flink底层RPC调用
Flink架构分析之RPC详解
参考spark rpc
总览
总结:
ActorSystem 和 Actor/ActorRef 的概念,工作方式,通信方式等,注意异步和 mailbox 这两个概念
1、ActorSystem 是管理 Actor生命周期的组件, Actor是负责进行通信的组
2、每个 Actor 都有一个 MailBox,别的 Actor 发送给它的消息都首先储存在 MailBox 中,通过这种
方式可以实现异步通信。
3、每个 Actor 是单线程的处理方式,不断的从 MailBox 拉取消息执行处理,所以对于 Actor 的消息处
理,不适合调用会阻塞的处理方法。
4、Actor 可以改变他自身的状态,可以接收消息,也可以发送消息,还可以生成新的 Actor
5、每一个ActorSystem 和 Actor都在启动的时候会给定一个 name,如果要从ActorSystem中,获取一
个 Actor,则通过以下的方式来进行 Actor的获取:akka.tcp://asname@bigdata02:9527/user/actorname
6、如果一个 Actor 要和另外一个 Actor进行通信,则必须先获取对方 Actor 的 ActorRef 对象,然
后通过该对象发送消息即可。
7、通过 tell 发送异步消息,不接收响应,通过 ask 发送异步消息,得到 Future 返回,通过异步回到
返回处理结果。
8、当在任意地方发现要创建这四个组件的任何一个组件的实例对象的时候,创建成功了之后,都会要去执
行他的 onStart() ,在集群启动的源码分析中,其实这些组件的很多的工作流程,都被放在 onStart() 里
面。 先执行构造方法,后执行onStart方法
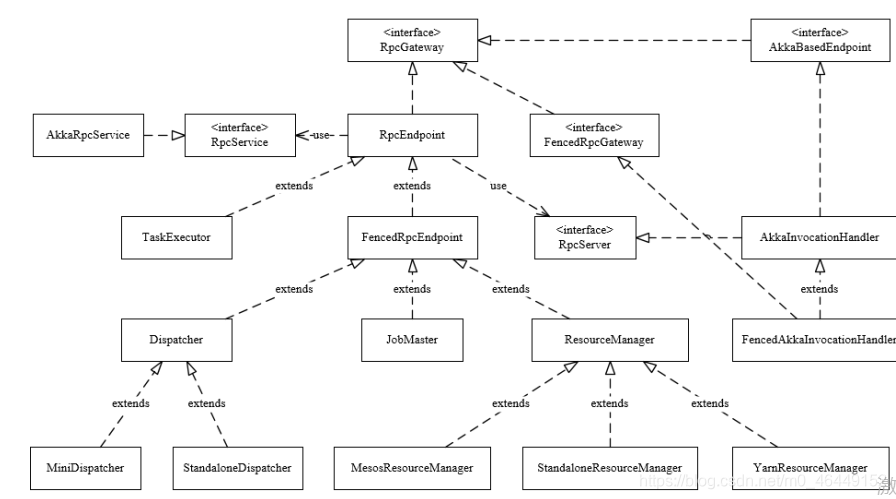
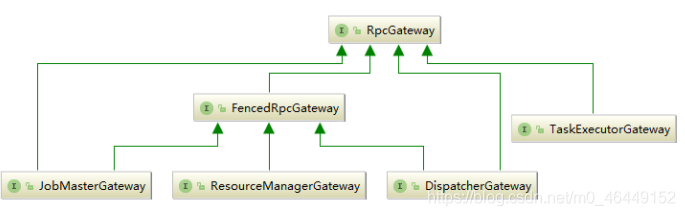
1、RpcGateway 网关(路由),RPC的老祖宗,各种其他RPC组件,都是 RpcGateWay 的子类
2、RpcServer RpcService 和 RpcEndpoint 之间的粘合层
3、RpcEndpoint 业务逻辑载体,对应的 Actor 的封装
4、RpcService 对应 ActorSystem 的封装
1、RpcGateway
相当于秘书,消息先发送到网关,再由对应组件处理
FencedRpcGateway :高可用组件的网关(JobMasterGateway,ResourceManagerGateway,DispatcherGateway)
Flink 的 RPC 协议通过 RpcGateway 来定义,主要定义通信行为;
用于远程调用 RpcEndpoint 的某些方法, 可以理解为对方的客服端代理;
若想与远端 Actor 通信,则必须提供地址(ip 和 port),
如在 Flink-on-Yarn 模式下,JobMaster 会先启动 ActorSystem,
此时 TaskExecutor 的 Container 还未分配,后面与
TaskExecutor 通信时,必须让其提供对应地址
/**
* Rpc gateway interface which has to be implemented by Rpc gateways.
