C#数据库数据导入导出系列之四 WinForm数据库导入导出到Excel
在日常的项目中,Excel,Word,txt等格式的数据导入到数据库中是很常见的,我在这里做一下总结
这里将分为Asp.net导入Sql Server,Oracle数据库和WinForm导入Sql Server,Oracle数据库。
C#数据库数据导入导出系列之一 ASP.NET Excel导入Sql Server数据库
C#数据库数据导入导出系列之四 WinForm数据库导入导出到Excel
(注意 这里四篇文章只是基础的方法,若有更高的要求,可以参考
http://www.cnblogs.com/atao/archive/2009/11/15/1603528.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/tonyqus/category/182110.html
http://www.yongfa365.com/Item/NPOI-MyXls-DataTable-To-Excel-From-Excel.html .net 通过NPOI或MyXls把DataTable导出到Excel
)
这里将的数据库数据库导入导出,其实对Sql Server 和Oracle都是通用的
如果使用ADO.Net连接Oracle数据库,需要在引用里添加“System.Data.OracleClient ”,其他方面与连接Sql Server数据库是一样的
SqlConnection cn = new SqlConnection();
OracleConnection oraleCn = new OracleConnection();
如果使用诸如Ibatis等持久层框架的话,唯一的区别就是在数据库连接语句上的差别而已。下面是两个例子
Oracle:Data Source=192.168.0.11/Contact;User ID=system;Password=ss;Unicode=True
Sql Server: Data Source=Contact;Server=localhost;uid=sa;pwd=ss
1,数据库导出到Excel
先看界面
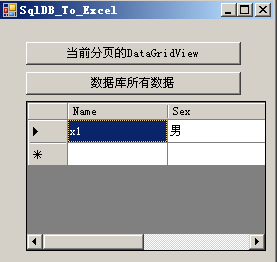
然后是代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Diagnostics;
using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
using System.Reflection;
using System.IO;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Data.OracleClient;
namespace SqlServer__Excel
{
public partial class SqlDB_To_Excel : Form
{
public SqlDB_To_Excel()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application myExcel = null;
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
print(dataGridView1);
}
public void print(DataGridView dataGridView1)
{
//导出到execl
try
{
SaveFileDialog saveFileDialog = new SaveFileDialog();
saveFileDialog.Filter = "导出Excel (*.xls)|*.xls";
saveFileDialog.FilterIndex = 0;
saveFileDialog.RestoreDirectory = true;
saveFileDialog.CreatePrompt = true;
saveFileDialog.Title = "导出文件保存路径";
saveFileDialog.ShowDialog();
string strName = saveFileDialog.FileName;
if(strName.Length != 0)
{
//没有数据的话就不往下执行
if(dataGridView1.Rows.Count == 0)
return;
// toolStripProgressBar1.Visible = true;
System.Reflection.Missing miss = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
//实例化一个Excel.Application对象
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application excel = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
excel.Application.Workbooks.Add(true);
excel.Visible = false;//若是true,则在导出的时候会显示EXcel界面。
if(excel == null)
{
MessageBox.Show("EXCEL无法启动!", "错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
return;
}
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbooks books = (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbooks)excel.Workbooks;
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook book = (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook)(books.Add(miss));
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet sheet = (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet)book.ActiveSheet;
sheet.Name = "test";
int m = 0, n = 0;
//生成Excel中列头名称
for(int i = 0; i < dataGridView1.Columns.Count; i++)
{
excel.Cells[1, i + 1] = dataGridView1.Columns[i].HeaderText;//输出DataGridView列头名
}
//把DataGridView当前页的数据保存在Excel中
for(int i = 0; i < dataGridView1.Rows.Count - 1; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < dataGridView1.Columns.Count; j++)
{
if(dataGridView1[j, i].ValueType == typeof(string))
{
excel.Cells[i + 2, j + 1] = "'" + dataGridView1[j, i].Value.ToString();
}
else
{
excel.Cells[i + 2, j + 1] = dataGridView1[j, i].Value.ToString();
}
}
}
sheet.SaveAs(strName, miss, miss, miss, miss, miss, Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.XlSaveAsAccessMode.xlNoChange, miss, miss, miss);
book.Close(false, miss, miss);
books.Close();
excel.Quit();
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(sheet);
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(book);
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(books);
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(excel);
GC.Collect();
MessageBox.Show("数据已经成功导出!", "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
// toolStripProgressBar1.Value = 0;
