南京信息工程大学实验报告
实验名称 C++简单程序设计-6 实验日期 2018-5-31得分 指导教师 耿学华
系 计软院 专业计科 年级 2016 级 班次 (2) 姓名 余佳奇 学号 20161326022
一、 实验结论
1. 某计算机硬件系统,为了实现特定的功能,在某个子模块设计了 ABC 三款芯片用于 数字计算。各个芯片的计算功能如下: A 芯片:计算两位整数的加法(m+n)、计算两位整数的减法(m-n) B 芯片:计算两位整数的加法(m+n)、计算两位整数的乘法(m*n) C 芯片:计算两位整数的加法(m+n)、计算两位整数的除法(m/n) 为 ABC 三个芯片分别定义类,描述上述芯片的功能,并在 main 函数中测试这三个类。
Code:
Base.h
#ifndef _Base_H_ #define _Base_H_ class Base{ public: Base(int M=10,int N=10); ~Base(); int add(); protected: int m,n; }; #endif
Base.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"base.h" using namespace std; int Base::add(){ cout<<m<<"与"<<n<<"相加为:"<<endl; return (m+n); } Base::~Base(){ cout<<"Deconstructor Base is called"<<endl; } Base::Base(int M,int N){ cout << "Constructor Base is called" << endl; m=M; n=N; }
A.h
#include"base.h" #ifndef _A_h #define _A_h class A:public Base{ public: A(int M,int N); ~A(); int sub(); }; #endif
A.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"A.h" using namespace std; int A::sub(){ cout<<m<<"与"<<n<<"相减为:"<<endl; return (m-n); } A::~A(){ cout<<"Deconstructor A is called"<<endl; } A::A(int M,int N){ cout << "Constructor A is called" << endl; m=M; n=N; }
B.h‘
#include"base.h" #ifndef _B_h #define _B_h class B:public Base{ public: B(int M,int N); ~B(); int mul(); }; #endif
B.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"B.h" using namespace std; int B::mul(){ cout<<m<<"与"<<n<<"相乘为:"<<endl; return (m*n); } B::~B(){ cout<<"Deconstructor B is called"<<endl; } B::B(int M,int N){ cout << "Constructor B is called" << endl; m=M; n=N; }
C.h
#include"base.h" #ifndef _C_h #define _C_h class C:public Base{ public: C(int M,int N); ~C(); int div(); }; #endif
C.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"C.h" using namespace std; int C::div(){ cout<<m<<"与"<<n<<"相除为:"<<endl; return (m/n); } C::~C(){ cout<<"Deconstructor C is called"<<endl; } C::C(int M,int N){ cout << "Constructor C is called" << endl; m=M; n=N; }
main.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"base.h" #include"A.h" #include"B.h" #include"C.h" using namespace std; int main(){ Base l(4,6); cout<<l.add()<<endl; A a(2,3); cout<<a.add()<<endl; cout<<a.sub()<<endl; B b(5,6); cout<<b.add()<<endl; cout<<b.mul()<<endl; C c(9,2); cout<<c.add()<<endl; cout<<c.div()<<endl; return 0; }
运行结果:

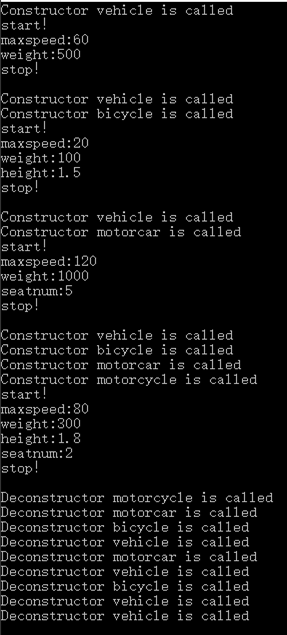
2. 定义一个车(vehicle)基类,具有数据成员 maxspeed, weight(均为 int 型), 函数 成员 run(), stop(),由此派生出自行车(bicycle)类、汽车(motorcar)类。其中, bicycle 类 新增数据成员高度(height), motorcar 类新增数据成员座位数(seatnum)属性。再从 bicycle 和 motorcar 派生出摩托车(motorcycle)类,并在主程序中测试这个类。(每个类都要求定 义构造函数和析构函数)
Code:
vehicle.h
#ifndef _VEHICLE_H_ #define _VEHICLE_H_ class vehicle{ protected: float maxspeed; float weight; public: ~vehicle(); vehicle(float m=60,float w=500); virtual void run(); virtual void stop(); }; #endif
vehicle.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"vehicle.h" using namespace std; void vehicle::run(){ cout<<"start!"<<endl; cout<<"maxspeed:"<<maxspeed<<endl; cout<<"weight:"<<weight<<endl; } void vehicle::stop(){ cout<<"stop!"<<endl<<endl; } vehicle::vehicle(float m,float w){ maxspeed=m; weight=w; cout<<"Constructor vehicle is called"<<endl; } vehicle::~vehicle(){ cout<<"Deconstructor vehicle is called"<<endl; }
bicycle.h
#ifndef _BICYCLE_H_ #define _BICYCLE_H_ #include"vehicle.h" class bicycle:virtual public vehicle{ protected: float height; public: ~bicycle(); bicycle(float m=20,float w=100,float h=1.5); void run1(); }; #endif
