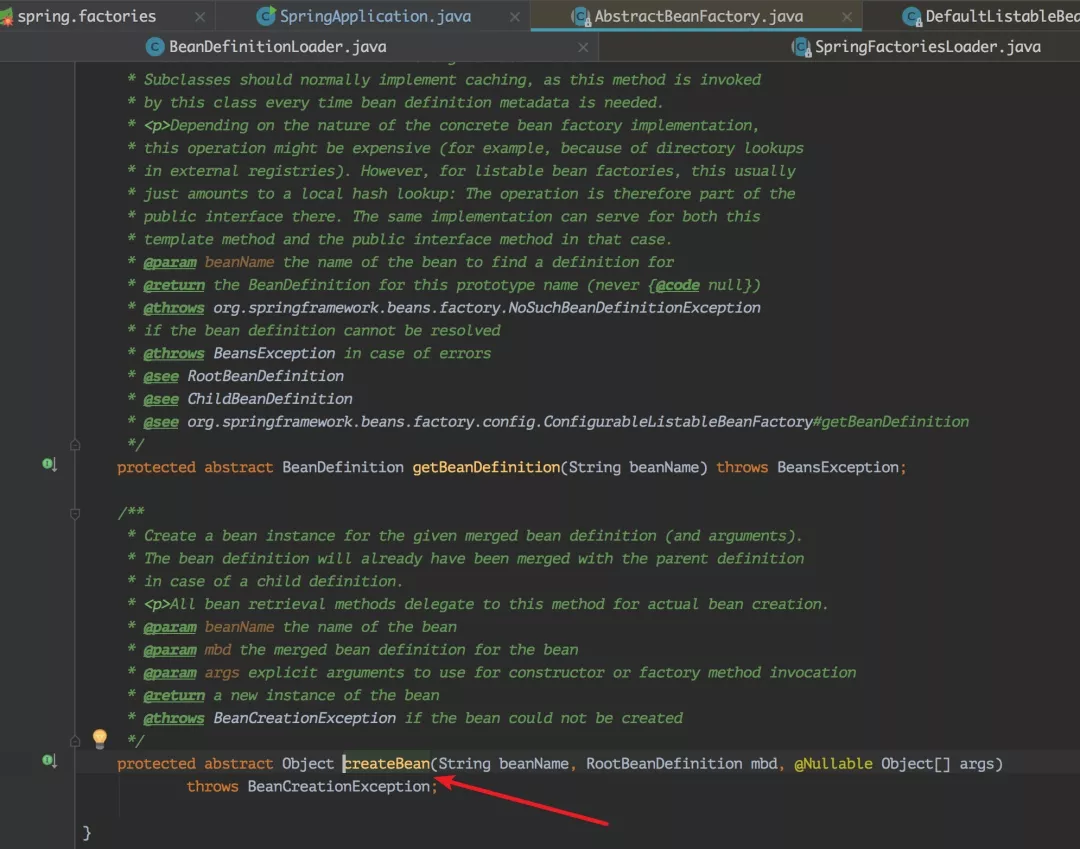
但是 createBean() 方法并没有得到实现,实现类在 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 中。这才是创建 bean 的核心方法。
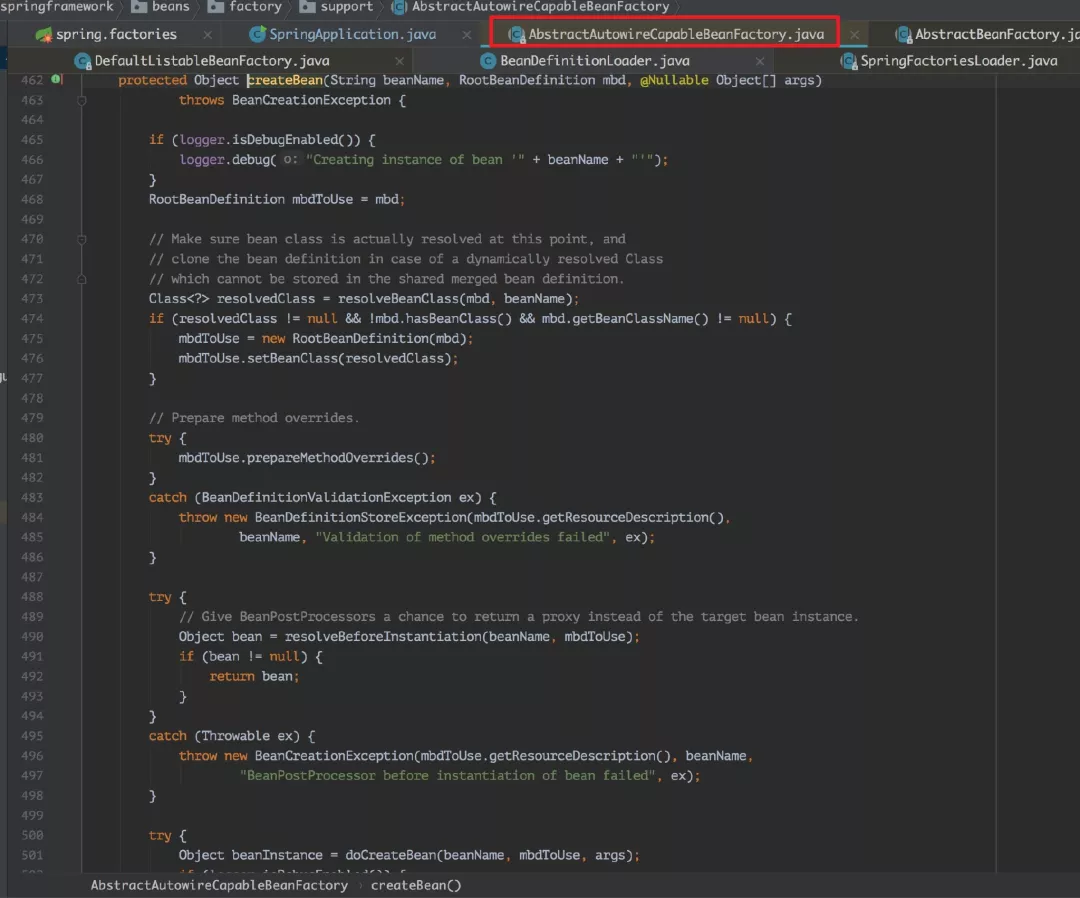
不知不觉,代码看的越来越深,感觉思维都差点回不去 run 方法了,切回大脑的上下文线程到 run 方法去。
11、afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments):在上下文刷新后调用该方法,其内部没有做任何操作。
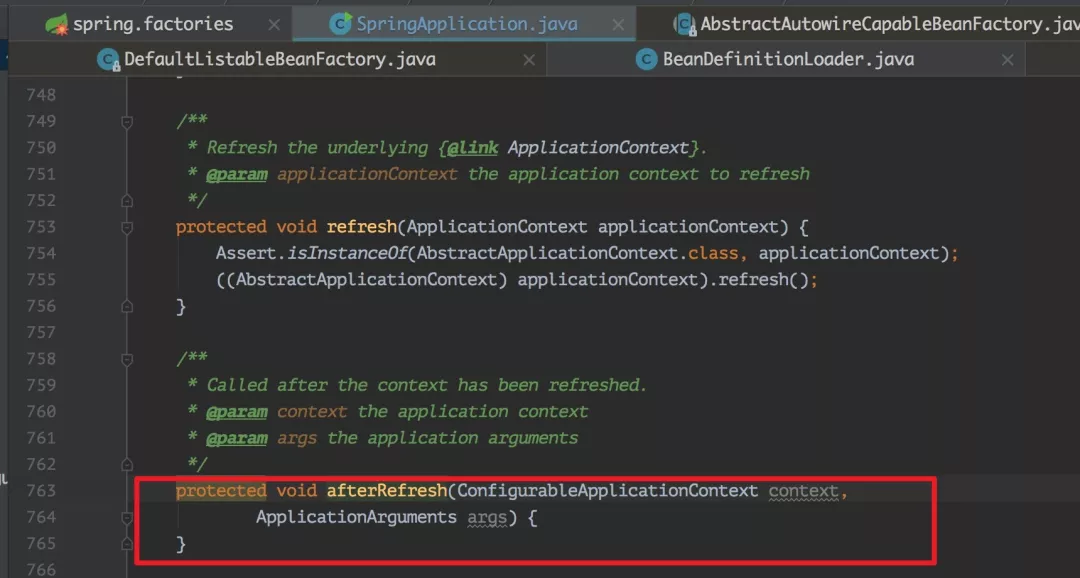