*/
public interface RpcGateway {
/**
* Returns the fully qualified address under which the associated rpc endpoint is reachable.
*
* @return Fully qualified (RPC) address under which the associated rpc endpoint is reachable
*/
String getAddress();
/**
* Returns the fully qualified hostname under which the associated rpc endpoint is reachable.
*
* @return Fully qualified hostname under which the associated rpc endpoint is reachable
*/
String getHostname();
}
/**
* Fenced {@link RpcGateway}. This gateway allows to have access to the associated
* fencing token.
*
* @param <F> type of the fencing token
*/
public interface FencedRpcGateway<F extends Serializable> extends RpcGateway {
/**
* Get the current fencing token.
*
* @return current fencing token
*/
F getFencingToken();
}
2、RpcEndpoint
RpcEndpoint 是通信终端, 提供 RPC 服务组件的生命周期管理(start、 stop)。 每个
RpcEndpoint对应了一个路径(endpointId和actorSystem共同确定),每个路径对应一个Actor,
其实现了 RpcGateway 接口,其构造函数如下
protected RpcEndpoint(final RpcService rpcService, final String endpointId) {
this.rpcService = checkNotNull(rpcService, "rpcService");
this.endpointId = checkNotNull(endpointId, "endpointId");
/*************************************************
* TODO
* 注释: 启动 ResourceManager 的 RPCServer 服务
* 这里启动的是 ResourceManager 的 Rpc 服务端。
* 接收 TaskManager启动好了而之后, 进行注册和心跳,来汇报 Taskmanagaer 的资源情况
* 通过动态代理的形式构建了一个Server、
*
* --> AkkaRpcService.startServer
*/
this.rpcServer = rpcService.startServer(this);
/*************************************************
* TODO
* 注释: 线程池的初始化
*/
this.mainThreadExecutor = new MainThreadExecutor(rpcServer, this::validateRunsInMainThread);
}
构造的时候调用rpcService.startServer()启动RpcServer,进入可以接收处理请求的状态,
最后将 RpcServer 绑定到主线程上真正执行起来。
在 RpcEndpoint 中还定义了一些方法如 runAsync(Runnable)、 callAsync(Callable, Time)方
法来执行 Rpc 调用,值得注意的是在 Flink 的设计中,对于同一个 Endpoint,所有的调用都
运行在主线程,因此不会有并发问题,当启动 RpcEndpoint/进行 Rpc 调用时,其会委托
RcpServer 进行处理
3、RpcService 和 RpcServer
RpcService 和 RpcServer 是 RpcEndPoint 的成员变量。
1) RpcService 是 Rpc 服务的接口,其主要作用如下:
⚫ 根据提供的 RpcEndpoint 来启动和停止 RpcServer(Actor);
⚫ 根据提供的地址连接到(对方的)RpcServer,并返回一个 RpcGateway;
⚫ 延迟/立刻调度 Runnable、 Callable;
在 Flink 中实现类为 AkkaRpcService, 是 Akka 的 ActorSystem 的封装,基本可以理
解成 ActorSystem 的一个适配器。在 ClusterEntrypoint(JobMaster)和 TaskManagerRunner
(TaskExecutor)启动的过程中初始化并启动。
AkkaRpcService 中封装了ActorSystem,并保存了ActorRef 到 RpcEndpoint的映射关系。
RpcService 跟 RpcGateway 类似,也提供了获取地址和端口的方法。
在构造 RpcEndpoint 时会启动指定 rpcEndpoint 上的 RpcServer,其会根据 RpcEndpoint
类型(FencedRpcEndpoint 或其他)来创建不同的 AkkaRpcActor(FencedAkkaRpcActor 或
AkkaRpcActor),并将RpcEndpoint和AkkaRpcActor对应的ActorRef保存起来, AkkaRpcActor
是底层 Akka 调用的实际接收者, RPC 的请求在客户端被封装成 RpcInvocation 对象,以 Akka
消息的形式发送。最终使用动态代理将所有的消息转发到 InvocationHandler
AkkaRpcService
public <C extends RpcEndpoint & RpcGateway> RpcServer startServer(C rpcEndpoint) {
......