bicycle.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"bicycle.h" using namespace std; bicycle::bicycle(float m,float w,float h):vehicle(m,w){ height=h; cout<<"Constructor bicycle is called"<<endl; } bicycle::~bicycle(){ cout<<"Deconstructor bicycle is called"<<endl; } void bicycle::run1(){ cout<<"start!"<<endl; cout<<"maxspeed:"<<maxspeed<<endl; cout<<"weight:"<<weight<<endl; cout<<"height:"<<height<<endl; }
motorcar.h
#ifndef _MOTORCAR_H_ #define _MOTORCAR_H_ #include"vehicle.h" class motorcar:virtual public vehicle{ protected: int seatnum; public: ~motorcar(); motorcar(float m=120,float w=1000,int s=5); void run2(); }; #endif
motorcar.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"motorcar.h" using namespace std; motorcar::motorcar(float m,float w,int s):vehicle(m,w){ seatnum=s; cout<<"Constructor motorcar is called"<<endl; } motorcar::~motorcar(){ cout<<"Deconstructor motorcar is called"<<endl; } void motorcar::run2(){ cout<<"start!"<<endl; cout<<"maxspeed:"<<maxspeed<<endl; cout<<"weight:"<<weight<<endl; cout<<"seatnum:"<<seatnum<<endl; }
motorcycle.h
#ifndef _MOTORCYCLE_H_ #define _MOTORCYCLE_H_ #include"bicycle.h" #include"motorcar.h" class motorcycle:public bicycle,public motorcar{ public: ~motorcycle(); motorcycle(float m=80,float w=300,float h=1.8,int s=2); void run3(); }; #endif
motorcycle.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"motorcycle.h" using namespace std; motorcycle::motorcycle(float m,float w,float h,int s):vehicle(m,w){ seatnum=s; height=h; cout<<"Constructor motorcycle is called"<<endl; } motorcycle::~motorcycle(){ cout<<"Deconstructor motorcycle is called"<<endl; } void motorcycle::run3(){ cout<<"start!"<<endl; cout<<"maxspeed:"<<maxspeed<<endl; cout<<"weight:"<<weight<<endl; cout<<"height:"<<height<<endl; cout<<"seatnum:"<<seatnum<<endl; }
main.cpp
#include"vehicle.h" #include"bicycle.h" #include"motorcar.h" #include"motorcycle.h" int main(){ vehicle a; a.run(); a.stop(); bicycle b; b.run1(); b.stop(); motorcar c; c.run2(); c.stop(); motorcycle d; d.run3(); d.stop(); return 0; }
运行结果:
3. 实验内容三
Code:
fraction.h
#include<iostream> #include<cmath> #ifndef _FRACTION_H_ #define _FRACTION_H_ using namespace std; class Fraction { protected: int top, bottom; public: Fraction(int t, int b); Fraction(int t); Fraction(); int gcd(int a, int b); void simplify(); void add(Fraction c1); void subtract(Fraction c1); void multiple(Fraction c1); void divde(Fraction c1); void compare(Fraction c1); void readln(); void writeln(); friend Fraction operator +(const Fraction &c1,const Fraction &c2); friend Fraction operator -(const Fraction &c1,const Fraction &c2); friend Fraction operator *(const Fraction &c1,const Fraction &c2); friend Fraction operator /(const Fraction &c1,const Fraction &c2); }; #endif
fraction.cpp
#include"Fraction.h" int Fraction::gcd(int t, int b) { //求两个数的最小公约数// return t % b == 0 ? b : gcd(b, t%b); } Fraction::Fraction(int t, int b) { //定义分数对象时,如果提供两个初始化参数,代表分数3/4// top = t; bottom = b; } Fraction::Fraction(int t) { //定义分数对象时,如果提供一个初始化参数,代表分数5/1// top = t; bottom = 1; } Fraction::Fraction() { //默认没有提供任何初始化数据时,分数的对象默认值为0/1// top = 0; bottom = 1; } void Fraction::simplify() { //用于分数的化简// if(bottom < 0) { top = - top; bottom = - bottom; } int g = gcd(abs(top),abs(bottom)); //求出最大公约数,分别用分子分母做除// top /= g; bottom /= g; } void Fraction::add(Fraction c1) { //求分数的和// bottom = bottom * c1.bottom; top = top * c1.bottom + c1.top * bottom; simplify(); } void Fraction::subtract(Fraction c1) { //求分数的差// bottom = bottom * c1.bottom; top = top * c1.bottom - c1.top * bottom; simplify(); } void Fraction::multiple(Fraction c1) { //求分数的积// top *= c1.top; bottom *= c1.bottom; simplify(); } void Fraction::divde(Fraction c1) { //求分数的商// if(c1.top == 0) { cout << "错误,0不能作除数.