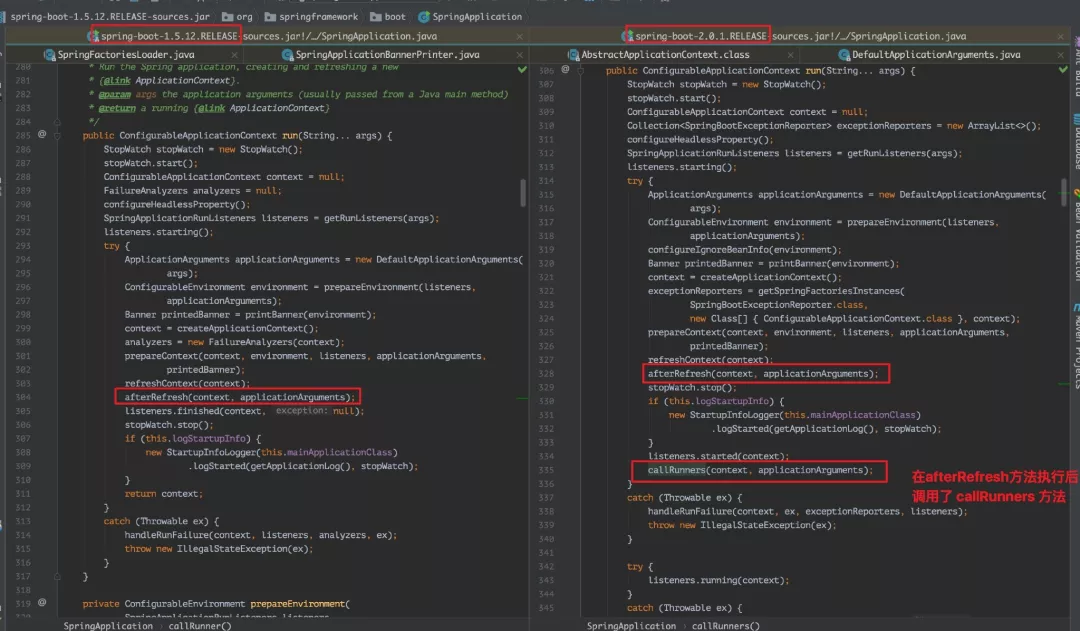
发现没做任何操作了之后,就觉得有点奇怪,所以把当前版本和 1.5.12 对比了下,发现:
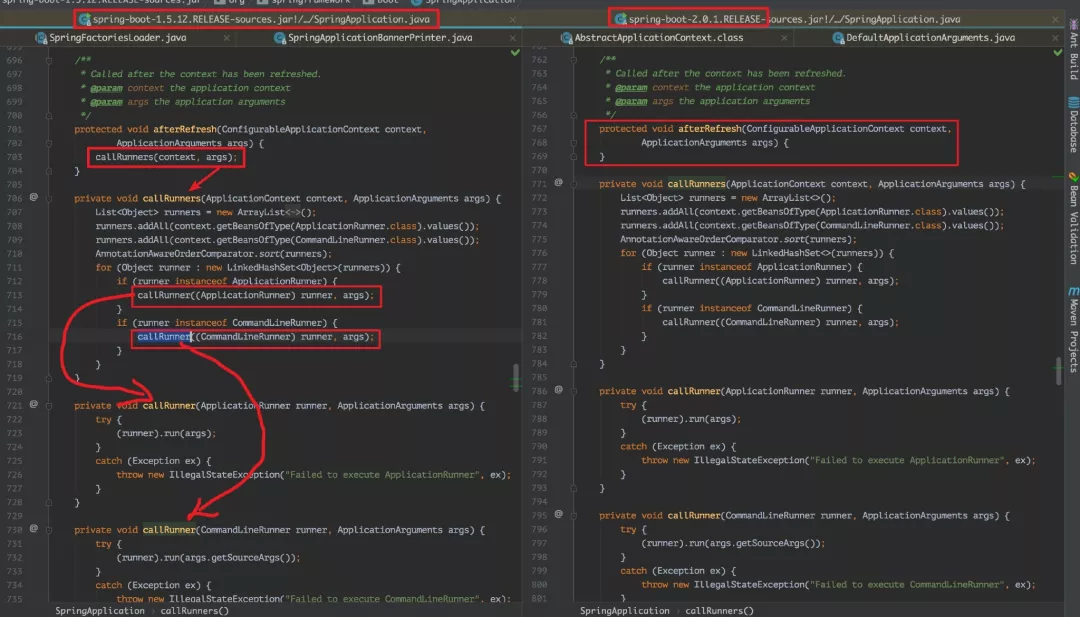
在 1.5.12 中的 afterRefresh() 方法中调用了 callRunners() 方法,但是在 2.0.1 版本中的 run 方法中调用了 callRunners () 方法:
这里不得不说 SpringApplicationRunListeners 在 2.0.1 中的改变:
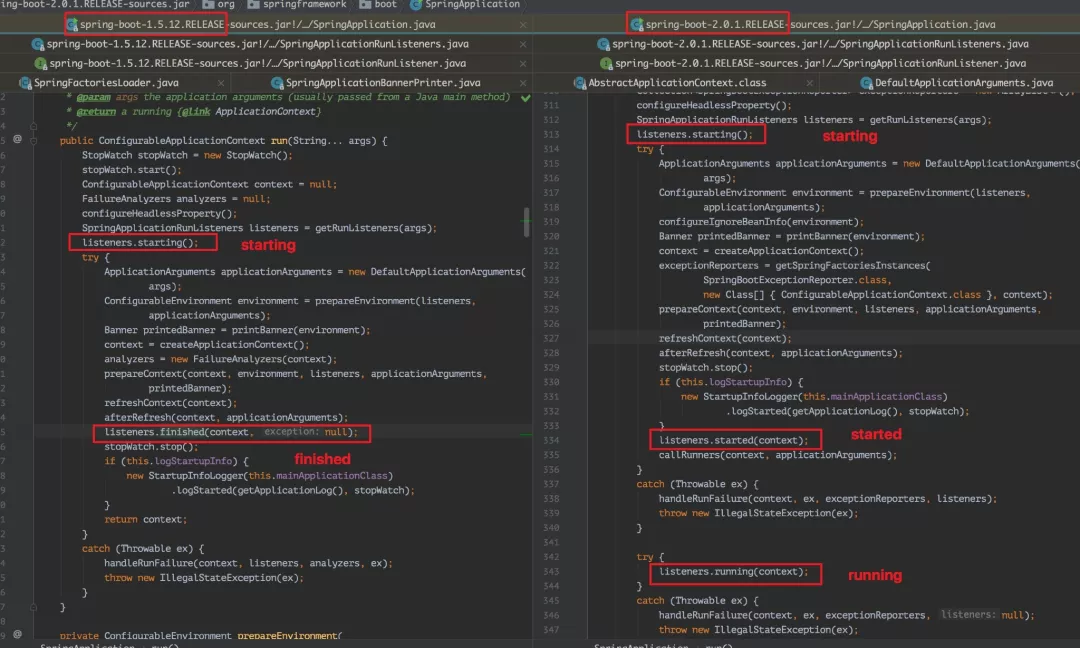