/*************************************************
* TODO 重点
* 注释: 获取 RpcServer 对象, 启动 RpcServer
* 生成 RpcServer 对象,而后对该 server 的调用都会进入 Handler 的 invoke 方法处理, handler 实现
* 了多个接口的方法
* 生成一个包含这些接口的代理,将调用转发到 InvocationHandler
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") RpcServer server = (RpcServer) Proxy
.newProxyInstance(classLoader, implementedRpcGateways.toArray(new Class<?>[implementedRpcGateways.size()]), akkaInvocationHandler);
return server;
--> AkkaInvocationHandler.invoke
2) RpcServer 负责接收响应远端 RPC 消息请求, 自身的代理对象。有两个实现:
⚫ AkkaInvocationHandler
⚫ FencedAkkaInvocationHandler
RpcServer 的启动是通知底层的 AkkaRpcActor 切换为 START 状态,开始处理远程调用
请求
AkkaInvocationHandler
public void start() {
rpcEndpoint.tell(ControlMessages.START, ActorRef.noSender());
}
4、AkkaRpcActor
AkkaRpcActor 是 Akka 的具体实现,主要负责处理如下类型消息:
1)本地 Rpc 调用 LocalRpcInvocation
会指派给 RpcEndpoint 进行处理,如果有响应结果,则将响应结果返还给 Sender。
2) RunAsync & CallAsync
这类消息带有可执行的代码,直接在 Actor 的线程中执行。
3)控制消息 ControlMessages
用来控制 Actor 行为, START 启动, STOP 停止,停止后收到的消息会丢弃掉。
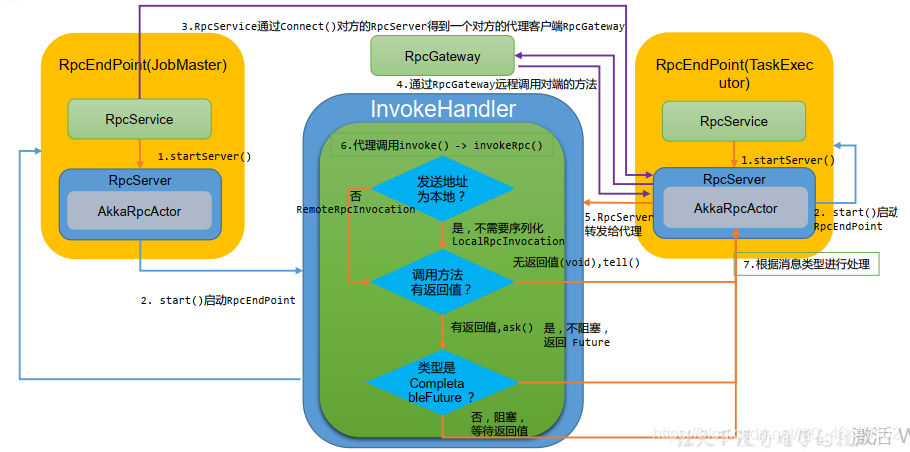
5、 RPC 交互过程
5.1 请求发送
在 RpcService 中调用 connect()方法与对端的 RpcEndpoint (RpcServer)建立连接, connect()
方 法 根 据 给 的 地 址 返 回 InvocationHandler(AkkaInvocationHandler 或
FencedAkkaInvocationHandler,也就是对方的代理)。
前面分析到客户端提供代理对象,代理对象会调用 AkkaInvocationHandler 的 invoke 方
法并传入 RPC 调用的方法和参数信息,代码如下
AkkaInvocationHandler
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
Object result;
if (declaringClass.equals(AkkaBasedEndpoint.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(Object.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(RpcGateway.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(StartStoppable.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(MainThreadExecutable.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(RpcServer.class)) {
/*TODO 如果是网关类的调用,走这里*/
result = method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (declaringClass.equals(FencedRpcGateway.class)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("AkkaInvocationHandler does not support the call FencedRpcGateway#" +
method.getName() + ". This indicates that you retrieved a FencedRpcGateway without specifying a " +
"fencing token. Please use RpcService#connect(RpcService, F, Time) with F being the fencing token to " +
"retrieve a properly FencedRpcGateway.");
} else {
/*TODO 如果不是网关类的,走这里,处理RPC请求*/
result = invokeRpc(method, args);
}
return result;
}
代码中判断所属的类,如果是 RPC 方法,则调用 invokeRpc 方法。将方法调用封装为
RPCInvocation 消息。如果是本地则生成 LocalRPCInvocation,本地消息不需要序列化,如果
是远程调用则创建 RemoteRPCInvocation。
判断远程方法调用是否需要等待结果,如果无需等待(void),则使用向 Actor 发送 tell 类
型的消息,如果需要返回结果,则向 Acrot 发送 ask 类型的消息,代码如下
--> invokeRpc
private Object invokeRpc(Method method, Object[] args) throws Exception {
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
Time futureTimeout = extractRpcTimeout(parameterAnnotations, args, timeout);
/*TODO 把消息封装成 RpcInvocation,如果是本地,那就创建Local类型;如果是远程,就创建Remote类型*/
final RpcInvocation rpcInvocation = createRpcInvocationMessage(methodName, parameterTypes, args);
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
final Object result;
if (Objects.equals(returnType, Void.TYPE)) {
/*TODO 如果方法的返回值是void,那么就使用 tell方式*/
tell(rpcInvocation);
result = null;
} else {
// 有返回值
// Capture the call stack. It is significantly faster to do that via an exception than
// via Thread.getStackTrace(), because exceptions lazily initialize the stack trace, initially only
// capture a lightweight native pointer, and convert that into the stack trace lazily when needed.