\n"; return ; } top *= c1.bottom; bottom *= c1.top; //两个数相除就相当于一个数乘另一个数的倒数// simplify(); } void Fraction::compare(Fraction c1) { //比较分数大小// int tmp=top * gcd(bottom, c1.bottom) - c1.top* gcd(bottom, c1.bottom); if(tmp==0) cout<<"两数大小相等!"<<endl; else if(tmp<0) cout<<"第一个数较大!" <<endl; else if(tmp>0) cout<<"第二个数较大!" <<endl; } void Fraction::readln() { //读入分数// cout << "请输入分子和分母" << endl; cin >> top; int ans; cin >> ans; while (ans == 0) { cout << "0不能作分母,请重试!" << endl; cin >> ans; } bottom = ans; } void Fraction::writeln() { //输出分数// if(bottom != 1) cout << top << "/" << bottom << endl; else cout << top <<endl; } Fraction operator +(const Fraction &c1,const Fraction &c2) { Fraction tmp; tmp.bottom = c1.bottom * c2.bottom; tmp.top = c2.top * c1.bottom + c1.top * c2.bottom; tmp.simplify(); return tmp; } Fraction operator -(const Fraction &c1,const Fraction &c2) { Fraction tmp; tmp.bottom = c1.bottom * c2.bottom; tmp.top = c1.top * c2.bottom - c2.top * c1.bottom; if(tmp.bottom < 0) { tmp.top = - tmp.top; tmp.bottom = - tmp.bottom; } tmp.simplify(); return tmp; } Fraction operator *(const Fraction &c1,const Fraction &c2) { Fraction tmp; tmp.top = c1.top * c2.top; tmp.bottom = c1.bottom * c2.bottom; tmp.simplify(); return tmp; } Fraction operator /(const Fraction &c1,const Fraction &c2) { Fraction tmp; if(c1.top == 0 || c2.top == 0) { return tmp; } tmp.top = c1.top * c2.bottom; tmp.bottom = c1.bottom * c2.top; tmp.simplify(); return tmp; }
ifraction.h
#include"fraction.h" #ifndef _IFRACTION_H #define _IFRACTION_H class ifraction:public Fraction{ public: ifraction(int t,int b,int I=0); ifraction(const ifraction &c1); void print(); friend ifraction convertF(const ifraction &c1); private: int i=0; }; #endif
ifraction.cpp
#include<iostream> #include"iFraction.h" #include <iomanip> using namespace std; ifraction::ifraction(int t,int b,int I):Fraction(t,b){ i=I; } ifraction::ifraction(const ifraction &c1):Fraction(c1){ i=c1.i; } void ifraction::print(){ if(top==0){ cout<<i<<endl; } cout<<setw(4)<<setfill(' ')<<top<<endl; cout<<setw(3)<<setfill(' ')<<i<<'-'<<endl; cout<<setw(4)<<setfill(' ')<<bottom<<endl; } ifraction convertF(const ifraction &c1){ ifraction tmp(c1); tmp.simplify(); int z=tmp.top/tmp.bottom; tmp.i+=z; tmp.top%=tmp.bottom; return tmp; }
main.cpp
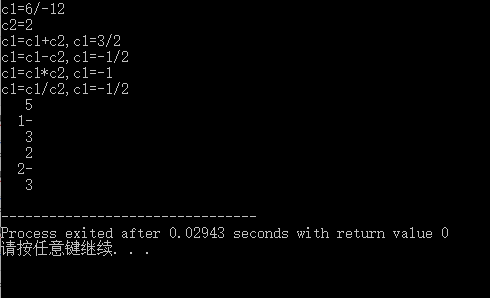
#include"fraction.h" #include"ifraction.h" #include <iomanip> #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { Fraction c1 (6,-12); Fraction c2 (2); Fraction c3 ; ifraction c4(5,3,1); cout<<"c1="; c1.writeln(); cout<<"c2="; c2.writeln(); c1=c1+c2; cout<<"c1=c1+c2,c1="; c1.writeln(); c1=c1-c2; cout<<"c1=c1-c2,c1="; c1.writeln(); c1=c1*c2; cout<<"c1=c1*c2,c1="; c1.writeln(); c1=c1/c2; cout<<"c1=c1/c2,c1="; c1.writeln(); c4.print(); c4=convertF(c4); c4.print(); return 0; }
运行结果:
三、实验总结与体会
本次实验理解了类的继承和派生,并且掌握了派生类的定义和使用。了解掌握了派生类构造函数和析构函数的定义。同时了解了运算符重载的目的,掌握了运算符重载函数的编写方法。总的来说,类的继承和多态是C++语言一种及其高效和灵活的运用。