可以发现在 run 方法中,SpringApplicationRunListeners 监听器的状态花生了变化,这也是通过对比不同版本的代码才知道的区别,所以说我们看源码需要多对比着看。
so,我们来看下这个 SpringApplicationRunListener 这个接口:
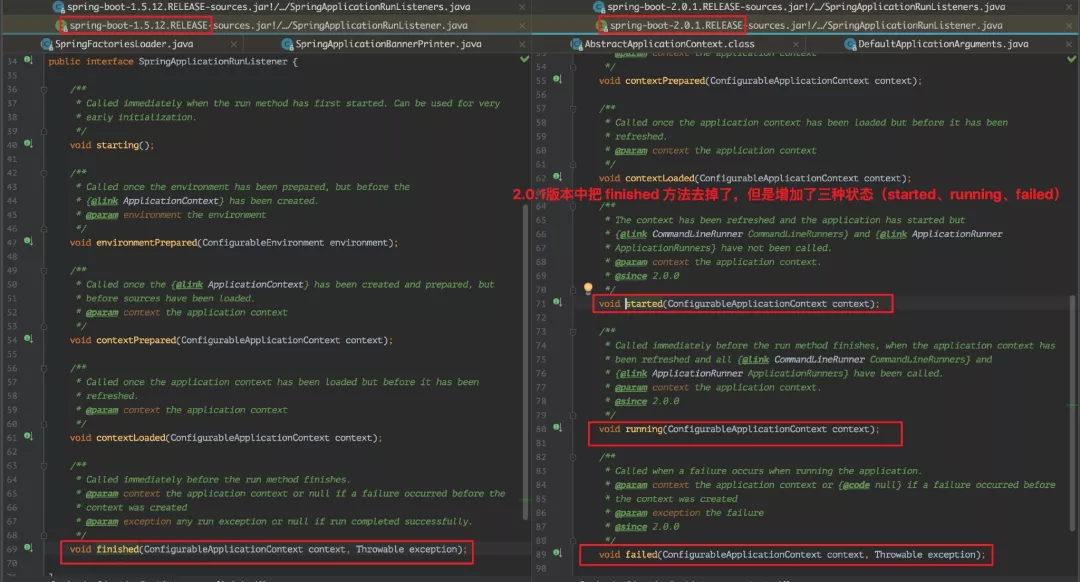
started 状态:The context has been refreshed and the application has started but CommandLineRunner and ApplicationRunner have not been called
running 状态:Called immediately before the run method finishes, when the application