final Throwable callStackCapture = captureAskCallStack ? new Throwable() : null;
// execute an asynchronous call
/*TODO 有返回值,使用 ask的方式*/
final CompletableFuture<?> resultFuture = ask(rpcInvocation, futureTimeout);
final CompletableFuture<Object> completableFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
resultFuture.whenComplete((resultValue, failure) -> {
if (failure != null) {
completableFuture.completeExceptionally(resolveTimeoutException(failure, callStackCapture, method));
} else {
completableFuture.complete(deserializeValueIfNeeded(resultValue, method));
}
});
if (Objects.equals(returnType, CompletableFuture.class)) {
/*TODO 如果返回类型是 CompletableFuture,直接把 CompletableFuture对象返回(不用阻塞)*/
result = completableFuture;
} else {
try {
/*TODO 如果返回类型不是CompletableFuture,那么就主动去获取结果(阻塞着等待结果返回)*/
result = completableFuture.get(futureTimeout.getSize(), futureTimeout.getUnit());
} catch (ExecutionException ee) {
throw new RpcException("Failure while obtaining synchronous RPC result.", ExceptionUtils.stripExecutionException(ee));
}
}
}
return result;
}
5.2 请求响应
RPC 消息通过 RpcEndpoint 所绑定的 Actor 的 ActorRef 发送的, AkkaRpcActor 是消息
接收的入口, AkkaRpcActor 在 RpcEndpoint 中构造生成,负责将消息交给不同的方法进行处
理。
AkkaRpcActor
public Receive createReceive() {
return ReceiveBuilder.create()
//1)握手消息
.match(RemoteHandshakeMessage.class, this::handleHandshakeMessage)
// 2)控制消息
.match(ControlMessages.class, this::handleControlMessage)
// 3)RPC 消息
.matchAny(this::handleMessage)
.build();
}
5.2.1 握手消息
在客户端构造时会通过 ActorSelection 发送过来。收到消息后检查接口、版本是否匹配。
private void handleHandshakeMessage(RemoteHandshakeMessage handshakeMessage) {
if (!isCompatibleVersion(handshakeMessage.getVersion())) {
sendErrorIfSender(new AkkaHandshakeException(
String.format(
"Version mismatch between source (%s) and target (%s) rpc component. Please verify that all components have the same version.",
handshakeMessage.getVersion(),
getVersion())));
} else if (!isGatewaySupported(handshakeMessage.getRpcGateway())) {
// RpcGateway 不匹配异常处理
sendErrorIfSender(new AkkaHandshakeException(
String.format(
"The rpc endpoint does not support the gateway %s.",
handshakeMessage.getRpcGateway().getSimpleName())));
} else {
// tell的方式回应
getSender().tell(new Status.Success(HandshakeSuccessMessage.INSTANCE), getSelf());
}
}
5.2.2 控制消息
在 RpcEndpoint 调用 start 方法后, 会向自身发送一条 Processing.START 消息来转
换当前 Actor 的状态为 STARTED, STOP 也类似,并且只有在 Actor 状态为 STARTED 时才
会处理 RPC 请求。
private void handleControlMessage(ControlMessages controlMessage) {
try {
switch (controlMessage) {
case START:
state = state.start(this);
break;
case STOP:
state = state.stop();
break;
case TERMINATE:
state = state.terminate(this);
break;
default:
handleUnknownControlMessage(controlMessage);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
this.rpcEndpointTerminationResult = RpcEndpointTerminationResult.failure(e);
throw e;
}
}
5.2.3 RPC 消息
通过解析 RpcInvocation 获取方法名和参数类型,并从 RpcEndpoint 类中找到 Method 对
象,通过反射调用该方法。如果有返回结果,会以 Akka 消息的形式发送回发送者
三种消息类型 RunAsync,CallAsync,RpcInvocation
protected void handleRpcMessage(Object message) {
if (message instanceof RunAsync) {
handleRunAsync((RunAsync) message);
} else if (message instanceof CallAsync) {
handleCallAsync((CallAsync) message);
} else if (message instanceof RpcInvocation) {
handleRpcInvocation((RpcInvocation) message);
} else {
log.warn(
"Received message of unknown type {} with value {}. Dropping this message!",
message.getClass().getName(),
message);
sendErrorIfSender(new AkkaUnknownMessageException("Received unknown message " + message +
" of type " + message.getClass().getSimpleName() + '.'));
}
}
总结