用途:
空xml负样本,用于降低目标检测测试过程中的误检率。
用法:
负样本图片和训练集图片放在同一个文件夹,空xml文件和训练集xml放在同一个文件夹,然后按照正常的目标检测训练流程即可完成训练。
附加功能:
把原有的label为背景的xml文件替换掉(主要用于比赛数据集中的背景label检索和修改)。
上代码(把输入输出文件夹改为自己的即可):
import os
import xml.dom.minidom
import cv2
img_path = 'C:\\Users\\hq\\Desktop\\none_test\\img\\'
xml_path = 'C:\\Users\\hq\\Desktop\\none_test\\xml\\'
# 删除所有label为背景的xml
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
for img_file in os.listdir(xml_path):
filename = os.path.join(xml_path, img_file)
root = ET.parse(filename).getroot()
for ob in root.findall('object'):
name = ob.find('name').text
#print(name)
if name=='Background':
os.remove(filename)
continue
# 创建新的xml文件(保留所有原有label为非背景的xml)
for img_file in os.listdir(img_path):
filename = os.path.join(img_path, img_file)
img_cv = cv2.imread(filename)
img_name = os.path.splitext(img_file)[0]
#create an empty dom document object
doc = xml.dom.minidom.Document()
#creat a root node which name is annotation
annotation = doc.createElement('annotation')
#add the root node to the dom document object
doc.appendChild(annotation)
#add the folder subnode
folder = doc.createElement('folder')
folder_text = doc.createTextNode('VOC2012')
folder.appendChild(folder_text)
annotation.appendChild(folder)
#add the filename subnode
filename = doc.createElement('filename')
filename_text = doc.createTextNode(img_file)
filename.appendChild(filename_text)
annotation.appendChild(filename)
# add the path subnode
path = doc.createElement('path')
path_text = doc.createTextNode(img_path + img_file)
path.appendChild(path_text)
annotation.appendChild(path)
#add the source subnode
source = doc.createElement('source')
database = doc.createElement('database')
database_text = doc.createTextNode('Unknown')
source.appendChild(database)
database.appendChild(database_text)
annotation.appendChild(source)
#add the size subnode
size = doc.createElement('size')
width = doc.createElement('width')
width_text = doc.createTextNode('%s'%img_cv.shape[1])
height = doc.createElement('height')
height_text = doc.createTextNode('%s'%img_cv.shape[0])
depth = doc.createElement('depth')
depth_text = doc.createTextNode('%s'%img_cv.shape[2])
size.appendChild(width)
width.appendChild(width_text)
size.appendChild(height)
height.appendChild(height_text)
size.appendChild(depth)
depth.appendChild(depth_text)
annotation.appendChild(size)
#add the segmented subnode
segmented = doc.createElement('segmented')
segmented_text = doc.createTextNode('0')
segmented.appendChild(segmented_text)
annotation.appendChild(segmented)
#write into the xml text file
#os.mknod(xml_path+'%s.xml'%img_name)
if not os.path.exists(xml_path+'%s.xml'%img_name):
with open(xml_path+'%s.xml'%img_name, mode="w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
fp = open(xml_path+'%s.xml'%img_name, 'w+')
doc.writexml(fp, indent='\t', addindent='\t', newl='\n', encoding='utf-8')
fp.close()
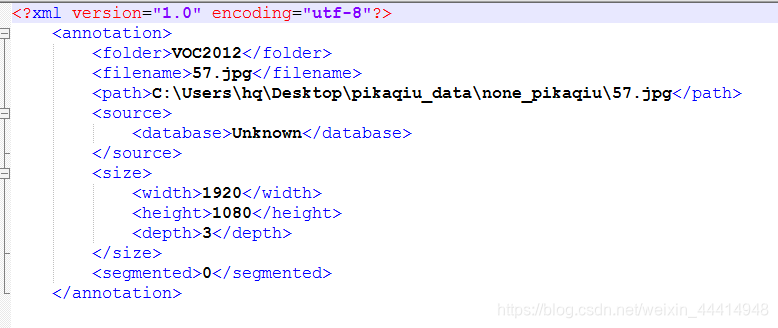
生成结果:
最后:非常感谢这篇大佬博客的启发https://blog.csdn.net/dulingwen/article/details/89669928