context has been refreshed and all CommandLineRunner and ApplicationRunners have been called.
相关文章
1、Spring Boot 2.0系列文章(一):Spring Boot 2.0 迁移指南
2、Spring Boot 2.0系列文章(二):Spring Boot 2.0 新特性详解
3、Spring Boot 2.0系列文章(三):Spring Boot 2.0 配置改变
4、Spring Boot 2.0系列文章(四):Spring Boot 2.0 源码阅读环境搭建
5、Spring Boot 2.0系列文章(五):Spring Boot 2.0 项目源码结构预览
6、Spring Boot 2.0系列文章(六):Spring boot 2.0 中 SpringBootApplication 注解详解
7、Spring Boot 2.0系列文章(七):SpringApplication 深入探索
总结
本文从源码级别分析了 Spring Boot 应用程序的启动过程,着重看了 SpringApplication 类中的构造函数的初始化和其 run 方法内部实现,并把涉及到的流程代码都过了一遍。
感悟:有时候跟代码跟着跟着,发现越陷越深,好难跳出来!后面还需多向别人请教阅读源码的技巧!
最后
虽然源码很难,但随着不断的探索,源码在你面前将会一览无遗,享受这种探索后的成就感!加油!骚年!
自己本人能力有限,源码看的不多,上面如有不对的还请留言交流。
为自己带盐:
这个里面主要分享一些非公开且确保有质量的分享,感兴趣可以加入。