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(strName);
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "错误提示");
}
}
public void printAll(System.Data.DataTable dt)
{
//导出到execl
try
{
SaveFileDialog saveFileDialog = new SaveFileDialog();
saveFileDialog.Filter = "导出Excel (*.xls)|*.xls";
saveFileDialog.FilterIndex = 0;
saveFileDialog.RestoreDirectory = true;
saveFileDialog.CreatePrompt = true;
saveFileDialog.Title = "导出文件保存路径";
saveFileDialog.ShowDialog();
string strName = saveFileDialog.FileName;
if(strName.Length != 0)
{
//没有数据的话就不往下执行
if(dt.Rows.Count == 0)
return;
// toolStripProgressBar1.Visible = true;
System.Reflection.Missing miss = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
//实例化一个Excel.Application对象
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application excel = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
excel.Application.Workbooks.Add(true);
excel.Visible = false;//若是true,则在导出的时候会显示EXcel界面。
if(excel == null)
{
MessageBox.Show("EXCEL无法启动!", "错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
return;
}
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbooks books = (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbooks)excel.Workbooks;
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook book = (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Workbook)(books.Add(miss));
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet sheet = (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Worksheet)book.ActiveSheet;
sheet.Name = "test";
int m = 0, n = 0;
//生成Excel中列头名称
for(int i = 0; i < dt.Columns.Count; i++)
{
excel.Cells[1, i + 1] = dataGridView1.Columns[i].HeaderText;//输出DataGridView列头名
}
//把DataGridView当前页的数据保存在Excel中
if(dt.Rows.Count > 0)
{
for(int i = 0; i < dt.Rows.Count; i++)//控制Excel中行,上下的距离,就是可以到Excel最下的行数,比数据长了报错,比数据短了会显示不完
{
for(int j = 0; j < dt.Columns.Count; j++)//控制Excel中列,左右的距离,就是可以到Excel最右的列数,比数据长了报错,比数据短了会显示不完
{
string str = dt.Rows[i][j].ToString();
excel.Cells[i + 2, j + 1] = "'" + str;//i控制行,从Excel中第2行开始输出第一行数据,j控制列,从Excel中第1列输出第1列数据,"'" +是以string形式保存,所以遇到数字不会转成16进制
}
}
}
sheet.SaveAs(strName, miss, miss, miss, miss, miss, Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.XlSaveAsAccessMode.xlNoChange, miss, miss, miss);
book.Close(false, miss, miss);
books.Close();
excel.Quit();
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(sheet);
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(book);
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(books);
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(excel);
GC.Collect();
MessageBox.Show("数据已经成功导出!", "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
// toolStripProgressBar1.Value = 0;
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(strName);
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "错误提示");
}
}
private void SqlDB_To_Excel_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
dataGridView1.DataSource = GetDataTableFromSqlServer();
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
printAll(GetDataTableFromSqlServer());
}
private System.Data.DataTable GetDataTableFromSqlServer()
{
string sqlconn = "database=database1;server=localhost;uid=sa;pwd=sa";
SqlConnection cn = new SqlConnection(sqlconn);
string cmdText = "select * from users";
SqlDataAdapter da = new SqlDataAdapter(cmdText, cn);
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
da.Fill(ds, "table1");
return ds.Tables[0];
}
private System.Data.DataTable GetDataTableFromOracle()
{
string oracleconn = "Data Source=192.168.2.105/Database1;User ID=system;Password=ss;Unicode=True";
OracleConnection cn = new OracleConnection(oracleconn);
string cmdText = "select * from users";
OracleDataAdapter da = new OracleDataAdapter(cmdText, cn);
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
da.Fill(ds, "table1");
return ds.Tables[0];
}
}
}
结果:
代码的思想就是将数据从数据库中读出到DataTable或者DataGridView中,然后遍历他们的每一个单元格的值,给Excel对应的单元格赋值。
使用DataTable作为遍历的对象,是为了去除分页的困扰。
看到这里,如果换一个List<T>对象集合,也应该能导出到数据库中了。
2,Excel数据导入到数据库
在WinForm中Excel导入到数据库中和在WebForm中的导入过程是一样的。可参见前面的内容。
这个系列的博客到此结束!